Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Advances in trusted network computing
- Pages: 1311-1312
- First Published: 30 May 2014
Smartphone security: understanding smartphone users' trust in information security management
- Pages: 1313-1321
- First Published: 11 July 2013
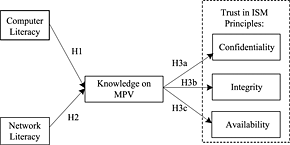
The research aims to study the relationships between smartphone users' computer literacy, network literacy, knowledge on mobile phone viruses (MPV), and trust in information security management (ISM) principles (i.e., confidentiality, integrity, and availability). The study results indicate that smartphone users' network literacy positively influences their knowledge on MPV, whereas users' computer literacy is not significantly associated with their knowledge on MPV. Moreover, smartphone users' knowledge on MPV would significantly affect their trusts in three ISM principles.
A trust model based on semantic distance for pervasive environments
- Pages: 1322-1330
- First Published: 09 May 2013
A semantic distance-based trust model is proposed. The semantic distance between entities and between trust categories is borrowed to calculate trustworthiness more precisely. In the model, the behavior trust and capability trust are distinguished and evaluated separately. The simulation experiment results proved the effectiveness of the model in improving the interaction success ratio and efficiency between entities under pervasive environments.
The approaches to contextual transaction trust computation in e-Commerce environments
- Pages: 1331-1351
- First Published: 12 February 2014
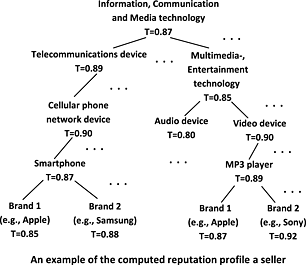
In e-commerce environments, most existing trust evaluation studies compute a single trust value to reflect the “general” trust level of a seller without any information of transaction context taken into account. In this paper, we first propose a new context-aware trust evaluation model for outlining a seller's reputation profile. Then we further propose several approaches in order to deliver prompt responses to a buyer's queries on a seller's trust value in different transaction contexts.
A game theoretic truthful reputation mechanism in mobile ad hoc networks
- Pages: 1352-1363
- First Published: 20 February 2014
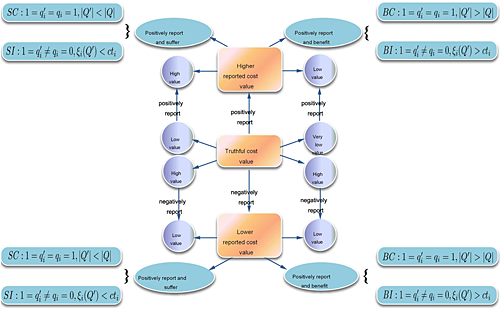
This paper proposes a truthful and group strategyproof reputation mechanism based on cooperative game theory. After studying two supermodular total compensatory payment functions, we construct a corresponding indirect revelation mechanism and a direct revelation mechanism called claiming compensation mechanism, which is proved to be group strategyproof. Simulation results show that when using the total compensatory payments function, which does not relate to cost values, the proposed mechanism is group strategyproof. Finally, all possible situations for a liar are demonstrated and discussed.
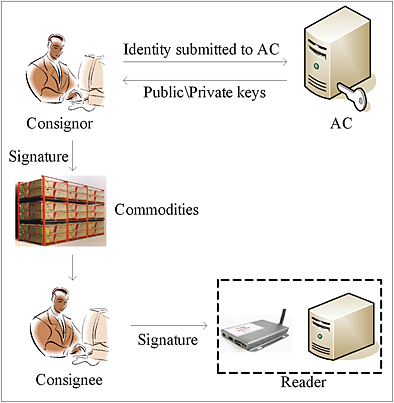
An aggregated signature-based fast RFID batch detection protocol
- Pages: 1364-1371
- First Published: 10 July 2013
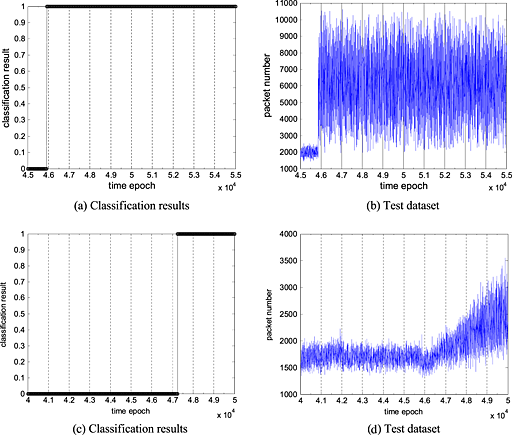
Anomaly diagnosis based on regression and classification analysis of statistical traffic features
- Pages: 1372-1383
- First Published: 30 September 2013
Obtaining K-obfuscation for profile privacy in social networks
- Pages: 1384-1398
- First Published: 17 January 2014
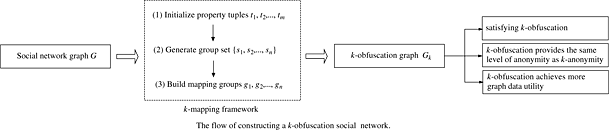
In this work, we formally present the definition of profile privacy leakage, which is a newly identified privacy leakage in social networks. We propose k-obfuscation to protect profiles against graph property based attacks. We develop a general framework for obtaining k-obfuscation. In this framework, we propose a novel safe vertex-profile mapping mechanism, named as k-mapping. We also design a number of techniques to make the k-mapping method efficient meanwhile maintaining the data utilities.
A secure K-automorphism privacy preserving approach with high data utility in social networks
- Pages: 1399-1411
- First Published: 30 September 2013
In this paper, we design a secure and high utility privacy preserving model, called AK-secure, to prevent node identity attack, path length leakage, and edge leakage effectively. On the basis of the AK-secure privacy preserving model, we propose a graph anonymous algorithm, which constructs an anonymous graph satisfying the AK-secure privacy preserving model, minimizing information loss and guaranteeing high data utility.
Memshepherd: comprehensive memory bug fault-tolerance system
- Pages: 1412-1419
- First Published: 06 November 2013
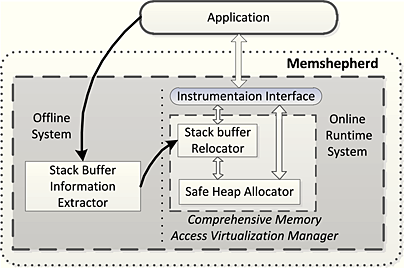
This paper presents Memshepherd, a system that can probabilistically prevent software from both stack and heap memory bugs and guarantee soundness of the software execution. It dynamically reallocates stack-based buffers in the heap space during software execution, and it keeps buffers far from each other by adaptively sizing buffers to be M times of their defined size and randomly placing them. When a buffer is to be deallocated, Memshepherd checks invalid and double frees.
A fixed point model for rate control and routing in cloud data center networks
- Pages: 1420-1436
- First Published: 16 December 2013
A fixed point framework was proposed to formulate the cloud network equilibrium problems. The existence and uniqueness of the network equilibrium points have also been proved. An augmented Lagrangian multiplier algorithm is proposed to obtain the network equilibrium point by solving the nonlinear programming optimization problem.