Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEWS
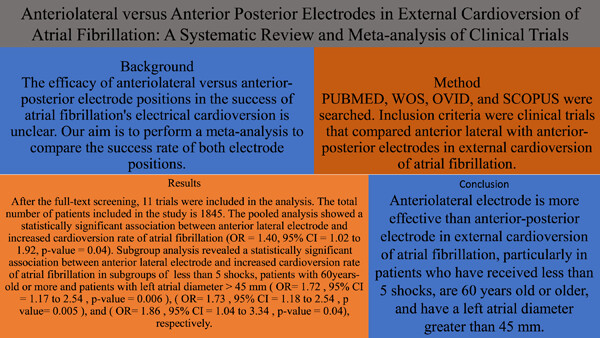
Anteriolateral versus anterior–posterior electrodes in external cardioversion of atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials
- Pages: 359-375
- First Published: 09 February 2023
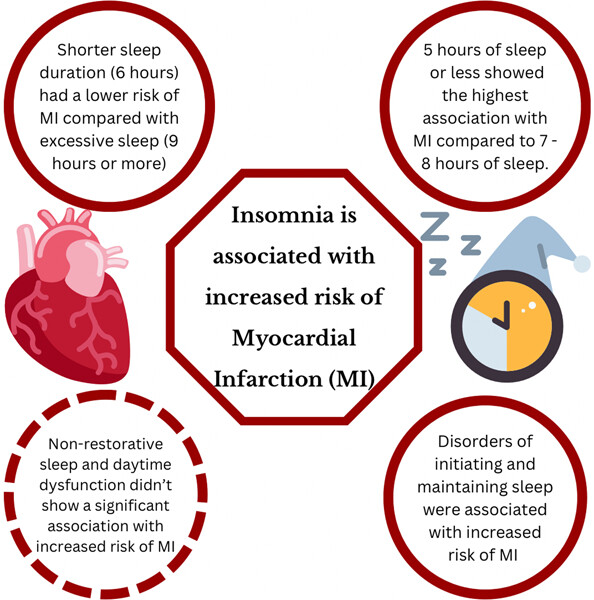
Association between insomnia and the incidence of myocardial infarction: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 376-385
- First Published: 25 February 2023
CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS
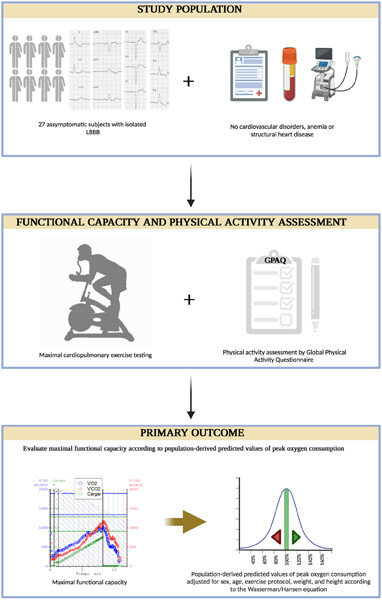
Maximal functional capacity in subjects with isolated left bundle branch block: A pilot study
- Pages: 386-389
- First Published: 08 February 2023
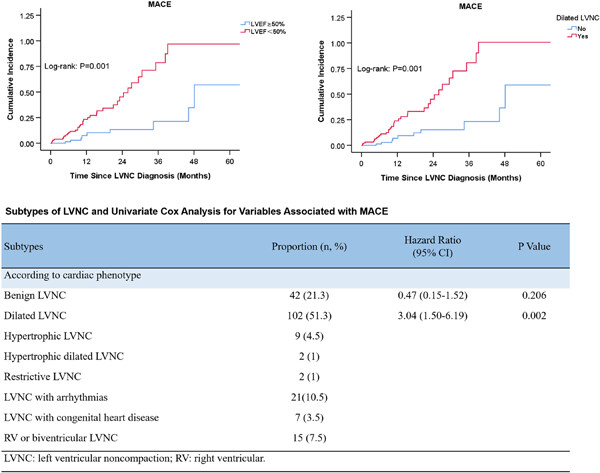
Prognosis and subtype analysis of left ventricular noncompaction in adults: A retrospective multicenter study
- Pages: 390-396
- First Published: 13 February 2023
P-wave parameters and their association with thrombi and spontaneous echo contrast in the left atrial appendage
- Pages: 397-406
- First Published: 17 February 2023
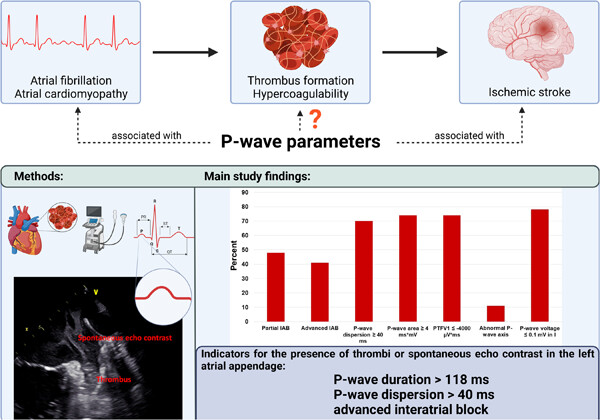
Several P-wave parameters are associated with atrial fibrillation and with ischemic stroke. However, it is uncertain whether P-wave parameters are associated with thrombus or spontaneous echo contrast in the left atrial appendage. Our study demonstrated a significant association of P-wave duration, P-wave dispersion, and advanced interatrial block with thrombus or spontaneous echo contrast in the left atrial appendage. IAB, interatrial block; PTFV1, P-wave terminal force in V1.
Addressing current challenges in optimization of lipid management following an ACS event: Outcomes of the ACS EuroPath III initiative
- Pages: 407-415
- First Published: 17 February 2023
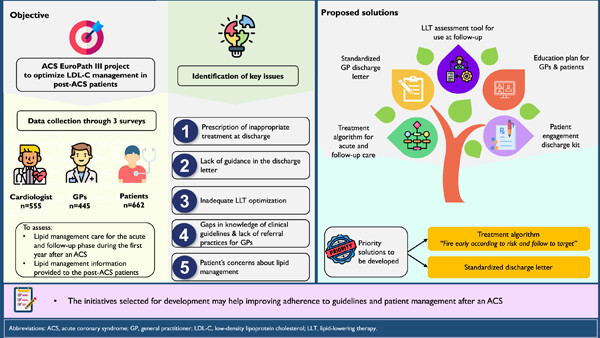
The ACS EuroPath III project was designed to optimize lipid management in post-ACS patients. Following data collection through 3 surveys, 5 key areas for improvement were identified including inappropriate treatment prescribed at discharge, lack of lipid guidance in the discharge letter, inadequate LLT optimization, gaps in guideline knowledge and lack of referral practices for GPs, and patients’ concerns about lipid management. Solutions were proposed for each of these issues, with the generation of a treatment algorithm and a standardized patient discharge letter prioritized for early development.
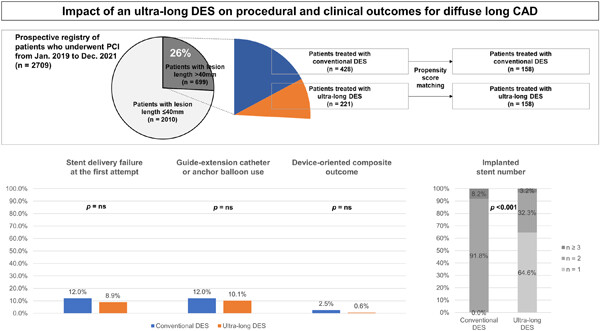
Impact of the ultra-long 48 mm drug-eluting stent on procedural and clinical outcomes in patients with diffuse long coronary artery disease
- Pages: 416-424
- First Published: 20 February 2023
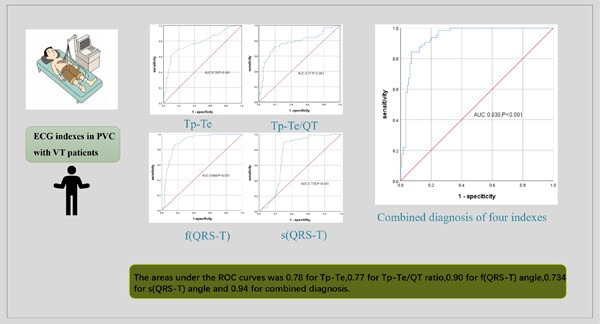
The predictive value of Tp−Te interval, Tp−Te/QT ratio, and QRS-T angle of idiopathic ventricular tachycardia in patients with ventricular premature beats
- Pages: 425-430
- First Published: 21 February 2023
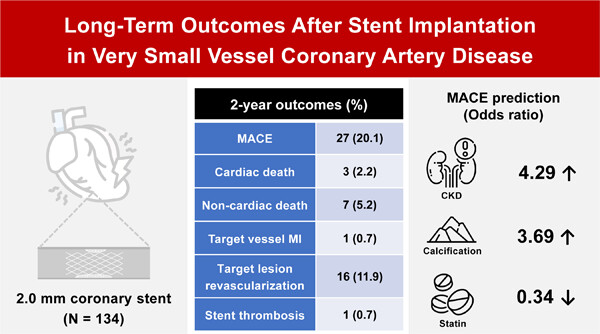
Long-term outcomes after stent implantation in very small vessel coronary artery disease
- Pages: 431-440
- First Published: 23 February 2023
CLINICAL TRIAL
Comparison of the safety and efficiency of temporary cardiac pacing methods during left bundle branch pacemaker implantation: Femoral vein pacing versus atrial spiral pacing with electrodes placed at the ventricle
- Pages: 441-448
- First Published: 16 February 2023
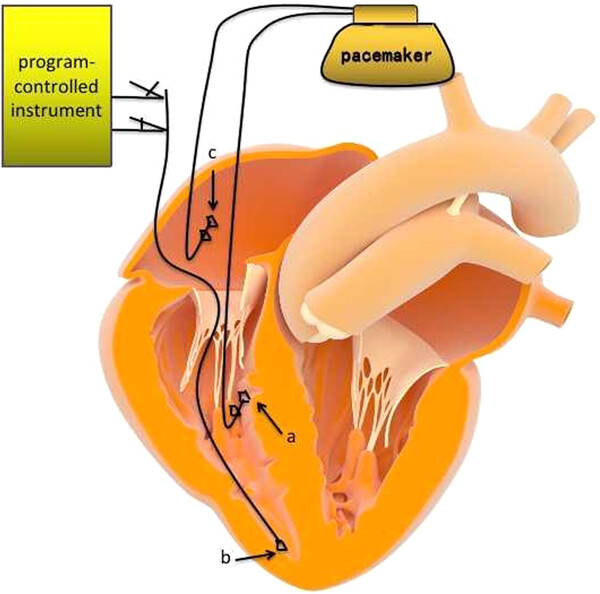
Figure 1: Femoral vein temporary pacing electrode application diagram. After femoral vein puncture, temporary cardiac pacing (TCP) electrodes were placed into the right ventricular apex through the inferior vena cava, right atrium, and tricuspid valve. Then, the end of the electrode was connected to the program-controlled instrument to test the parameters satisfiedly for TCP.
(a) Ventricular spiral pacing electrode. (b) Femoral vein temporary pacing electrode. (c) Atrial spiral pacing electrode.
CLINICAL TRIAL RESULT
Predictive value of serum iron on heart failure in patients with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction
- Pages: 449-453
- First Published: 13 February 2023
LETTERS TO THE EDITOR
Optimal device selection: Leadless versus conventional transvenous pacemakers
- Page: 454
- First Published: 25 January 2023
Fibrinogen–albumin ratio predicting major adverse cardiovascular outcomes post-percutaneous coronary intervention: A systematic review and exploratory meta-analysis
- Pages: 455-458
- First Published: 01 February 2023
Development of myocarditis and pericarditis after COVID-19 vaccination: Comment
- Page: 459
- First Published: 20 February 2023
CORRESPONDENCE
Development of myocarditis and pericarditis after COVID-19 vaccination: A deeper insight
- Pages: 460-461
- First Published: 20 February 2023