Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
MEDICAL TREATMENT
Research Article
Translating the 2021 ESC heart failure guideline recommendations in daily practice: Results from a heart failure survey. A scientific statement of the ESC Council for Cardiology Practice and the Heart Failure Association of the ESC
- Pages: 412-420
- First Published: 24 September 2024
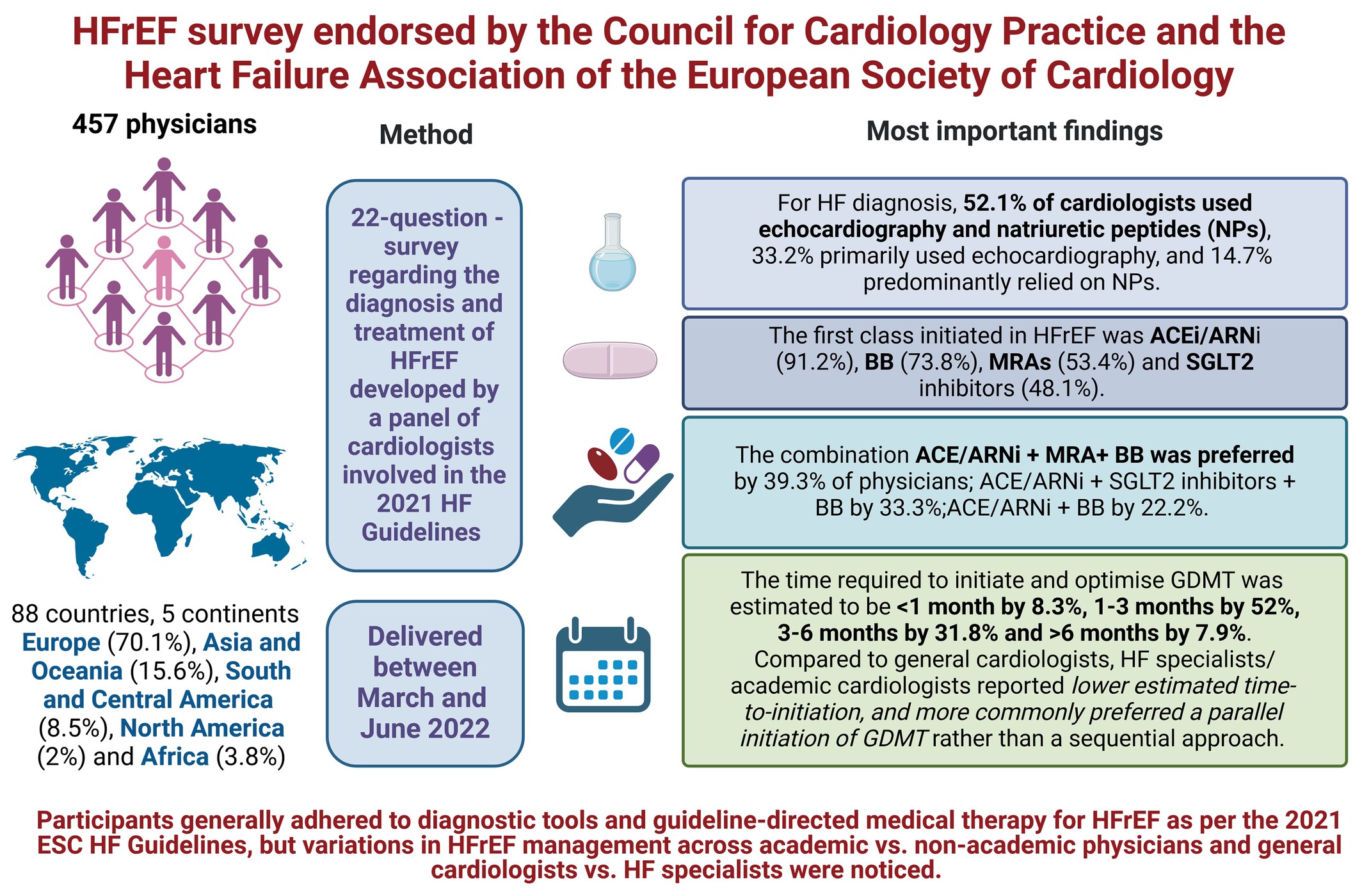
Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) survey endorsed by the Council for Cardiology Practice and the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). HF, heart failure ACEi, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; ARNi, angiotensin receptor–neprilysin inhibitor; BB, beta-blocker; GDMT, guideline-directed medical therapy; MRA, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist; SGLT2, sodium–glucose cotransporter 2.
Implementation of guideline-recommended therapies in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction according to heart failure duration: An analysis of 55 581 patients from the Swedish Heart Failure (SwedeHF) Registry
- Pages: 421-431
- First Published: 09 January 2025
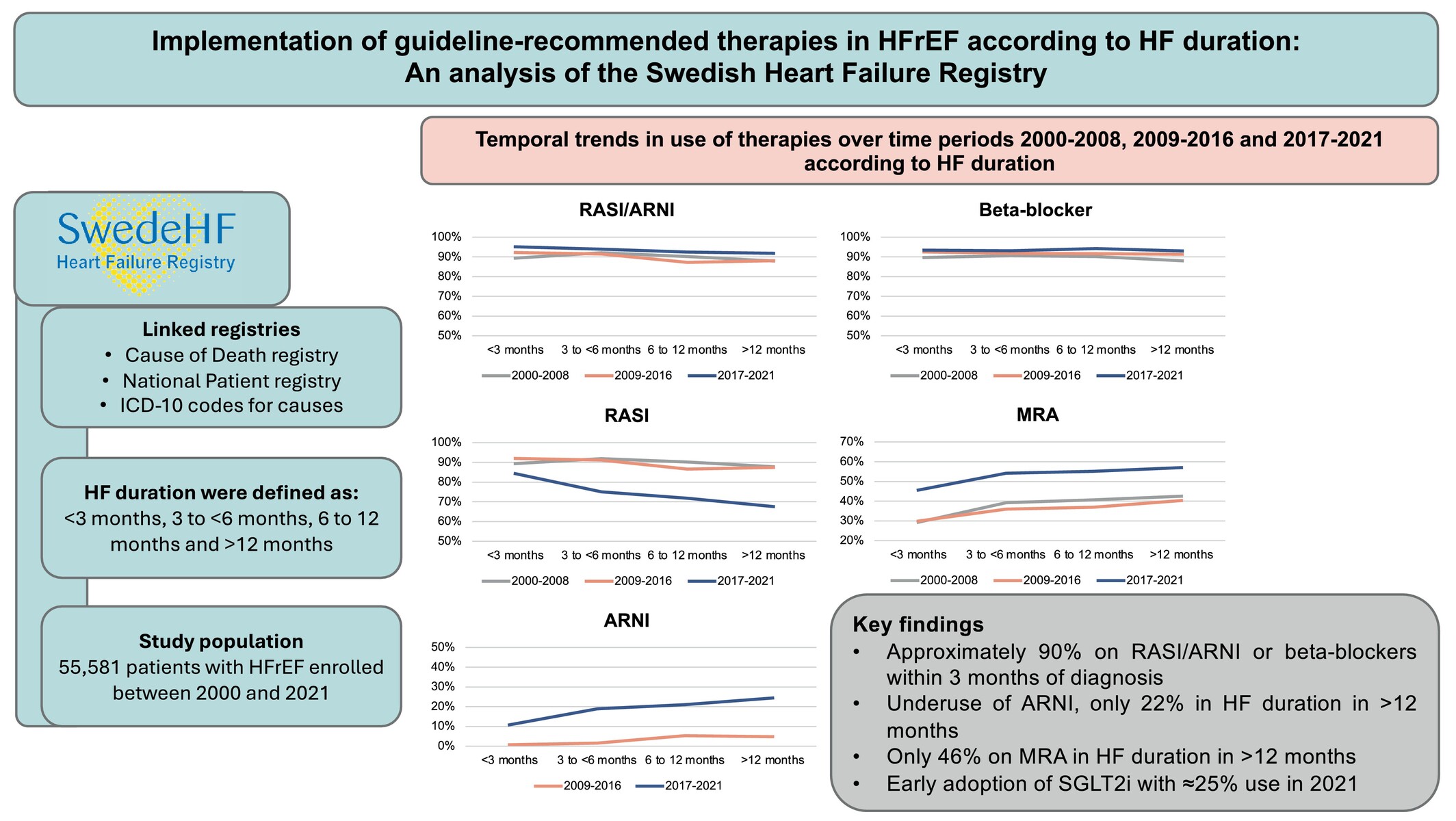
Heart failure (HF) duration and guideline-recommended therapy implementation. ARNI, angiotensin receptor–neprilysin inhibitor; HFrEF, heart failure with reduced ejection fraction; ICD-10, International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision; MRA, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist; RASI, renin–angiotensin system inhibitor; SGLT2i, sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor.
Invited Editorial
Research Article
Applicability of heart failure clinical practice guidelines in low- and middle-income countries
- Pages: 435-441
- First Published: 25 October 2024
Guideline-directed medical therapy for heart failure in arrhythmia-induced cardiomyopathy with improved left ventricular ejection fraction
- Pages: 442-452
- First Published: 18 December 2024
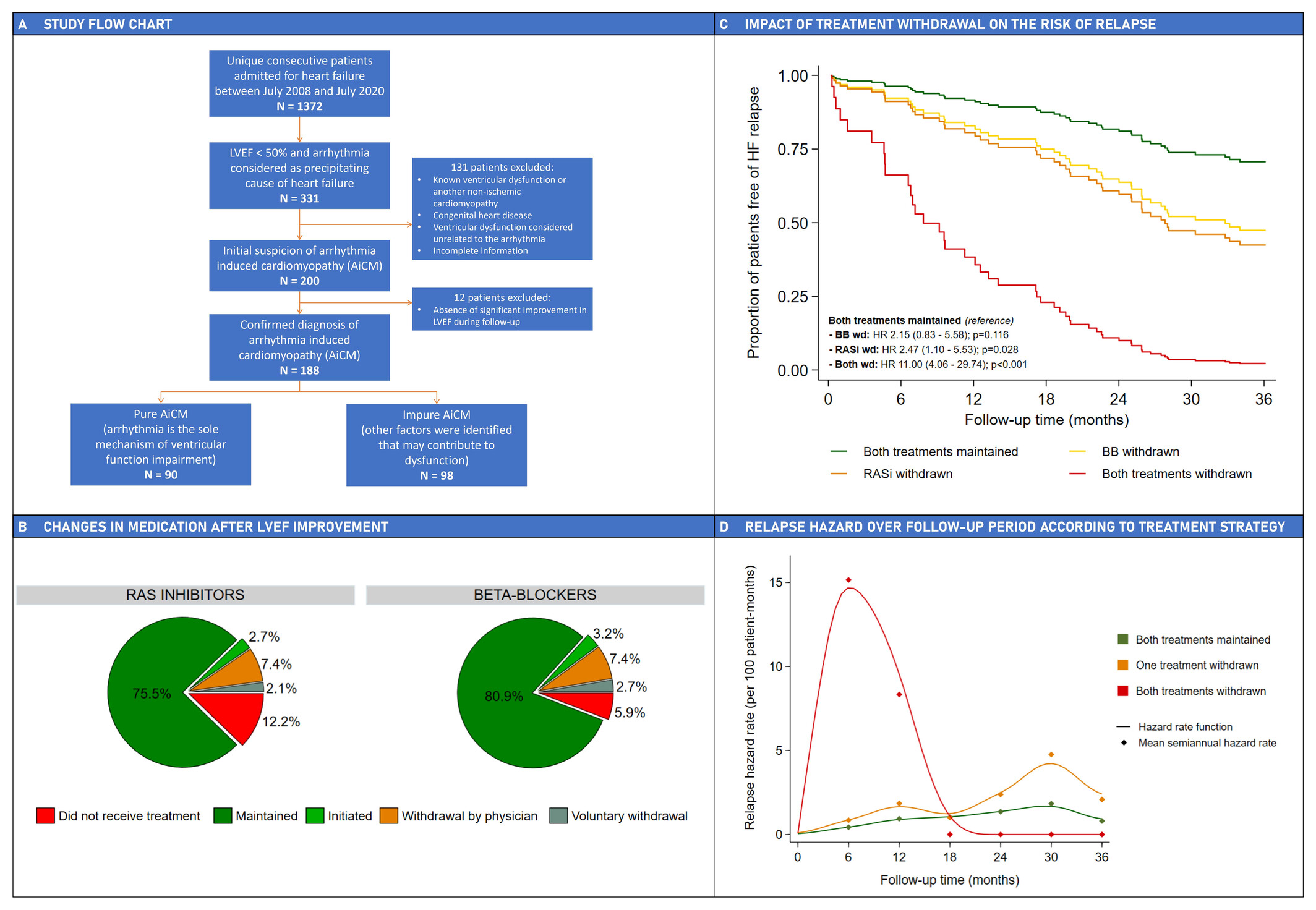
Impact of guideline-directed medical therapy for heart failure after left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) improvement in arrhythmia-induced cardiomyopathy (AiCM). (A) Study flow chart. (B) Changes in renin-angiotensin-system (RAS) inhibitors and beta-blocker (BB) prescriptions after LVEF improvement. (C) Time-to-relapse curves based on treatment strategies. (D) Mean hazard rates of relapse (expressed in number of events per 100 patient-months) for each semester and treatment strategy. A Gaussian kernel local polynomial smoothing was employed for hazard function plotting. RASi, renin-angiotensin system inhibitor; wd, withdrawn.
Invited Editorial
Withdrawal of medical therapy for heart failure after rhythm control in arrhythmia-induced cardiomyopathy—a call for caution
- Pages: 453-455
- First Published: 27 January 2025
Aficamten in non-obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: Unlocking new horizons?
- Pages: 456-458
- First Published: 18 September 2024
THE HEART IN SYSTEMIC DISEASE MIC CONDITIONS
Review Article
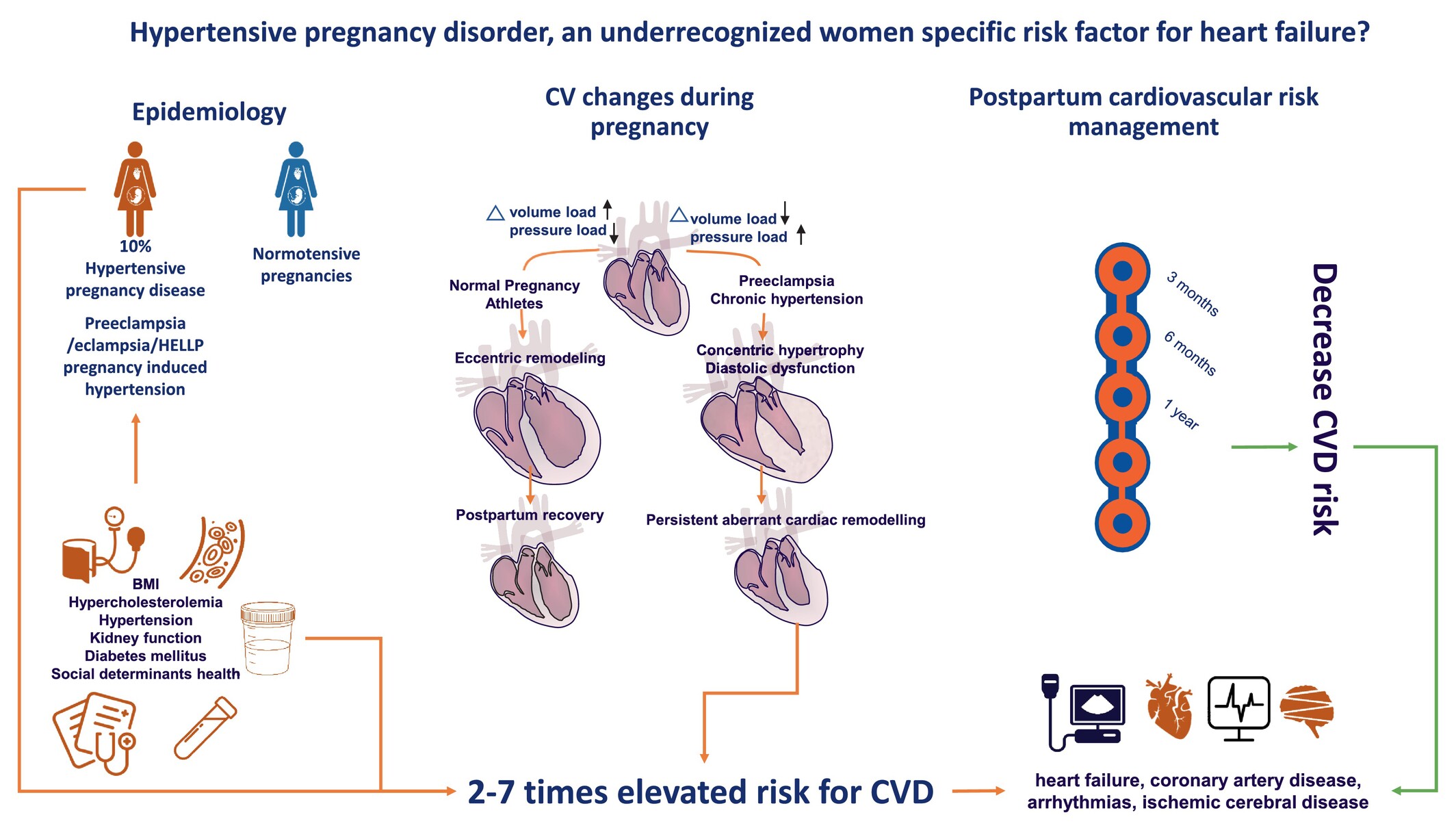
Hypertensive pregnancy disorder, an under-recognized women specific risk factor for heart failure?
- Pages: 459-472
- First Published: 19 November 2024
Research Letter
Add-on rituximab for primary heart involvement associated with systemic sclerosis: A step forward in the tailored treatment of myocarditis?
- Pages: 473-475
- First Published: 24 September 2024
Invited Editorial
Tailored therapies for patients affected by systemic sclerosis with primary heart involvement: The role of rituximab
- Pages: 476-478
- First Published: 10 December 2024
Research Article
Long-term rate of heart failure in patients with autoimmune disease: A nationwide cohort study
- Pages: 479-487
- First Published: 09 December 2024
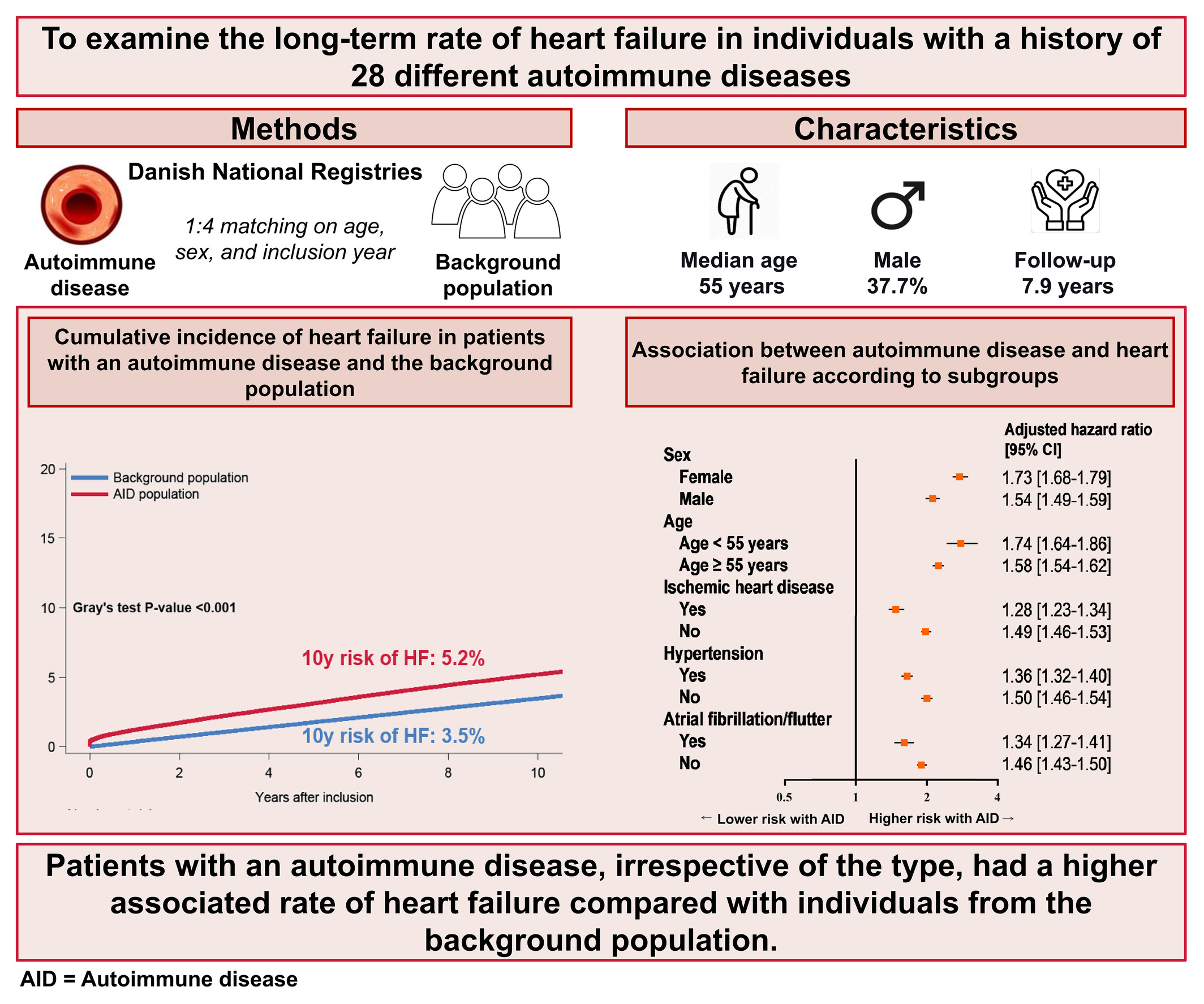
In a nationwide study, patients with autoimmune disease (AID), irrespective of type, had a higher associated rate of heart failure (HF) than matched individuals from the background population. AHA, autoimmune haemolytic anaemia; CLE, cutaneous lupus erythematosus; GPA, granulomatosis with polyangiitis; ITP, immune thrombocytopenic purpura; PsA, psoriatic and enteropathic arthropathy; SLE, systemic lupus erythematosus; SSc, systemic or localized sclerosis.
Endomyocardial biopsy in the diagnosis of cardiac sarcoidosis
- Pages: 488-497
- First Published: 05 December 2024
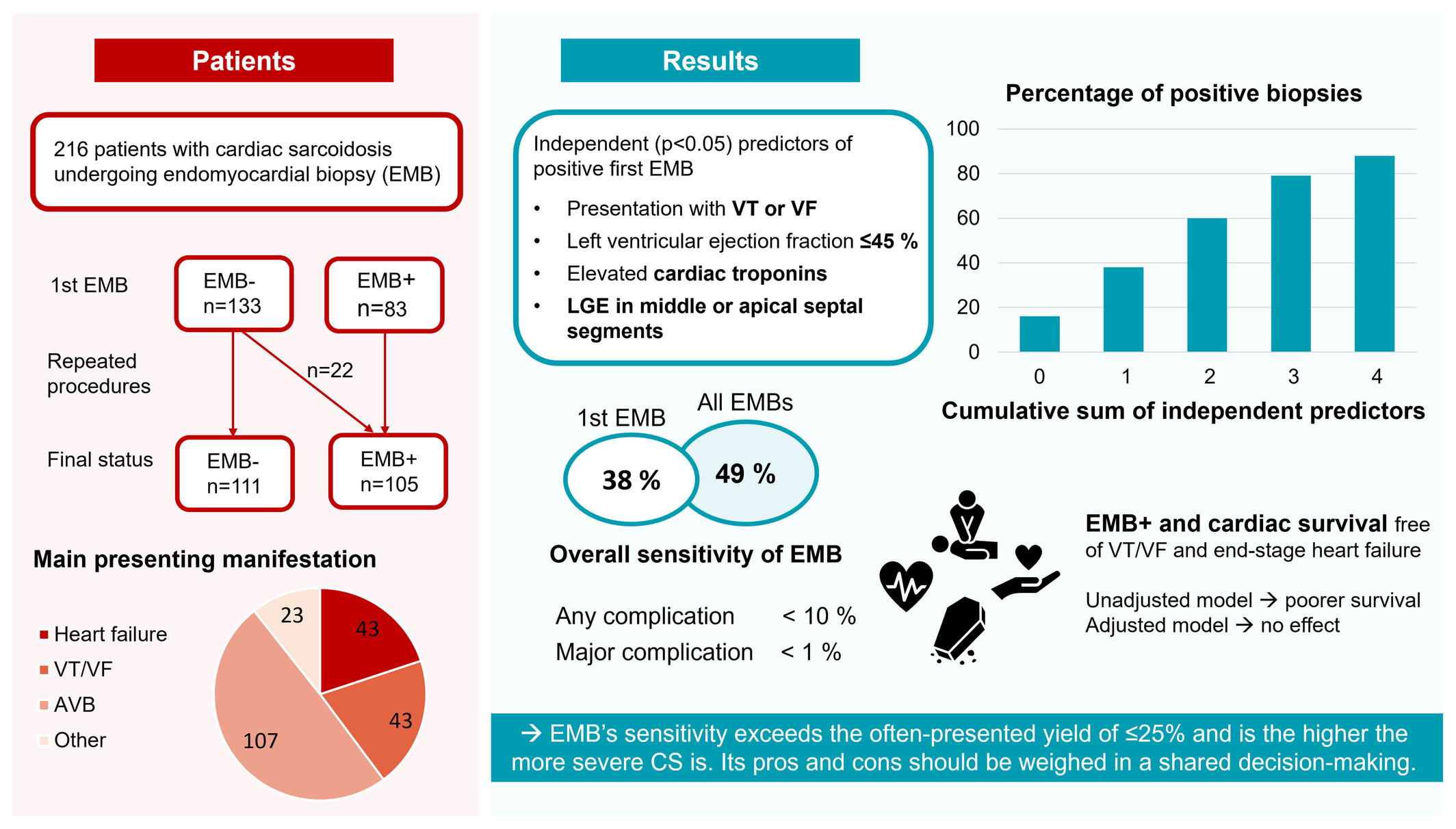
The diagnostic performance of endomyocardial biopsy (EMB) in 216 patients with cardiac sarcoidosis (CS). The overall sensitivity of the first EMB was 38%, although it varied markedly depending on the extent and severity of the disease. Major complications were rare (<1%) and no deaths or permanent sequels were observed. Positive EMB was not an independent prognostic factor. AVB, atrioventricular block; LGE, late gadolinium enhancement; VF, ventricular fibrillation; VT, ventricular tachycardia.
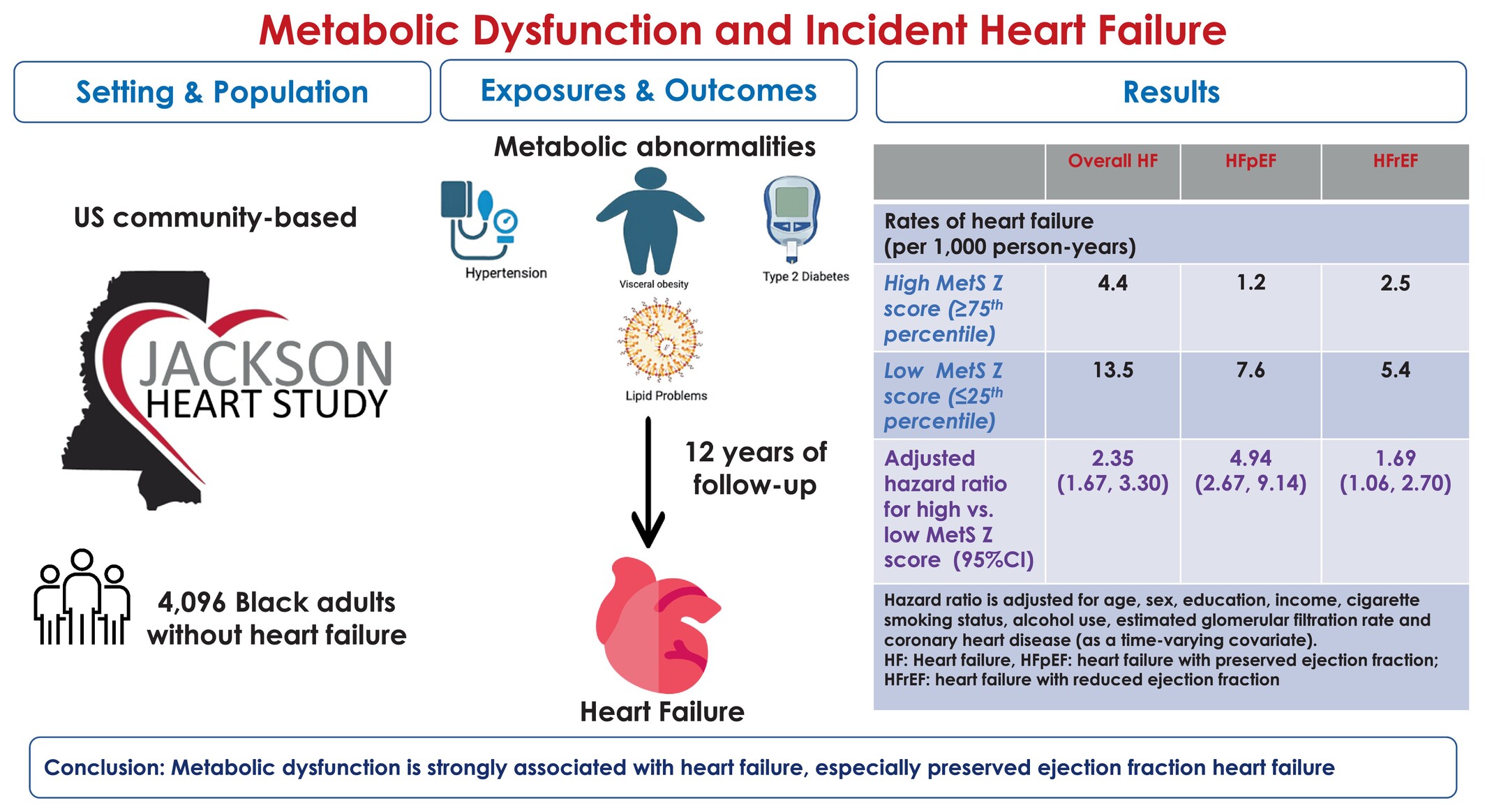
Metabolic dysfunction and incidence of heart failure subtypes among Black individuals: The Jackson Heart Study
- Pages: 498-507
- First Published: 03 September 2024
Invited Editorial
Metabolic dysfunction: An important driver of incident heart failure with preserved and reduced ejection fraction
- Pages: 508-511
- First Published: 08 November 2024
Research Article
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease is associated with increased risks of heart failure
- Pages: 512-520
- First Published: 08 January 2025
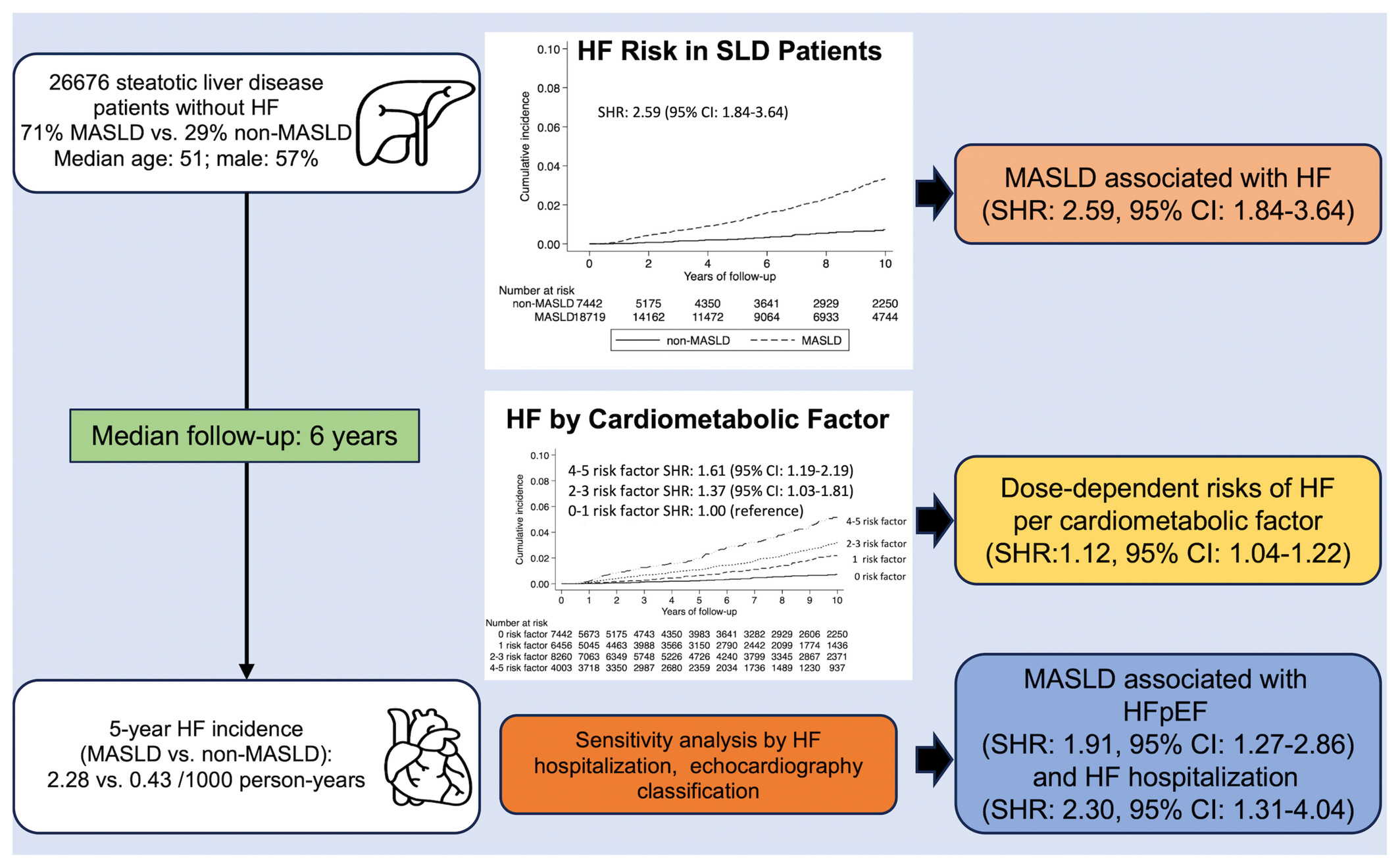
In this cohort study, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) was associated with a higher risk of heart failure (HF), specifically HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF). There was a dose-dependent relationship between cardiometabolic risk factors and HF. CI, confidence interval; SHR, sub-distribution hazard ratio; SLD, steatotic liver disease.
Short Report
Heart failure outcomes captured by adverse event reporting in participants with type 2 diabetes and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: Observations from the VERTIS CV trial
- Pages: 521-526
- First Published: 10 January 2025
Research Article
Anthropometric measures and long-term mortality in non-ischaemic heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: Questioning the obesity paradox
- Pages: 527-536
- First Published: 18 August 2024
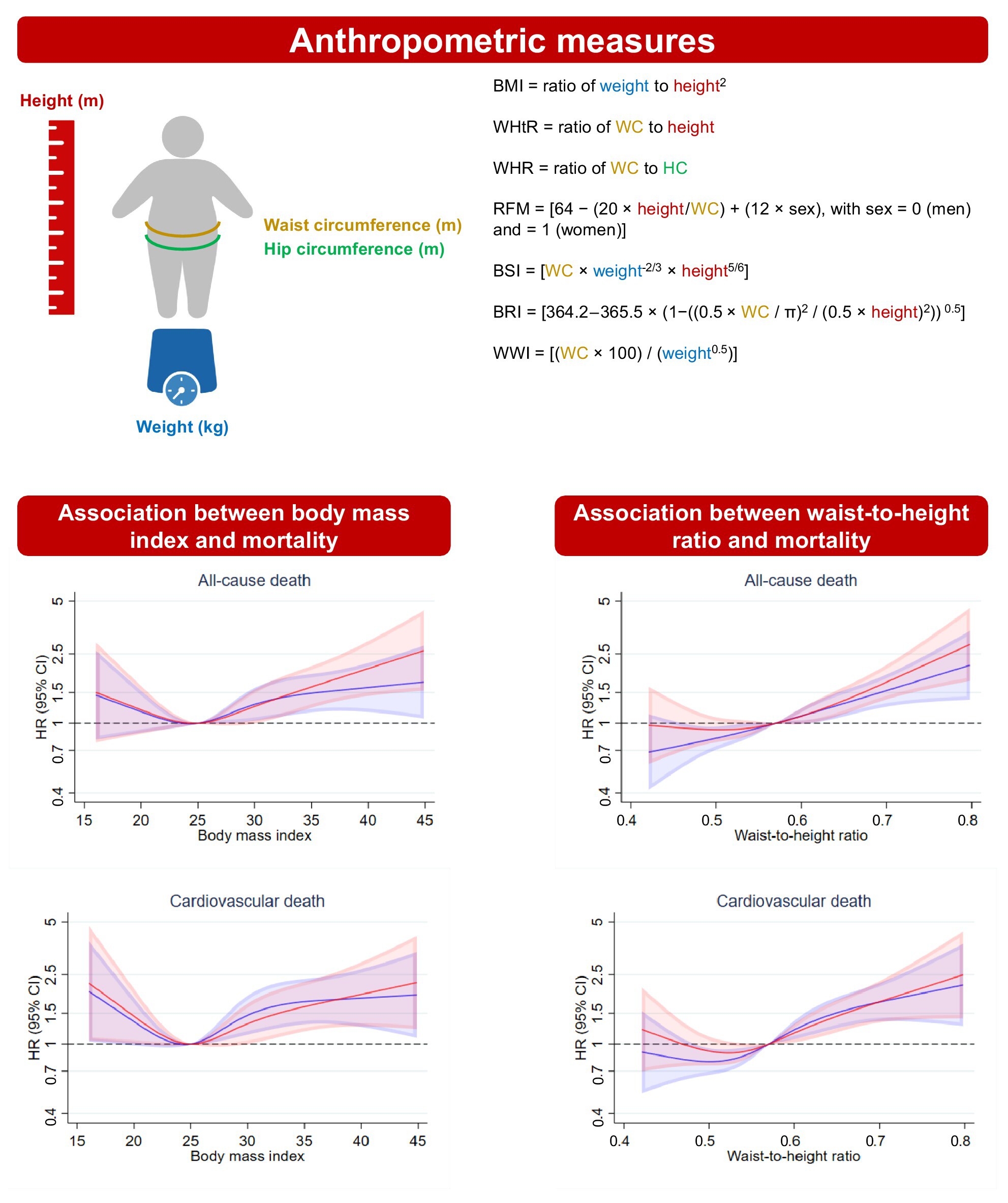
Prognostic value of several alternative anthropometric measures in patients with non-ischaemic heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. The upper part of the figure describes the calculation of each of the anthropometric measures. The lower part of the figure shows the risk of mortality according to continuous body mass index (BMI) (left panel) and waist-to-height ratio (WHtR) (right panel). The solid line represents the hazard ratio (HR) and the shaded area the 95% confidence interval (CI). The blue spline is adjusted for randomization. The red spline is adjusted for randomization, age, sex, cardiac resynchronization therapy (pre-existing or planned), trial centre, systolic blood pressure, heart rate, estimated glomerular filtration rate, left ventricular ejection fraction, log of N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide, New York Heart Association functional class, duration of heart failure, a history of diabetes, and atrial fibrillation. BRI, body roundness index; BSI, body shape index; RFM, relative fat mass; WHR, waist-to-hip ratio; WWI, weight-adjusted-waist index.
Invited Editorial
Time for differential weight management in heart failure
- Pages: 537-539
- First Published: 25 October 2024
Research Article
Cardiovascular outcomes with exenatide in type 2 diabetes according to ejection fraction: The EXSCEL trial
- Pages: 540-551
- First Published: 09 October 2024
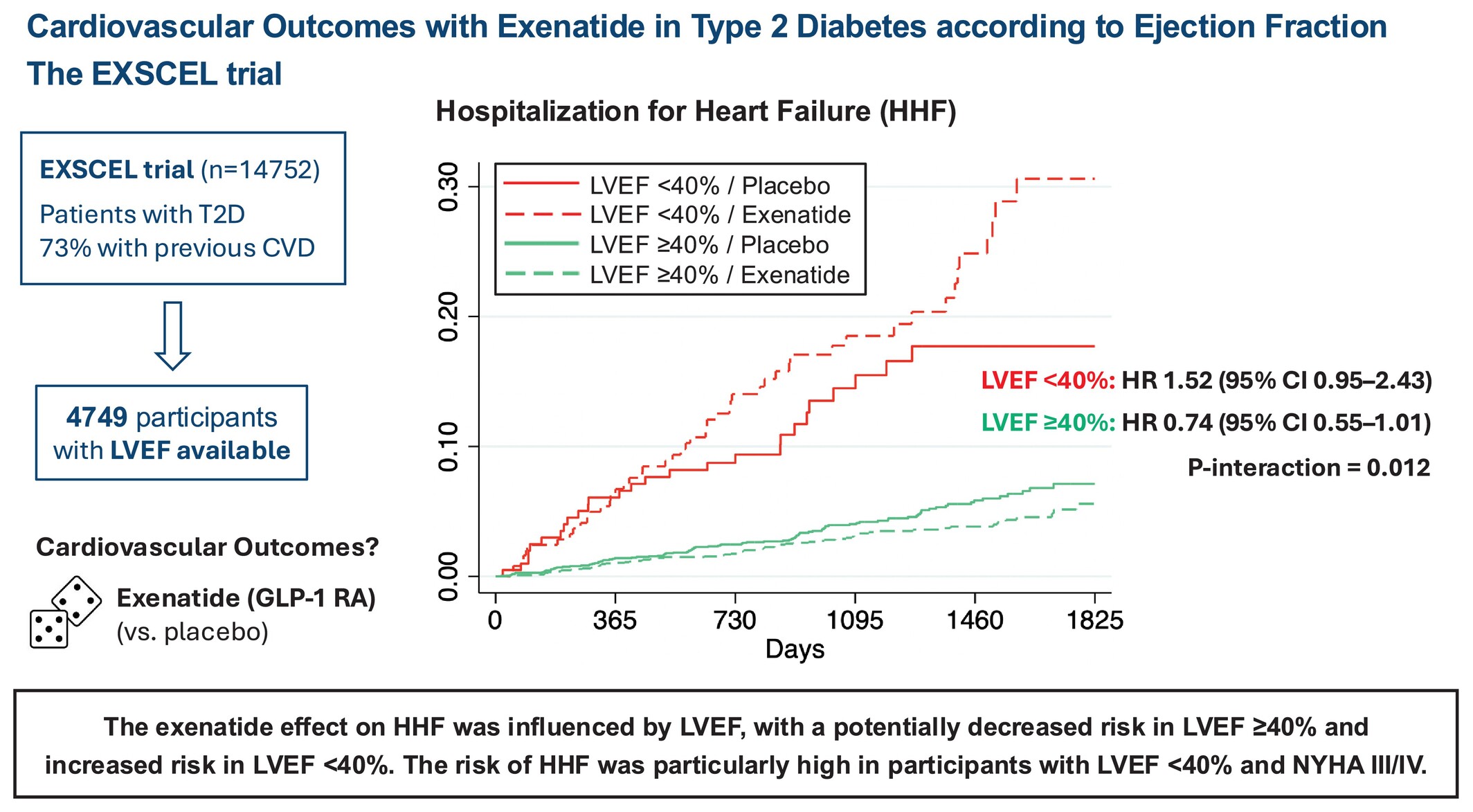
Cardiovascular outcomes with exenatide in type 2 diabetes (T2D) according to left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF): the EXSCEL trial. CI, confidence interval; CVD, cardiovascular disease; GLP-1 RA, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist; HHF, hospitalization for heart failure; HR, hazard ratio; NYHA, New York Heart Association.
Invited Editorial
Clonal haematopoiesis of indeterminate potential: A new biomarker for heart failure patients? Potential lessons to be learned from cardio-oncology
- Pages: 552-554
- First Published: 24 September 2024
Myeloperoxidase: Reviving an old ally for immunomodulation in heart failure?
- Pages: 555-557
- First Published: 18 September 2024
POST-MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION
Research Article
Association between body mass index and clinical outcomes in patients with acute myocardial infarction and reduced systolic function: Analysis of PARADISE-MI trial data
- Pages: 558-565
- First Published: 18 December 2024
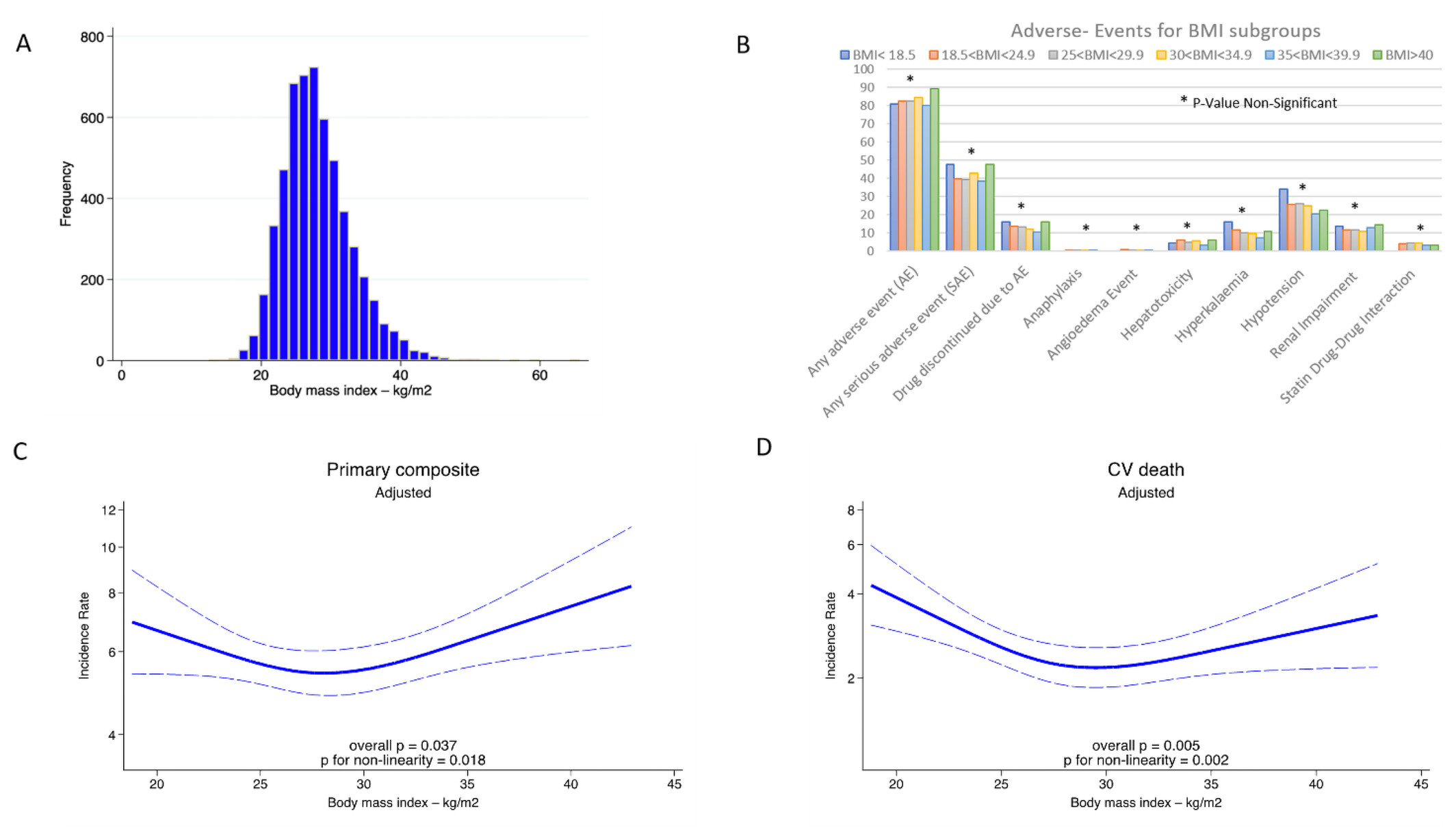
Association between body mass index (BMI) and clinical outcomes in PARADISE-MI. (A) Histogram for BMI (kg/m2), (B) adverse events for BMI subgroups, and spline model curves for (C) the primary composite outcome and (D) cardiovascular (CV) death by BMI subgroups. Covariates were adjusted for age (years), pulmonary congestion, percutaneous coronary intervention, left ventricular ejection fraction (%) and hypertension.
Empagliflozin to prevent worsening of left ventricular volumes and systolic function after myocardial infarction (EMPRESS-MI)
- Pages: 566-576
- First Published: 15 December 2024
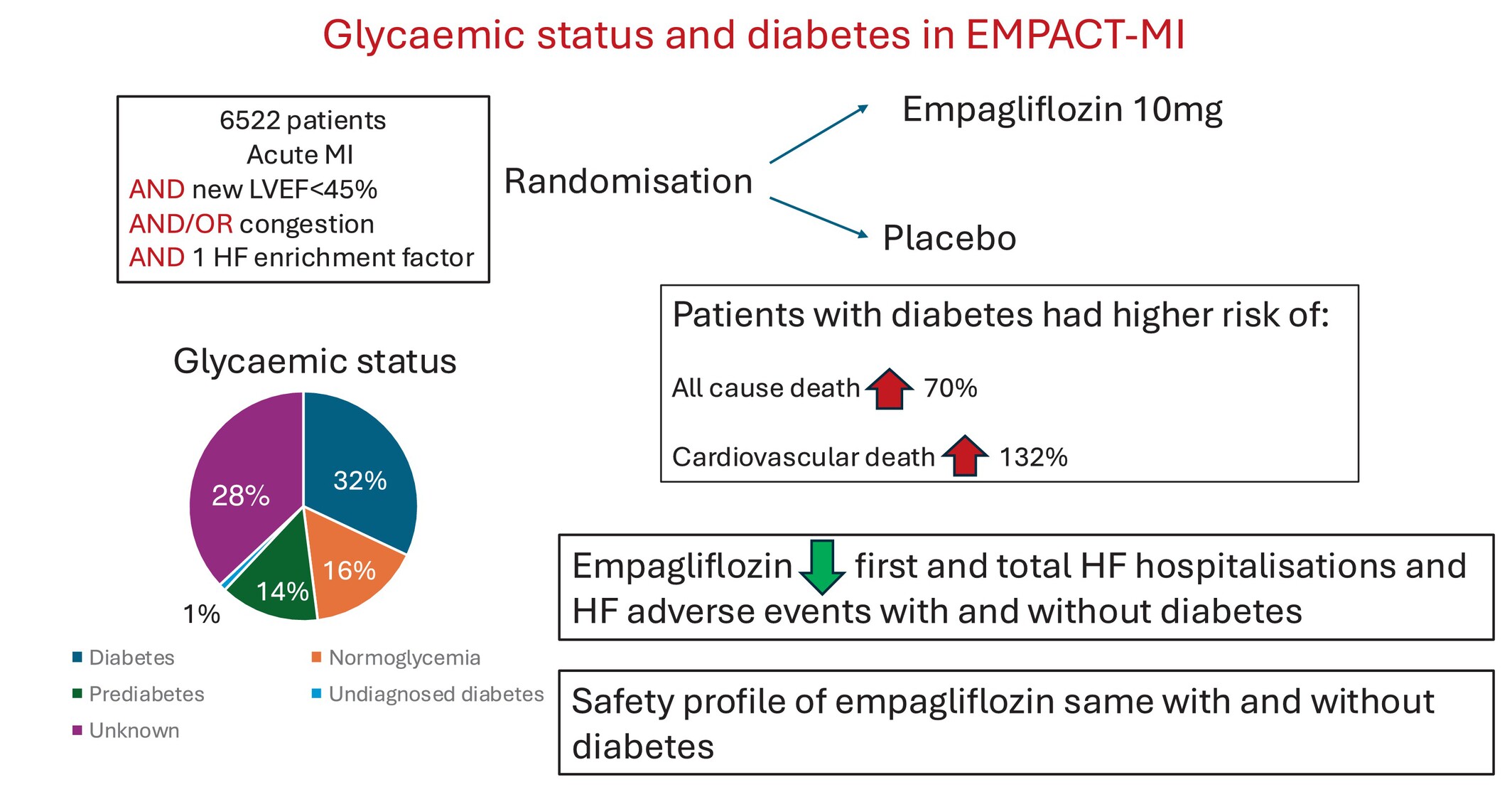
Empagliflozin in acute myocardial infarction in patients with and without type 2 diabetes: A pre-specified analysis of the EMPACT-MI trial
- Pages: 577-588
- First Published: 26 December 2024
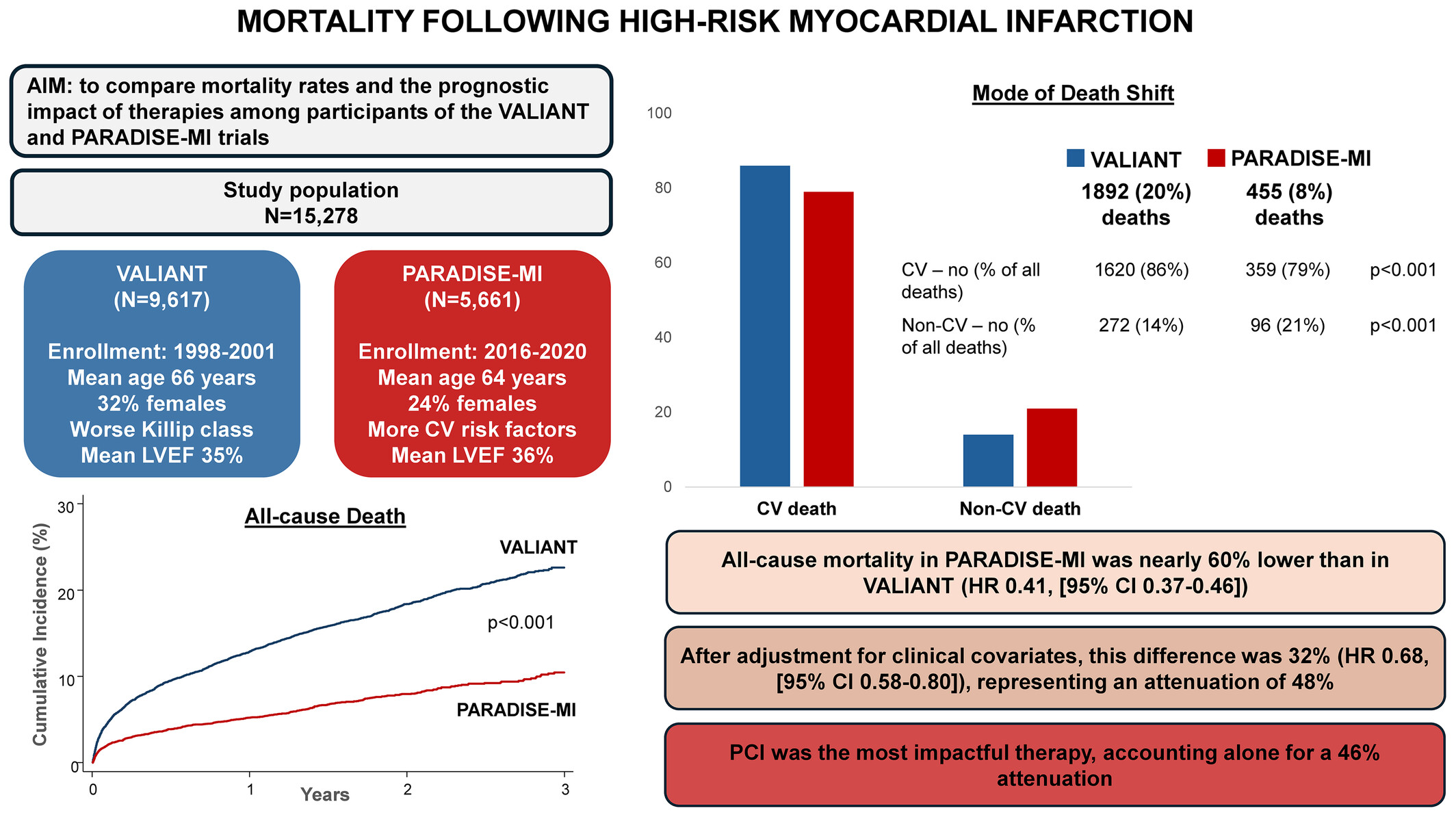
Mortality after high-risk myocardial infarction over the last 20 years: Insights from the VALIANT and PARADISE-MI trials
- Pages: 589-597
- First Published: 18 December 2024
Revascularization and outcomes in ischaemic left ventricular dysfunction after heart failure admission: The RevascHeart study
- Pages: 598-605
- First Published: 02 October 2024
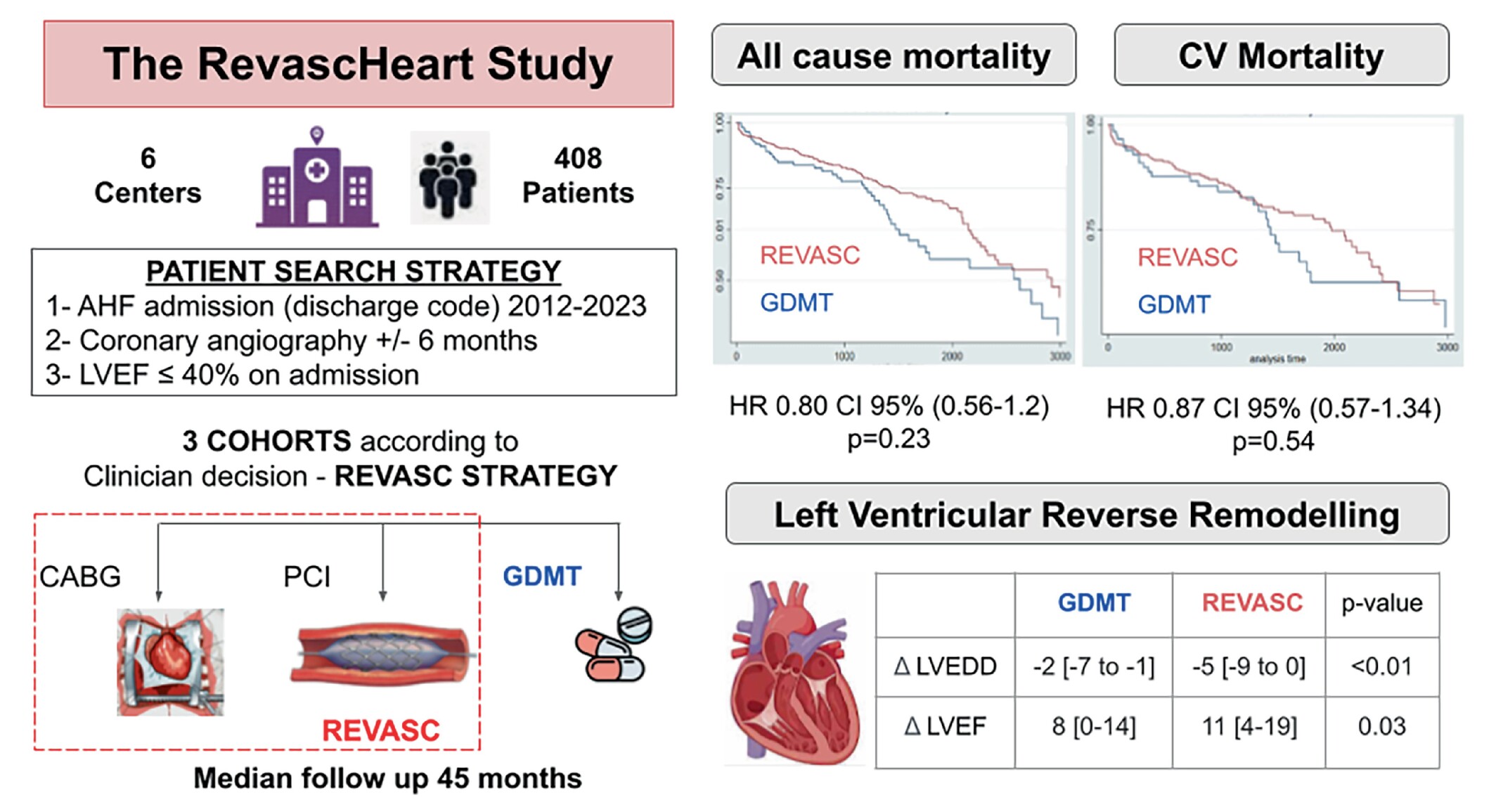
The RevascHeart study. AHF, acute heart failure; CABG, coronary artery bypass graft; CI, confidence interval; CV, cardiovascular; GDMT, guideline-directed medical therapy; LVEDD, left ventricular end-diastolic diameter; LVEF, left ventricular ejection fraction; OR, odds ratio; PCI, percutaneous coronary intervention.
RESEARCH LETTER
The DIGIT-HF trial: Key amendments of study design
- Pages: 606-608
- First Published: 21 January 2025
SCIENTIFIC CORRESPONDENCE
Aetiology and clinical manifestations of patients with non-dilated left ventricular cardiomyopathy. Some comments
- Page: 609
- First Published: 10 January 2025
Reply to ‘Aetiology and clinical manifestations of patients with non-dilated left ventricular cardiomyopathy. Some comments’
- Page: 610
- First Published: 09 January 2025