Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLE
The Signalled Licking/Avoidance of Punishment (SLAP) Paradigm in Rats: Capacity for Insight Between Goal Conditioning and Signalling Contingencies
- First Published: 09 July 2025
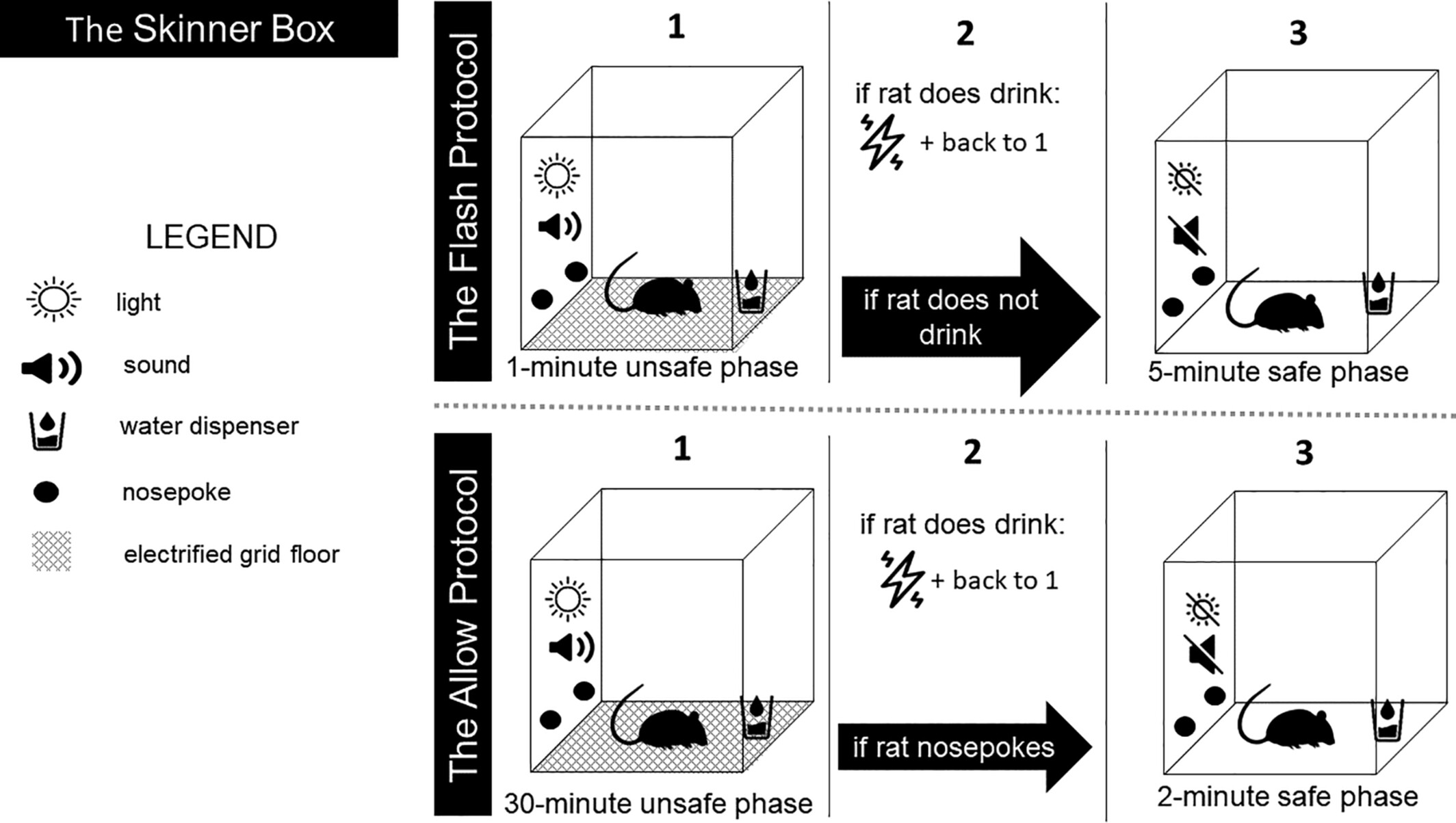
The SLAP protocols run within a Skinnerbox apparatus. The environment includes an electrified grid floor that can deliver electric foot shocks (1.5 mA; 2 s), a speaker (emitter of sound with a frequency of 3000 Hz; 75 dB). Two nose poke devices on the side wall, a green nose poke cue within, a single white lamp in the centre of the front wall, and a water dispenser that is linked to a digital lickometer. Two protocols were run. The ‘Flash’ protocol consists in 1 min of unsafe phase (i.e., sound and light on during which the licking is punished by a footshock) followed by 5 min of safe phase (i.e., sound and light off, for signalled free drinking) and so on subjects cannot stop the unsafe phase and should just wait by withholding licks. The ‘Allow’ protocol starts with a 30-min unsafe phase (signalled by sound and light). If subjects lick to drink water during this phase, they receive the electric foot shock. Rats can interrupt it and shift to a 2-min safe phase: by means of a single nose poke, both light and sound are turned off, the green nose poke cue flashes and rats are signalled about a free drinking contingency.
Navigating the Autism Journey: Parental Experiences, Barriers and the Role of Early Intervention in India
- First Published: 06 July 2025
This study explores the lived experiences of Indian parents navigating autism spectrum disorder (ASD) services. Through focus groups, parents shared challenges related to delayed diagnosis, limited support availability and high caregiving demands. The findings emphasize the need for culturally responsive, accessible and family-centred intervention models to better support families.
SHORT COMMUNICATION
Pontocerebellar Hypoplasia and Periventricular Leukomalacia Associated With p.Phe262Val Homozygous Variant in TTC1 Gene: A Report of 4 Cases
- First Published: 08 July 2025
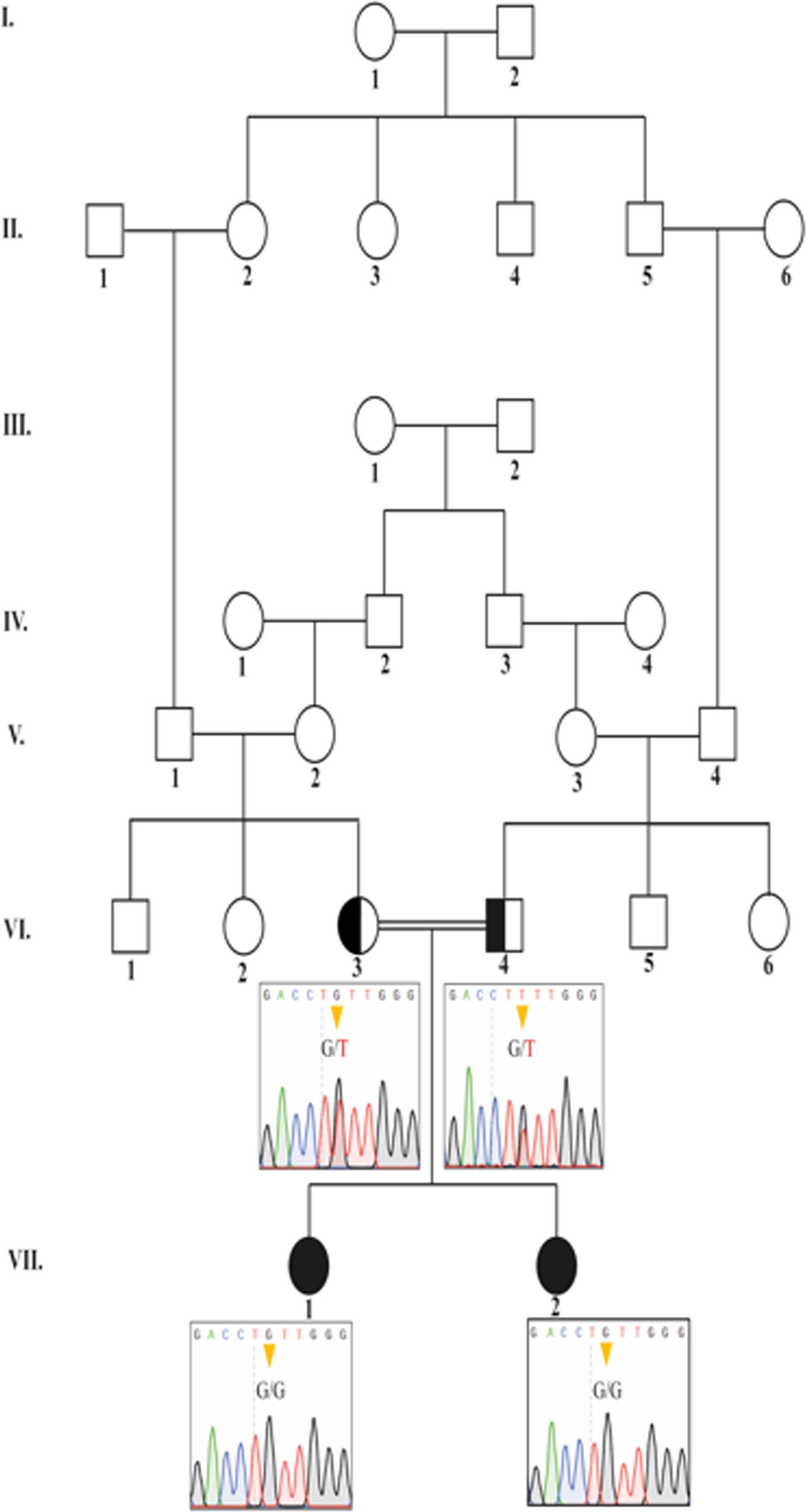
Pontocerebellar hypoplasia (PCH) encompasses a heterogeneous group of neurodevelopmental disorders, currently comprising 28 subtypes listed in the Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) database (as of May 2025). No clinical phenotype has been associated with the TTC1 gene. In this report, we present four female patients from two unrelated families with brain malformations. We identified a homozygous missense variant in TTC1 (NM_003314.3: c.784 T > G, p.Phe262Val) in all affected individuals. This variant is classified as likely pathogenic in the ClinVar database. Our findings in four patients confirm that this variant in the TTC1 gene may be associated with PCH and cerebral periventricular leukomalacia. To our knowledge, this is the first report implicating TTC1 in congenital brain malformations.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
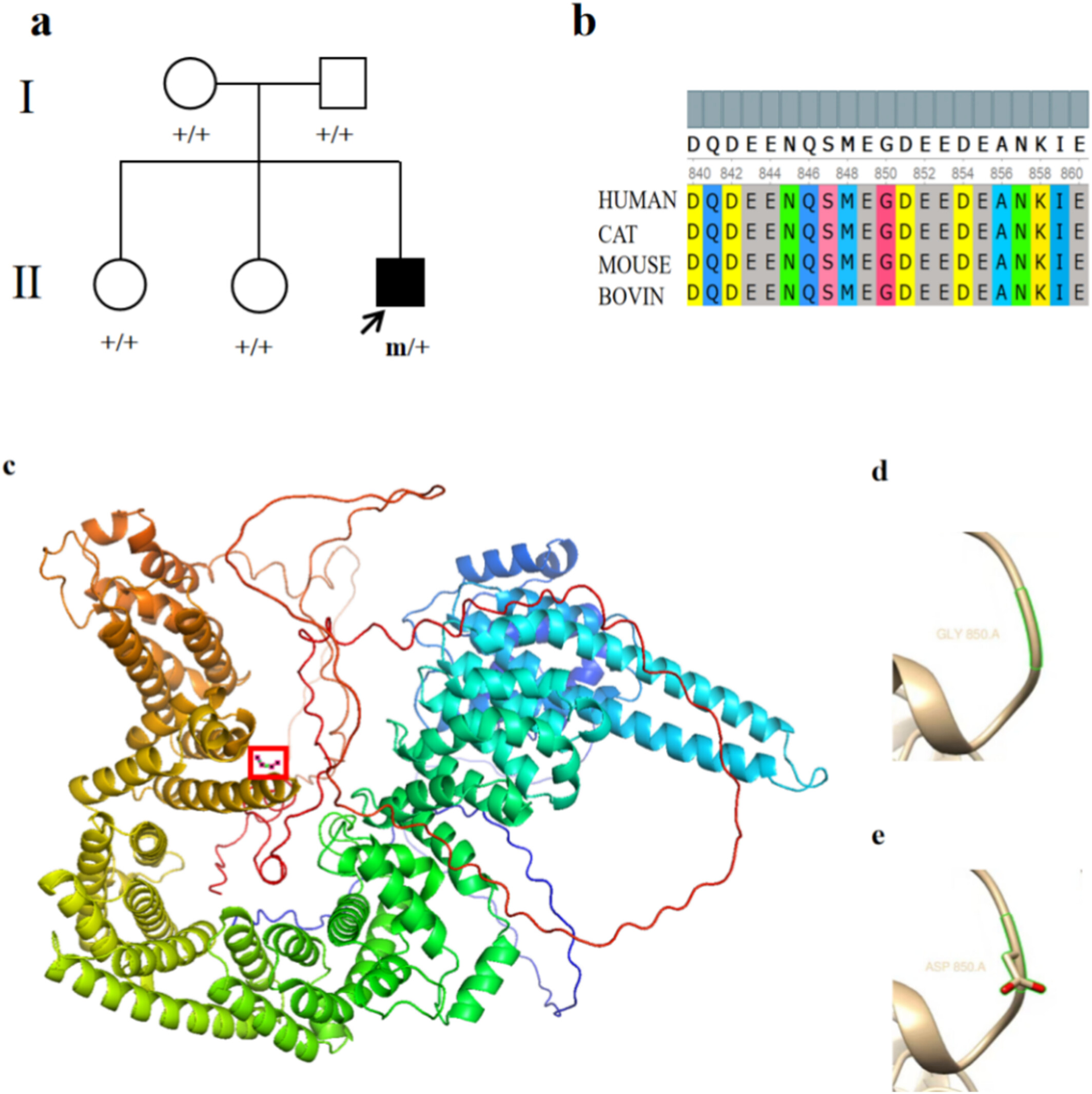
Neurological Disease Syndrome Caused by a STAG1 Gene Variant: A Case Report and Literature Review
- First Published: 08 July 2025
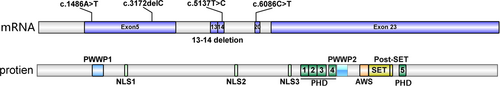
Sotos Syndrome With NSD1 Mutations in a Chinese Cohort: Identification of Two Novel Mutations and Literature Review
- First Published: 22 July 2025
Contribution of an Ambidirectional Cohort Study on the Epidemiology of 186 Autism Spectrum Disorder Cases in an Algerian Population
- First Published: 29 July 2025
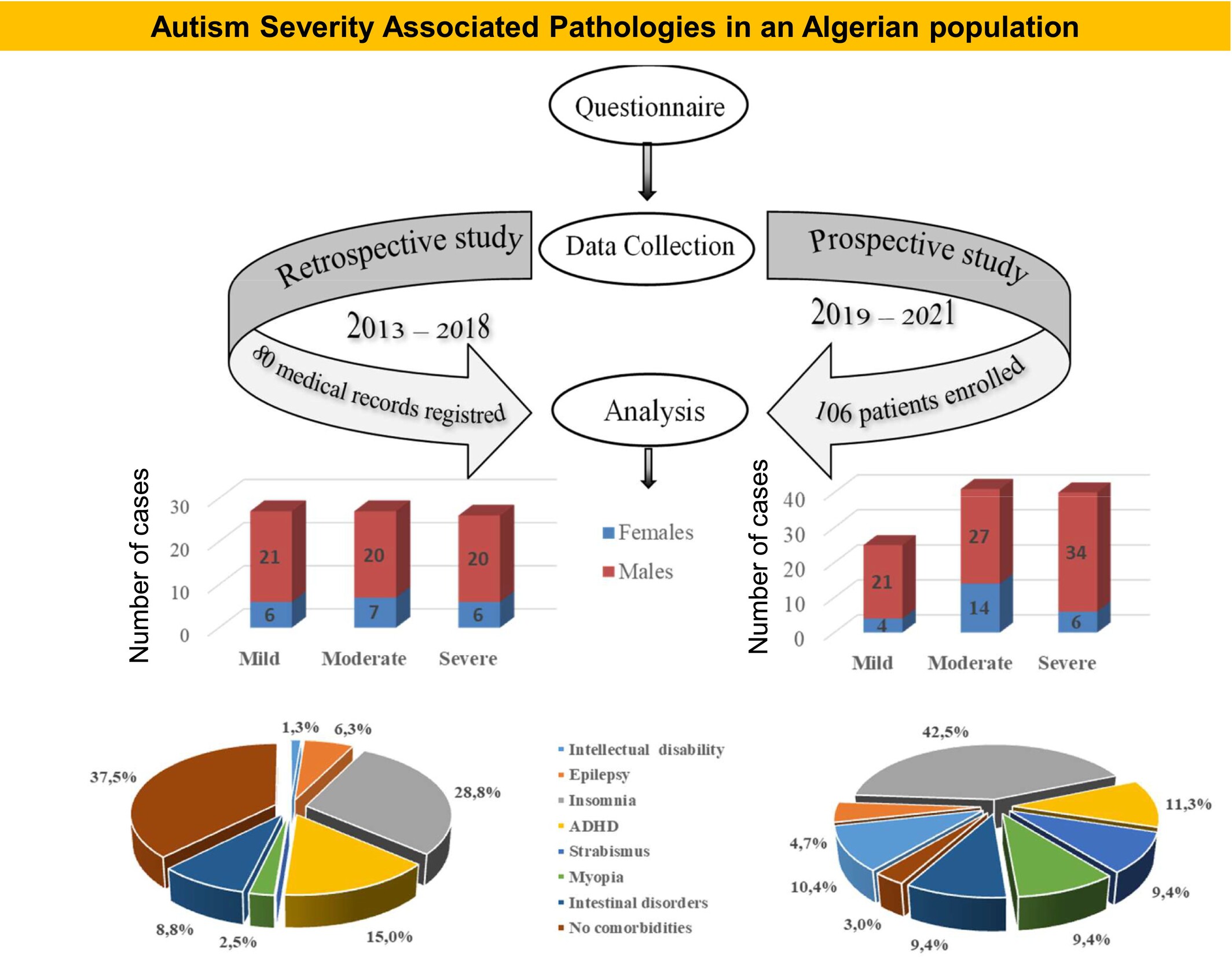
This study is the first to report clinical and paraclinical profiles of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in Algeria, as well as the prenatal, perinatal and postnatal factors. Findings were similar to other countries. The study highlights the need for increased awareness and training to improve early recognition of ASD in Algeria.