Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Effects of Weight-Compatible Design on Ingot Solidification
- First Published: 02 March 2021

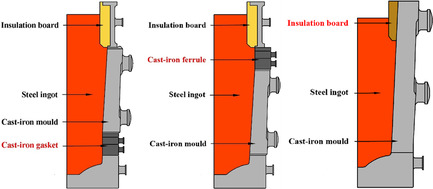
Three types of ingot moulds for weight-compatible are designed. Based on the prototype of 39t ingot mould, the 39-45t ingots could be produced by assembling the fittings. These three designs’ main characteristics of structure and quality of the ingot are introduced in the article, number 2000560, by Changjun Xu, and co-workers in detail.
Masthead
Contents
Reviews
A Review of Mathematical Process Models for the Electric Arc Furnace Process
- First Published: 30 September 2020
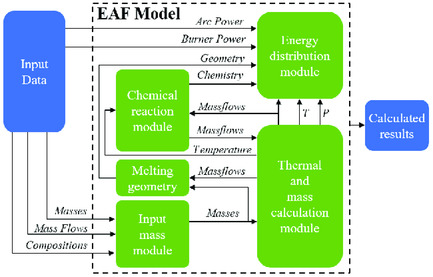
Mathematical process models for the electric arc furnace process are reviewed and compared with each other as well as other frequently used approaches such as statistical endpoint models and computational fluid dynamics. The different solutions used for problems such as the heat and mass transfer or the determination of scrap melting rates and the models’ capabilities are analyzed and evaluated.
Full Papers
Multi-Objective Optimization of Slab Heating Process in Walking Beam Reheating Furnace Based on Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm
- First Published: 19 October 2020
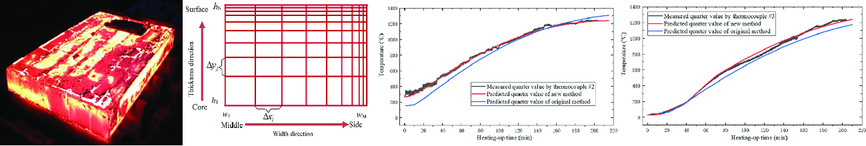
A 2D model of the finite difference scheme, in which the thickness and width are unequally partitioned, is investigated. Then, multi-objective optimization function of the temperature setting is established based on particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm. The application results show that the energy consumption of the reheating furnace is decreased and the production cost is minimized considerably.
Numerical Estimation of the Geometry and Temperature of An Alternating Current Steelmaking Electric Arc
- First Published: 09 October 2020
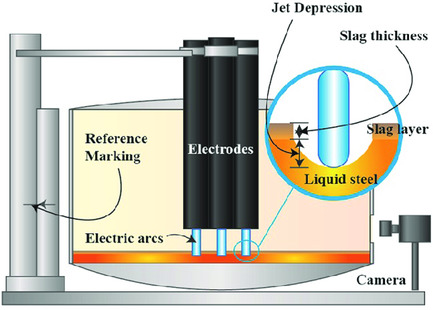
A model that predicts the length and the temperature of a steelmaking electric arc is presented. The model is validated using experimental data and the predictions are characterized with a maximum error of 3%. In comparison, the errors in the predictions from the empirical and the implicit formula proposed by Bowman are 9% and 12%.
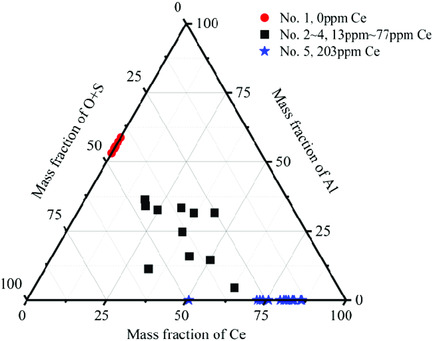
Effect of Ce Addition on Inclusions and Grain Structure in Gear Steel 20CrNiMo
- First Published: 04 November 2020
TiC–High Mn Steel-Bonded Cermets with Improved Strength and Impact Toughness
- First Published: 14 October 2020
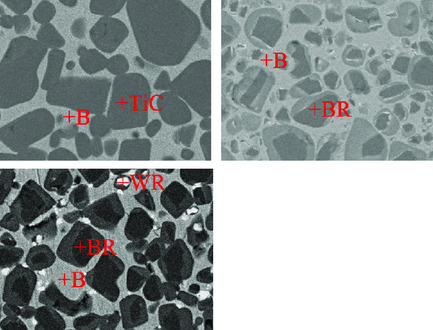
TiC–high Mn steel-bonded cermets are prepared by powder metallurgy techniques. The cermets have the highest impact toughness (IM) of 15.12 J cm−2 and transverse rupture strength (TRS) of 2510 MPa with (Ti0.5W0.5)C additive. Black core–gray outer rim structure forms with WC additives. White core–gray rim structure forms with (Ti0.5W0.5)C additives.
Microstructure, Mechanical Properties, and Strain-Hardening Behavior of V–N Microalloyed Pipeline Steels Consisted of Polygonal Ferrite and Acicular Ferrite
- First Published: 04 November 2020
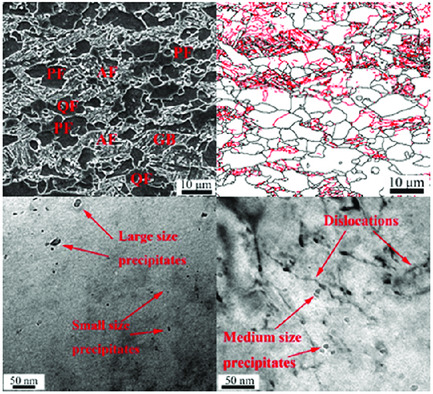
V–N microalloyed pipeline steels mainly consisted of polygonal ferrite and acicular ferrite exhibit a good combination of strength and toughness. Strain-induced V(C, N) precipitates of 20–30 nm facilitate intragranular nucleation of acicular ferrite, resulting in ferrite grain refinement. V(C, N) precipitates of 3–10 nm formed during or after ferrite transformation are beneficial for precipitation strengthening.
Investigating the Effect of Cementite Particle Size and Distribution on Local Stress and Strain Evolution in Spheroidized Medium Carbon Steels using Crystal Plasticity-Based Numerical Simulations
- First Published: 26 November 2020
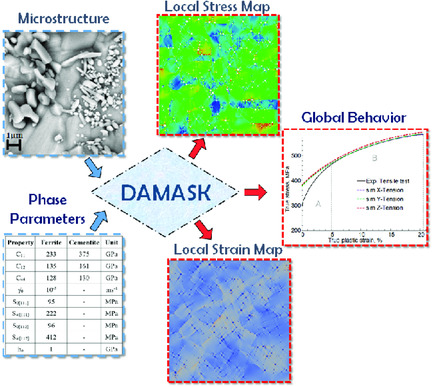
Micromechanical deformation behavior of C45EC steel under uniaxial tensile loading is modeled by varying cementite particle size and distribution in the ferrite matrix. Representative volume elements (RVEs) are virtually generated and simulated with—an open-source crystal plasticity-based modern computational tool—DAMASK. Factors influencing the global and local deformation are discussed with flow curves and the local stress and strain maps.
Energy Absorption and Deformation Behavior of 3D Printed Triply Periodic Minimal Surface Stainless Steel Cellular Structures under Compression
- First Published: 03 November 2020
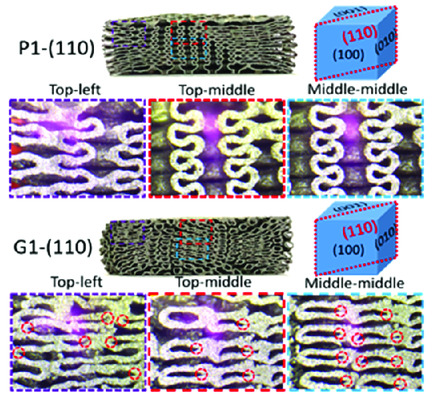
The energy absorption performance and deformation mechanism of 316L triply periodic minimal surface (TPMS) structures are investigated. Both primitive (P)- and gyroid (G)-type TPMS structures possess a high-energy absorption capacity. P-type outperforms G-type structure at relative densities <0.35. The P-type structure deforms locally in a diagonal shear geometry, whereas G-type structure deforms uniformly with a strong strain hardening effect.
A Novel Method for Evaluating the Combustion Characteristics of Carbon Materials and Mold Fluxes
- First Published: 10 November 2020
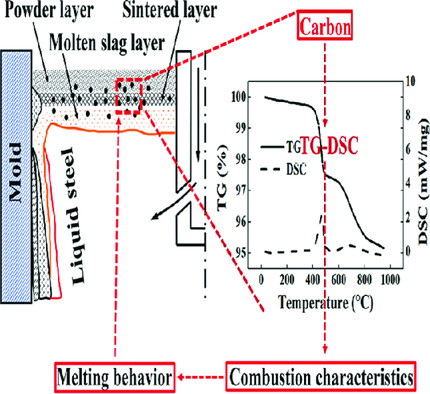
A novel method is proposed to research the combustion characteristics of different carbon materials added to mold fluxes, and then, the effect of different carbon materials on the combustion and melting behavior of mold fluxes is analyzed. The results show that the novel method can well characterize the combustion properties of carbon materials and be easily operated.
Effect of Reduction Degree on Characteristics of Slag Formed by Melting Hydrogen-Reduced DRI and Partitions of P and V between Slag and Metal
- First Published: 04 November 2020

Hydrogen-reduced iron is melted at 1873 K to study the phosphorus and vanadium partitions and the slag characteristics as a function of reduction degree. Phosphorus partition is maximum at 96.8% reduction, whereas vanadium partition increases with decreased reduction degree. Vanadium is concentrated in the solid magnesiowüstite and spinel phases.
The Flow Stress Behavior and Constitutive Model of Cr8Mo2SiV Tool Steel during Hot Deformation
- First Published: 01 December 2020
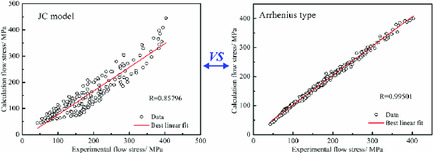
The Johnson–Cook (JC) model and the modified Arrhenius-type equation considering the compensation of strain are proposed for estimation of flow stress of the tool steel. The values of correlation coefficient (R) in JC model and modified Arrhenius-type model are calculated to be 0.85796 and 0.99501, respectively. The developed Arrhenius equation is more accurate.
Effect of Temperature on Dephosphorization of Hot Metal in Double-Slag Converter Steelmaking Process by High-Temperature Laboratorial Experiments
- First Published: 01 October 2020
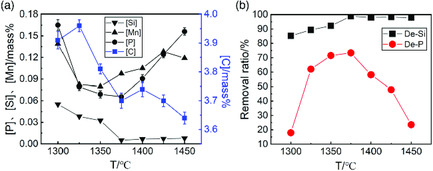
The influence of temperature on the dephosphorization of hot metal at the low temperature range of 1300–1450 °C with the slag basicity (CaO/SiO2) of about 1.8 is investigated using high-temperature laboratorial experiments. The results show that the phosphorus contents in hot metal decrease first and then increase with increasing temperature.
Microstructural Evolution during Homogenization and Hot Deformation for As-Cast H13 Steel
- First Published: 07 December 2020
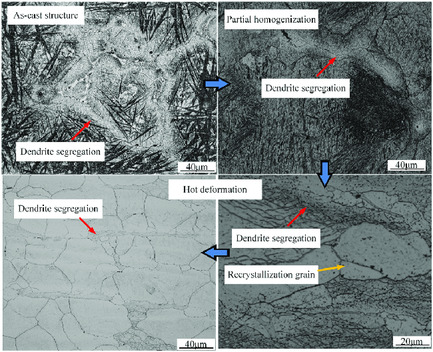
There exists the extensive dendrite segregation in as-cast H13 steel. After partial homogenization, the recrystallized grains prefer to nucleate in the dendrite region, and the enriched alloying atoms and carbide particles in the dendrite segregation region will obviously inhibit the recrystallization grain growth. The partial homogenization before hot deformation is beneficial to achieve the fine microstructure.
Microstructure Evolution and Kinetics of Static Recrystallization of Medium Mn Steel in the Two-Hit Isothermal Compression
- First Published: 13 October 2020
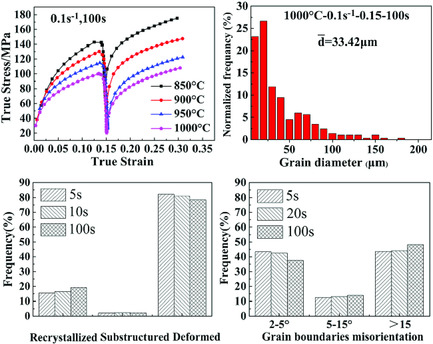
Microstructure evolution and kinetics of static recrystallization (SRX) of medium Mn steel are investigated by the two-hit compression. Electron backscatter diffraction analysis shows that both static recovery (SRV) and SRX contribute to static softening, but the predominant softening mechanism is SRV. In addition, temperature, interval time, and strain rate have influence on the distribution and average magnitude of grain size.
Mineral Transform and Specific Heat Capacity Characterization of Blast Furnace Slag with High Al2O3 in Heating Process
- First Published: 03 November 2020
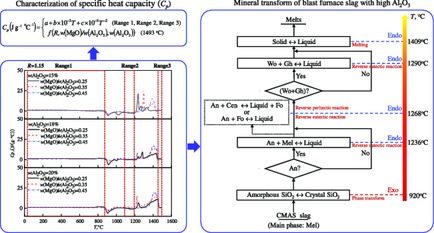
Herein, mineral transform and specific heat capacity (Cp) characterization of blast furnace slag in heating process are investigated. There are phase transforms from amorphous to crystal and from solid to liquid in all cases. Reverse peritectic reaction or reverse eutectic reaction would proceed in some cases. The relationships of Cp with temperatures and compositions are established with a good fit.
Effect of Simulated Annealing Conditions on Scale Formation and Neutral Electrolytic Pickling
- First Published: 14 November 2020
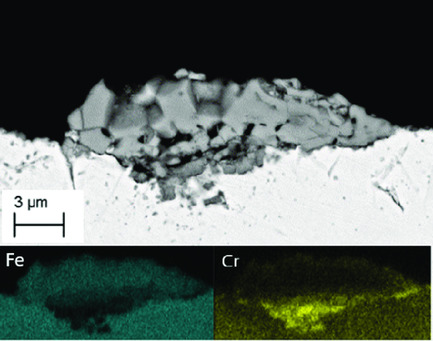
Final annealing of cold-rolled, AISI 304 stainless steel is simulated in a humid atmosphere. The characteristics of oxide scales are influenced by the success of the electrolyte pickling process. Annealing conditions in which the growth of oxide scale remains steady and the pickling process is effective are presented. The evaluation of the pickling effectiveness is performed by image analysis.
Evaluation of Mechanical Properties and Microstructures of Direct-Quenched and Direct-Quenched and Tempered Microalloyed Ultrahigh-Strength Steels
- First Published: 23 October 2020
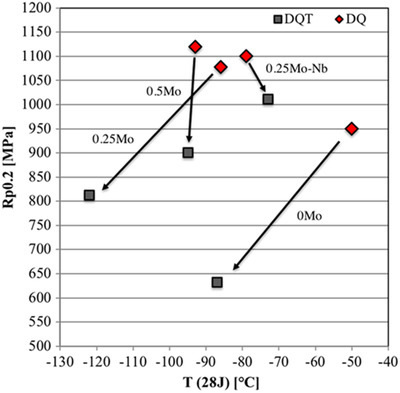
The alloying of molybdenum and niobium in high strength steels has been investigated in both direct-quenched and direct-quenched and tempered conditions. Results indicate that molybdenum prevents softening during tempering mainly by solute drag. Addition of niobium combines strong precipitation strengthening and solute drag. Superior mechanical properties can be achieved with studied compositions in both direct-quenched and tempered conditions.
Coke Gasification in Blast Furnace Shaft Conditions with H2 and H2O Containing Atmospheres
- First Published: 02 November 2020

The gasification of coke is studied in simulated blast furnace (BF) atmosphere acquired from an actual BF using a Multi-Point Vertical Probe and consisting of CO, CO2, H2, H2O, and N2. This allows the examination of effect H2O and the location (wall versus center) have on the coke gasification behavior.
Heat Transfer Correlations for Secondary Cooling in Continuous Casting
- First Published: 16 November 2020

Herein, a correlation for heat transfer coefficient is given. The results are valid for spray cooling of hot surfaces with film boiling, starting at temperatures of about 1200 °C and finishing at the Leidenfrost point. This study uses both water and mist nozzles. It is experimentally verified why equations based only on the water impingement density cannot provide sufficiently precise predictions of HTC.
The Role of Microstructural Constituents on Strength–Ductility–Local Formability of a Transformation-Induced-Plasticity-Aided Bainitic Steel
- First Published: 03 October 2020
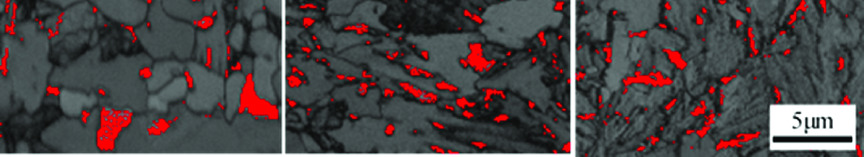
The ferrite and transformation-induced-plasticity (TRIP) effect provided by blocky retained austenite contribute to higher uniform elongation but lower post uniform elongation (PEL). Both hole expansion ratio and bending ratio have a linear relationship with PEL and yield ratio (YR). Uniform bainitic microstructure increases the balance of strength and local formability, in which the role of PEL is consistent with YR.
Effect of Ta and Ti on Modified Reduced Activation Ferritic/Martensitic Steels with a Thermo-mechanical Control Process
- First Published: 28 October 2020
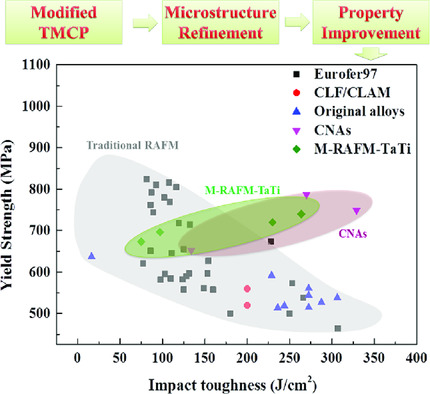
Modified reduced activation ferritic/martensitic steels with different contents of Ta and Ti are fabricated with the thermo-mechanical control process (TMCP). They show greatly improved comprehensive mechanical properties compared with traditional reduced activation ferritic/martensitic steels. The effect of Ta and Ti on both microstructure and properties in the condition of TMCP is analyzed in detail.
Continuous Severe Plastic Deformation of Low-Carbon Steel: Physical–Mechanical Properties and Multiscale Structure Analysis
- First Published: 06 November 2020
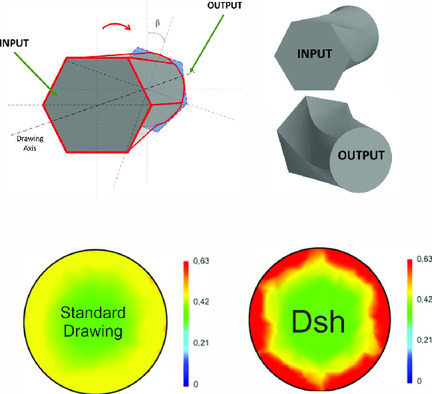
A successful attempt to incorporate knowledge obtained from severe plastic deformations into continuous processes is made. The modeling of plasticity resource prediction, and based on this effective deformation routine is developed. The incorporation of SPD advantages allows controlling of plasticity during drawing deformation. All side investigation of structure and properties is made.
Modeling of Two-Phase Flow in Blast Furnace Trough
- First Published: 17 November 2020
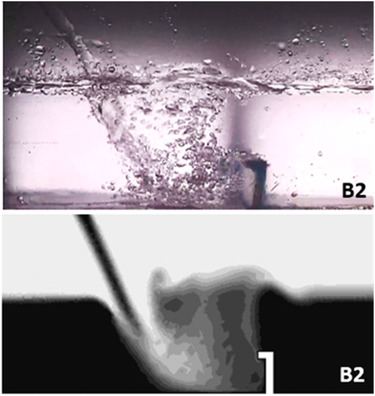
Metal losses during the blast furnace casting operation are due to dispersion of metal droplets in the slag. The economical impact of metal losses is important because large tonnages are involved. Metal losses change as a function of slag–metal ratio of flow rates as well as geometry of the runner. These aspects are highlighted by physical and mathematical modeling.
Investigation on Hot Compression Precipitation and Recrystallization Behavior of 23.7Cr–2.2Ni–1.3Mo–14Mn–0.26N High-Manganese Low-Nickel Duplex Stainless Steel
- First Published: 20 October 2020
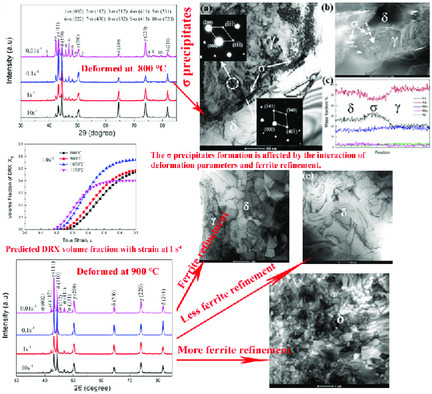
Herein, the hot compression behavior of 23.7Cr–2.2Ni–1.3Mo–14Mn–0.26N low-nickel duplex stainless steel is investigated, and the influencing rules and mechanism of deformation parameters on dynamic recrystallization (DRX) and σ precipitate are obtained. The relationship between the critical conditions for DRX initiating and Zener–Hollomon parameters and modified DRX kinetics model are established.