Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Picture: steel research int. 6/2019
- First Published: 03 June 2019

Cover Photo:
Since 90 years, the Institute of Metal Forming at TU Bergakademie Freiberg is active in the development of efficient forming technologies for metallic materials with tailored properties. Recent work is focusing on low alloyed hot rolled bainitic steel. The best ratio between tensile strength (1340 MPa) and total fracture elongation (22%) was found for a microstructure (EBSDImage on cover) with blocky retained austenite offering an attractive material for building, mining and even lightweight automotive construction. Further details can be found in the article 1800386 by Korpala and co-workers.
Masthead
Contents
Special Section: MEFORM 2018 (Guest-Editors: Rudolf Kawalla, Ulrich Prahl)
The Influence of Hot-Rolling Conditions on the Content and Morphology of Retained Austenite in Ultra-High Strength Bainitic Steel and Its Mechanical Properties
- First Published: 07 March 2019
The Kinetics of Dynamic Recrystallization of Fe–16Cr–xMn–4Ni–0.05C–0.17N Steel
- First Published: 12 October 2018
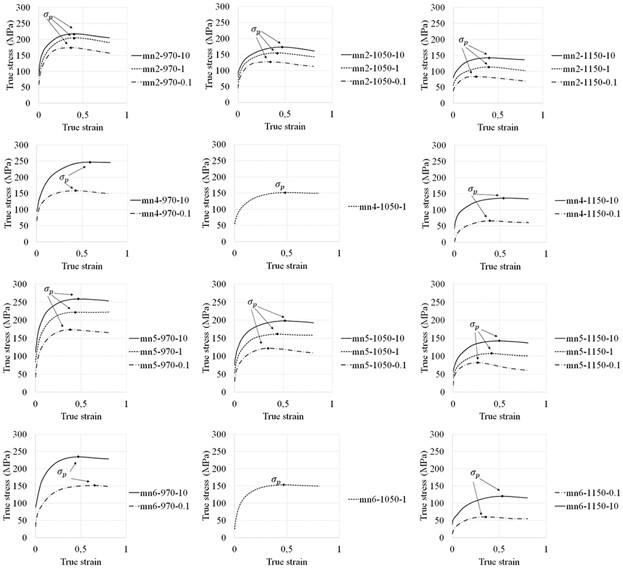
The kinetics of dynamic recrystallization of Fe–16Cr–xMn–4Ni–0.05C–0.17N steel is investigated in dependence of the Mn content (2 to 6 wt%) by isothermal compression tests. The results show a slight effect on the peak stress. The dynamic recrystallization is modeled by JMAK equation, which is expanded by including the linear dependency of material constants of the Mn content.
Mathematical Description of the Microstructural Modifications and Changes in the Mechanical Properties during Spheroidization of Medium-Carbon Steel
- First Published: 31 October 2018
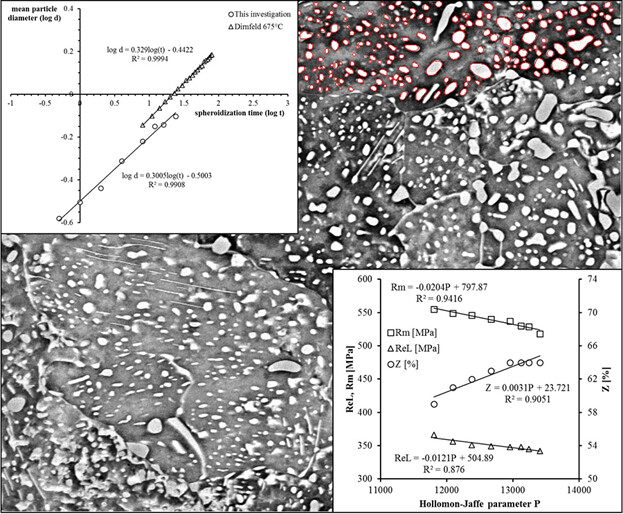
In this work, the authors carry out a critical comparative analysis of all current empirical-physical models of the kinetics of spheroidization and the coarsening of cementite as well as the relationship between the microstructure and tensile properties during intercritical spheroidization annealing using AISI 1024 steel. The experimental data are used to calibrate the models found in the literature, and the resulting equations may be of interest for researchers involved in the heat treatment of steel.
Effect of hot Rolling and Cooling Conditions on the Microstructure, MA Constituent Formation, and Pipeline Steels Mechanical Properties
- First Published: 24 September 2018

The influence of MA phase amount and size is studied on two-microalloyed pipeline steels produced with varying rolling temperature and accelerated cooling rate. Thus, application of thermomechanical rolling with high cooling rate positively influences on MA constituents and microstructure refinement, and has positive effect on elongation and impact toughness results.
Experimental Investigations and Multiscale Modeling to Study the Effect of Sulfur Content on Formability of 16MnCr5 Alloy Steel
- First Published: 27 December 2018
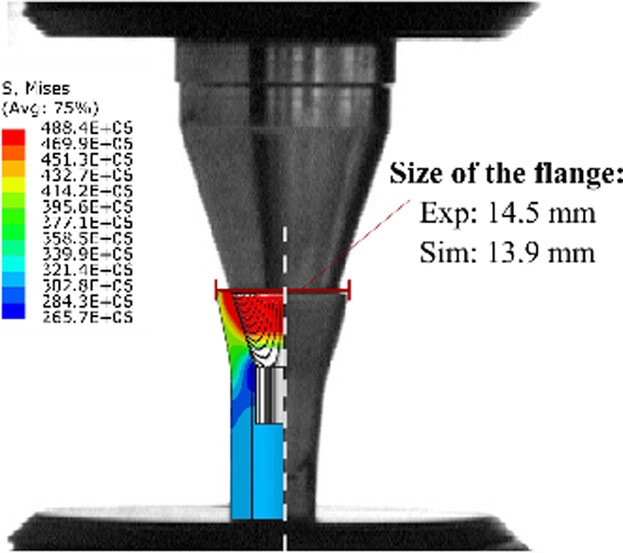
Effect of varying Sulfur content in 16MnCr5 alloy steel on the formability of this steel grade is studied. Tensile tests, transverse extrusion tests, expansion tests, and compression tests on spherodized and normalized samples are performed. Developed multiscale numerical simulation models help in studying the macroscopic deformation behavior and microscopic interplay of different phases during forming.
Deformation Behavior of Particle Reinforced TRIP Steel/MgPSZ Composite at Hot Working Temperatures
- First Published: 31 October 2018
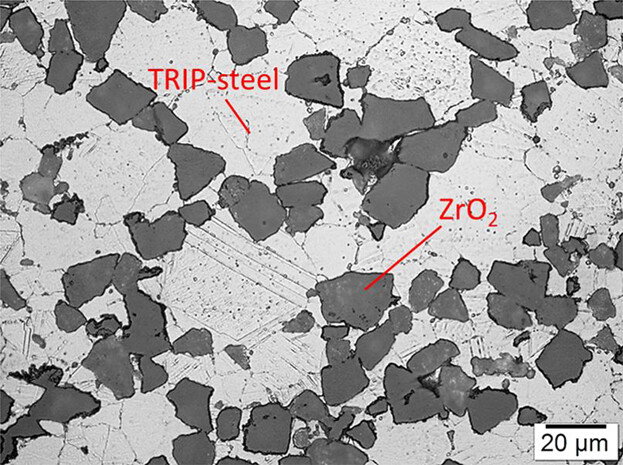

In this article, the formability of ZrO2 particle-reinforced TRIP matrix composites under hot working temperatures is investigated in detail. The main focus is on the flow behavior of the matrix and the particles as well as the particle orientation after forming. Pressure forming processes and temperatures between 700 and 1200 °C are used to form the specimens accord-ingly.
The Influence of Segregations after Forming on the Heat Treatment Result of Bevel Gears
- First Published: 28 February 2019
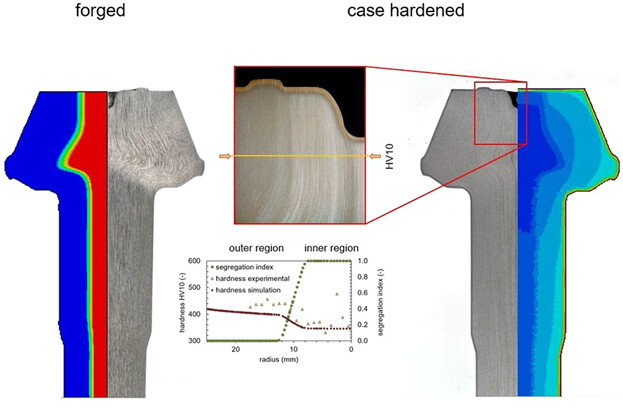
In forged components, segregations cannot be avoided. In this paper, segregations within the hot rolled bar and after cold forging to bevel gears are analyzed during forming and the influence on the microstructure after heat treatment is discussed. Therefore, a coupled forming-heat treatment simulation is presented including segregations. The final microstructure and hardness distribution of formed parts is calculated and discussed in comparison with the experimental results.
Copper-Alloyed Precipitation-Hardenable-Ferritic-Pearlitic Steel for Energy-Efficient and Distortion-Reduced Production of Cold-Formed, High-Strength Structural Components
- First Published: 29 April 2019
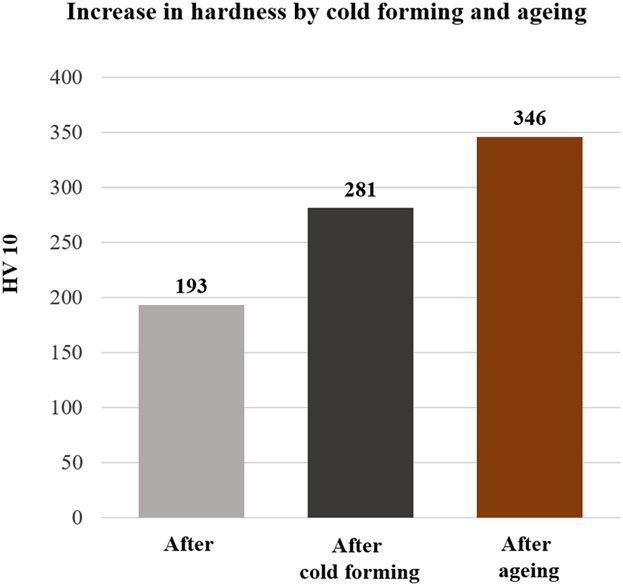
A significantly increased copper content and the development of an appropriate rolling and heat treatment technology produce ultrafine copper precipitates in a cold-formed microstructure of a hardenable ferritic perlite steel. An increase in strength of up to 200 MPa by aging is possible without conventional quenching and tempering and the resulting post-processing steps.
Full Papers
Influence of the Crystallographic Orientation on the Yield Strength and Deformation Mechanisms of Austenitic Grains in Metastable Stainless Steels Investigated by Spherical Nanoindentation
- First Published: 28 March 2019
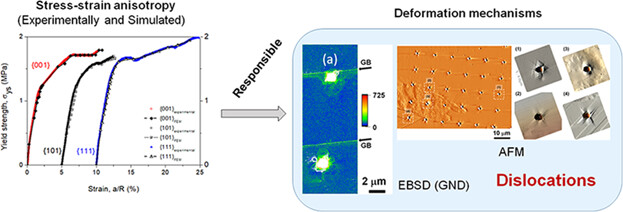
Mechanical behavior of a metastable stainless steel is studied by spherical nanoindentation as a function of crystallographic orientation. Residual imprints are analyzed by EBSD and AFM. Results show that austenite grains with different crystallographic orientations display similar trend, being the Frank-Read source the main deformation mechanisms. No evidence of stress-induced phase transformation is observed.
On the Correlation between Suitable Material Parameters for the Prediction of Local Formability of Advanced High Strength Steels
- First Published: 28 March 2019

Recently, the parameter “true fracture strain” (TFS) is discussed in order to assess local formability of AHSS more reliably. The present studies show that a general correlation of TFS and local formability does not exist particularly when considering hot rolled steel grades. It is concluded that for any material classification scheme crack resistivity must be considered additionally to TFS.
Flash Reduction Behavior of Magnetite Concentrate Particles in Methane–Nitrogen Atmospheres
- First Published: 27 February 2019
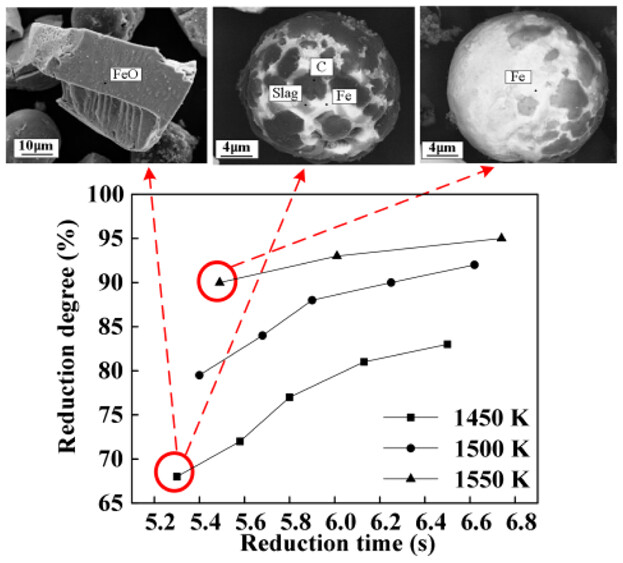
The flash reduction behavior of magnetite by CH4 is investigated at 1450–1550 K by means of thermodynamic analysis and experiment to obtain the influences of methane concentration and reduction temperature on the reduction degree, phase, external morphology, and internal morphology of reduced particles and reveal the reaction mechanism.
Compression Deformation Behavior of a Fe–26Mn–7Al–1.3C Austenitic Steel after Precipitation-Hardened Treatment
- First Published: 25 February 2019
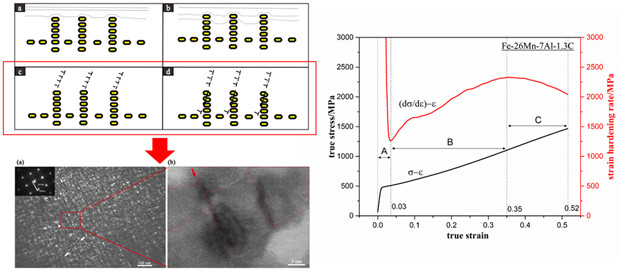
True stress (σ) and strain hardening rate (dσ/dϵ) against true strain (ϵ) curves exhibit continuous strain hardening characteristics. Due to the multi-faceted interactions between the κ-carbides and different types of dislocation, it brings excellent strain hardening ability. The experimental steel obtains an excellent combination of yield strength and toughness associated with multiple-stage strain hardening.
Effect of Intercritical Austenitizing Temperature during Quenching–Intercritical Quenching–Tempering Process on Toughness of 25Mn2Si2Cr Bainitic Steel
- First Published: 27 February 2019
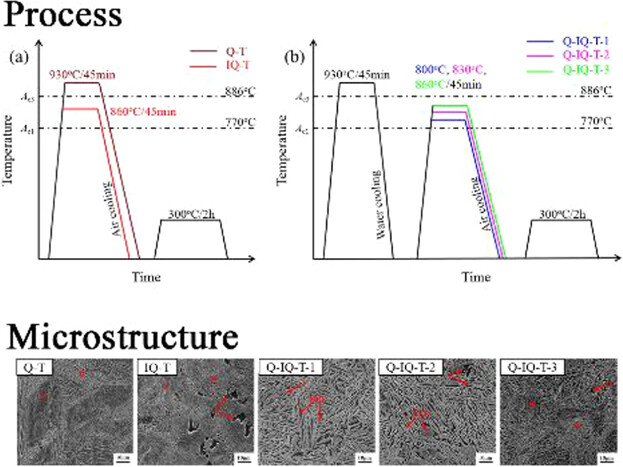
An intercritical quenching process is introduced between conventional water quenching and tempering to 25Mn2Si2Cr bainitic steel. Compared with the quenching–tempering (Q–T) process, quenching–intercritical quenching–tempering (Q–IQ–T) process can improve mechanical properties of 25Mn2Si2Cr steel. When intercritical quenching temperature is 860 °C, the objective of improving both strength and toughness is achieved.
Experimental Investigation of the Influence of a Centered Line Sparger on the Jet from the Shroud in a 1:3 Water Model of a Tundish
- First Published: 08 April 2019
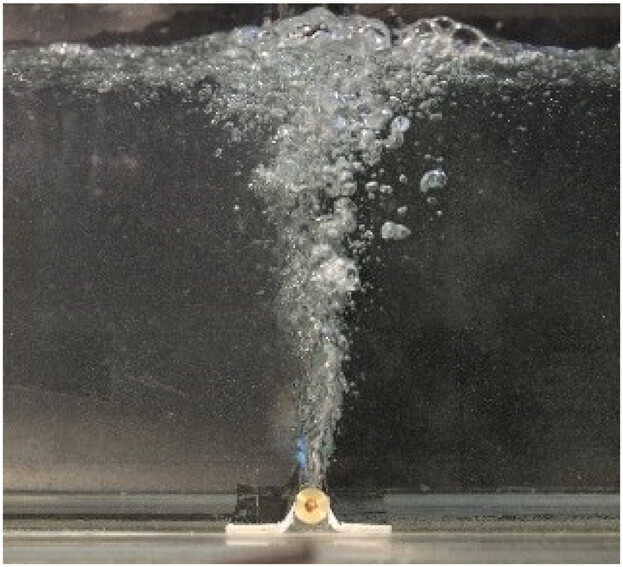
The tundish of a continuous casting plant is a main tool to remove non-metallic particles from the melt. In order to remove very small particles floatation is a valuable tool. This paper focuses on the influence of the floatation bubbles on the liquid flow field and proposes a dimensionless number to quantify the impact.
Influence of V and Nb Micro-Alloying on Direct Quenched and Tempered Ultra-High Strength Steels
- First Published: 18 March 2019
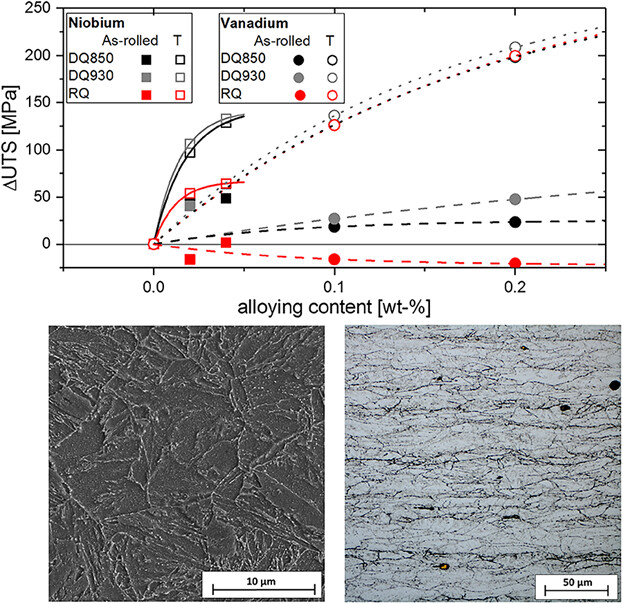
This paper contains an investigation of the influence of V and Nb on different production routes of ultra-high strength (UHS) steels. The mechanical properties and anisotropy of TM rolled and direct quenched steels are compared to those produced via a conventional Q + T route. This investigation provides insight into the microstructure-property relationship of UHS steels in as-rolled and tempered condition.
Flow Interaction in Continuous Casting Tundish Due to Bubble Curtain Operation
- First Published: 08 April 2019
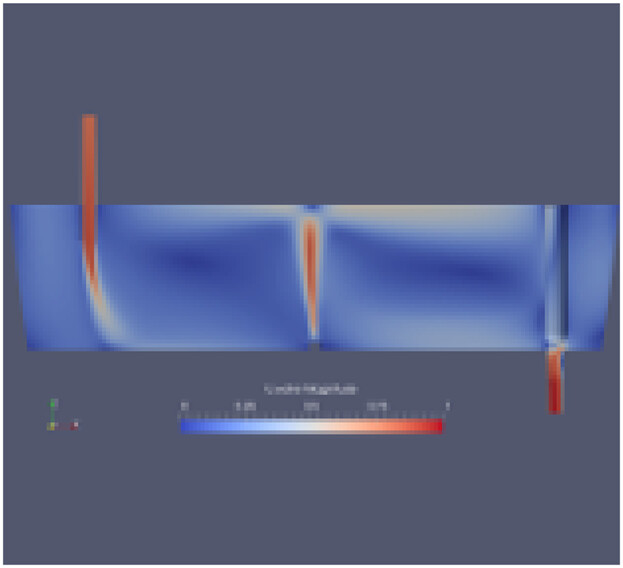
Gas bubbling in a tundish leads to an interaction between the liquid jet from the ladle shroud and recirculation caused by the bubble plume. If the interaction is sufficiently strong, the liquid jet will be deflected. This deflection constitutes an adverse effect of the gas bubbling on the internal flow of the tundish.
Impact Toughness and Fracture Structure about Welded Joints of Low Chromium Nickel Ferritic Stainless Steel Containing Ce/Ti
- First Published: 06 March 2019
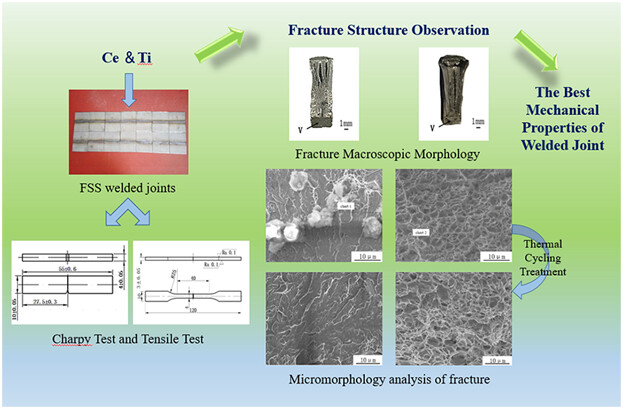
Ce and Ti are added in ferritic stainless steel welded joints to improve impact toughness. Charpy test and tensile test are carried out and the fracture structure is analyzed. The fracture is main ductile fracture and dimple, the dimples is parabolic. After thermal cycling, the oxide particles reduce and so the impact toughness is improved.
A Sequence-Coupled Mathematical Model of Magneto-Hydrodynamic Two-Phase Flow and Heat Transfer in a Triplex-Electrode Electroslag Remelting Furnace
- First Published: 12 April 2019
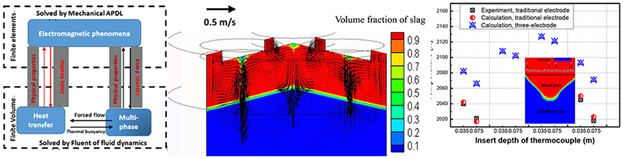
The triplex-electrode electroslag remelting furnace has the advantages of balanced load and reason able short network structure. A transient three dimensional (3D) sequence-coupled mathematical model is developed to explore magneto-hydrodynamic two-phase flow and heat transfer in the TE-ESR furnace. Compared to the traditional ESR process, the electromagnetic field, fluid flow, temperature, and solidification in the TE-ESR completely system is different.
Modeling of Turbulent Flow around Bubbles in Molten Steel
- First Published: 16 April 2019
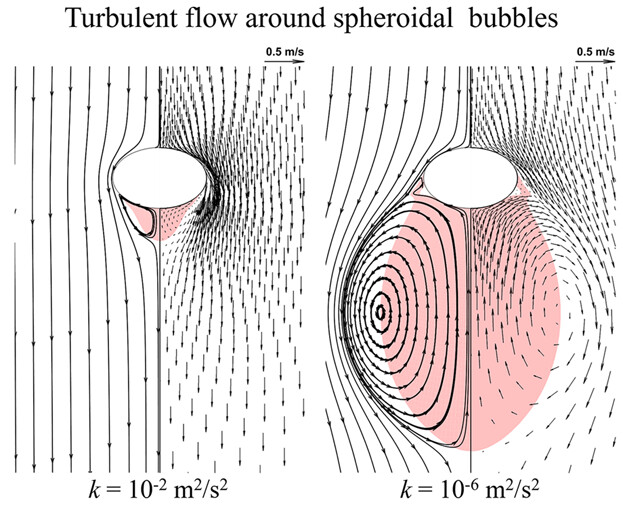
Turbulent flow around bubbles in the molten steel is predicted as a function of the global turbulent kinetic energy. The dependence of bubble terminal velocity and bubble shape on its size is taken into account. The recirculation region at the rear of bubbles with different shapes is discussed and the flow fields around rigid bubbles and free bubbles are compared.
Occurrence and Behavior of Phosphorus-Bearing Minerals in Metallurgical Coke
- First Published: 27 February 2019
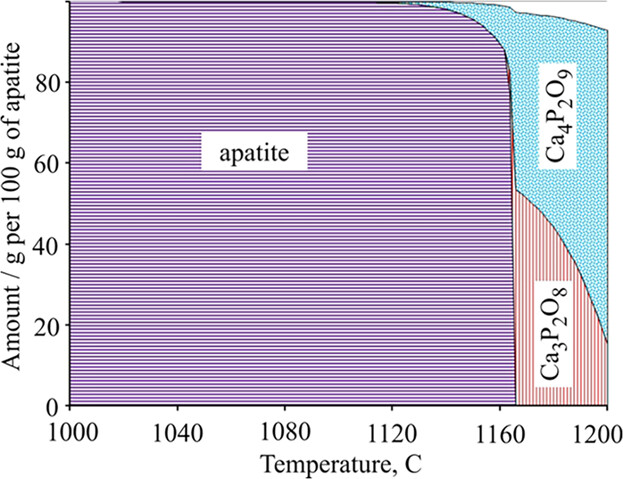
The behavior of phosphorus-bearing minerals is characterized from coking coals to the feed and blast furnace (BF) coke using scanning electron microscope and thermodynamic calculations. In coals, they are represented mostly by apatite, which fully transforms to Ca4P2O9 and Ca3P2O8 at coking temperatures. In the BF, it is transformed to Fe3P and Fe2P.