Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
New metastasectomy criteria for peritoneal metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma: A study of the Japanese Society of Hepato-Biliary-Pancreatic Surgery
- Pages: 673-681
- First Published: 29 June 2020
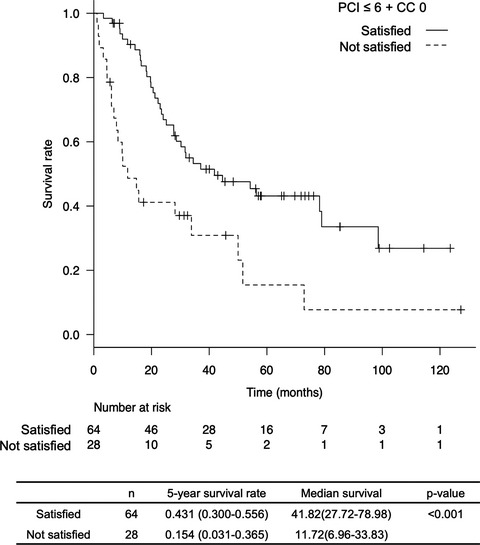
Highlight
On behalf of the Japanese Society of Hepato-Biliary-Pancreatic Surgery, Iida and colleagues conducted a multi-center study to establish the indications for peritoneal metastasectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma. The results suggest that peritoneal metastasectomy may enhance survival in patients with a peritoneal cancer index score of 6 or less without residual tumors.
Prognostic value of expanded liver transplantation criteria—the 5-5-500 rule—in patients with hepatic resection for intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma
- Pages: 682-689
- First Published: 23 June 2020
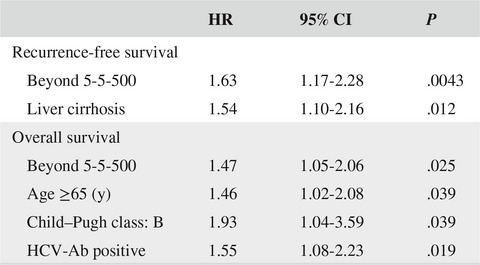
Highlight
Shinkawa and colleagues showed that the new expanded liver transplantation criteria, known as the 5-5-500 rule, could predict prognosis after hepatic resection in patients with Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer classification B, the intermediate stage, of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatic resection might provide survival benefit for selected patients within the 5-5-500 rule.
A multicenter prospective randomized controlled trial for preoperative biliary drainage with uncovered metal versus plastic stents for resectable periampullary cancer
- Pages: 690-699
- First Published: 26 July 2020
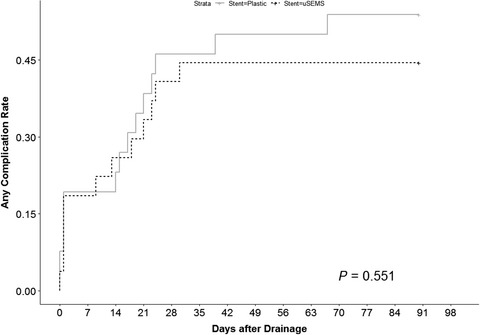
Highlight
In this prospective randomized trial, Cho and colleagues demonstrated no superiority of self- expandable metal stents over plastic stents for patients with resectable periampullary cancer who received surgery within 2 weeks after preoperative biliary drainage. Considering the cost, stent selection should be made according to the expected waiting time for surgery.
The placement of multiple plastic stents still has important roles in candidates for chemotherapy for unresectable perihilar cholangiocarcinoma
- Pages: 700-711
- First Published: 12 August 2020
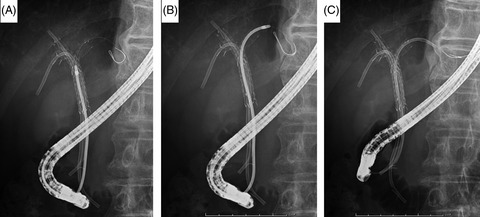
Highlight
Placement of uncovered self-expandable metallic stents is recommended as the treatment of choice in patients with unresectable perihilar cholangiocarcinoma. Iwasaki and colleagues conclude that plastic stent placement could enhance the success rate of reintervention in these patients and might facilitate sustainable chemotherapy. Stent selection, however, may not affect the prognosis.
Prognostic significance of regional lymph node metastasis according to station in ampullary carcinoma
- Pages: 712-720
- First Published: 23 June 2020
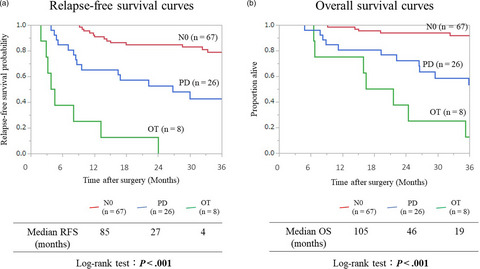
Highlight
Tashiro and colleagues explored outcomes following radical resection of ampullary carcinoma according to the station of lymph node metastasis, based on a subclassification of regional lymph nodes into pancreatoduodenal and other lymph nodes. Other lymph node metastasis was associated with poor outcomes and was an independent prognostic factor on multivariate analysis.
Does adjuvant treatment improve prognosis after curative resection of ampulla of Vater carcinoma? A multicenter retrospective study
- Pages: 721-730
- First Published: 11 July 2020
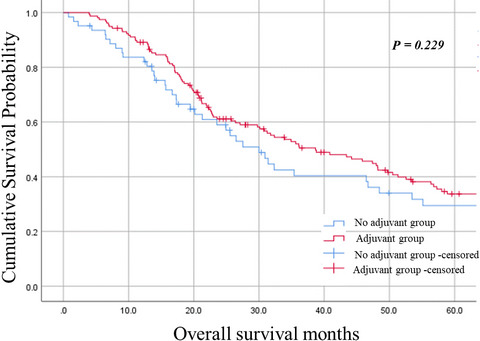
Highlight
This multicenter study investigated the effectiveness of adjuvant treatment in ampulla of Vater carcinoma following curative resection. Although adjuvant treatment in high-risk patients, defined as node-positive or having advanced T stage, was not statistically associated with improved survival, Kim and colleagues concluded that it might help achieve better patient outcomes.
Clinical impact of pancreaticoduodenectomy for pancreatic cancer with resection of the secondary or later branches of the superior mesenteric vein
- Pages: 731-738
- First Published: 20 June 2020
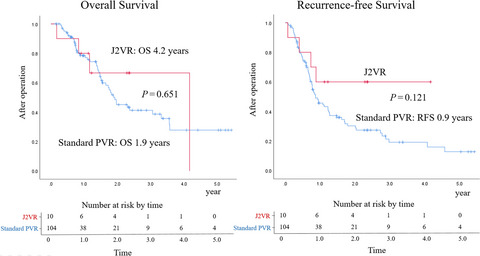
Highlight
Honda and colleagues analyzed the outcomes of pancreaticoduodenectomy for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma with resection of the secondary or later branches of the superior mesenteric vein. They concluded that the procedure is safe and has satisfactory overall survival rates. Although technically difficult, resection should not be abandoned for such pancreatic cancer.
Prediction of the progression of walled-off necrosis in patients with acute pancreatitis on whole pancreatic perfusion CT
- Pages: 739-746
- First Published: 11 July 2020
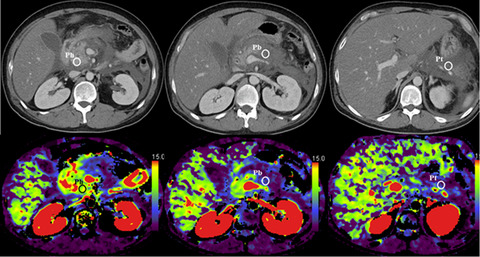
Highlight
In this retrospective study, Yamamiya and colleagues demonstrated that whole pancreatic perfusion computed tomography allowed both visual and quantitative evaluation of pancreatic ischemia, and concluded that the minimum pancreatic blood volume measurement within 72 hours after the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis was useful for predicting the progression of walled-off necrosis.
Mortality analysis of Aeromonas hydrophila infection in hepato-biliary pancreatic surgery: Multicenter retrospective observational study
- Pages: 747-755
- First Published: 21 July 2020

Highlight
Although Aeromonas hydrophila isolation was low after hepato-biliary-pancreatic surgery in this first large cohort study, seven deaths occurred in 52 patients with A. Hydrophila isolated after pancreatoduodenectomy or hepatectomy with biliary reconstruction, five of which within 3 days after onset. Ueno and colleagues caution against overlooking A. hydrophila after hepato-biliary-pancreatic surgery.
Diagnostic potential of presepsin in bacterial infection following hepato-biliary-pancreatic surgery: A prospective observational study
- Pages: 756-766
- First Published: 11 July 2020
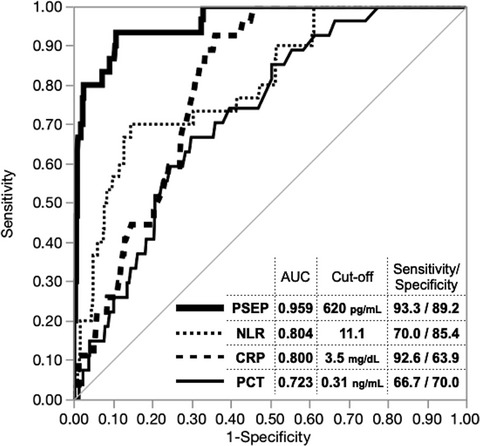
Highlight
In this prospective study, Yao and colleagues demonstrated that presepsin may have better predictive ability than existing biomarkers for infection following major hepato-biliary-pancreatic surgery. As it shows a rapid and specific increase in response to the presence of bacteria, presepsin may help physicians achieve early and accurate detection of bacterial infections.
Serum procalcitonin as an early diagnostic marker of severe postoperative complications after elective pancreaticoduodenectomy
- Pages: 767-775
- First Published: 22 July 2020
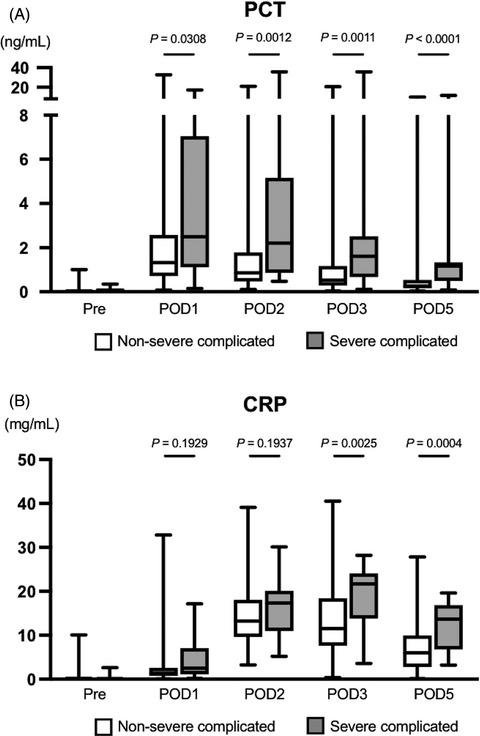
Highlight
Hata and colleagues evaluated the diagnostic impact of serum procalcitonin for the development of severe postoperative complications (Clavien-Dindo Grade IVa and higher) after pancreaticoduodenectomy. Serum procalcitonin in the early postoperative period (postoperative day 2) can serve as an early diagnostic marker, especially in combination with C-reactive protein (postoperative day 3).
Acute and subacute effects of irreversible electroporation on normal common bile ducts in a rabbit model
- Pages: 776-784
- First Published: 22 July 2020
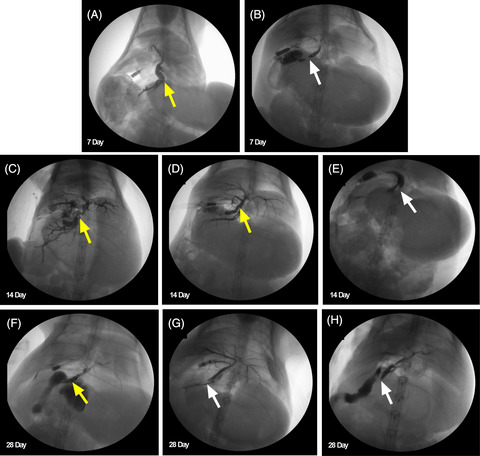
Highlight
Li and colleagues evaluated the acute and subacute effects of irreversible electroporation on normal common bile ducts in vitro and in vivo, showing that the common bile ducts retained lumen wall integrity following electroporation. The presence of biliary complications, however, warrants further exploration of the proper parameters of irreversible electroporation.
HOW I DO IT
Basic knowledge of and a small trick for atraumatic needle driving in laparoscopic suturing
- Pages: 785-788
- First Published: 11 August 2020
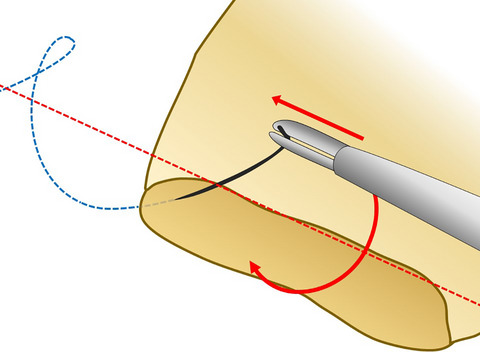
Highlight
Although recent advances in robotic surgery have enabled more precise movements of the needle driver, a sophisticated laparoscopic suturing technique is still desired. Honda and colleagues describe the basic knowledge of and a small but useful trick for atraumatic needle driving in laparoscopic suturing, based on mechanistic considerations.
Laparoscopic excision of type II choledochal cyst arising from the intrapancreatic common bile duct in an adult
- Pages: 789-790
- First Published: 21 July 2020
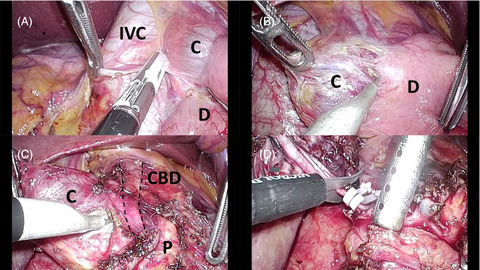
Highlight
In this video article, Lee and colleagues present the first report of laparoscopic excision of a type II choledochal cyst located in the intrapancreatic bile duct, which remains technically demanding. The authors recommend sharp dissection of the cyst from the pancreas using a bipolar energy device to control small vessels.
EUS-guided gastrojejunostomy: Double-balloon occlusion theory with experimental study (with video)
- Pages: 791-792
- First Published: 21 July 2020
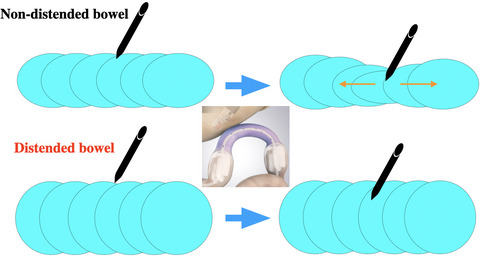
Highlight
This experimental study using a plastic globe and fine-needle aspiration needle demonstrated that distention of the jejunum is the most important point to avoid mispuncture and misdeployment of devices in endoscopic ultrasonography-guided gastrojejunostomy. Itoi and colleagues recommend the double-balloon occlusion method to endosonographers for safe and reliable endoscopic ultrasonography-guided gastrojejunostomy.





