Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER PICTURE
Front Cover
- First Published: 02 June 2022

A comparison of multicolor Gaussian and Bessel light-sheet microscopy under the same excitation objective is depicted. The intrinsic FOV's mismatch's effects due to the different beams chromatic defocusing and the aside object blurring of the images are minimized and alleviated using multicolor Bessel beams over Gaussian beams. Multicolor LSFM imaging over perithecia samples of the fungus Sordaria macrospora demonstrates the advantages of using Bessel beams.
Further details can be found in the article by Yryx Y. Luna-Palacios, Jacob Licea-Rodriguez, M. Dolores Camacho-Lopez, Ines Teichert, Meritxell Riquelme, and Israel Rocha-Mendoza (e202100359)
Inside Cover
- First Published: 02 June 2022
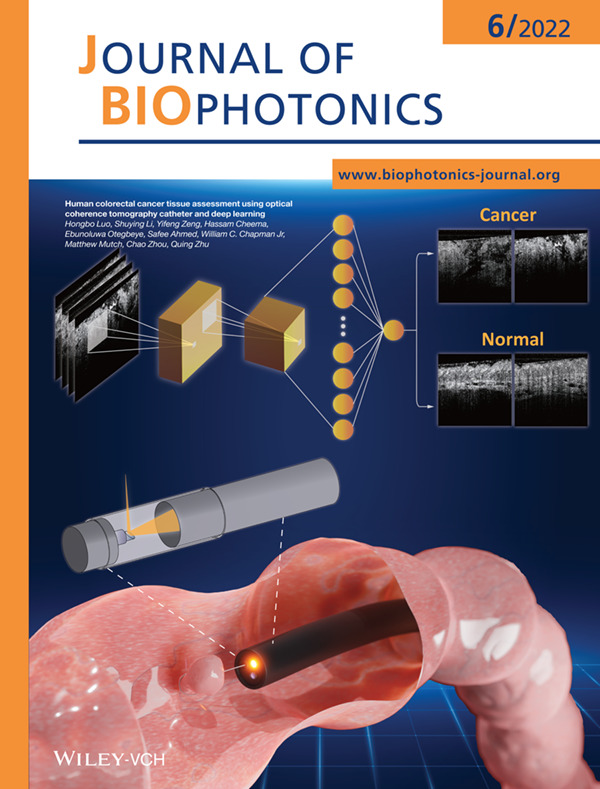
We describe a miniaturized optical coherence tomography (OCT) catheter and a residual neural network (ResNet)-based deep learning model to perform human colorectal tissue classification. An area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve (AUC) of 0.975 is achieved to distinguish between normal and cancerous colorectal tissue images.
Further details can be found in the article by Hongbo Luo, Shuying Li, Yifeng Zeng, Hassam Cheema, Ebunoluwa Otegbeye, Safee Ahmed, William C. Chapman Jr, Matthew Mutch, Chao Zhou, and Quing Zhu (e202100349)
Inside Cover
- First Published: 02 June 2022
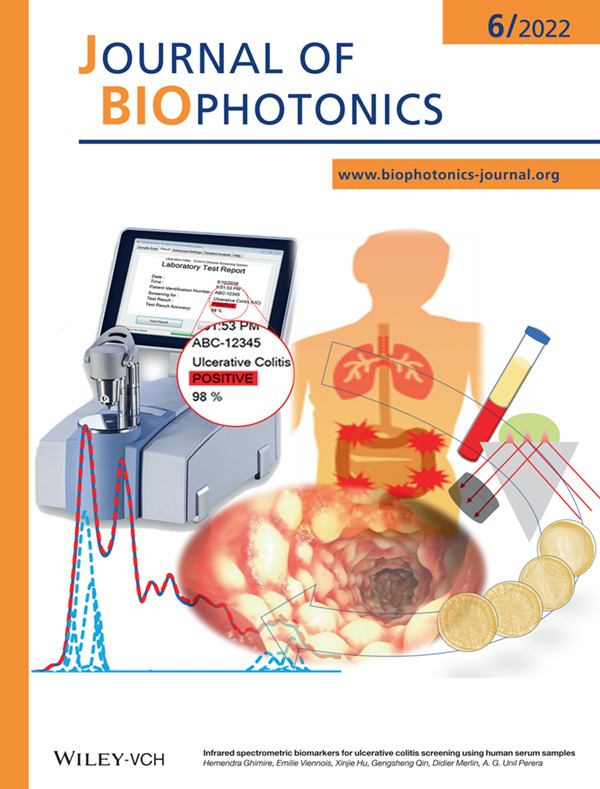
Rapid, reliable, minimally invasive, and cost-effective screening for ulcerative colitis (UC). Gold-standard endoscopic tests are expensive, invasive, with associated risks, and are not comfortable to use, affecting compliance rates. This novel approach could provide an indication of UC encouraging them on endoscopic tests.
Further details can be found in the article by Hemendra Ghimire, Emilie Viennois, Xinjie Hu, Gengsheng Qin, Didier Merlin, and A. G. Unil Perera (e202100307)
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW ARTICLES
Review of optical methods for fetal monitoring in utero
- First Published: 13 March 2022
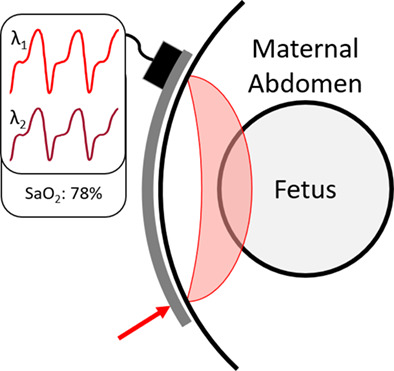
Transabdominal fetal pulse oximetry works by illuminated a spot on the abdomen of the mother and detecting the output light over time in order to analyze the time traces. After obtaining the time signals from the system, various algorithms can be applied to determine the oxygen saturation (SaO2%) of the fetus noninvasively.
Imaging approaches for monitoring three-dimensional cell and tissue culture systems
- First Published: 31 March 2022
There has been increasing demand for more complex tissue cultures, that are reproducible, scalable and validated, aimed at replicating biophysical features of living tissue. To demonstrate these attributes, it is crucial to have reliable and reproducible means of monitoring and quantification. This review highlights not only the opportunities, and innovative methods biophysicists are implementing, but also the challenges, limitations, compromises and special considerations each tool requires for imaging biological tissues.
LETTER
Degree of polarization uniformity for dental calculus visualization
- First Published: 06 March 2022
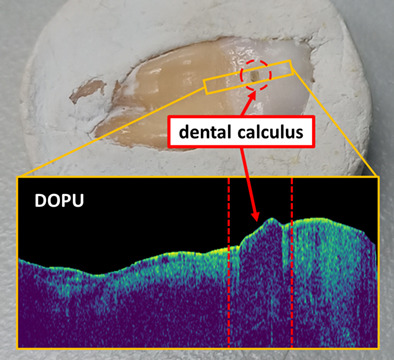
The identification and removal of dental calculus are crucial during the treatment of periodontitis. We demonstrated the degree of polarization uniformity as a superb contrast for dental calculus visualization. To our knowledge, it is the first time that the depolarization property of dental calculus be reported. The proposed approach for dental calculus identification is promising and can likely improve the current clinical practice.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Multicolor light-sheet microscopy for a large field of view imaging: A comparative study between Bessel and Gaussian light-sheets configurations
- First Published: 20 February 2022
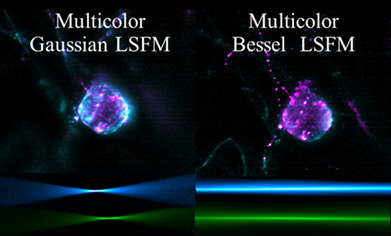
The chromatic implications of implementing multicolor Bessel and Gaussian light-sheet microscopy to achieve colocalized and large field of views under the same excitation objective are discussed. The intrinsic FOV's mismatch's effects due to the chromatic defocusing and the aside object blurring of the images are minimized and alleviated using multicolor Bessel beams over Gaussian beams. Multicolor LSFM imaging over perithecia samples of the fungus Sordaria macrospora demonstrates such advantages.
Human colorectal cancer tissue assessment using optical coherence tomography catheter and deep learning
- First Published: 11 February 2022
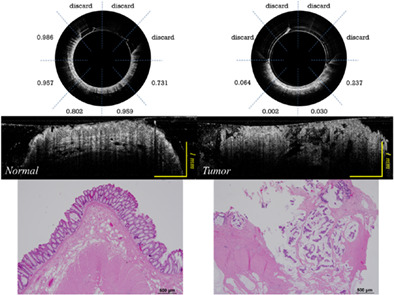
A miniaturized OCT catheter is developed for ex vivo human colorectal tissue imaging. The OCT catheter has an outer diameter of 3.8 mm, a lateral resolution of ~7 μm, and an axial resolution of ~6 μm. By incorporating a customized ResNet classifier, our approach has the potential for real-time classification of normal and neoplastic human colorectal tissues based on the high-resolution label-free OCT images.
Thermodynamic basis for comparative photobiomodulation dosing with multiple wavelengths to direct odontoblast differentiation
- First Published: 15 February 2022
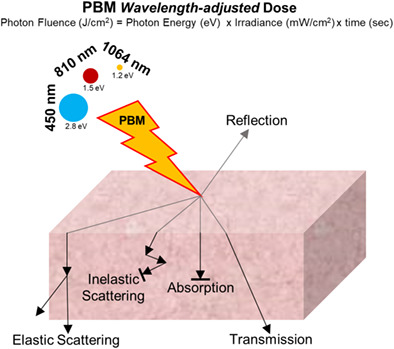
The use of low dose light treatments is termed photobiomodulation that has shown inconsistent clinical outcomes. This is, in part, attributed to the very low dose, and several available wavelengths being used. This work outlines a fundamental thermodynamic basis of photobiomodulation dosing as a photon energy transfer process. This subtle, but important, novel dose concept could contribute to improved rigor and reproducibility of PBM biological responses.
Infrared spectrometric biomarkers for ulcerative colitis screening using human serum samples
- First Published: 08 February 2022
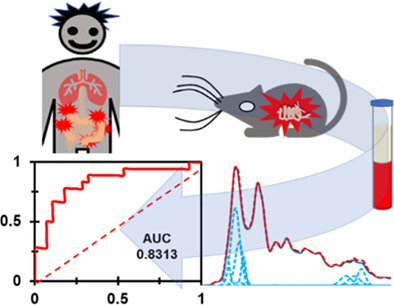
This study uses infrared spectrometry coupled with data analysis techniques to understand colitis-induced alterations in the molecular components of serum samples. Using samples from 18 ulcerative colitis patients and 28 healthy volunteers, we assessed features such as absorbance values at wavenumbers of 1033 and 1076 cm−1, and the ratios at 1121 versus 1020 cm−1 and 1629 versus 1737 cm−1. The results of the study show statistically significant differences in five identifying spectral signatures.
Development of multimodal micro-endoscopic system with oblique illumination for simultaneous fluorescence imaging and spectroscopy of oral cancer
- First Published: 03 January 2022
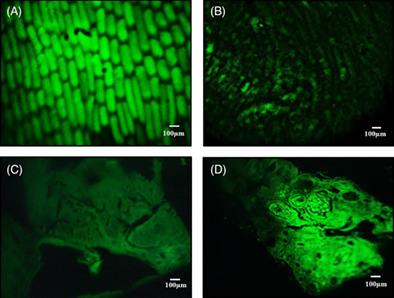
Multimodality of an optical system implies the use of one or more optical techniques to improve the system's overall performance and maximum utility. In this article, we demonstrate a multimodal system with oblique illumination that combines two different techniques; fluorescence micro-endoscopy and spectroscopy simultaneously and can be utilized to obtain diverse information from the same location of biological samples. In present system, use of graded index (GRIN) rod-lens makes it highly compact and oblique incidence decouples illumination geometry with collection geometry, preventing CCD cameras from saturation and reduces number of optical elements, thereby making system more miniaturized and field-portable. It also overcomes disadvantages of undesired reflections from different optical elements. The experimental results of simultaneous imaging and spectroscopy of the biological samples are presented along with quantitative spectroscopic parameters; peak wavelength shift, area under the curve and full width half maximum (FWHM)
Different brain activation patterns in the prefrontal area between self-paced and high-speed driving tasks
- First Published: 01 February 2022
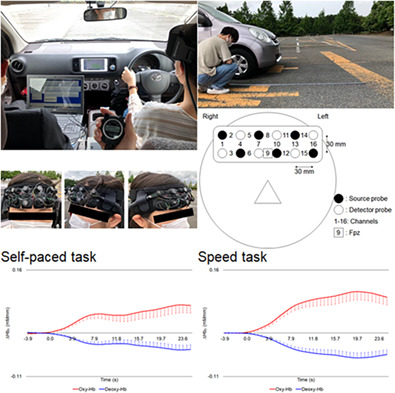
Monitoring brain activity with functional near-infrared spectroscopy can be useful in real driving situations. We examined the differences in prefrontal cortex activity when participants attempted to stop a car accurately at a stop line when driving at different speeds. Oxygenated hemoglobin concentration in the prefrontal cortex was significantly higher in the high-speed task than in the self-paced task, although the variation in the distance between the stop line and the car was not significantly different between both tasks.
Noninvasive examination of the cardiac properties of insect embryos enabled by optical coherence tomography
- First Published: 02 March 2022
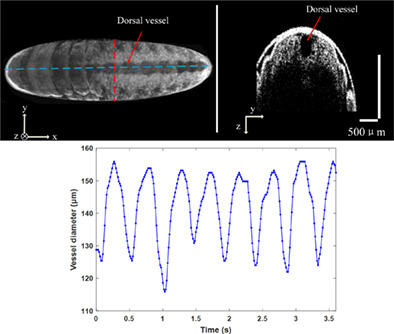
We propose and demonstrate the first use of optical coherence tomography (OCT) to noninvasively exam the cardiac functions of insects' embryos as they develop, providing the ability to fast screen the effectiveness on the embryos' heart activities when certain genes are suppression by RNA interference. Applying the OCT capabilities with locusts as the model organism is also beneficial to better understand the human congenital diseases.
Weighted model-based optoacoustic reconstruction for partial-view geometries
- First Published: 08 February 2022
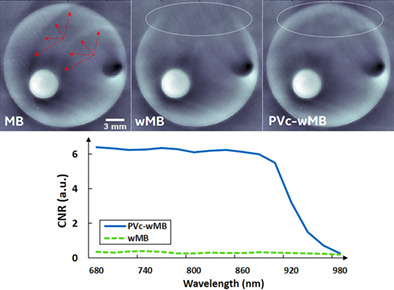
Acoustic heterogeneities in biological samples are known to cause artifacts in tomographic optoacoustic (photoacoustic) image reconstruction. In this article, a weighted model-based reconstruction algorithm is extended in order to generate optoacoustic reconstructions with less distortions in partial-view multispectral detection geometries. Using phantom and in vivo data, the proposed algorithm is shown to mitigate reflection artifacts and/or suppress streaking artifacts in reconstructed images without distorting structures or boundaries, compared with both conventional model-based and the uncorrected weighted model-based algorithms.
Engineering a better light sheet in an axicon-based system using a flattened Gaussian beam of low order
- First Published: 01 February 2022
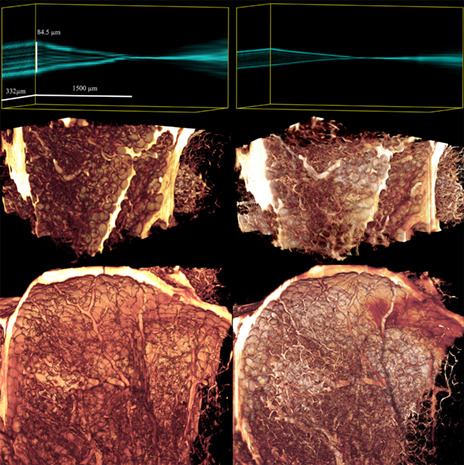
The shape of an incident laser beam directly affects the results when it propagates through complex structured meso-aspheric optical elements. In conic-based systems utilizing elements such as axicons, the impact of secondary lobes is mostly overlooked. We investigate the interaction of two axicons (160° and 170°) with incident beams approximated by Gaussian, high-order Flattened-Gaussian, and low-order Flattened-Gaussian functions. Replacing an incident Gaussian beam with a low-order Flattened-Gaussian beam reduced the secondary lobes and significantly improved the uniformity of the intensity profile.
In vivo Raman spectroscopy for bladder cancer detection using a superficial Raman probe compared to a nonsuperficial Raman probe
- First Published: 01 March 2022
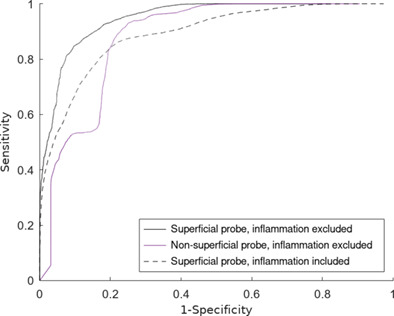
In vivo, we compared a superficial to a nonsuperficial Raman probe, in 104 bladder cancer patients. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve improved from 0.80 to 0.95 and sensitivity from 85% to 90% when using the superficial probe. The specificity was approximately equal: 87% vs 88%. Thus, the superficial probe improves Raman bladder cancer diagnosis. Inflammation was a confounder. An indication of gradual transition from benign to low-grade to high-grade urothelial carcinoma was found.
Collagen signature as a novel biomarker to predict axillary lymph node metastasis in breast cancer using multiphoton microscopy
- First Published: 27 January 2022
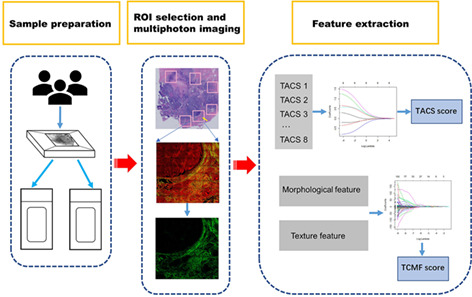
Accurate axillary lymph node (ALN) assessment is critical for tumor staging and decision making. In this study, collagen signatures (TACS and TCMF) extracted from multiphoton images are associated with ALN metastasis. Our study indicated that MPM method should be a promising method to predict the probability of ALN metastasis.
Ex vivo confocal laser scanning microscopy: A diagnostic technique for easy real-time evaluation of benign and malignant skin tumours
- First Published: 01 March 2022
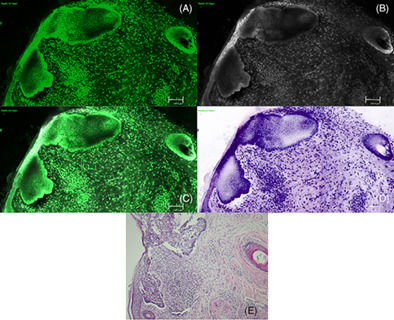
The aim of this study was to prove the suitability of ex vivo confocal laser scanning microscopy for performing a fast and reliable microscopic examination of skin tumours in a real-life setting. The results were verified by means of conventional histopathology. Furthermore, we examined the applicability of the newly added digital staining mode and could confirm its similarity to conventional histopathology.
Direct inactivation of SARS-CoV-2 by low level blue photobiomodulation LED at 470, 454 and 450 nm
- First Published: 06 February 2022
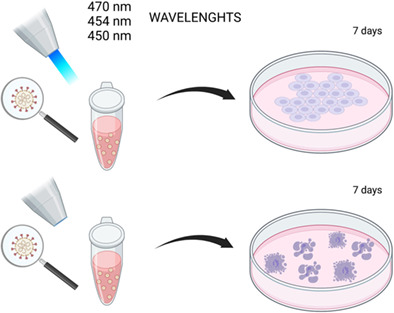
Blue light has been already reported as able to counteract different types of microorganisms including Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, fungi and viruses, especially the enveloped ones. It has been reported that both blue and visible light can efficiently impact SARS-CoV-2 by affecting its ability to replicate in in vitro cellular models of infection. In this study, blue light at 450, 454 and 470 nm was tested on SARS-CoV-2 to evaluate the residual viral infectious potential on Vero E6, Caco-2 and Calu-3 cells, after the irradiation of viral particles.
Noises investigations and image denoising in femtosecond stimulated Raman scattering microscopy
- First Published: 24 March 2022
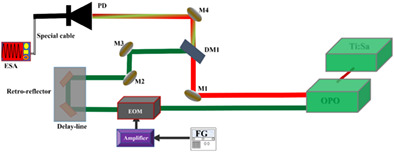
Appetizer: Stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) microscopy offers a broad application for label-free imaging with varieties of advantages. Nevertheless, due to the weak Raman cross-section of biomolecules, SRS images often suffer from low signal to noise ratio. In this article, noise sources quantifications, statistical properties analysis of image noise and image denoising in SRS microscopy are reported. We focus on simple, efficient and high accuracy denoising methods, which can provide an essential perspective for increasing the diffusion of SRS microscopy and the number of its applications.
Biosafety and differentially expressed genes analysis of melanoma cells treated with cold atmospheric plasma
- First Published: 08 March 2022
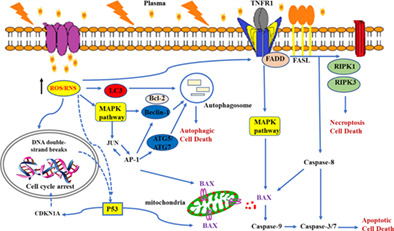
In this study, we focused on different biological effects of cold atmospheric plasma (CAP) on melanoma cells and HaCaT cells to explore the biosafety of CAP, combining the reactive species injection efficiency and tumor cell physiological characteristic system. Subsequently, RNA-sequencing analysis was used to comprehensively elucidate the differences in the expression of apoptosis-related genes in melanoma cells treated by CAP. We identified that the MAPK pathway and p53 pathway played main roles in apoptosis, and found that necroptosis and autophagy were also involved in CAP anti-tumor effect.
Multilayer subwavelength gratings or sandwiches with periodic structure shape light reflection in the tapetum lucidum of taxonomically diverse vertebrate animals
- First Published: 03 March 2022

The reflective properties of the tapetum are due to their specialized cellular subwavelength microstructure (photonic crystals). Optical mechanisms of reflection in the tapetum are very similar even for widely separated species. In this review, we summarize electron microscopic and functional studies of tapetal structures in the main vertebrate classes. This allows data on the microstructure of the tapetum to be used to improve our understanding of the visual system.
Randomized multi-angle illumination for improved linear array photoacoustic computed tomography in brain
- First Published: 13 March 2022
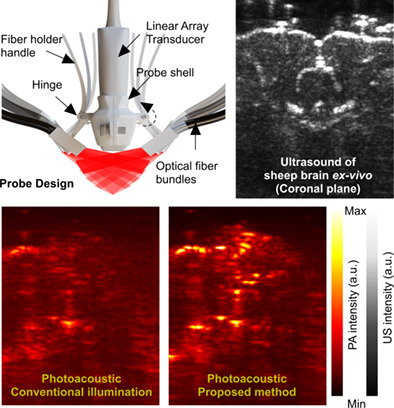
One of the challenges of linear array-based photoacoustic computed tomography of the brain is to image structures embedded deep within the brain tissue. We developed a manually controlled multi-angle illumination technique to allow the incident photons to interact with the imaging target more effectively and diffuse further in all directions. The performance of this method has been evaluated by imaging complex blood vessel phantoms in-vitro and sheep brain samples ex-vivo.