Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Contents
Masthead
Research Articles
Microalgal Cultivation Using Animal Production Exhaust Air: Technical and Economic Feasibility
- First Published: 01 February 2017
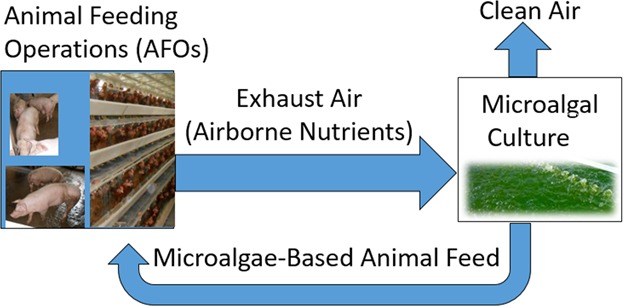
Fixing airborne nutrients from animal feeding operations (AFOs) into microalgal biomass can alleviate AFOs air emissions and reduce microalgal production cost. A technical and economic assessment of integrating air emissions mitigation with microalgal cultivation is conducted. The results demonstrated technical feasibility, and a net revenue can be achieved by the integrated system with improved microalgal biomass productivity.
Application of Partial Least Squares-Kernel Calibration in Competitive Adsorption Studies Using an Effective Chemically Activated Biochar
- First Published: 04 February 2017
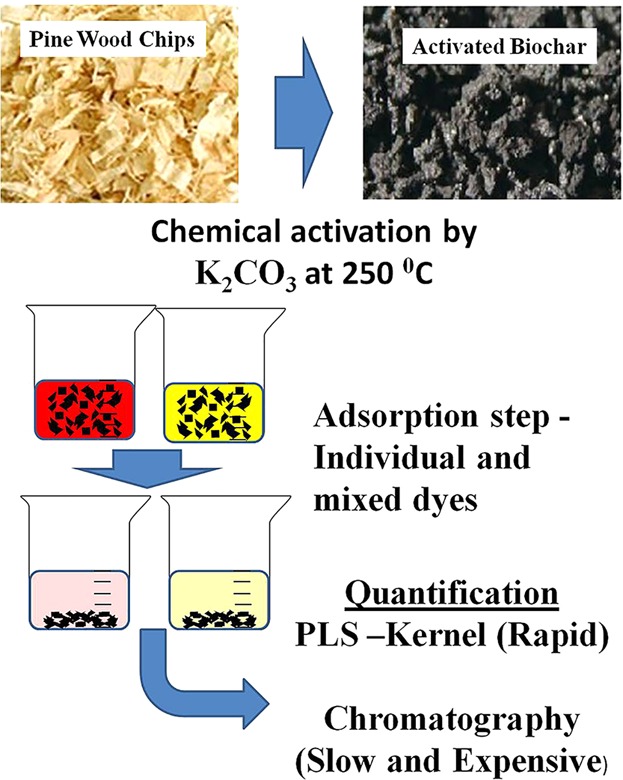
Chemically activated pine wood-based biochar is used to study the competitive adsorption behavior of four colorants alone and in mixtures. The effects of dosage of adsorbent, pH, and number of competing solutes on %Removal and retention capacity are studied. A PLS-Kernel calibration technique is usefully applied for studying competitive adsorption behavior of four food dyes with minimum experimental demands.
Mycosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles as Potent Growth Inhibitory Agents Against Selected Waterborne Human Pathogens
- First Published: 17 January 2017
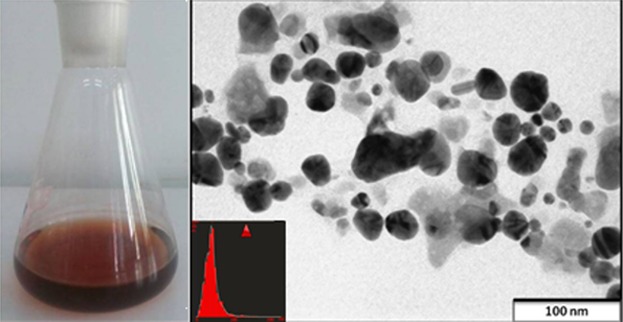
Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) synthesized by using fungal extract are antimicrobial agents, which can control waterborne pathogens. AgNPs with a diameter of 20–25 nm were synthesized and analyzed for their growth inhibitory activity against Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Chromobacterium violaceum, and Brevibacillus borstelensis. The positive results of the present study indicate utility of AgNPs in water purification technologies.
Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Nanotubes/Polyethersulfone Blend Membranes for Removing Emerging Micropollutants
- First Published: 13 February 2017
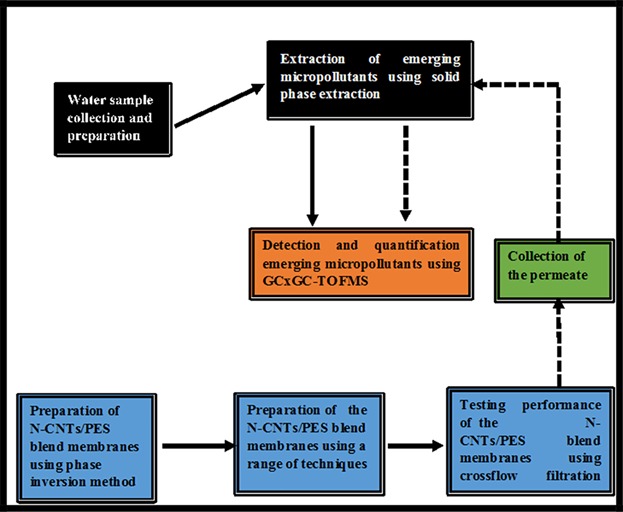
Water pollution by emerging micropollutants (EMPs) is a major global challenge. Conventional water treatment methods are not very effective in removing most EMPs. Nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes/polyethersulfone (N-CNT/PES) blend membranes are fabricated using modified a phase inversion method for the removal of EMPs from water. The results show the superior capability of the N-CNT/PES blend membranes in removing EMPs from water.
A Detailed Analysis of Sediment Particle Sizes and Clogging in Permeable Pavements
- First Published: 13 February 2017
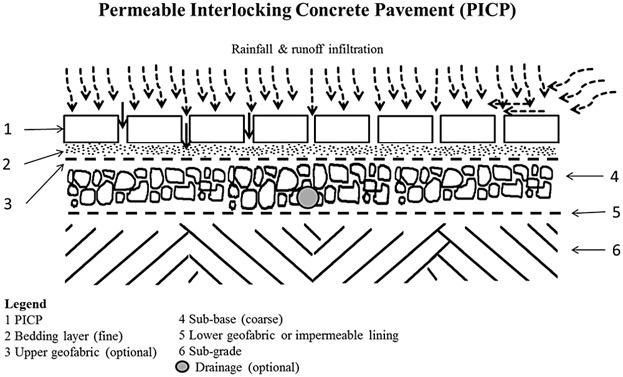
The focus of this study is to identify factors which are most likely to influence clogging in permeable interlocking concrete pavements, with a focus on sediment particle sizes. The study finds that sites with similar sediment particle size distribution can have different surface infiltration rates and the 251–550 µm particle sizes that explain the most variation at sites with lower measured infiltration rates are identified.
Abiological Granular Sludge Formation Benefit for Heavy Metal Wastewater Treatment Using Sulfide Precipitation
- First Published: 23 November 2016
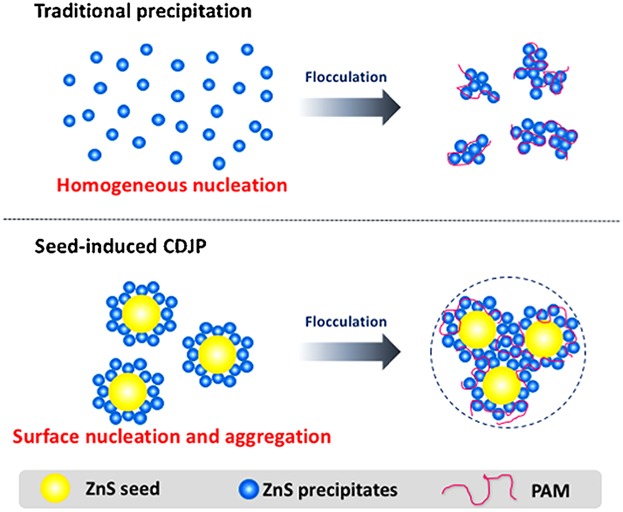
Metal sulfide precipitation features low sludge settling performance in heavy metal wastewater treatment. To solve this problem, an ABGS formation strategy is developed. The sludge settling performance can be significantly increased from 0.4 to 3.7 cm/s under optimal conditions. Besides, a surface nucleation and aggregation mechanism for ABGS formation is first proposed in this study.
Implication of Nitrifying and Denitrifying Bacteria for Nitrogen Removal in a Shallow Lake
- First Published: 05 January 2017

Common reed is a ubiquitous emergent plant that can be used for shallow lake remediation. This study implies that the amoA-type nitrifier and nirS-type denitrifier assemblages are effective for nitrogen removal. Influences of reed growth rates, air temperature, and water level variation should be considered when establishing the nitrogen removal regime for a shallow lake in the future.
Hydroxytyrosol Recovery From Olive Mill Wastewater: Process Optimization and Development of a Pilot Plant
- First Published: 29 November 2016
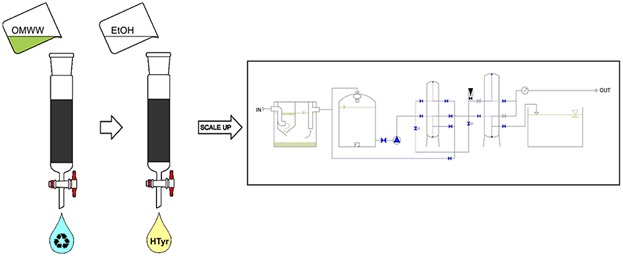
Olive mill wastewater (OMWW) represents both an environmental issue and a potential source of valuable biomolecules. Activated charcoal is efficient in the depollution of OMWW and permits selective recover of a hydroxytyrosol-enriched fraction. The process is scale-up and a pilot plant prototype is developed. Pure polyphenols, depolluted water, and an organic compost from OMWW is obtained.
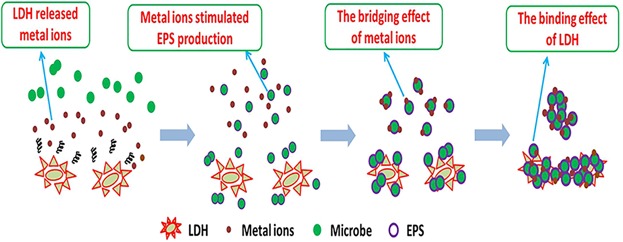
Role of Layered Double Hydroxide in Improving the Stability of Aerobic Granular Sludge
- First Published: 01 February 2017
Biodegradation of Malachite Green by the Ligninolytic Fungus Aspergillus flavus
- First Published: 18 January 2017
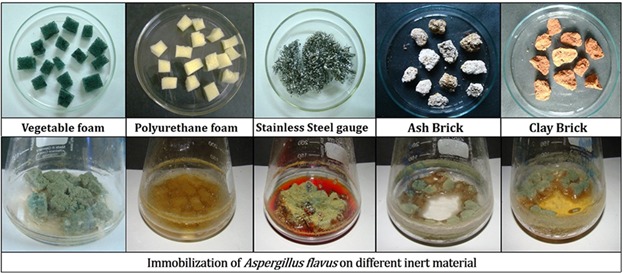
Malachite green (MG), an azo dye, is recalcitrant and toxic. It was degraded through the ligninolytic fungus Aspergillus flavus. Characterization of MG degradation products confirm the involvement of laccase and manganese peroxidase enzymes. Immobilization of A. flavus on different natural and synthetic inert matrices enhanced the MG degradation, as compared to free fungal cells.