Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Association of the programmed death ligand-1 combined positive score in tumors and clinicopathological features in esophageal cancer
- Pages: 523-532
- First Published: 24 December 2021
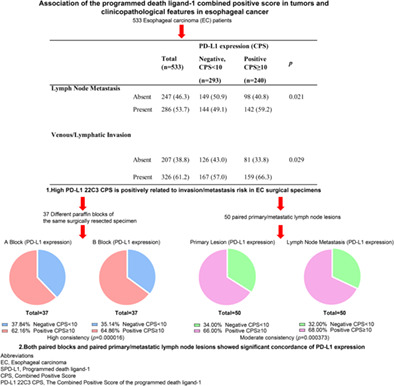
The combined positive score (CPS) of the programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) 22C3 assay is a predictive marker of pembrolizumab monotherapy for advanced esophageal cancer (EC) patients. We examined the association of the PD-L1 22C3 CPS with clinicopathological characteristics in 533 surgically resected EC specimens. Further, we independently compared 37 cases' different paraffin blocks of the same surgically resected specimen and 50 paired primary/metastatic lymph node lesions to investigate the heterogeneity of the PD-L1 expression. PD-L1 positive expression was positively associated with the presence of lymph node metastasis (59.2% chance, p = 0.021) and venous/lymphatic invasion (66.3% chance, p = 0.029). PD-L1 expression was highly consistent in different paraffin blocks of the same surgically resected specimen (p = 0.000016) and a moderate consistency (p = 0.000373) for the primary and metastatic lymph node lesion comparison. This is the novel study to demonstrate a positively correlation between a high PD-L1 22C3 CPS and invasion/metastasis risk in EC surgical specimens. Both paired blocks and paired primary/metastatic lymph node lesions showed significant concordance.
Efficacy and safety of EBUS-TBNA under conscious sedation with meperidine and midazolam
- Pages: 533-538
- First Published: 07 January 2022
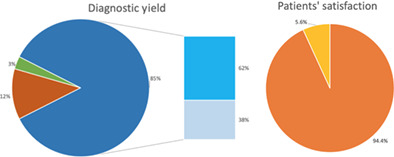
In this study involving 302 patients, EBUS-TBNA performed under conscious sedation with meperidine and midazolam led to 85% exams with adequate samples, of whom 62% were diagnostic and 38% showed normal lymph node tissue. A total of 12% were inadequate and 3% of scheduled exams were not performed. Severe and persistent adverse events have not been observed. A total of 94.4% of patients declared that they strongly agree to repeat the exam if necessary.
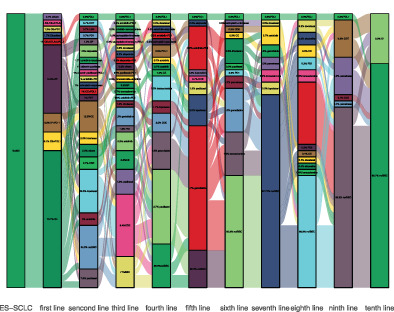
Clinical characteristics and prognostic model for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer: A retrospective study over an 8-year period
- Pages: 539-548
- First Published: 30 December 2021
Impact of sarcopenia on chemotherapy-triggered exacerbation of interstitial lung disease in patients with non-small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 549-556
- First Published: 28 December 2021
Psoas major cross-sectional area / height squared less than 6.36 for men and less than 3.92 for females was defined as sarcopenia. Sarcopenia was a predictor of ILD exacerbation by chemotherapy. The prognosis for the sarcopenia group was worse than that for the nonsarcopenia group. Treatment targeting sarcopenia may be a breakthrough in lung cancer with ILD.
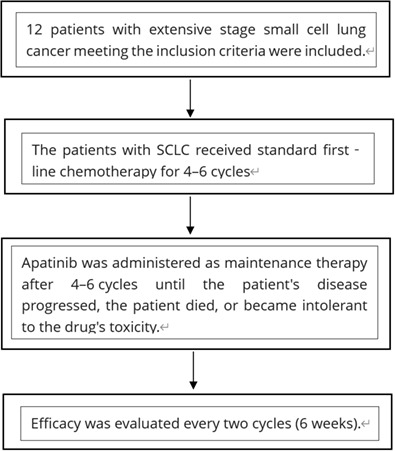
Apatinib as maintenance therapy following standard first-line chemotherapy in extensive disease small cell lung cancer: A phase II single-arm trial
- Pages: 557-562
- First Published: 14 January 2022
Efficacy and safety of WBRT+EGFR-TKI versus WBRT only in the treatment of NSCLC patients with brain metastasis: An updated meta-analysis
- Pages: 563-570
- First Published: 30 December 2021
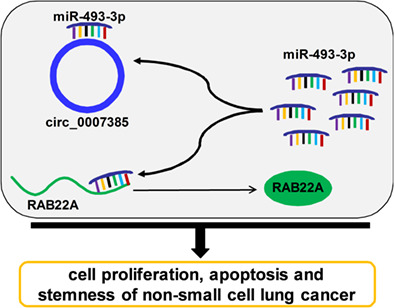
Circ_0007385 regulates cell proliferation, apoptosis and stemness via targeting miR-493-3p/RAB22A axis in non-small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 571-581
- First Published: 05 January 2022
Circ_0026134 promotes NSCLC progression by the miR-3619-5p/CHAF1B axis
- Pages: 582-592
- First Published: 05 January 2022
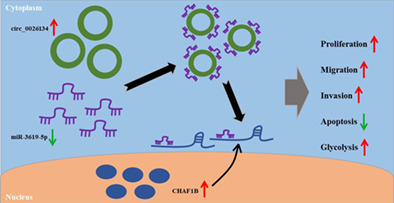
Schematic model of the circ_0026134/miR-3619-5p/CHAF1B axis in NSCLC progression. In NSCLC cells, circ_0026134 was overexpressed, and miR-0026134 overexpression reduced the level of miR-3619-5p. The downregulation of miR-3619-5p resulted in an increase in the level of CHAF1B. Finally, the upregulation of CHAF1B enhanced cell proliferation, migration, invasion, glycolysis and repressed apoptosis, and thus promoted NSCLC progression.
Retrospective analysis of long-term survival factors in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer treated with nivolumab
- Pages: 593-601
- First Published: 05 January 2022
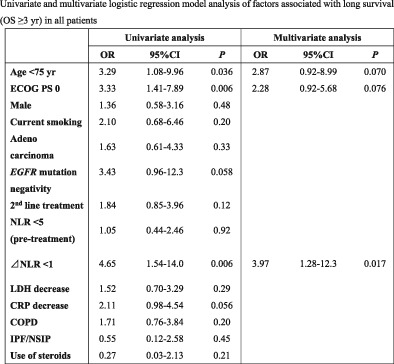
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of consecutive patients with advanced NSCLC with ECOG-PS ≤1 treated with nivolumab. We evaluated the differences between nonlong-term survivors and long-term survivors and performed univariate and multivariate analyses of factors associated with long-term survival. ΔNLR <1 was a significant long-term survival factor compared to ΔNLR ≥1 in advanced NSCLC patients treated with nivolumab.
Development of a deep learning-based method to diagnose pulmonary ground-glass nodules by sequential computed tomography imaging
- Pages: 602-612
- First Published: 06 January 2022
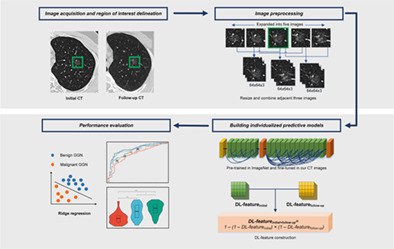
This retrospective study enrolled patients with ground-glass nodules (GGN) and developed a deep learning (DL)-based method by using sequential computed tomography imaging to differentiate benign from malignant GGN, and then compared the DL method with radiologists. The results showed that DL can achieve diagnostic performance on the par with or better than radiologists in identify pulmonary GGNs.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease assessment test for the measurement of deterioration and recovery of health status of patients undergoing lung surgery
- Pages: 613-623
- First Published: 06 January 2022
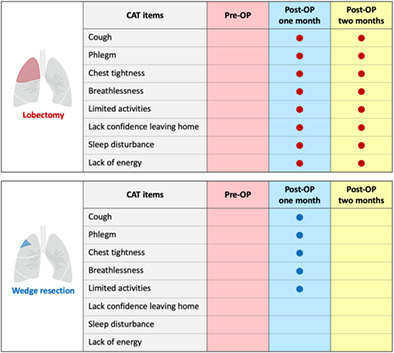
For patients who underwent lobectomy, CAT symptoms such as cough, excessive phlegm, chest tightness, breathlessness, limited activities, lack of confidence leaving home, sleep disturbance, and lack of energy deteriorated significantly in the first month after surgery and lasted in the second month. For patients with wedge resection, cough, excessive phlegm, chest tightness, breathlessness, and limited activities deteriorated significantly in the first month after surgery and subsided in the second month.
Efficacy and predictors of rechallenge with immune checkpoint inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 624-630
- First Published: 06 January 2022
Rechallenge with ICIs is less likely to result in a better response than initial ICI therapy. However, in the group of patients who achieved SD or better in the initial efficacy assessment after rechallenge with ICIs, ICI therapy can be continued for a longer period of time. This may be associated with prolonged survival.
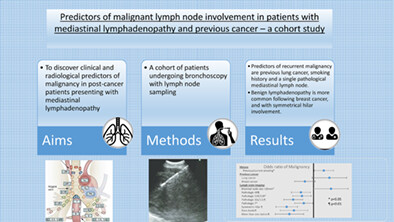
Predictors of malignant lymph node involvement in patients with mediastinal lymphadenopathy and previous cancer: A cohort study
- Pages: 631-636
- First Published: 14 January 2022
BRIEF REPORT
Effectiveness of alectinib and osimertinib in a brain metastasized lung adenocarcinoma patient with concurrent EGFR mutations and DCTN1-ALK fusion
- Pages: 637-642
- First Published: 28 December 2021
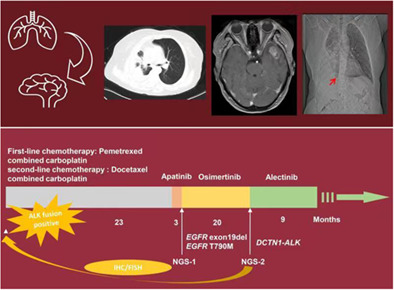
We report a female lung adenocarcinoma patient (T3N2M1a) with brain metastases and possible coexistence of primary EGFR T790M mutation/EGFR exon 19 del/DCTN1-ALK translocation. The patient was sensitive to multiple treatment, including initial chemotherapy as well as the later administration of apatinib, osimertinib, and alectinib. We also summarize 22 published cases of lung adenocarcinoma patients with concurrent EGFR mutation and ALK rearrangement.
CASE REPORTS
The rarest of rare cases within the one thousand faces of atypical carcinoid: Pseudomesotheliomatous manifestation in a pregnant woman
- Pages: 643-647
- First Published: 30 December 2021
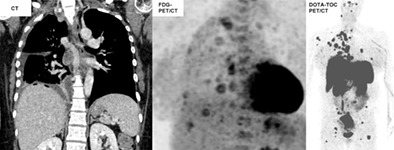
We present an extremely rare case of pseudomesotheliomatous manifestation of atypical carcinoid in a pregnant woman, focusing on the image findings and discrepancy between performance status and extensive metastasis. Our case shows that atypical carcinoids with multiple metastatic lesions can exhibit variability in vascularity and metabolism, resulting in heterogeneous image characteristics among metastatic lesions. In addition, even with extensive metastasis, patients can exhibit good performance explained by long-standing presentation of indolent cancer.
A single dose of pembrolizumab treatment causing a profound and durable response in lung cancer
- Pages: 648-652
- First Published: 12 January 2022
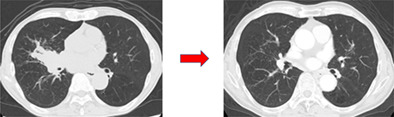
Metastatic pulmonary nodule after a seventeen-year disease-free interval resected through thoracoscopic subsegmentectomy: A case report
- Pages: 653-655
- First Published: 11 January 2022
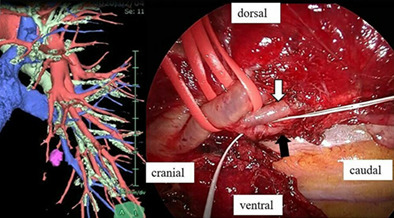
A three-dimensional CT indicated that S8b subsegmentectomy was sufficient. The pulmonary artery was dissected to the A8a (white arrow) and b (black arrow) branches. This case demonstrated that early-stage metastatic clear cell renal carcinoma could recur after over 17 years. Thoracoscopic segmentectomy is less invasive and can preserve pulmonary function.
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Chemoimmunotherapy versus immune checkpoint inhibitors monotherapy as first-line treatment for advanced non-small cell lung cancer
- Page: 656
- First Published: 13 January 2022