Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Expression and prognostic value of Cripto-1 in early non-small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 1203-1208
- First Published: 01 August 2023
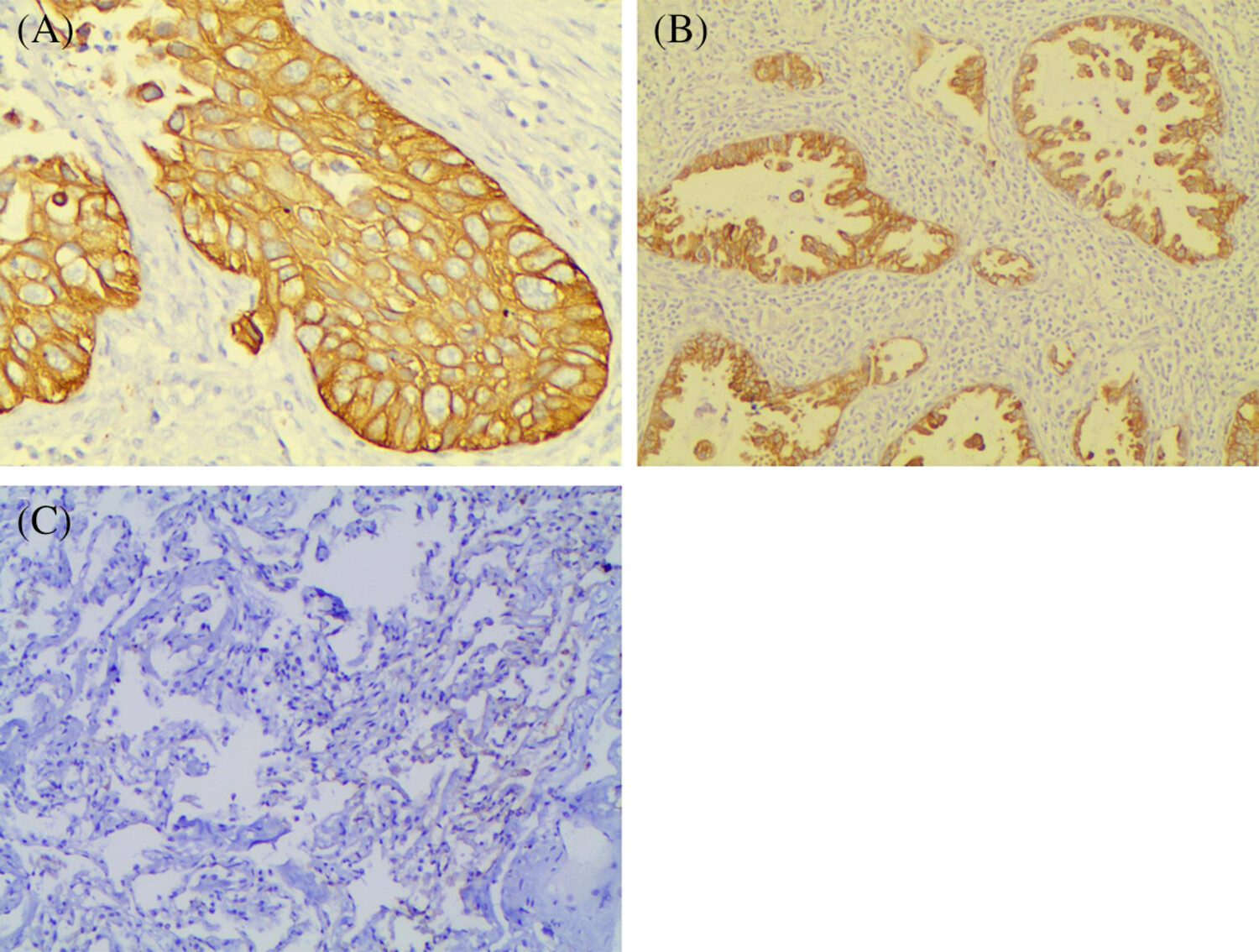
The positive expression of CR-1 protein in early stage NSCLC was higher than that in normal lung tissue. Cox multivariate regression analysis showed that the expression of CR-1 protein was an independent prognostic factor for early stage NSCLC. Detecting the expression of CR-1 protein is helpful to predict the prognosis and recurrence of early stage NSCLC patients.
Impact of selexipag use within 12 months of pulmonary arterial hypertension diagnosis on hospitalizations and medical costs: A retrospective cohort study
- Pages: 1209-1222
- First Published: 07 October 2023
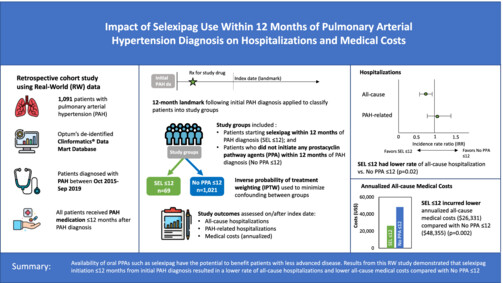
Prostacyclin pathway agents are effective in improving health outcomes in pulmonary arterial hypertension patients. Availability of oral prostacyclin pathway agents such as selexipag have the potential to benefit patients with less advanced disease. We sought to assess the impact of early selexipag use on hospitalization rates and medical costs in real-world clinical practice.
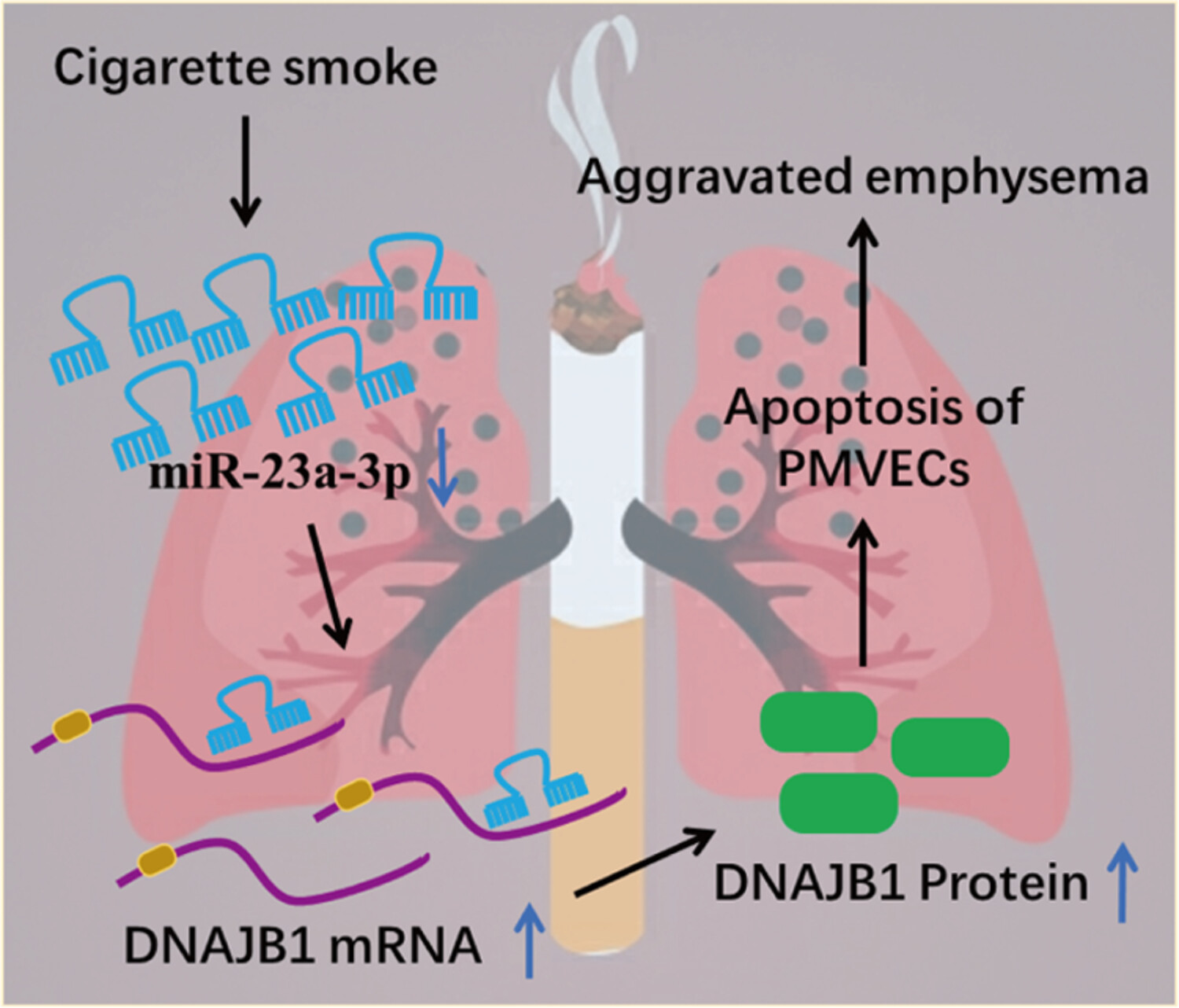
MiR-23a-3p alleviates cigarette smoke extract-induced pulmonary vascular endothelial cell apoptosis by targeting DNAJB1 in emphysema
- Pages: 1223-1232
- First Published: 12 October 2023
SCN4B inhibits the progression of lung adenocarcinoma and is associated with better prognosis
- Pages: 1233-1245
- First Published: 12 October 2023
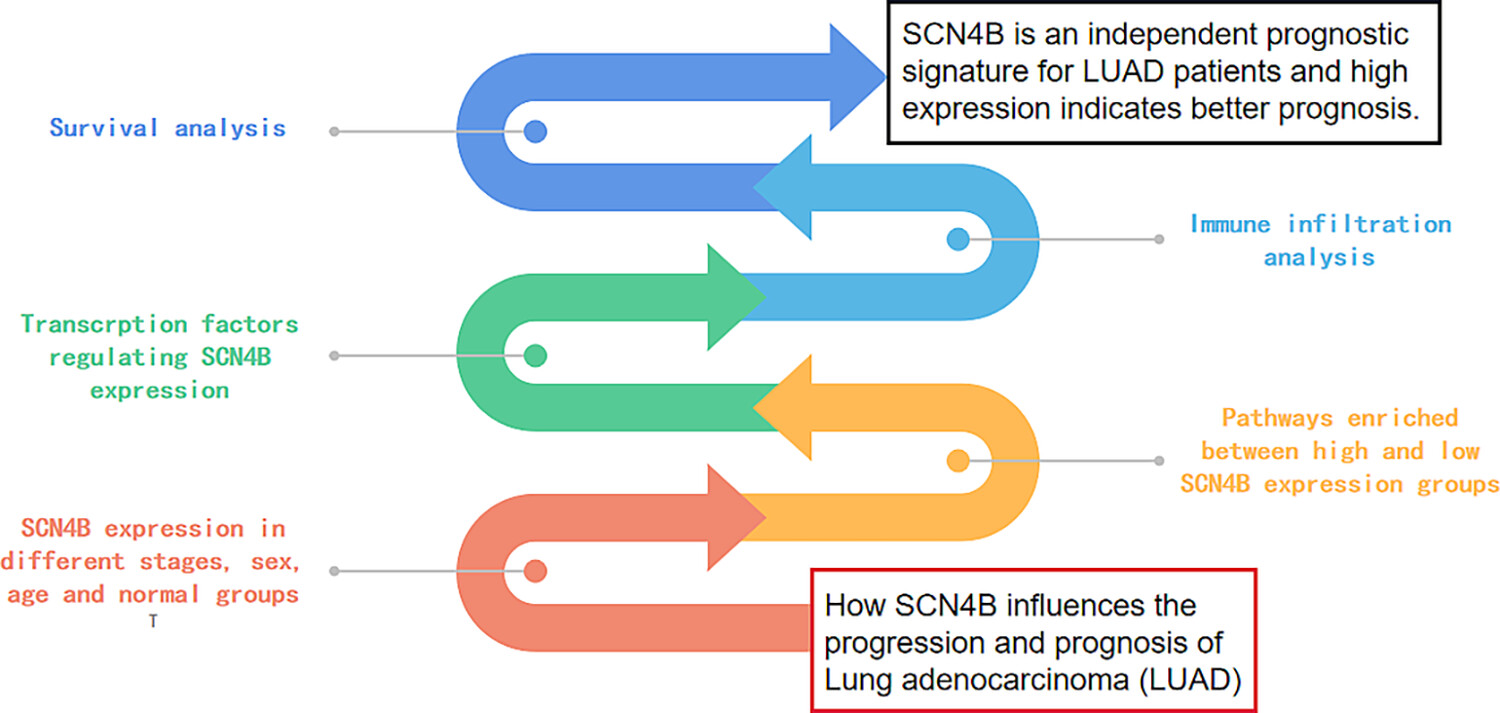
SCN4B encoding voltage-gated sodium channel β subunit is regarded as metastasis-suppressor gene, and it expresses higher in normal samples than lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) samples. SCN4B is an independent prognostic signature for LUAD patients, and its higher expression in LUAD samples represents better prognosis. Transcription factors TAL1 and ERG may regulate the expression of SCN4B by binding its upstream sequences.
Isolation of Epstein-Barr virus-deoxyribonucleic acid in the lower respiratory tract for distinguishing critically ill patients from those with influenza-associated pneumonia: A pilot study
- Pages: 1246-1253
- First Published: 12 October 2023
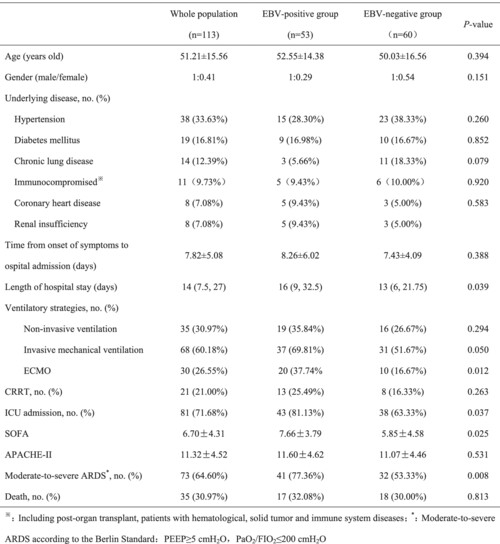
The detection rate of EBV-DNA in the lower respiratory tract was high. When patients have positive EBV-DNA results in the lower respiratory tract, their disease is often more severe. EBV-DNA-positive and low lymphocyte count are independent risk factors for the development of moderate-to-severe ARDS in patients with influenza A-related pneumonia.
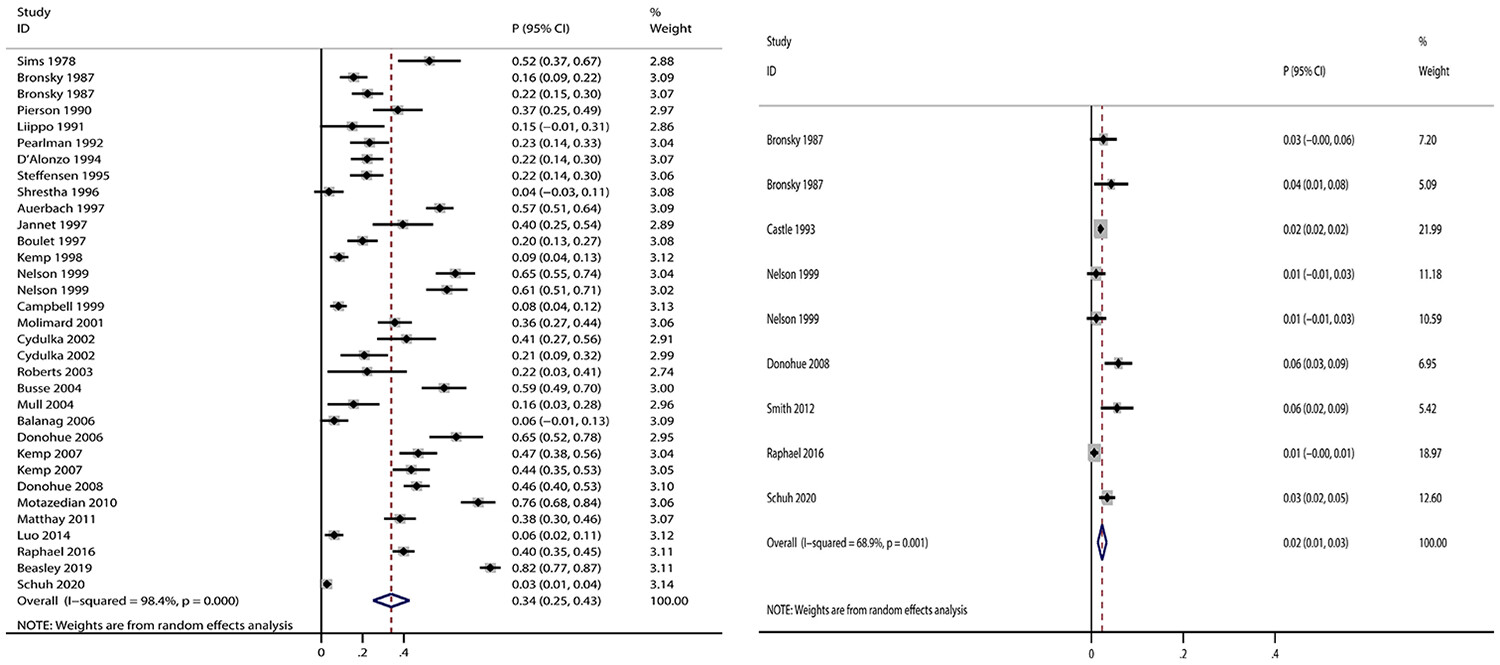
Safety outcomes of salbutamol: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 1254-1264
- First Published: 16 October 2023
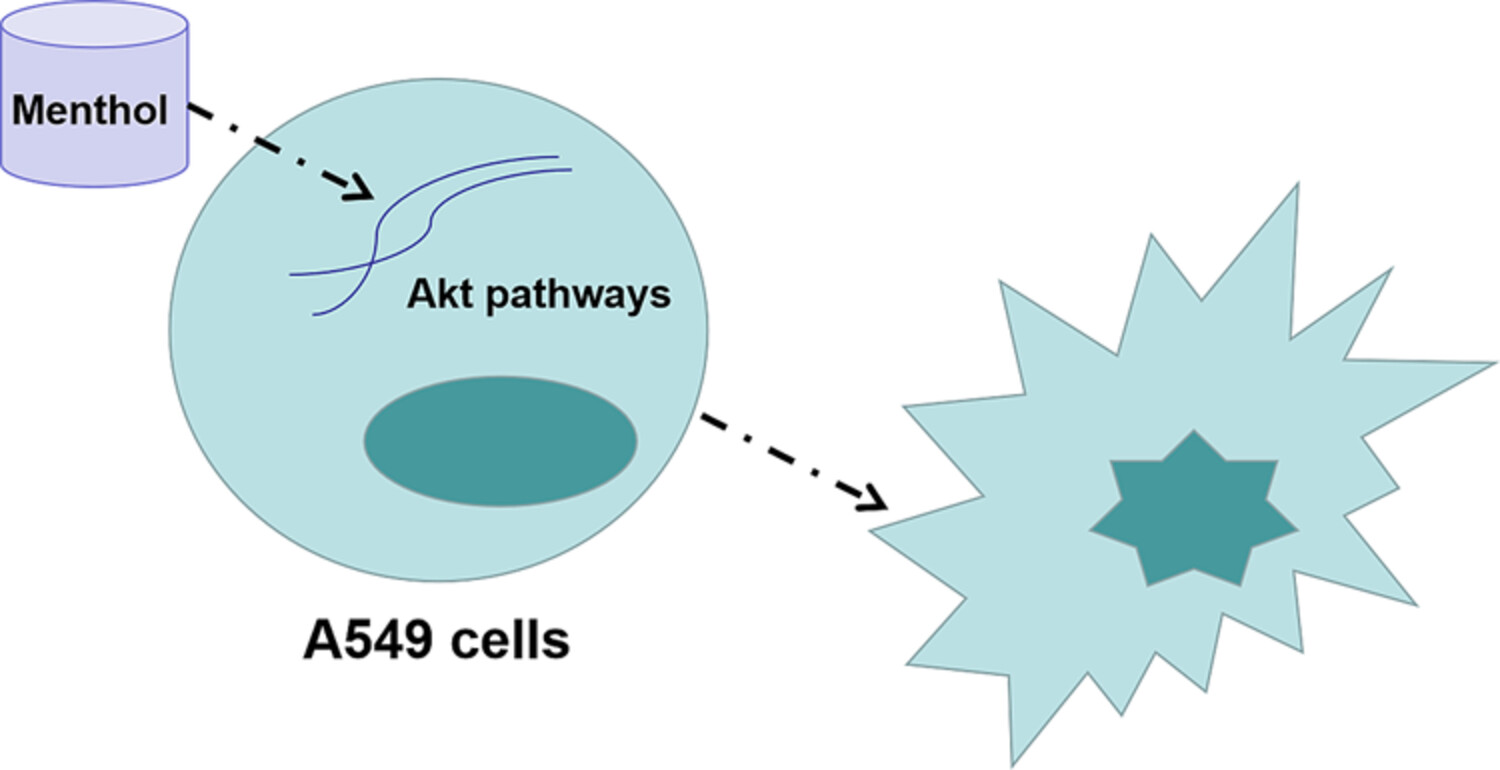
Menthol induces apoptosis and inhibits proliferation and migration of nonsmall cell lung carcinoma in vitro and in vivo through Akt pathway
- Pages: 1265-1275
- First Published: 27 November 2023
Association between IL10 rs1800896 polymorphism and risk of pediatric asthma: A meta-analysis
- Pages: 1276-1285
- First Published: 08 November 2023
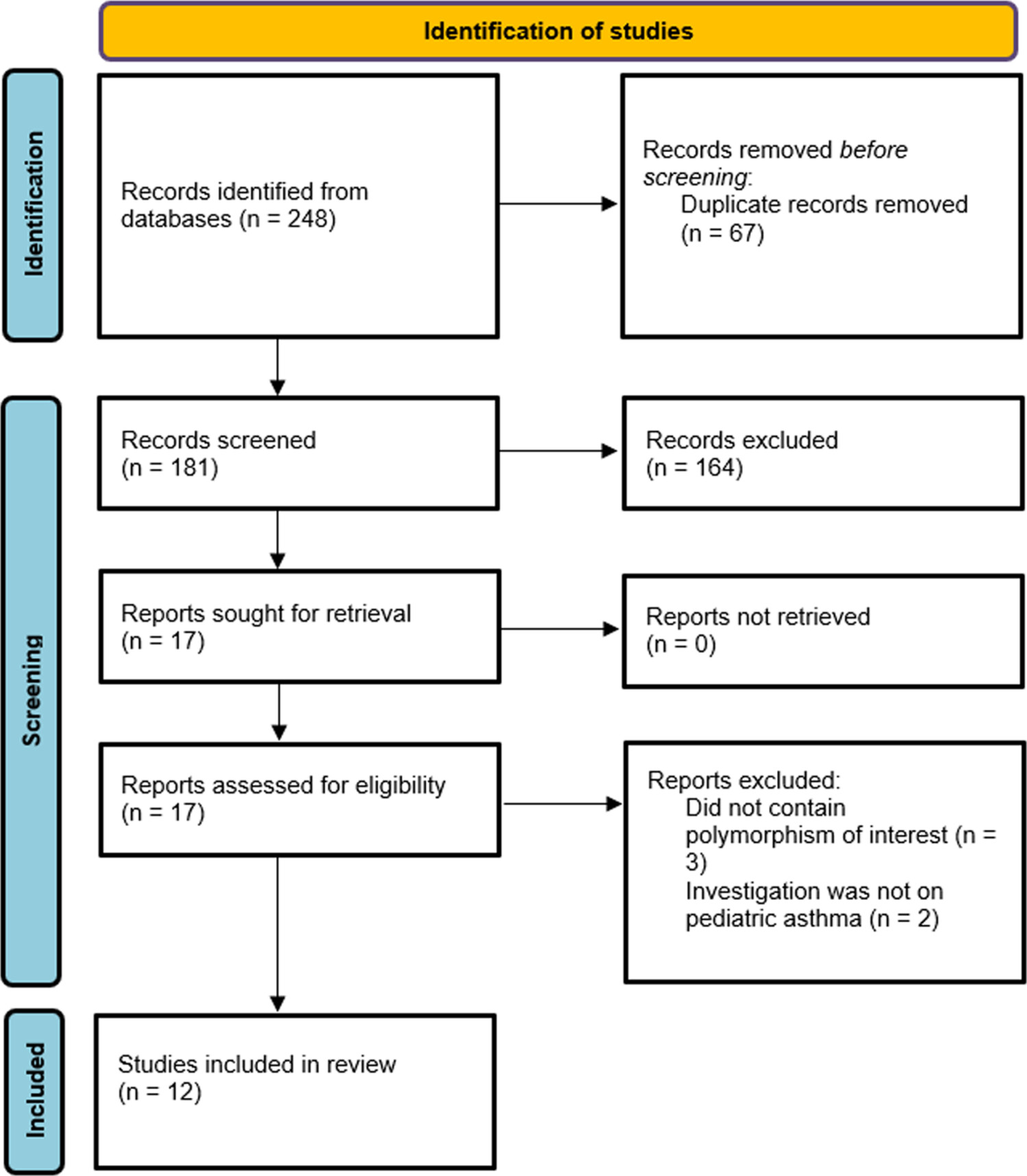
The association between IL10 rs1800896 polymorphisms and pediatric asthma risk was evaluated using a meta-analysis. A total of 12 studies with 1645 cases and 1447 controls were included. It was found that IL10 rs1800896 polymorphism was not significantly associated with risk of childhood asthma in all genetic models studied, although subgroup analysis revealed that the polymorphism was significantly associated with a lower risk of pediatric asthma in Asians.
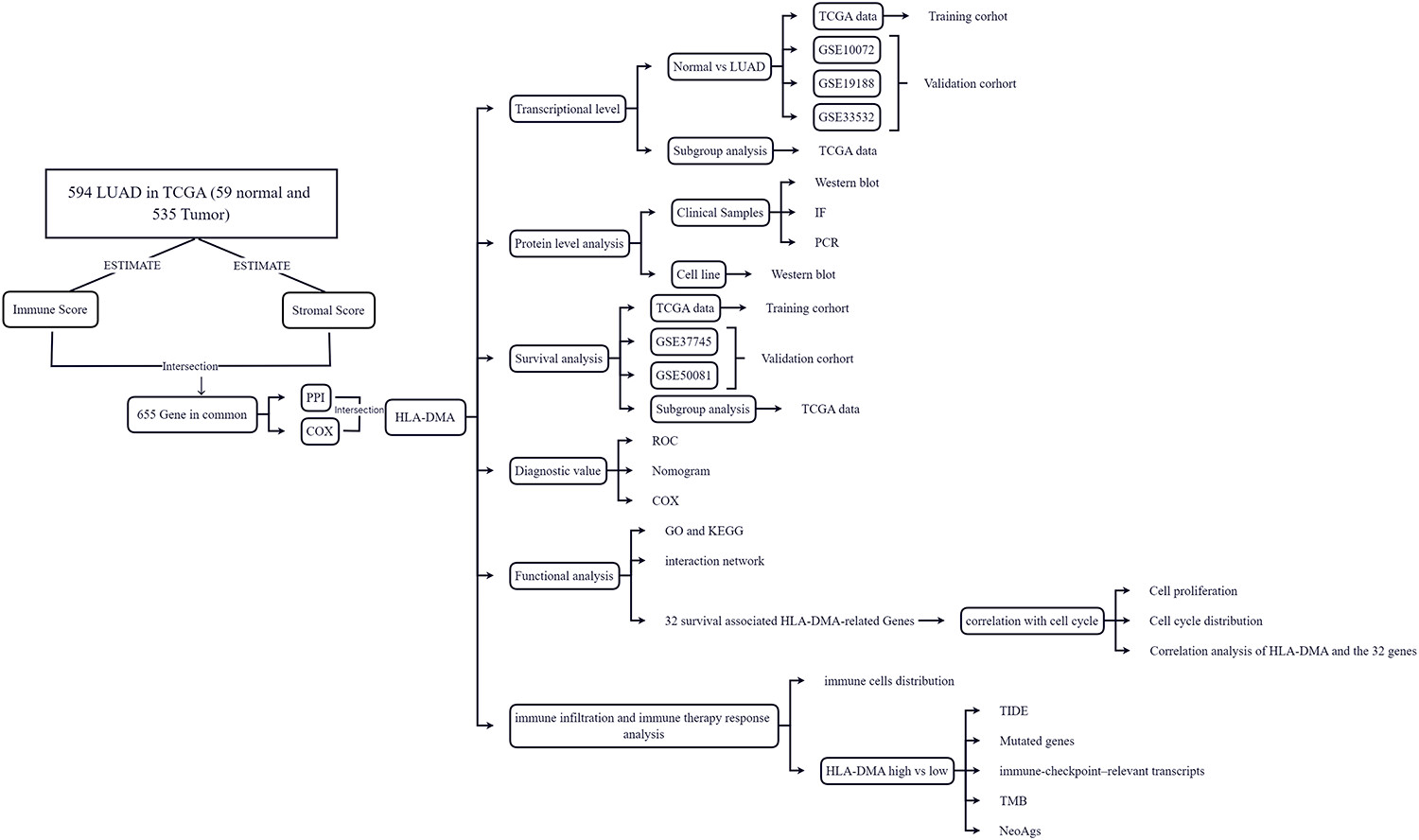
Prognostic gene HLA-DMA associated with cell cycle and immune infiltrates in LUAD
- Pages: 1286-1300
- First Published: 16 November 2023
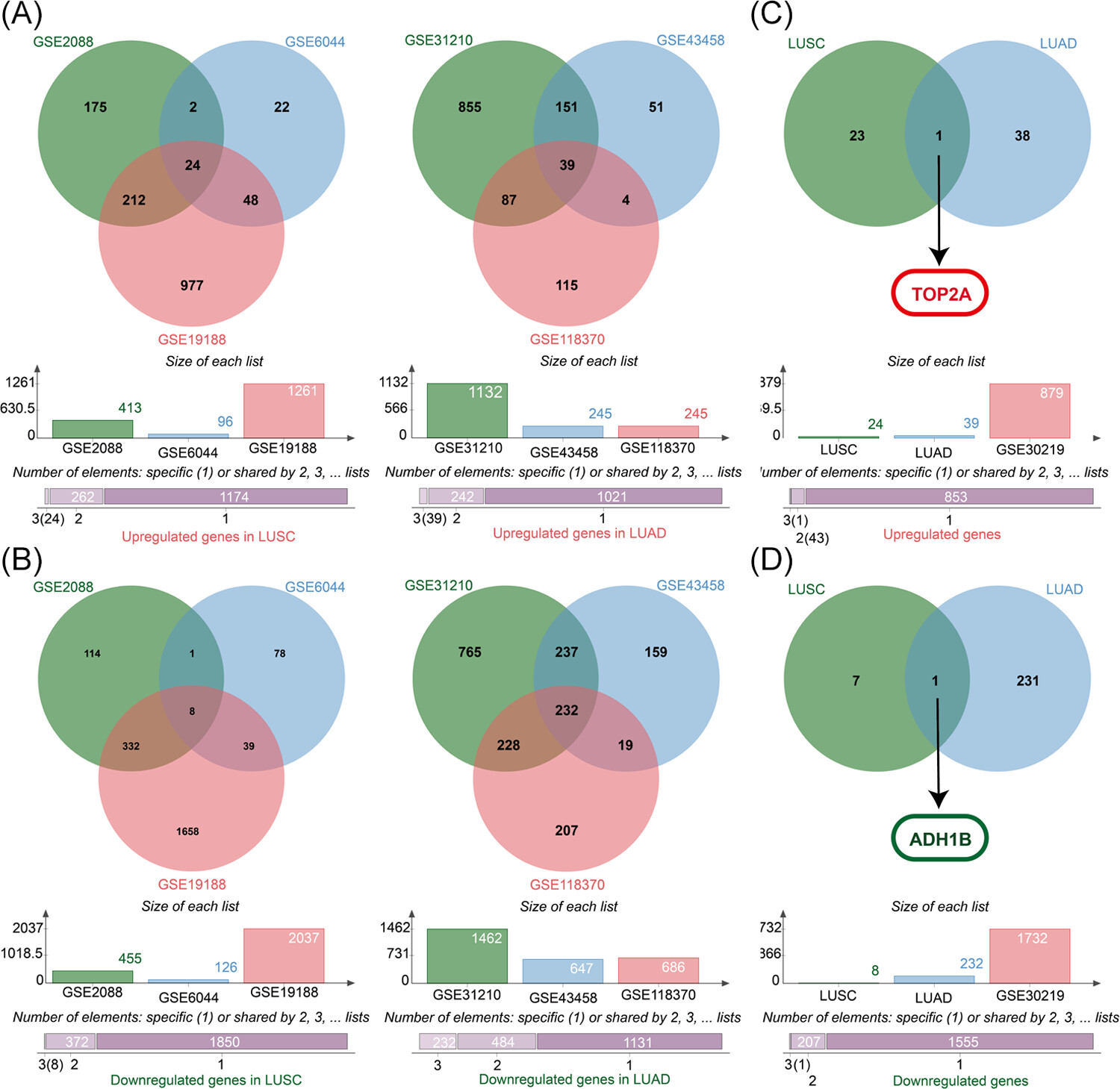
Association of TOP2A and ADH1B with lipid levels and prognosis in patients with lung adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma
- Pages: 1301-1315
- First Published: 20 November 2023
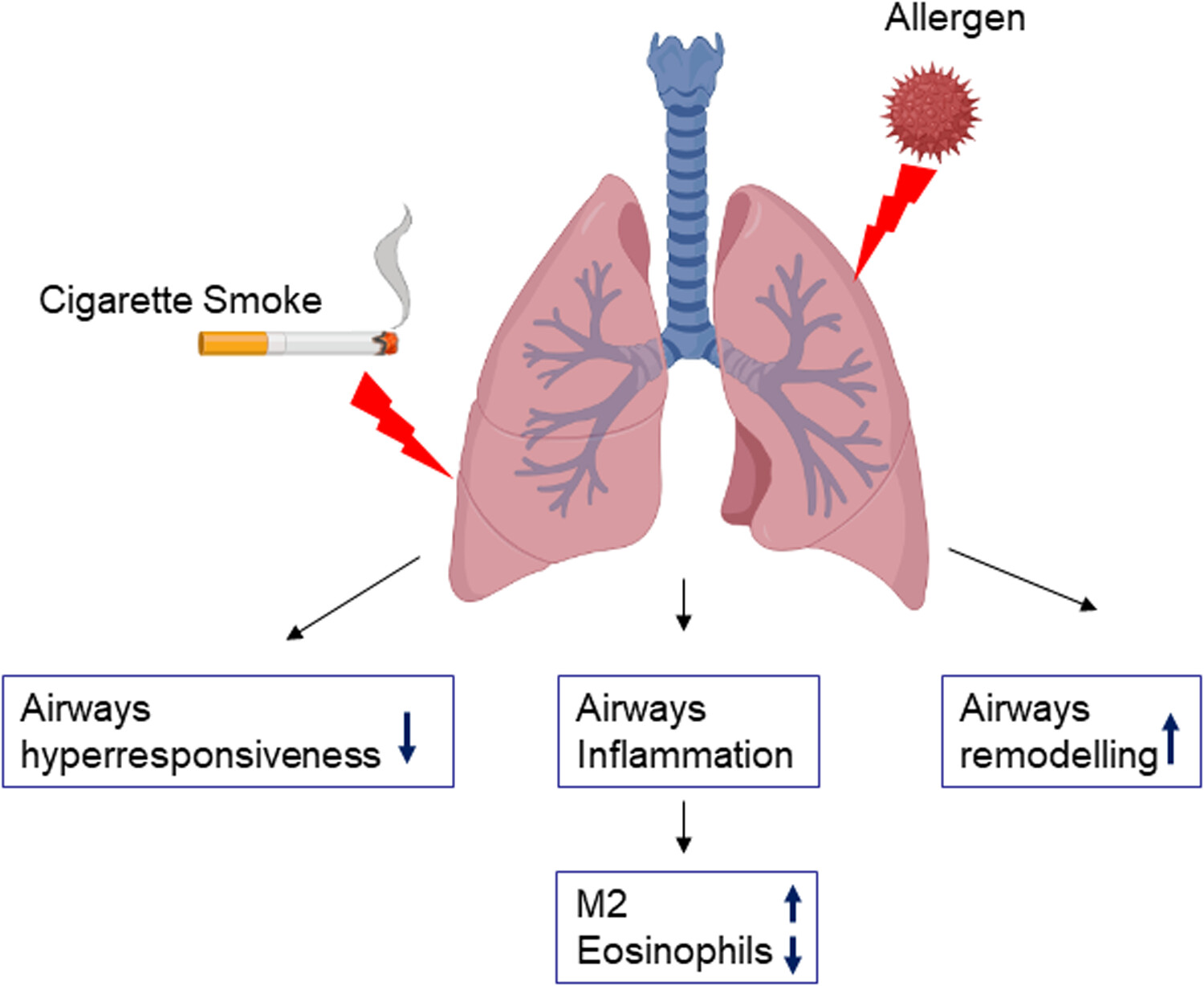
Cigarette smoke aggravates asthma via altering airways inflammation phenotypes and remodelling
- Pages: 1316-1327
- First Published: 14 November 2023
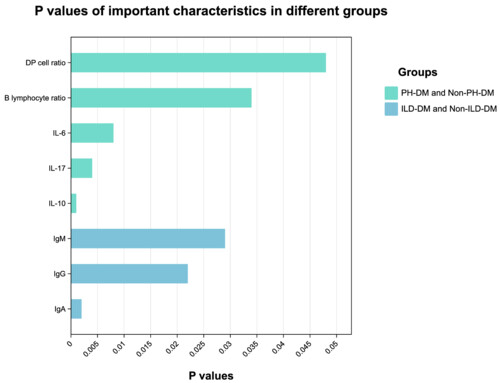
Analysis of characteristics related to interstitial lung disease or pulmonary hypertension in patients with dermatomyositis
- Pages: 1328-1340
- First Published: 20 November 2023
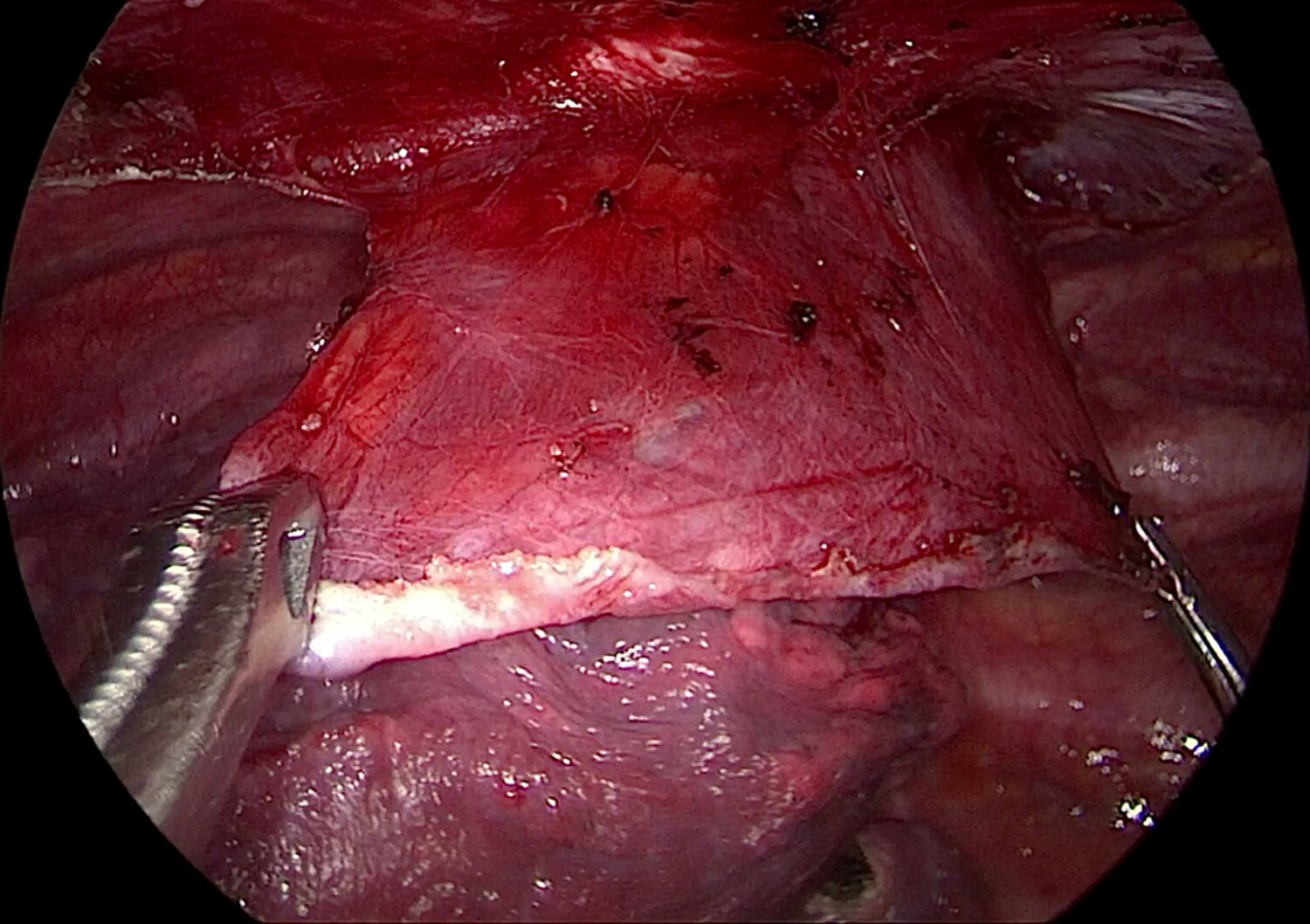
Uniportal thoracoscopic bullectomy with improved parietal pleurectomy for primary spontaneous pneumothorax
- Pages: 1341-1348
- First Published: 03 December 2023
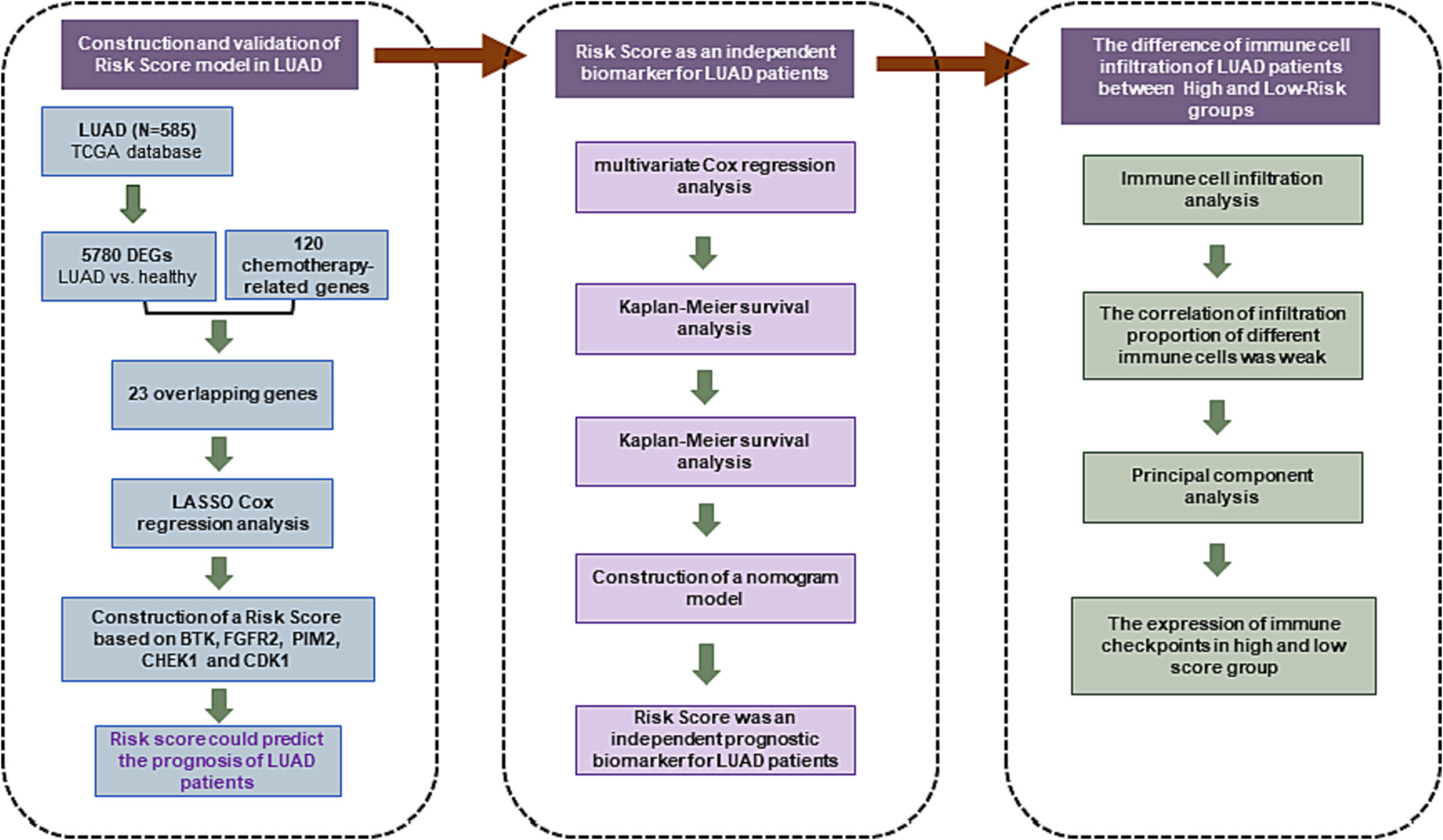
A prognostic signature for lung adenocarcinoma by five genes associated with chemotherapy in lung adenocarcinoma
- Pages: 1349-1360
- First Published: 10 December 2023
PROTOCOL
Rationale and design of a multicenter, randomized phase II trial of durvalumab with or without multitarget tyrosine kinase inhibitor as maintenance treatment in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer patients (DURABLE study)
- Pages: 1361-1367
- First Published: 10 November 2023
BRIEF REPORT
A rare case of hepatoid adenocarcinoma of the lung
- Pages: 1368-1371
- First Published: 10 December 2023
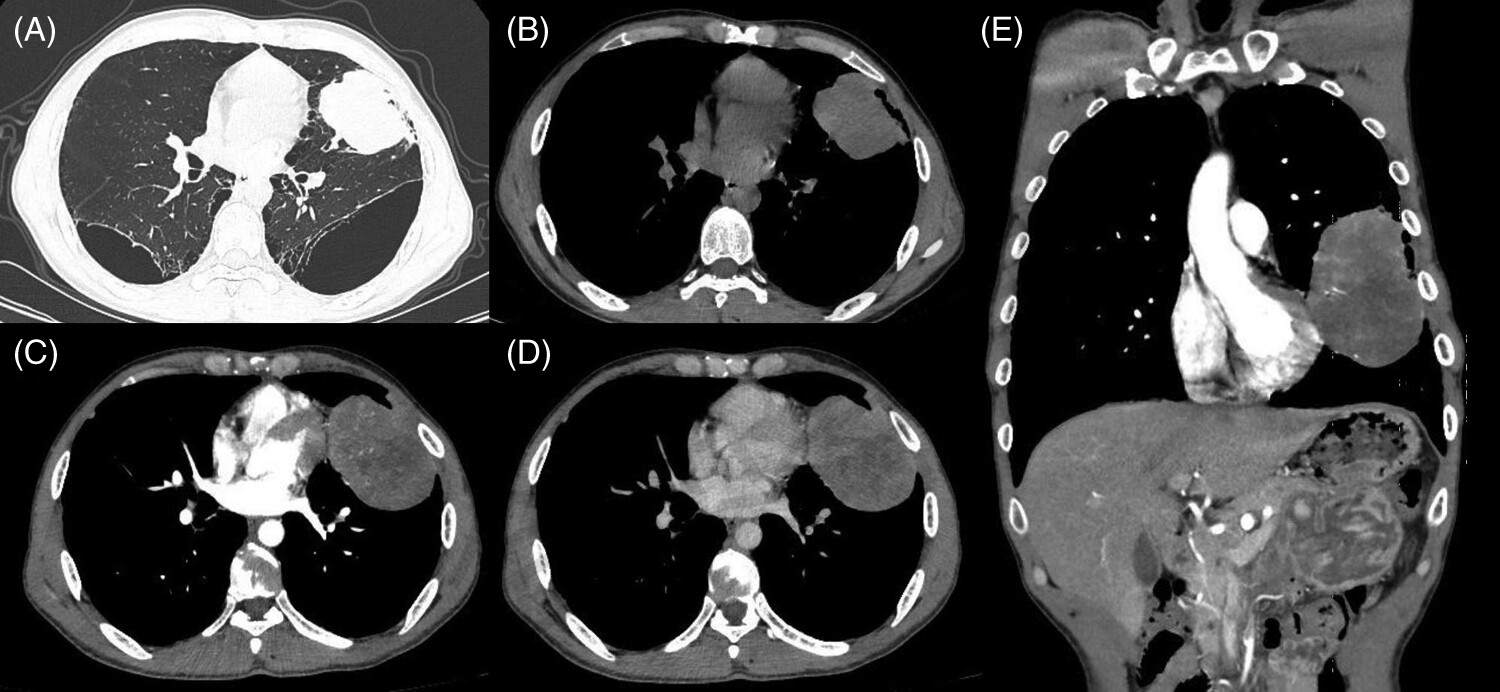
We report a case of hepatoid adenocarcinoma with the primary lesion located in the left upper lung. The patient was treated by four cycles of combined therapy, and the tumour had significantly reduced in size. Subsequent postoperative pathology proved that the patient had achieved a complete remission.