Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW ARTICLES
Risk factors for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in never-smokers: A systematic review
- Pages: 261-275
- First Published: 10 February 2022
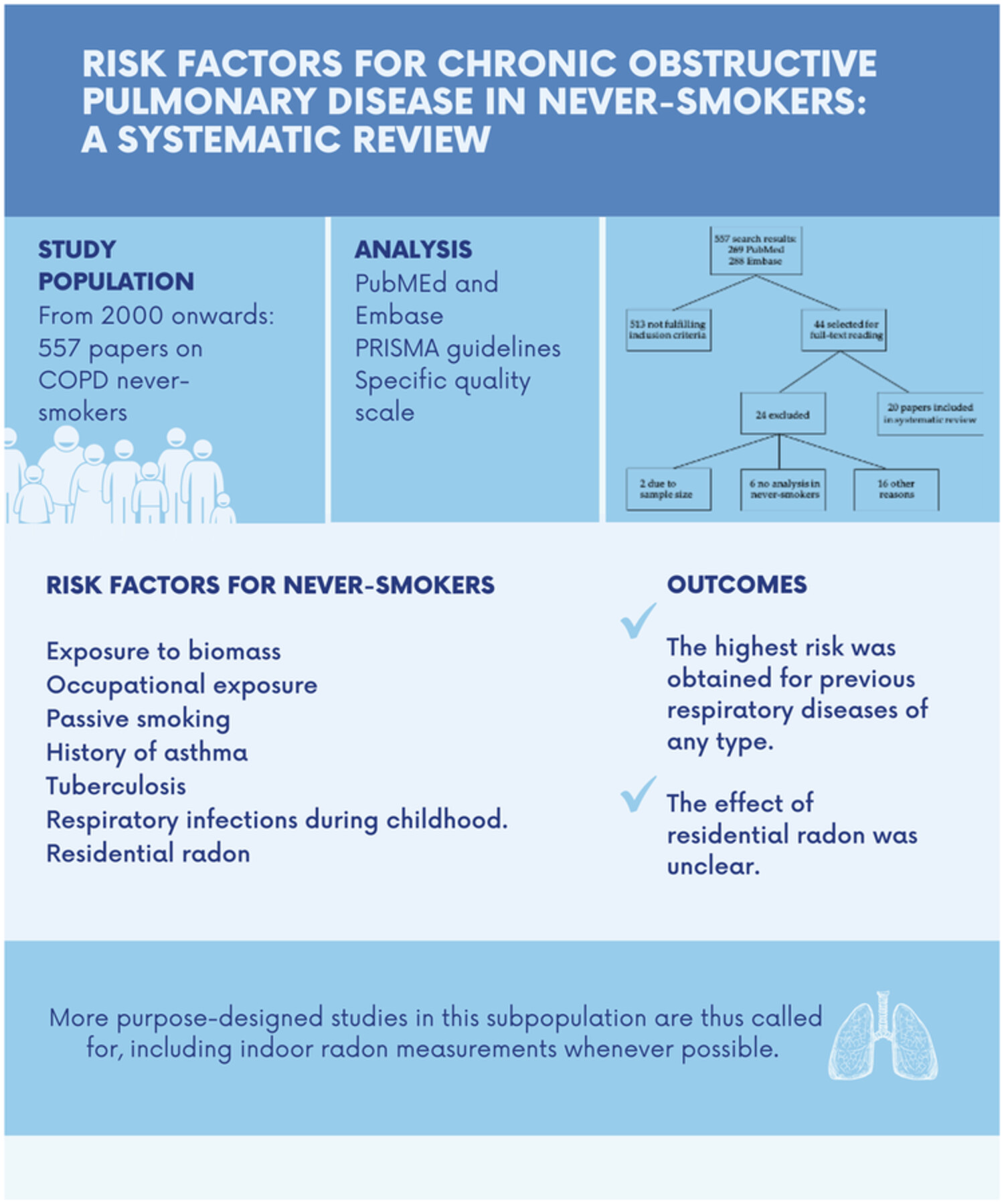
A sizeable proportion of COPD patients are never-smokers and many risk factors are implicated in the disease's development, fundamentally exposure to biomass fuel, risk occupations, a history of asthma or tuberculosis, and exposure to passive smoking. The effect of residential radon was unclear. More studies in this subpopulation are thus called for, including indoor radon measurements.
Diagnostic value of computed tomography-based pulmonary artery to aorta ratio measurement in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease with pulmonary hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 276-283
- First Published: 14 March 2022
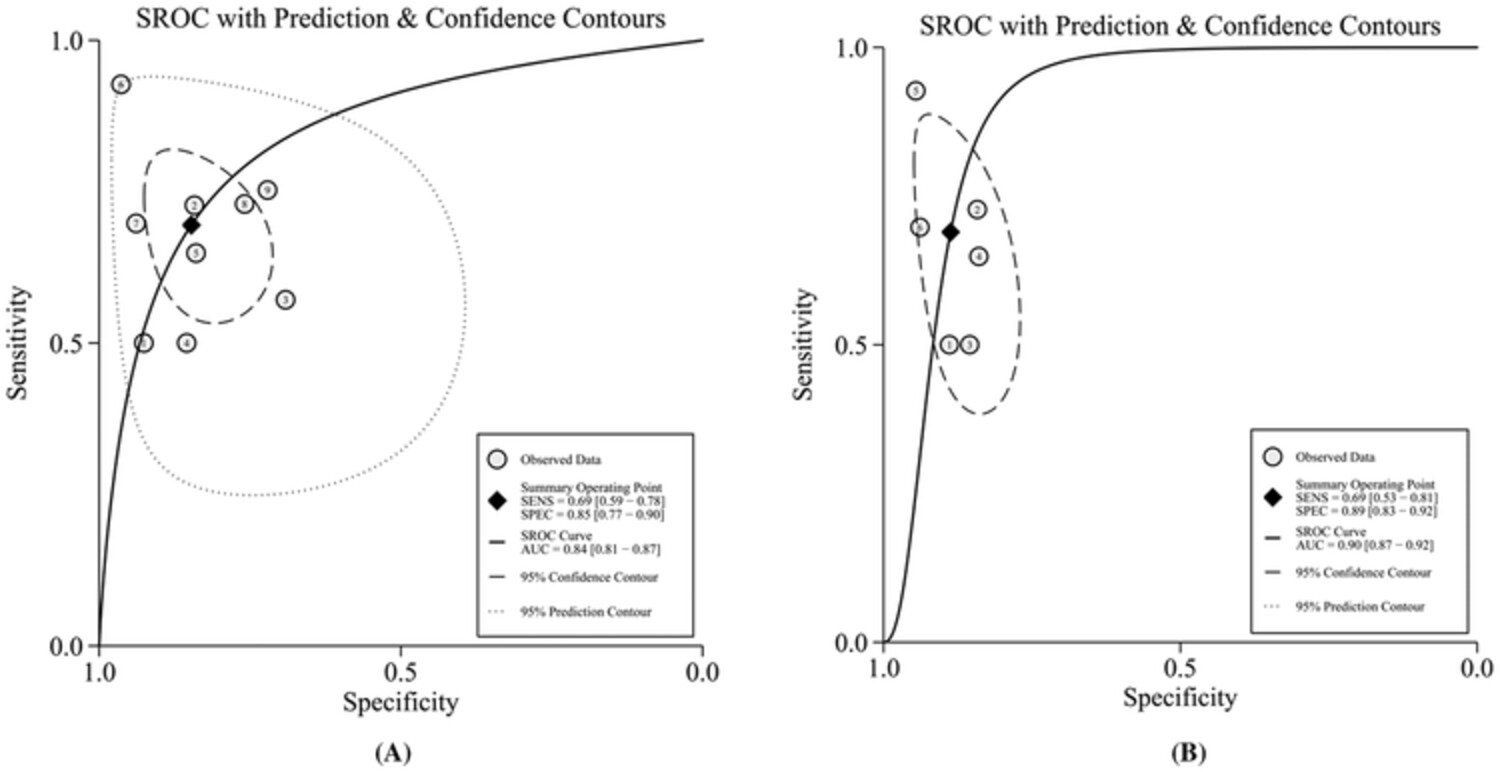
We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of available evidence on the accuracy of PA: A ratio for the diagnosis of pulmonary hypertension with COPD(COPD-PH) and proved that CT-based PA:A ratio measurement was a distinctively non-invasive biomarker to complement diagnosis of COPD-PH in the aspect of accuracy and specificity. Meanwhile, PA/A ≥ 1 may be an appropriate select.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
The alterations of retinal vasculature detected on optical coherence tomography angiography associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Pages: 284-292
- First Published: 11 February 2022
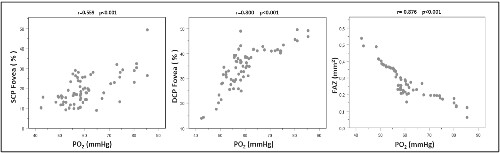
To evaluate the retinal vasculature of the macula and optic disc in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) by optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA).The right eyes of 70 COPD patients and 71 healthy individuals were evaluated. Superficial and deep capillary plexus vascular densities, foveal avascular zone (FAZ) width, and optic disc parameters were measured with OCTA. The COPD group had a significant decrease in the vascular density in the superficial (fovea (p = 0.019); parafovea (p = 0.013); perifovea (p = 0.001)) and deep capillary plexus (fovea (p = 0.028); parafovea (p = 0.005); perifovea (p = 0.002)). Also, the enlargement of the FAZ (p = 0.002), and a decrease in the peripapillary vascular density (p = 0.006), were observed in the chronic obstructive pulmonary disease group. There was a positive correlation between pO2 level and superficial, deep and peripapillary vascular density in COPD patients, and a negative correlation with FAZ (r = 0.559-0,900). OCTA can be a very important tool in the follow-up and treatment of these patients.
Asthma, from mild to severe, is an independent prognostic factor for mild to severe Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
- Pages: 293-300
- First Published: 11 February 2022
Both mild and severe asthma are independent prognostic factors for Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). They are associated with more severe disease with respiratory and systemic complications.
Severe COVID-19 pneumonia in an intensive care setting and comparisons with historic severe viral pneumonia due to other viruses
- Pages: 301-308
- First Published: 24 February 2022
Safety and accuracy of transbronchial lung cryobiopsy in diagnosing desquamative interstitial pneumonia
- Pages: 309-316
- First Published: 01 March 2022
Effectiveness of 12-week inspiratory muscle training with manual therapy in patients with COPD: A randomized controlled study
- Pages: 317-328
- First Published: 24 March 2022
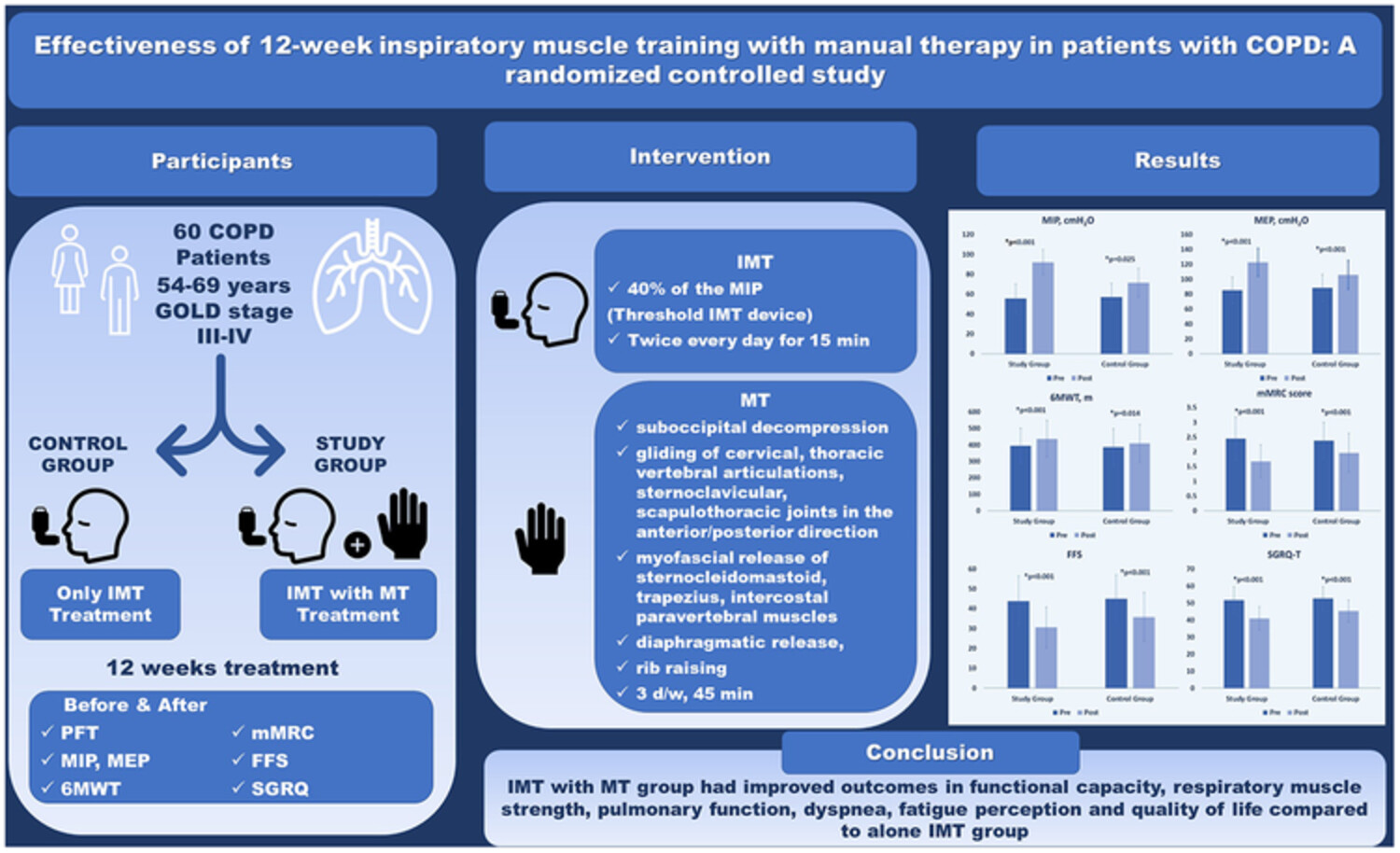
This randomized controlled single-blind study demonstrated that the group of COPD patients receiving IMT with MT showed improved FEV1 and FVC values, improved functional capacity, increased respiratory muscle strength, improved pulmonary function, reduced dyspnea and fatigue perception, and improved quality of life compared with the group of patients treated with IMT alone. This study brings a new perspective to the application of IMT and its beneficial effects.
BRIEF REPORT
Cytological patterns of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in mechanically ventilated COVID-19 patients on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation
- Pages: 329-334
- First Published: 11 March 2022
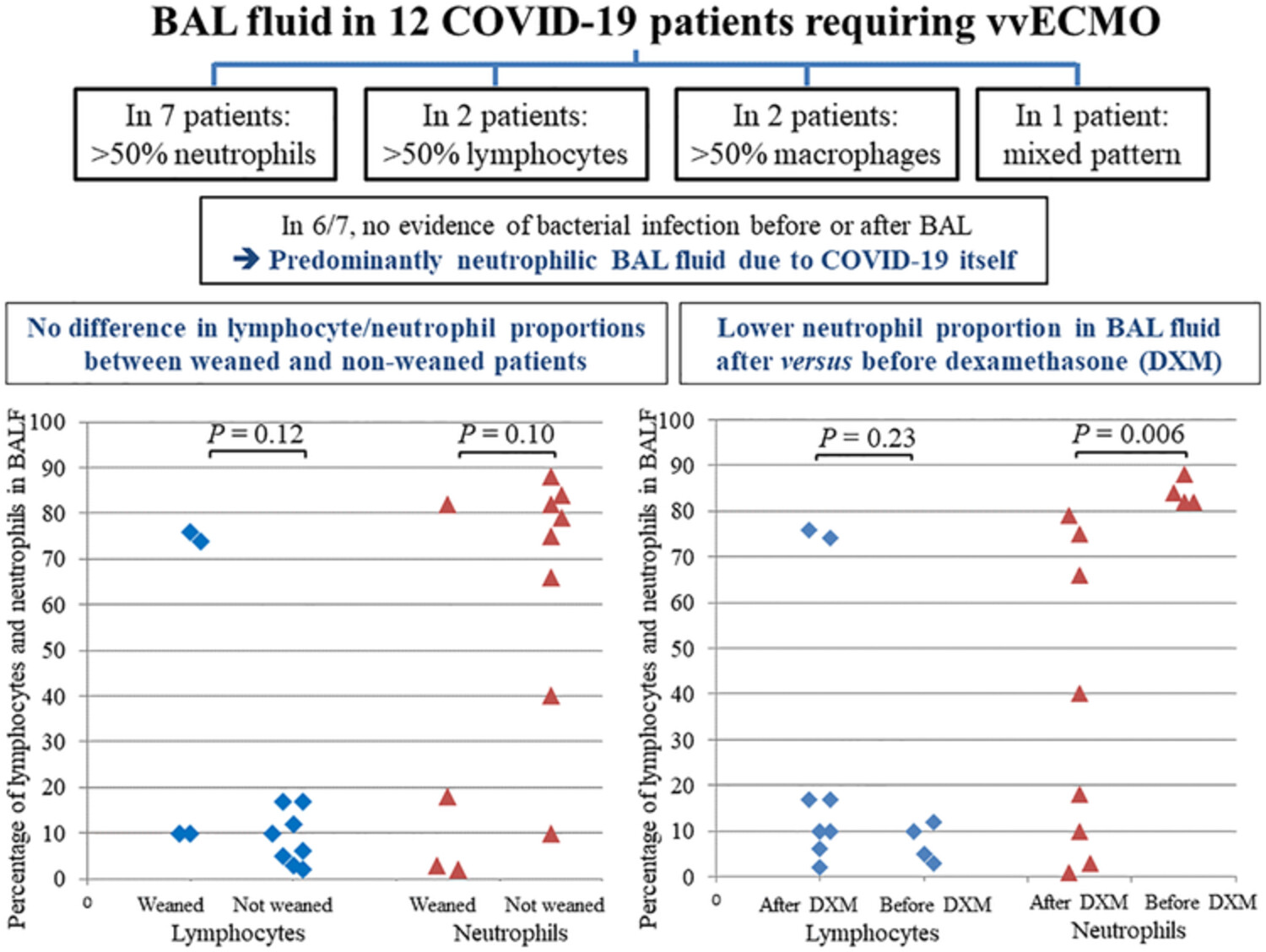
In critically ill COVID-19 patients treated with ECMO, a high neutrophil proportion in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid is possible despite the absence of evidence for bacterial infection. Neutrophil proportion is significantly lower in patients treated with dexamethasone at the time of bronchoalveolar lavage.
The impact of COVID-19 upon the delivery of exercise services within cystic fibrosis clinics in the United Kingdom
- Pages: 335-340
- First Published: 01 March 2022