Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Editorial
Preface: 50th American Society for Photobiology Anniversary Issue†
- Pages: 197-198
- First Published: 30 March 2023
Special Issue Correspondence
Photodynamic Therapy: Critical PDT Theory
- Pages: 199-203
- First Published: 15 March 2022
Special Issue Invited Review
Aromatic Endoperoxides
- Pages: 204-220
- First Published: 15 July 2022
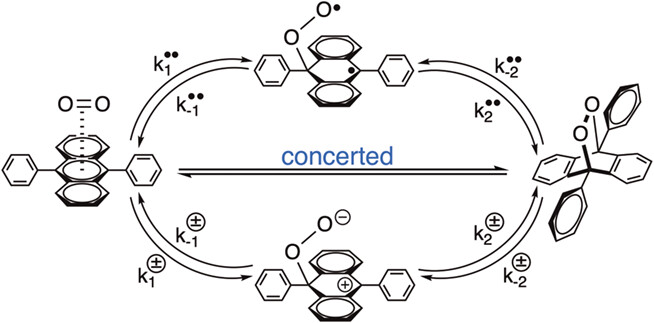
Aromatic endoperoxides have been extensively exploited as valuable thermal precursors of cytotoxic singlet oxygen. On the other hand, formations of aromatic endoperoxides are also detrimental to the lifetime of organic electronic and photonic devices. This review will provide insight into a variety of aspects of the syntheses, reactions, and mechanisms of formation and decomposition of aromatic endoperoxides that will enhance their design for applications in both the material and biological sciences.
Photolabile Protecting Groups Based on the Excited State Meta Effect: Development and Application
- Pages: 221-234
- First Published: 15 August 2022
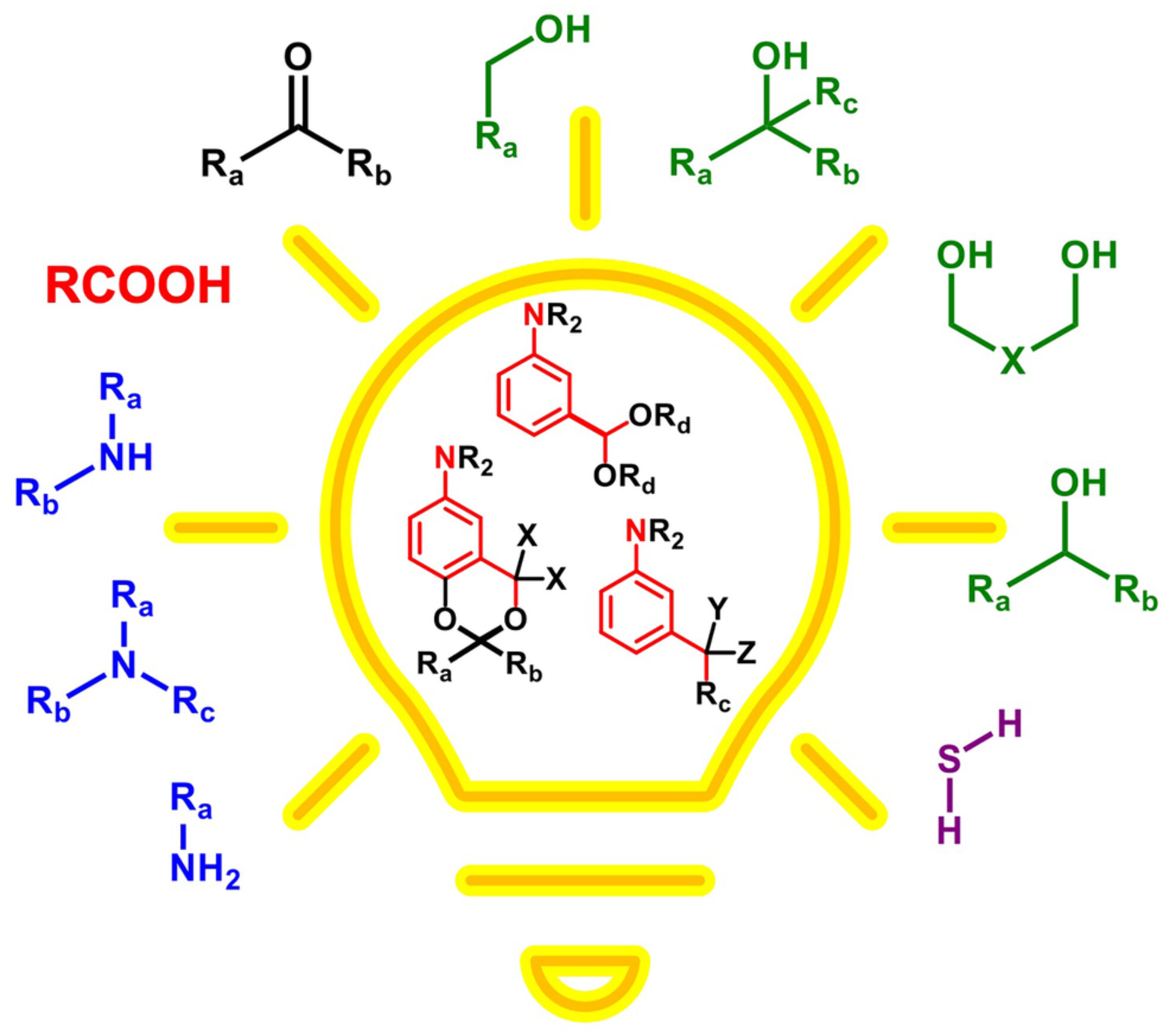
Structurally simple photolabile protecting groups based on the excited state meta effect (ESME) release carbonyl, hydroxyl, carboxyl, amino and thiol groups effectively. They can find various applications in synthesis, release of biologically important molecules, materials science and biomedical engineering.
An Update on General Chemiexcitation Mechanisms in Cyclic Organic Peroxide Decomposition and the Chemiluminescent Peroxyoxalate Reaction in Aqueous Media
- Pages: 235-250
- First Published: 15 July 2022
Cyclic peroxide decomposition can lead to efficient chemiexcitation, important for chemiluminescence (CL) and bioluminescence (BL), by different mechanisms. CL efficiency is generally much lower in aqueous than in anhydrous environment, specifically true for the peroxyoxalate reaction, whose mechanisms and emission efficiencies in aqueous media will be discussed and examples of recent applications given.
Chemiexcitation: Mammalian Photochemistry in the Dark†
- Pages: 251-276
- First Published: 22 January 2023
A 1,2-dioxetane, which thermally decomposes between the two oxygens and two carbons to yield two carbonyls, one of which is excited to a high-energy triplet state in a process termed “chemiexcitation”. Chemiexcited molecules underlie invertebrate bioluminescence but recently have been found to occur in mammalian cells, sometimes causing pathogenic effects.
Adjacent and Nonadjacent Dipyrimidine Photoproducts as Intrinsic Probes of DNA Secondary and Tertiary Structure†
- Pages: 277-295
- First Published: 18 August 2022
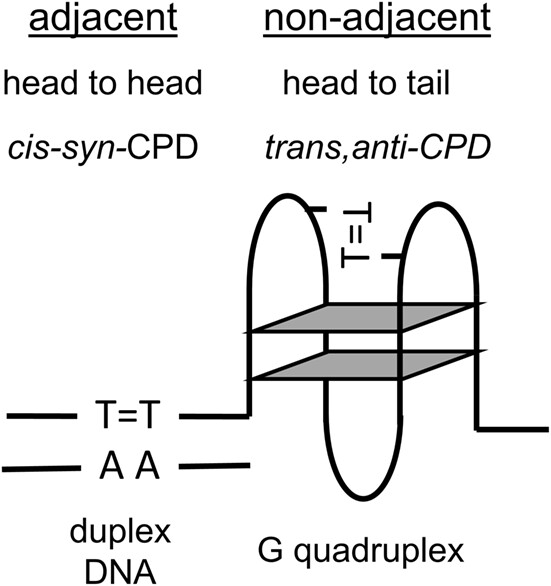
While irradiation of duplex DNA produces adjacent cis,syn cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPDs), irradiation of other structures can produce other isomers, such as the nonadjacent trans,anti CPD formed in G-quadruplexes. This review investigates the various types of adjacent and nonadjacent dipyrimidine photoproducts and methods for their detection that could be used to identify the presence of various types of unusual structures in DNA.
Capturing Protein–Nucleic Acid Interactions by High-Intensity Laser-Induced Covalent Cross-Linking†
- Pages: 296-312
- First Published: 23 August 2022
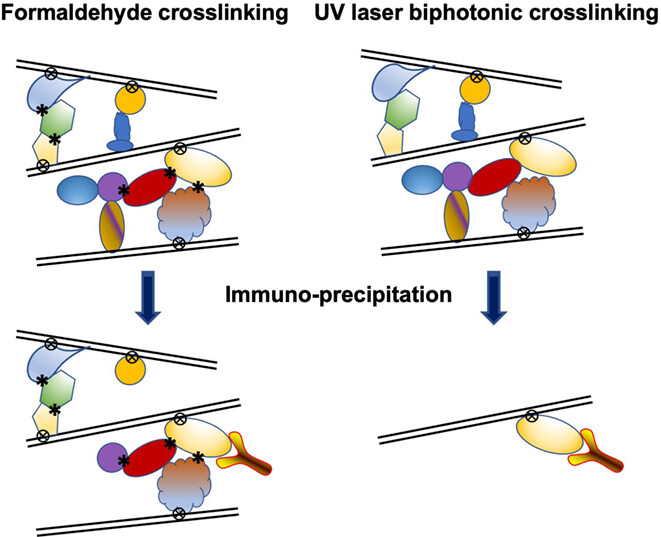
Formaldehyde DNA–protein cross-linking: protein–protein and DNA–protein XLs; capturing both direct and nondirect DNA–protein interactions; epitope loss; presence of artifacts DNA–protein interactions; ChIP-grade antibodies required; suitable for Hi-C and 3C genome conformation mapping; no special equipment required. Biphotonic UV laser DNA–protein cross-linking: only DNA–protein XLs; capturing only direct DNA–protein interactions; no epitope loss; no ChIP-grade antibodies required; no suitable for Hi-C and 3C genome conformation mapping; special, noncommercially available, equipment needed.
Practical Aspects in the Study of Biological Photosensitization Including Reaction Mechanisms and Product Analyses: A Do's and Don'ts Guide†
- Pages: 313-334
- First Published: 27 December 2022
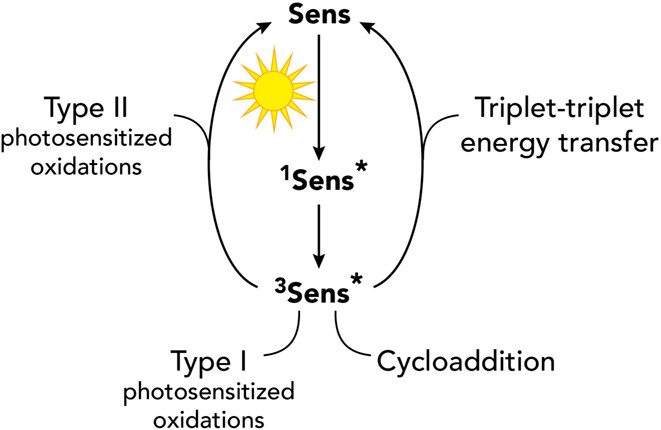
With the main goal of facilitating the understanding of photosensitized reactions, efforts were made to critically survey the main experimental approaches that were developed for this purpose. Time-resolved and steady-state spectroscopic methods as well as the role of additives and quenchers are discussed, thus highlighting their potential and limitations. We hope that the reported study, essentially educational, will provide good standard practices, with clear hints on how to gain mechanistic insights into photosensitized oxidation reactions.
Biological Impact of Shorter Wavelength Ultraviolet Radiation-C†
- Pages: 335-343
- First Published: 10 November 2022
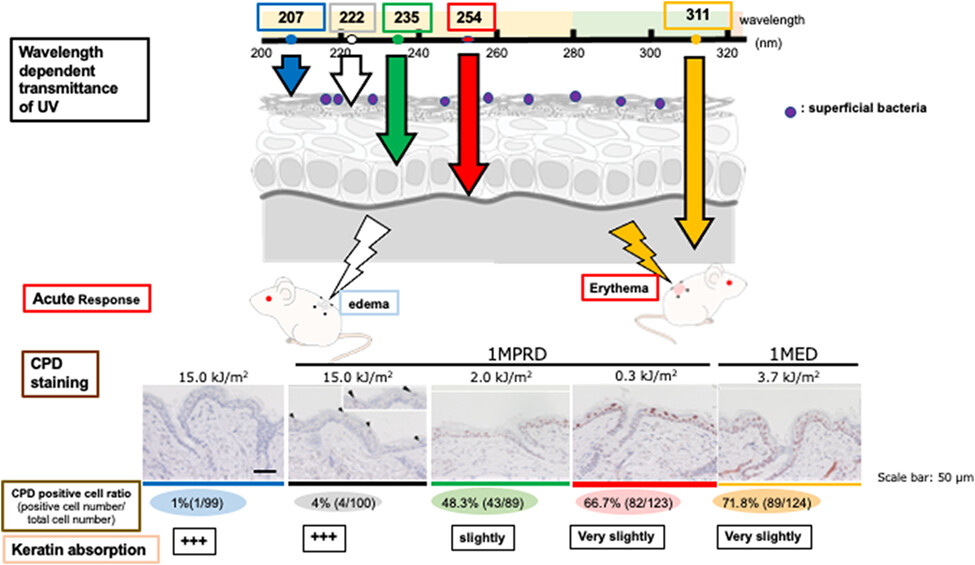
In the present manuscript, recent accumulating findings on the shorter wavelength UV-C were summarized especially on its biological impacts. Accumulating recent investigations indicate that the far-UVC is effective in inactivation of microorganisms and it is safe for human, as it reach the surface of the cell, but does not reach the basal layer. However, detailed mechanisms of cellular injury remain to be elucidated. Much more investigations on the biological impacts of far-UVC is encouraged.
Ultraviolet Radiation Exposure and its Impacts on Cutaneous Phosphorylation Signaling in Carcinogenesis: Focusing on Protein Tyrosine Phosphatases†
- Pages: 344-355
- First Published: 27 August 2022
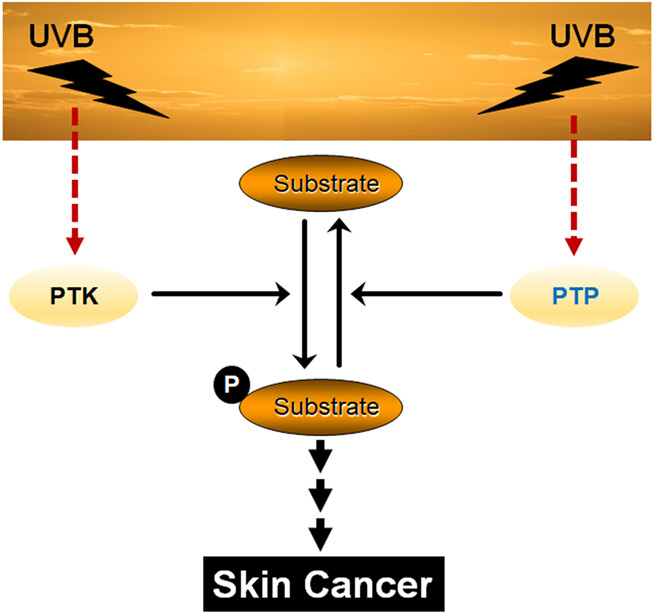
Protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs) negatively regulate phosphotyrosine signaling as an endogenous negative mechanism against protein tyrosine kinases. There are 107 PTPs identified in the human genome. PTPs are involved in different types of human cancer either as tumor suppressive PTPs or oncogenic PTPs depending on the tissue and their target mechanism. PTPs have not been studied extensively in photocarcinogenesis due to their inactivation by UVB. However, studies indicate that PTPs are initially activated by UVB and contribute to downregulate oncogenic signaling pathways. In this review, we will focus on recent advances in PTP signaling and its impact on skin photocarcinogenesis.
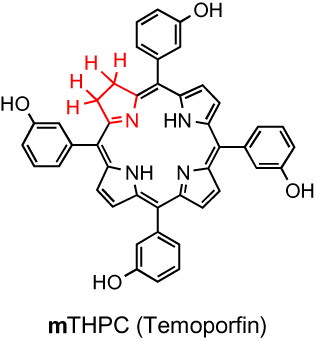
The Photosensitizer Temoporfin (mTHPC) – Chemical, Pre-clinical and Clinical Developments in the Last Decade
- Pages: 356-419
- First Published: 26 September 2022
Photodynamic Therapy for Bladder Cancers, A Focused Review†
- Pages: 420-436
- First Published: 22 September 2022
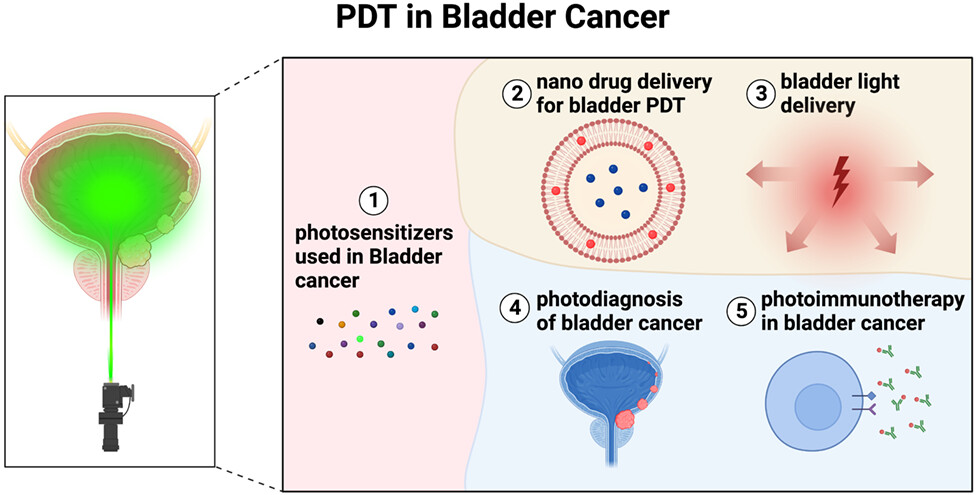
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is an FDA-approved treatment modality for various types of cancer. While PDT is currently being tested in different clinical trials for bladder cancer, it has a long way to go to obtain regulatory approval. The main components of PDT are photosensitizers, light and molecular oxygen. We discuss the recent progress in developing photosensitizers and their local bladder delivery. Successful PDT in bladder cancer requires a photosensitizer with minimal off-target effects. Light delivery also greatly influences treatment efficacy and selectivity. As PDT is combined with chemotherapy or immunotherapy, it should be more successful in treating bladder cancer.
Combination of 5-Fluorouracil with Photodynamic Therapy: Enhancement of Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses in a Murine Model of Actinic Keratosis†
- Pages: 437-447
- First Published: 30 August 2022
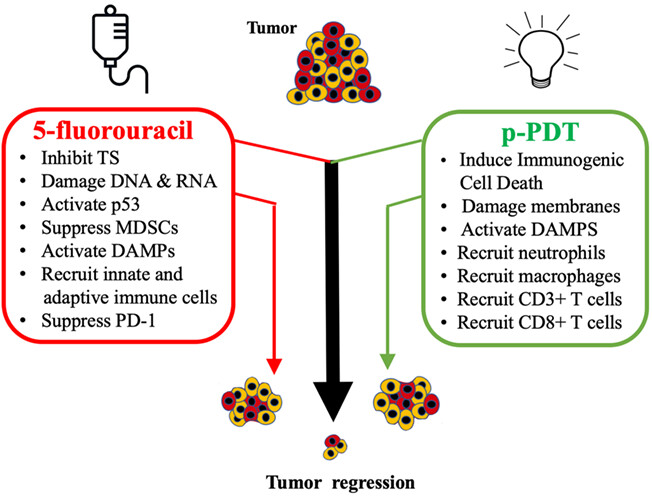
Mechanisms of action when 5-fluorouracil (5FU) and photodynamic therapy (PDT) are combined to treat squamous precancer lesions. 5FU inhibits thymidylate synthase, damages DNA and RNA and activates p53. 5FU also induces antitumor immunity by suppressing myeloid-derived suppressor cells, activating damage-associated molecules (DAMPs), recruiting immune cells and suppressing immune checkpoint receptors (PD-1). Painless PDT (pPDT) exerts nonoverlapping effects. pPDT induces immunogenic cell death instead of apoptosis, thereby activating DAMPs and recruiting innate and adaptive immune cells. 5FU and PDT, each known to induce antitumor immunity in addition to their antimetabolite and cytotoxic effects, are therapeutically more effective when combined.
Photochemical Targeting of Mitochondria to Overcome Chemoresistance in Ovarian Cancer
- Pages: 448-468
- First Published: 19 September 2022
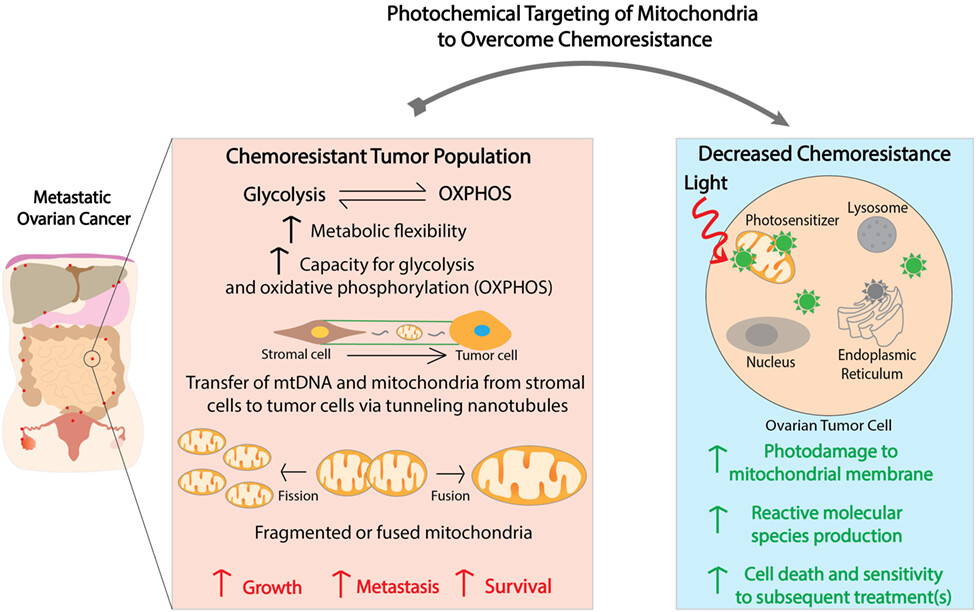
In metastatic ovarian cancer, chemoresistant tumor populations demonstrate increased metabolic flexibility, enhanced capacity for glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation, increased numbers of mitochondria and of mitochondrial DNA through mitochondrial transfer and altered mitochondrial dynamics (fission/fusion). Photodynamic therapy reverses chemoresistance in ovarian cancer and synergizes with conventional therapies. The role of mechanism-based combinations using photosensitizers that are, in part, synthesized in mitochondria, or localize to subcellular organelles, including mitochondria, is presented. The effects of photodamage to mitochondria leading to enhanced cell death, as well as priming for increased sensitivity to subsequent treatments, are discussed.
Recent Photosensitizer Developments, Delivery Strategies and Combination-based Approaches for Photodynamic Therapy†
- Pages: 469-497
- First Published: 26 November 2022
Ultraviolet Light, Unfolded Protein Response and Autophagy†
- Pages: 498-508
- First Published: 02 January 2023
Solar Ultraviolet Radiation, Skin Cancer and Photoprotective Strategies in South Africa†
- Pages: 509-518
- First Published: 16 July 2022
Could Light-Based Technologies Improve Stem Cell Therapy for Skin Wounds? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Preclinical Studies†
- Pages: 519-528
- First Published: 25 August 2022
Skin regeneration still challenges healthcare worldwide. Stem cell and light-based therapies are novel technologies that have been proposed to ameliorate wound healing. This study systematically assessed whether light-based therapies could improve cutaneous repair at pre or postexposure of stem cells using preclinical animal models. Although all included studies have shown a lack of information related to selection, performance and detection bias, an overall positive effect on wound closure and strength was noticed through the meta-analysis. These results may guide future laboratory and clinical studies in hopes of offering wound care patients a better quality of life.
Special Issue Research Article
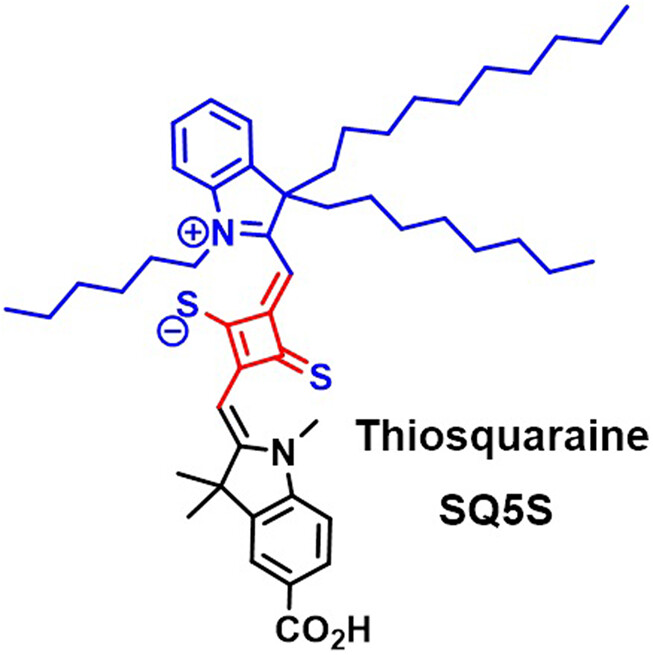
D-A-D-based Unsymmetrical Thiosquaraine Dye for the Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells†
- Pages: 529-537
- First Published: 29 December 2022
Site-specific Heterogeneity of Multi-domain Human Serum Albumin and its Origin: A Red Edge Excitation Shift Study†
- Pages: 538-546
- First Published: 10 September 2022
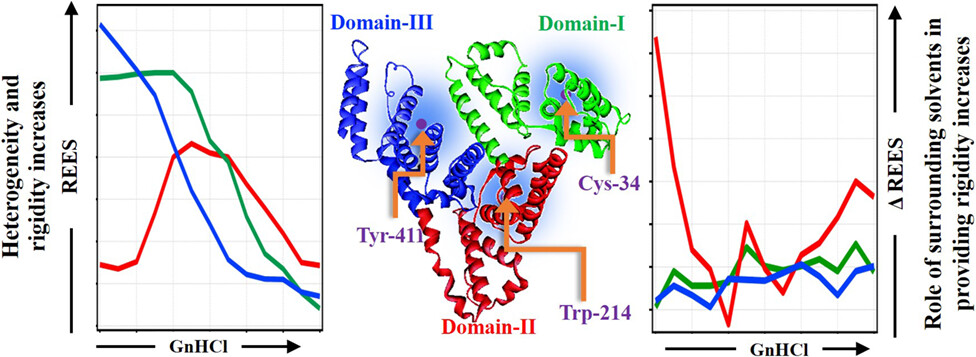
Domain-specific rigidity, alternate side chain packing of protein core and its modulation along the chemical denaturation is contemplated using red edge excitation shift (REES) and compared with reported time-resolved measurements. Our results suggest—(1) Different extent of heterogeneity and environmental rigidity for different domains of multi-domain HSA. (2) On unfolding, the dynamics of the side chain and associated water becomes faster. (3) For domain-I and domain-III, the rigidity is provided by rigid protein matrix, whereas, for domain-II, the role of solvent is also significant.
Electronic Characterization of Vis–NIR Absorbing Noninnocent Ruthenium Oxyquinolate–merocyanine Complexes and their Photoacoustic Emission in Aqueous Micellar Solution†
- Pages: 547-561
- First Published: 14 September 2022
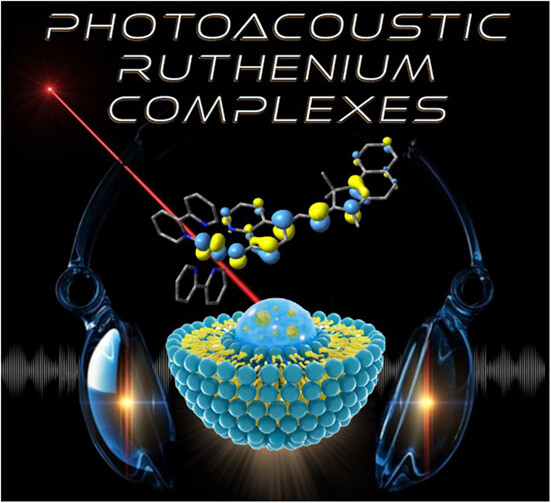

A series of bis-heteroleptic ruthenium(II) polypyridyl dyes incorporating π-accepting 5-(vinyl-cyanine)-8-oxyquinolate ligands are reported. Trends in the HOMO–LUMO bandgap exhibit an excellent correlation with increasing electron-acceptor strength of the terminal cyanine moiety. Intense vis–NIR molar extinction coefficients combined with rapid nonradiative decay, imparted by mixing of the Ru(dπ) − OQN(π) frontier orbitals, makes these complexes highly suited to photoacoustic applications.
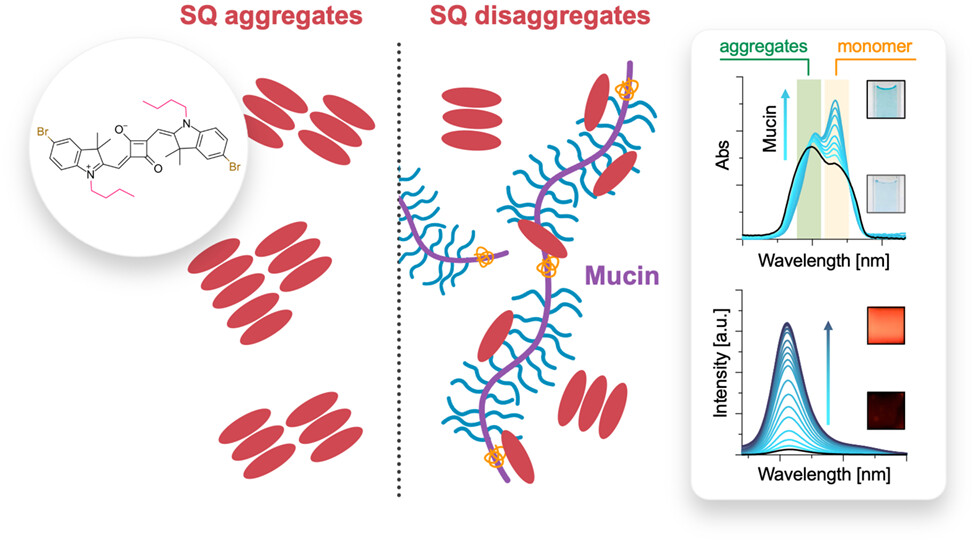
Squaraine Dyes as Fluorescent Turn-on Probes for Mucins: A Step Toward Selectivity†
- Pages: 562-569
- First Published: 17 September 2022
Avoiding One-Electron Oxidation of Biomolecules by 3,4-Dihydroxy-L-Phenylalanine (DOPA)†
- Pages: 570-579
- First Published: 17 September 2022
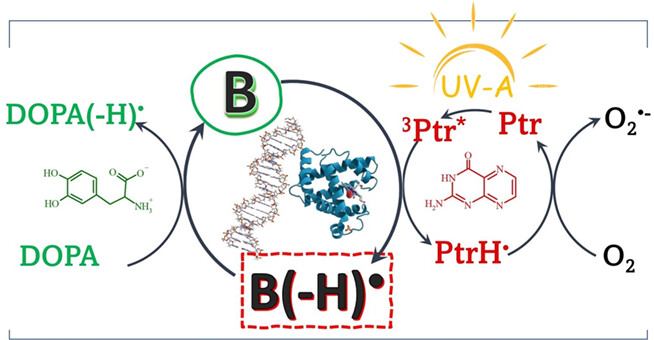
In this work, the antioxidant capacity of the natural amino acid 3,4-dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine (DOPA) is evaluated during pterin (Ptr) photosensitized degradation of amino acids and nucleotides (B). Pterin is an aromatic compound that, under UV-A irradiation, degrades biomolecules mainly through a type I photosensitized oxidation mechanism. Time-resolved and steady-state experiments were performed in the absence and presence of DOPA. Experimental evidence indicates that, although DOPA deactivates the excited states of the photosensitizer, the antioxidant action observed is due to an electron-transfer reaction between DOPA and the biomolecule radical (B(–H)•), where the damaging effect of the photosensitization process is reversed.
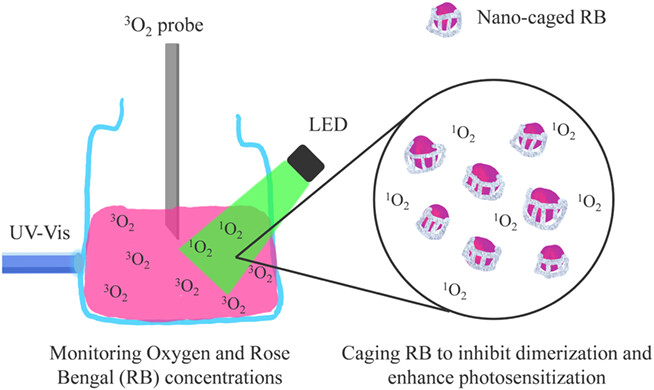
Nanocaging Rose Bengal to Inhibit Aggregation and Enhance Photo-induced Oxygen Consumption†
- Pages: 580-592
- First Published: 21 November 2022
Synthesis, Characterization and Photocleavage of Bis-decyl Pteroic Acid: A Folate Derivative with Affinity to Biomembranes†
- Pages: 593-604
- First Published: 07 December 2022
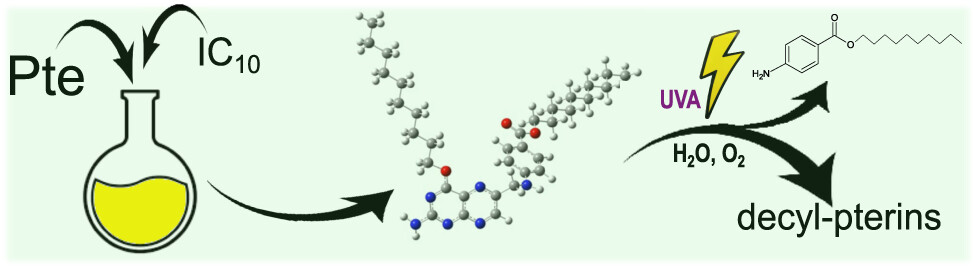
A new lipophilic folate derivative namely bis-decyl-Pte was synthesized, structurally and photophysically characterized. Decylation of pteroic acid (Pte) occurred at keto O4 and at the p-aminobenzoic acid carboxylic acid group, pointing to a kinetically-controlled process based on results from DFT calculations. The photochemistry of bis-decyl-Pte was investigated detecting a photocleavage attributed to a hydrolysis of the methylene bridge, as observed for Pte and folic acid. Moreover, as bis-decyl-Pte is able to interact with lipid membranes, efforts would be focused on investigating the photosensitizing properties of this compound and the photoproducts.
Formation of Stilbene Azo-Dimer by Direct Irradiation of p-Azidostilbene†
- Pages: 605-615
- First Published: 02 June 2022
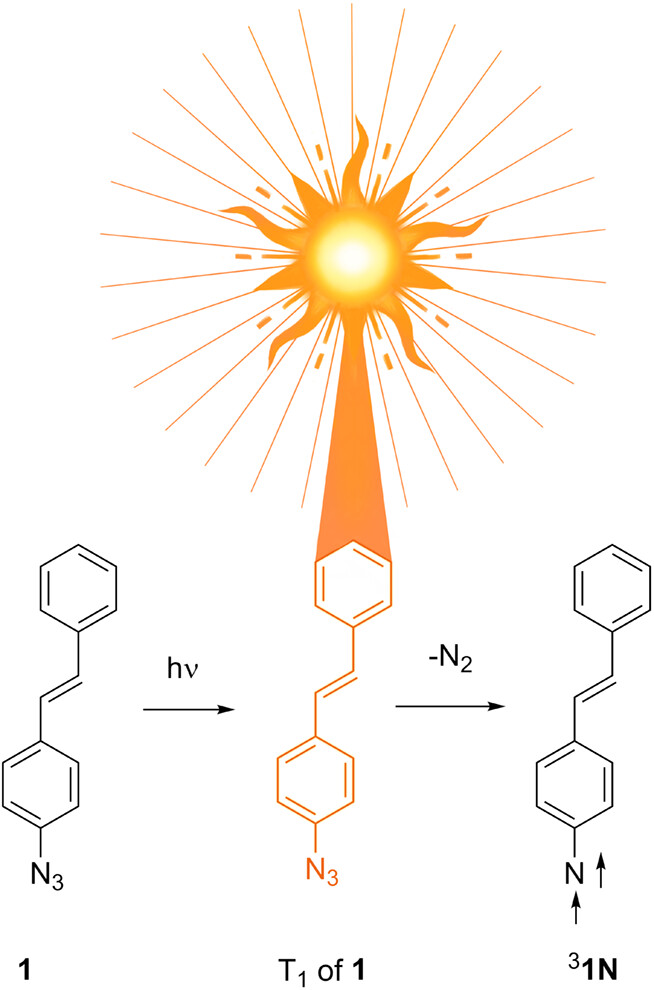
Irradiation of p-azidostilbene (1) in argon-saturated methanol yielded stilbene azo-dimer through the dimerization of triplet p-nitrenostilbene (31N). The formation of 31N was verified by electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy and absorption spectroscopy in cryogenic matrices. At ambient temperature, laser flash photolysis of 1 in methanol formed the triplet excited state of 1 that decayed to form 31N. CASPT2 calculations gave a singlet–triplet energy gap of 16.6 kcal/mol for 1N; thus, intersystem crossing of 11N to 31N is unlikely at ambient temperature, supporting the formation of 31N from triplet precursor of 1.
Comparison of Phosphorescent Pt(II) Complexes with C^N^N vs N^N^N Chelators and Caffeine-Based NHC-co-ligands†
- Pages: 616-623
- First Published: 22 August 2022
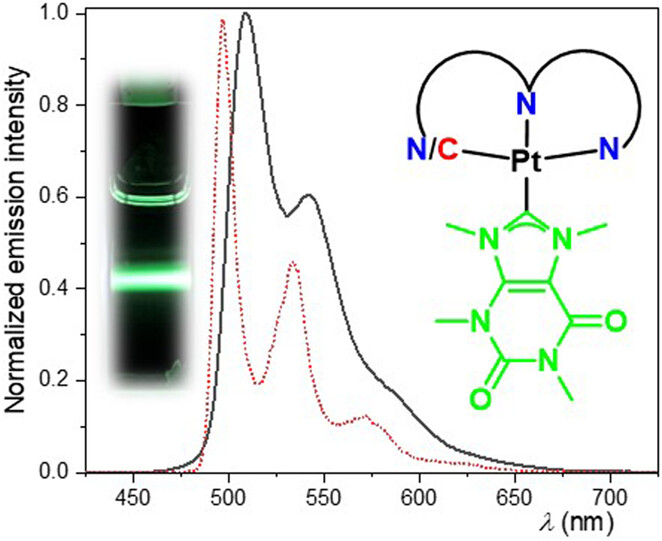
We explored coordination compounds featuring caffeine-based carbene-co-ligands and tridentate dianionic pincer luminophores for phosphorescent Pt(II) complexes. The influence of the different substituents at the chelating luminophores and of the caffeine-based NHC-co-ligand on the photophysical properties was assessed.
Reversible Photoisomerization of Norbornadiene-Quadricyclane within a Confined Capsule†
- Pages: 624-636
- First Published: 17 August 2022
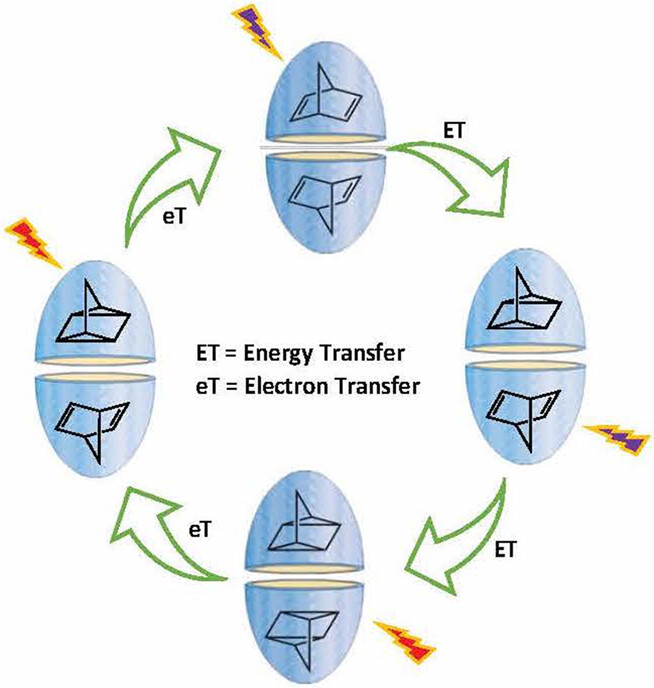
A green sustainable method to store solar energy in quadricyclane (QC) from norbornadiene (NBD) is achieved using supramolecular water-soluble octa acid as host. The NBD forms 2:2 complex with the host and upon UV (violet in the graphic) irradiation, and the guest molecules transform to energy-rich QC one by one via triplet energy transfer. Energy release is achieved by irradiating the encapsulated QC 2:2 complex in the visible region with the aid of electron transfer sensitizer methylene blue. At the intermediate stages of transformation, evidence for the co-existence of the duo (QC and NBD) inside the same capsule is obtained.
Sensitized Photooxidation of Ortho-Prenyl Phenol: Biomimetic Dihydrobenzofuran Synthesis and Total 1O2 Quenching
- Pages: 637-641
- First Published: 17 August 2022
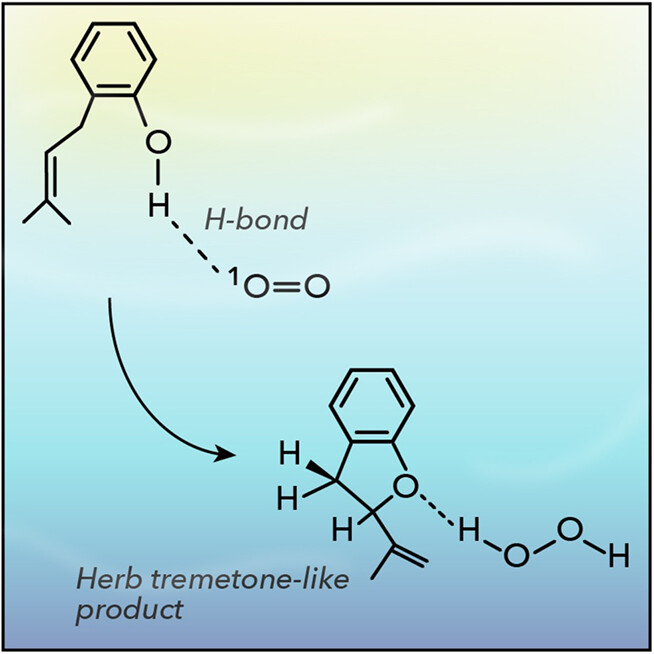
Visible-light strategies for the synthesis of dihydrobenzofurans are challenging. Progress has been made based with the preferential addition of 1O2 to ortho-prenyl phenol due to H-bonding interaction in aprotic solvent, leading to a propenyl dihydrobenzofuran as the major product. This is a mixed photooxidized system since an epoxide also arises by a type I sensitized photooxidation process.
Synthesis and Photophysical Characterizations of Pyrroloquinolone Photosensitizers for Singlet Oxygen Production†
- Pages: 642-651
- First Published: 28 July 2022
Singlet Oxygen's Potential Role as a Nonoxidative Facilitator of Disulfide S–S Bond Rotation†
- Pages: 652-660
- First Published: 23 September 2022
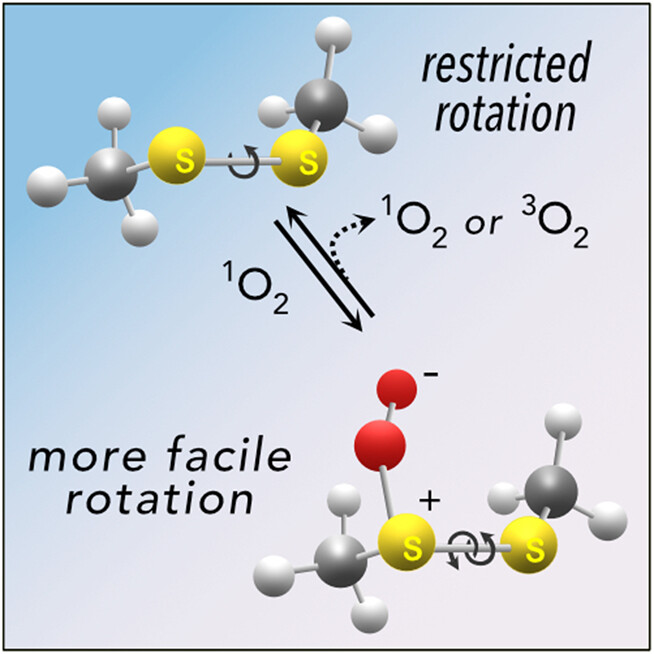
A density functional theory study provides evidence that singlet oxygen binds to 1,2-dimethyldisulfane to form a peroxy intermediate. Mechanistic detail is provided for the singlet oxygen reaction, where a reduced energy for rotation about the S–S bond is found prior to departure of molecular oxygen. Notably, this disulfide O2-capture and release reaction is reminiscent of alkenes and polyenes that form peroxy intermediates, thereby facilitating their cis-trans isomerizations.
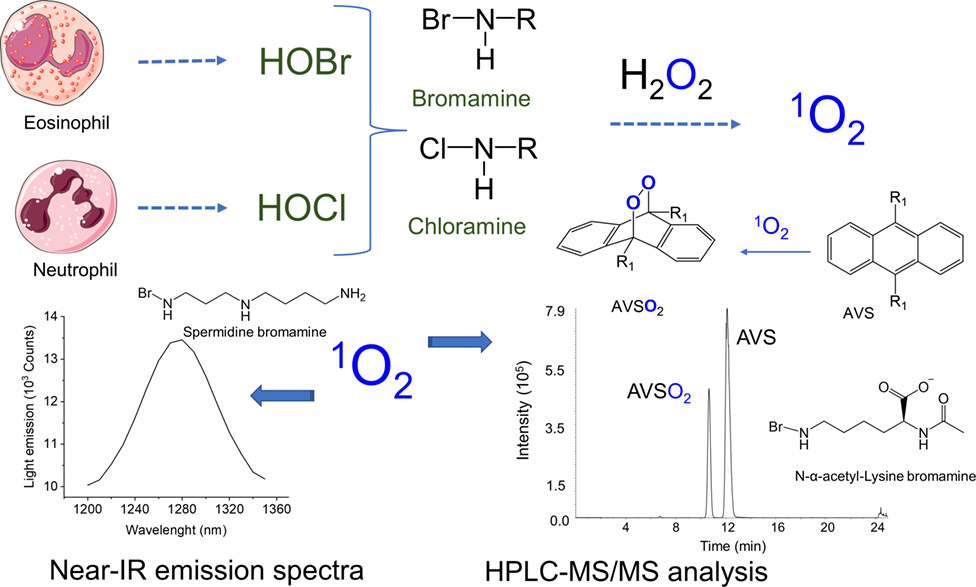
Singlet Molecular Oxygen Generation in the Reaction of Biological Haloamines of Amino Acids and Polyamines with Hydrogen Peroxide†
- Pages: 661-671
- First Published: 01 September 2022
Singlet Oxygen Quenching by Resveratrol Derivatives
- Pages: 672-679
- First Published: 28 August 2022
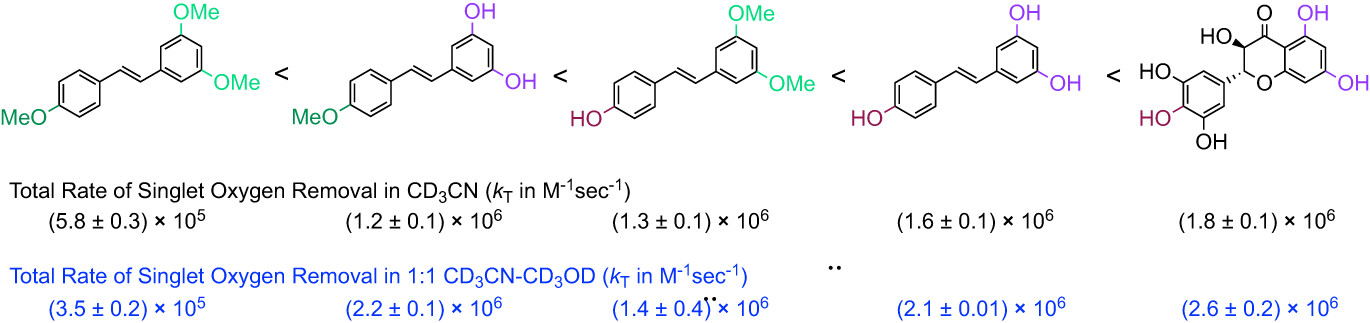
While trans-resveratrol and its methylated and partially methylated derivatives do not sensitize the production of singlet oxygen, they are moderately strong quenchers of singlet oxygen. Methylation of the hydroxy groups decreases the total rate of singlet oxygen scavenging (kT) while a protic solvent system results in higher kT values, except for the completely methylated derivative.
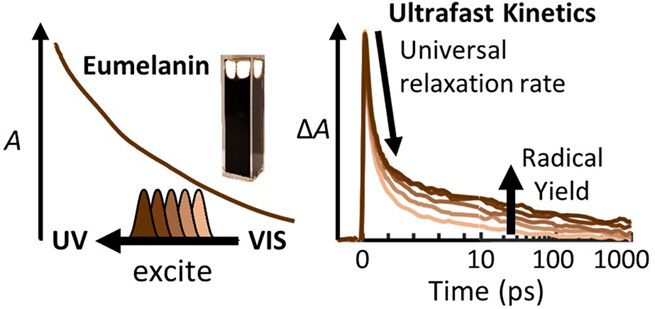
Ultrafast Radical Photogeneration Pathways in Eumelanin
- Pages: 680-692
- First Published: 30 September 2022
Resolving Ultrafast Photoinitiated Dynamics of the Hachimoji 5-aza-7-deazaguanine Nucleobase: Impact of Synthetically Expanding the Genetic Alphabet†
- Pages: 693-705
- First Published: 08 August 2022
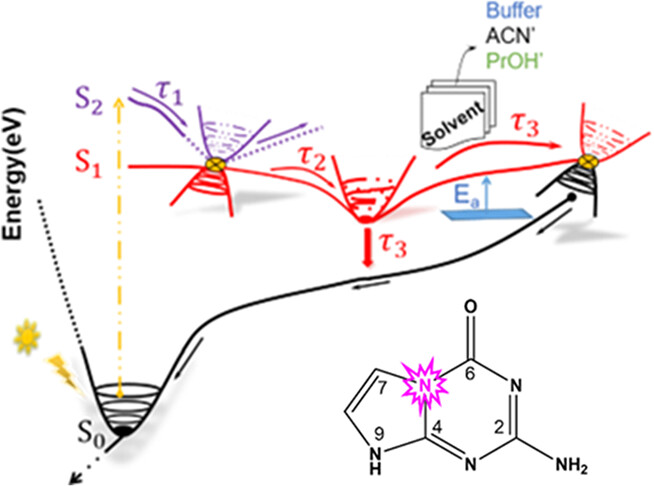
The guanine derivative, 5-aza-7-deazaguanine (5N7CG) has recently been proposed as one of four unnatural bases, termed Hachimoji (8-letter) to expand the genetic code. In this study, it is demonstrated that excitation to the lowest energy 1ππ* state of 5N7CG results in complex dynamics leading to ca. 10- to 30-fold slower relaxation (depending on solvent) compared with guanine. A significant conformational change occurs at the S1 minimum, resulting in a 10-fold greater fluorescence quantum yield compared with guanine. The longer lifetimes might make 5N7CG more photochemically active to adjacent nucleobases than guanine or other nucleobases within DNA on UVC excitation.
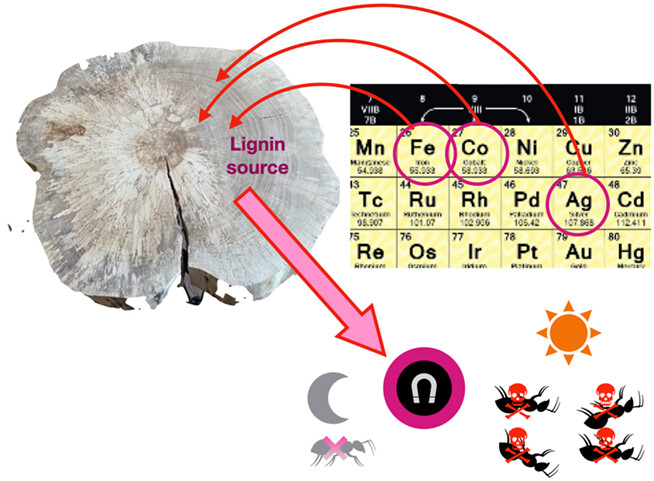
Exploring the Antibacterial Properties of Lignin-coated Magnetic Nanoparticles Synthesized in a One-pot Process†
- Pages: 706-715
- First Published: 05 August 2022
Photodynamic Inactivation of Bacteria in Ionic Environments Using the Photosensitizer SAPYR and the Chelator Citrate†
- Pages: 716-731
- First Published: 24 August 2022
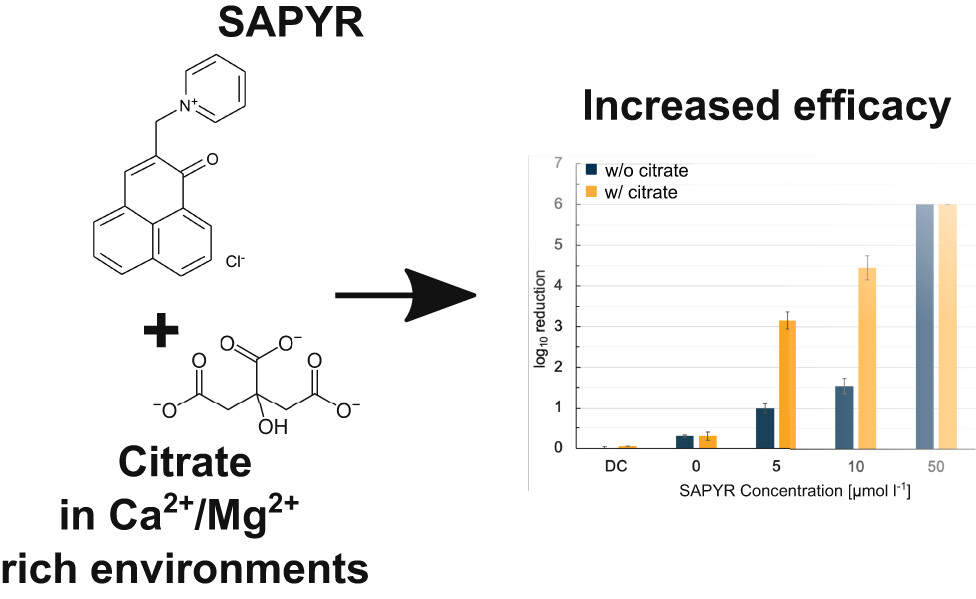
Photodynamic inactivation (PDI) represents a powerful tool regarding the killing of microorganisms. Most studies in this field used standardized, artificial in vitro conditions but efficacy has been investigated scarcely under real life conditions potentially hampering the efficacy unpredictably. Therefore, we investigated PDI with SAPYR against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus in calcium and magnesium ion solutions and realistic environments like tap water or sweat. To enhance the efficacy, addition of citrate as chelator was elucidated. The results indicate that PDI is affected by ubiquitous ions depending on its concentration, but the application of citrate enhanced the PDI in most cases.
Red Wine Inspired Chromophores as Photodynamic Therapy Sensitizers
- Pages: 732-741
- First Published: 29 July 2022
The Biochemical Mechanisms of Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy†
- Pages: 742-750
- First Published: 01 August 2022
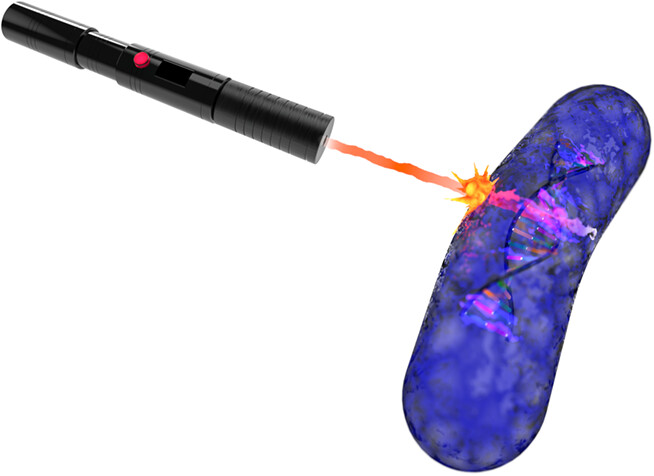
Microbial drug resistance emerged as a critical challenge for human and animal health worldwide, emphasizing the need for disrupting antimicrobial strategies. Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy (aPDT) has the potential to overcome drug-resistant infections because it does not rely on specific targets. Herein, we investigated the microbial inactivation kinetics promoted by aPDT alongside the molecular damage caused to cell membrane, DNA, and proteins of Klebsiella pneumoniae. We concluded that bacterial cell death is closely associated with protein degradation while the membrane and DNA damages are secondary effects. Such knowledge indicates the most effective pathways for the development of optimized therapeutic protocols.
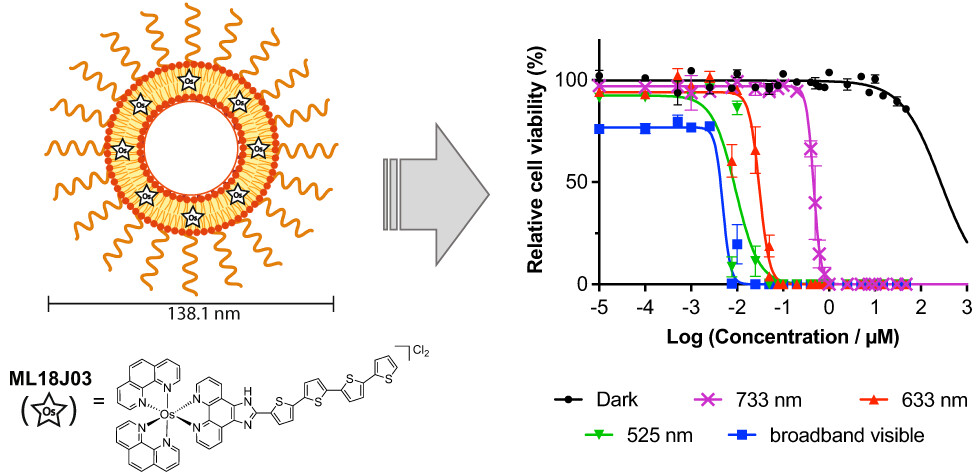
Establishing a Robust and Reliable Response from a Potent Osmium-Based Photosensitizer Via Lipid Nanoformulation†
- Pages: 751-760
- First Published: 08 December 2022
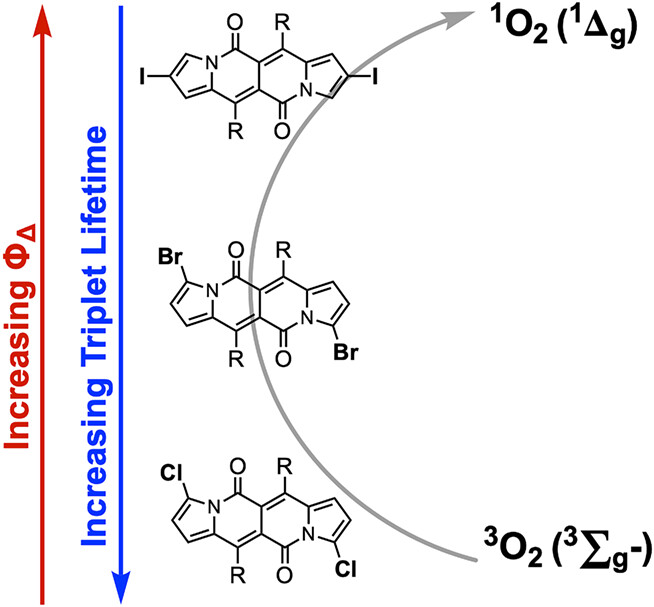
Photophysical Insights of Halogenated Dipyrrolonaphthyridine-Diones as Potential Photodynamic Therapy Agents†
- Pages: 761-768
- First Published: 07 December 2022
Redaporfin Development for Photodynamic Therapy and its Combination with Glycolysis Inhibitors
- Pages: 769-776
- First Published: 23 December 2022
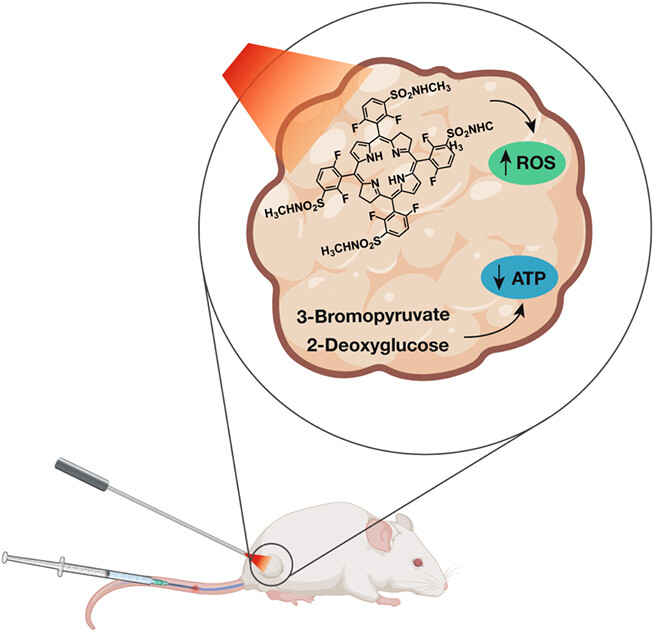
Redaporfin (Rdp) is a photostable bacteriochlorin photosensitizer in Phase II clinical trials for advanced head & neck cancer, whose development is briefly reviewed in this work. Recognizing that multidisciplinary approaches and combination therapies are usually preferred in oncology, we present the combination of Rdp with two glycolysis inhibitors, 2-deoxygluose (2DG) and 3-bromopyruvate (3BP), to take advantage of hyper aerobic glycolysis of cancer cells. We show that Rdp-PDT in combination with 3BP increases survival of mice with subcutaneous CT26 tumors relative to monotherapies with the same doses.
A Lock-and-Kill Anticancer Photoactivated Chemotherapy Agent†
- Pages: 777-786
- First Published: 31 October 2022
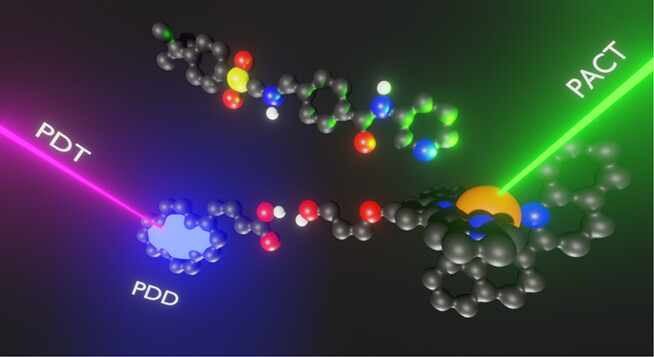
The liposome-embedded ruthenium complex presented in this paper bears a quenched pyrene fluorophore that, following cellular uptake, is released by enzymatic cleavage. Once cleaved off, the fluorescence of the tag is unlocked for photodynamic diagnosis (PDD), thereby unraveling the (pro)drug location. While UV or blue light irradiation of the free pyrene leads to singlet oxygen generation, green light irradiation in vitro leads to increased cytotoxicity as a consequence of the photochemical release of the cytotoxic inhibitor STF-31, a light activation mechanism called photoactivated chemotherapy (PACT).
Analysis of Renal Cell Carcinoma Cell Response to the Enhancement of 5-aminolevulinic Acid-mediated Protoporphyrin IX Fluorescence by Iron Chelator Deferoxamine†
- Pages: 787-792
- First Published: 20 July 2022
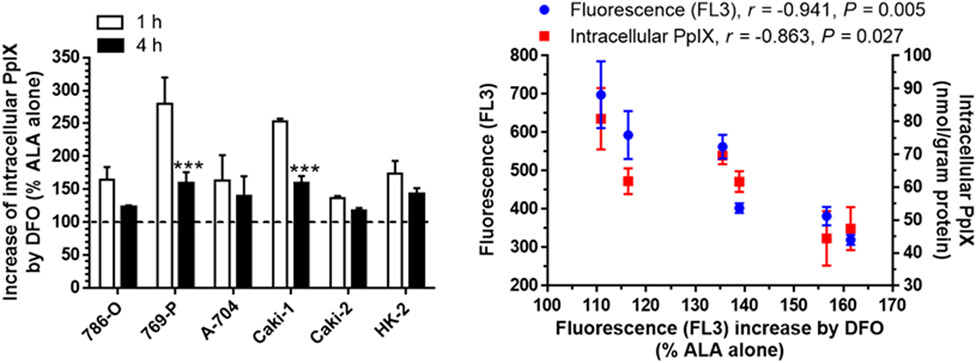
Effects of iron chelator deferoxamine (DFO) on the enhancement of ALA-PpIX fluorescence were analyzed in a panel of human renal cell carcinoma cell lines and non-tumor HK-2 cell lines. We found that DFO increased intracellular PpIX in both tumor and non-tumor cells, resulting in no gain in tumor/non-tumor fluorescence ratios. DFO increased ALA-PpIX more at 1-h than at 4-h treatment. There was an inverse correlation between ALA-PpIX fluorescence and the enhancement effect of DFO.
Photodynamic Priming Overcomes Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substance (PFAS)-Induced Platinum Resistance in Ovarian Cancer†
- Pages: 793-813
- First Published: 23 September 2022
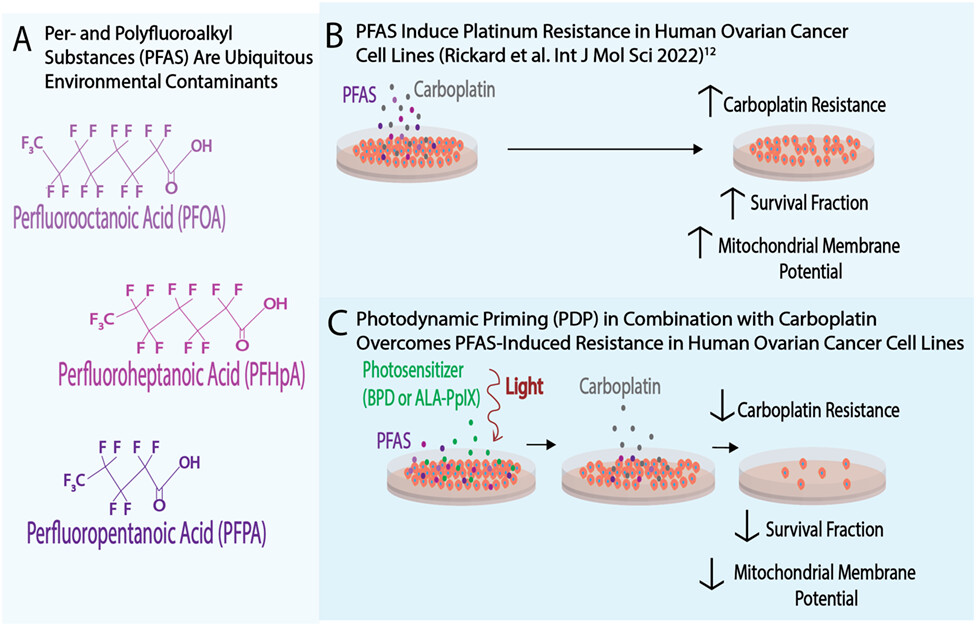
Select per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) have been shown to induce resistance to carboplatin, a platinum-based chemotherapeutic agent, in two ovarian cancer cell lines. A concomitant increase in mitochondrial membrane potential was observed. In the present study, photodynamic priming (PDP) to overcome PFAS-induced resistance was explored, using either benzoporphyrin derivative (BPD) or aminolevulinic acid-induced protoporphyrin IX (ALA-PpIX). PDP in combination with low-dose carboplatin effectively reduced survival fraction in PFAS-exposed cells. A decrease in mitochondrial membrane potential following PDP was observed, suggesting that PDP modulates mitochondrial health to re-sensitize ovarian cancer cells to chemotherapy.
Evaluation of Detector Position and Light Fluence Distribution Using an Infrared Navigation System during Pleural Photodynamic Therapy†
- Pages: 814-825
- First Published: 23 August 2022
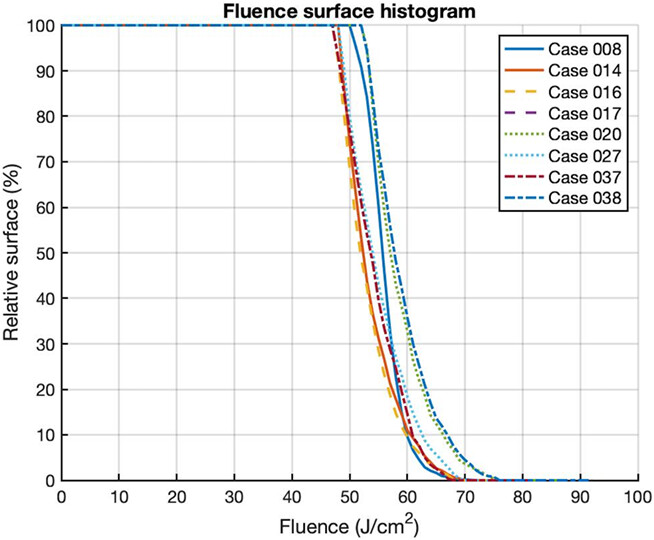
Accurate light fluence delivery is crucial to the efficiency of photodynamic therapy (PDT). With an infrared (IR) navigation system, the location of the light point source was tracked throughout PDT. Together with an automatic detector position calculation algorithm, the recorded data was used to calculate the light fluence to the whole cavity after treatment. Fluence-surface histogram (FSH) was calculated for 8 cases, which demonstrates that, for each case, 80% of pleural surface area is covered to 50 J cm−2 (83.3% of the prescribed does, 60 J cm−2).
The Glycolysis-derived α-Dicarbonyl Metabolite Methylglyoxal is a UVA-photosensitizer Causing the Photooxidative Elimination of HaCaT Keratinocytes with Induction of Oxidative and Proteotoxic Stress Response Gene Expression†
- Pages: 826-834
- First Published: 15 September 2022
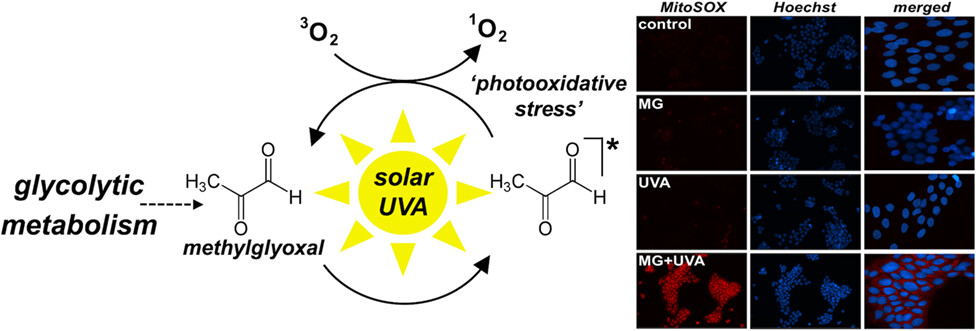
Methylglyoxal (MG), a glycolytic byproduct bearing a UV-active α-dicarbonyl-chromophore, is generated under metabolic conditions of increased glycolytic flux, associated with posttranslational protein adduction in human tissue. Here, we undertook a photophysical and photochemical characterization of MG substantiating its fluorescence properties, phosphorescence lifetime, and quantum yield of singlet oxygen (1O2) formation. Strikingly, MG acts as a micromolar UVA-photosensitizer targeting cultured human keratinocytes inducing photooxidative stress and caspase-dependent cell death, observations substantiated by expression array-based transcriptomic analysis. Given the metabolic origin of MG and its established role in human pathology, the heretofore unrecognized MG-photosensitizer activity might be involved in human skin photodamage.
The Drinking Water and Swimming Pool Disinfectant Trichloroisocyanuric Acid Causes Chlorination Stress Enhancing Solar UV-Induced Inflammatory Gene Expression in AP-1 Transgenic SKH-1 Luciferase Reporter Mouse Skin
- Pages: 835-843
- First Published: 16 July 2022
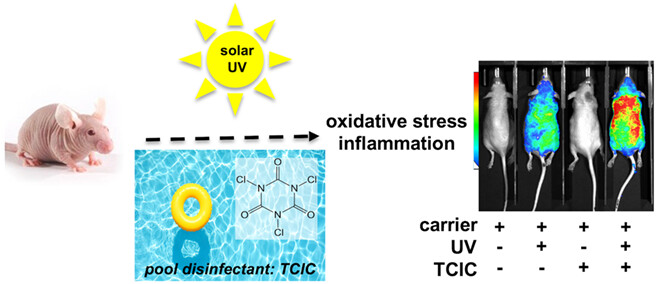
Freshwater disinfection using a variety of chemical entities as chlorination agents is an essential public health intervention. Chlorinated isocyanuric acid derivatives (including the chloramine trichloroisocyanuric acid [TCIC]) are used worldwide as chlorination agents serving as hypochlorous acid (HOCl) precursor and stabilizer ensuring sustained release in aqueous environments including public water systems, recreational pools and residential hot tubs. Here, for the first time, we have examined the cutaneous TCIC-induced transcriptional stress response (in both an organotypic epidermal model and in bioluminescent AP-1 reporter mouse skin), also examining molecular consequences of subsequent treatment with solar ultraviolet (UV) radiation.
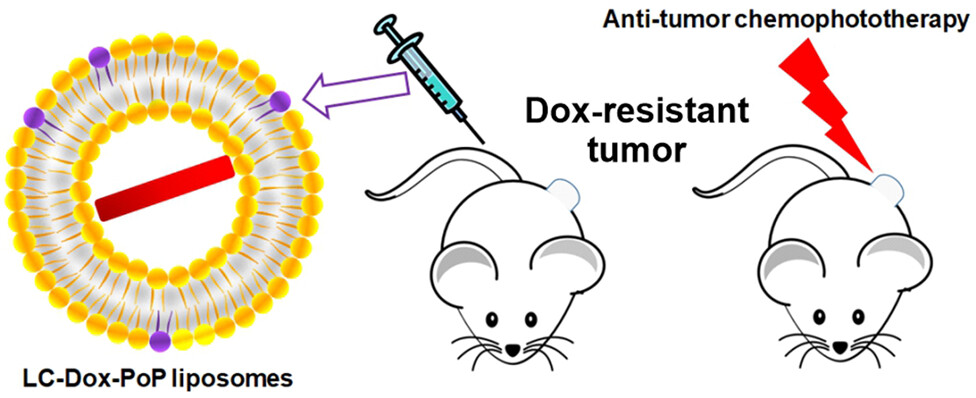
Chemophototherapeutic Ablation of Doxorubicin-Resistant Human Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pages: 844-849
- First Published: 16 July 2022
Moderate Low UVB Irradiation Modulates Tumor-associated Macrophages and Dendritic Cells and Promotes Antitumor Immunity in Tumor-bearing Mice
- Pages: 850-856
- First Published: 29 July 2022
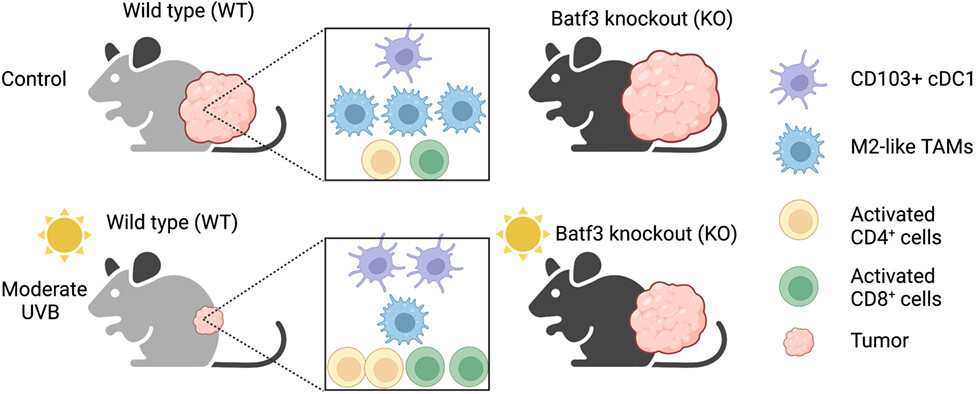
Using tumor-bearing mouse models, we show that moderate low UVB irradiation increases the number of activated CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, CD103+ cDC1 dendritic cells, while it decreases the number of immunosuppressive, tumor-promoting M2-like tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs). Deletion of Batf3 increases tumor growth in both sham- and UVB-irradiated mice. Our findings demonstrate that moderate UVB irradiation promotes antitumor immunity in tumor-bearing mice. (Created with BioRender.com).
Highlight Article (Invited)
Understanding How a New Hachimoji Nucleobase Alters Photodynamics of Genetic Building Blocks†
- Pages: 857-859
- First Published: 05 September 2022
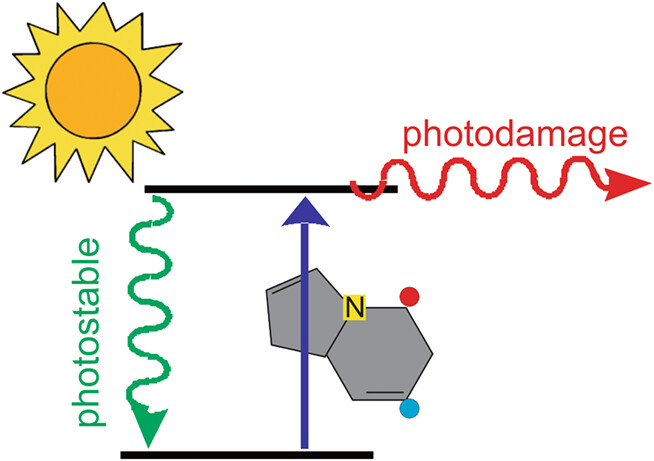
5-aza-7-deazaguanine (5N7CG ) is an alternative nucleobase that has been proposed as part of an expanded genetic alphabet. Krul et al. in this issue show that its photochemistry differs from that of its canonical sanalogue, guanine. The excited sate dynamics, following UV excitation, make 5N7CG less photostable. As a result, this base is a less likely candidate for chemical origin of life scenarios under prebiotic conditions on an early earth.
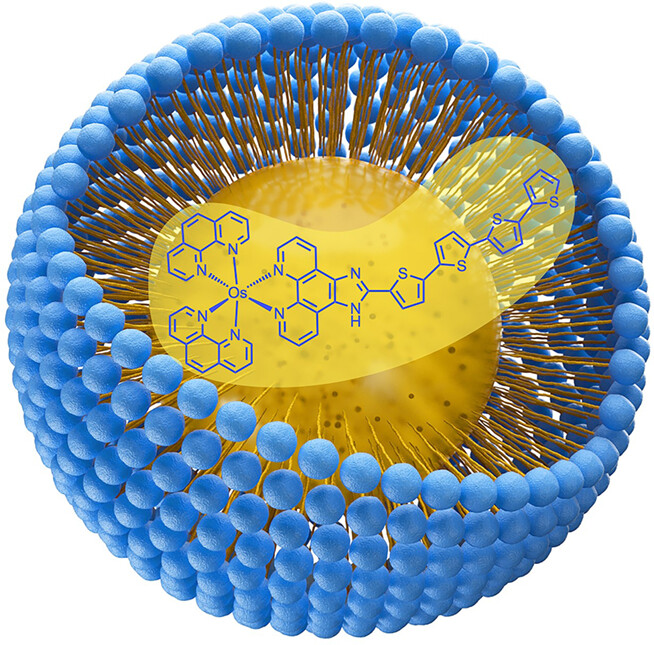
Shine, Shine, Ruthenium Caged Drug
- Pages: 860-862
- First Published: 23 December 2022
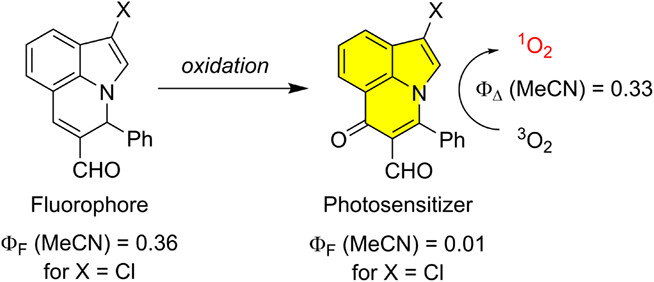
Pyrroloquinolines, a New Platform for Developing Organic Photosensitizers: When Synthetic Methodology Meets Photophysics†
- Pages: 863-865
- First Published: 05 November 2022
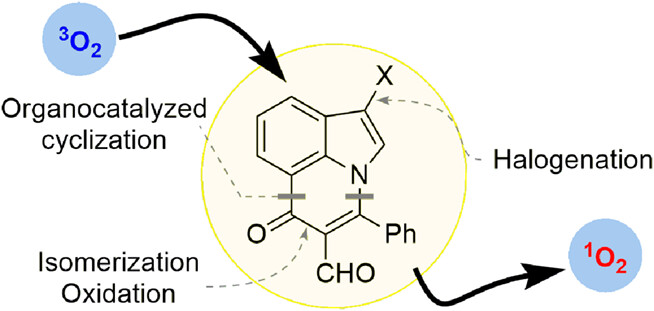
New molecular architectures for photochemistry. This commentary article highlights the work of de Bonfils et al. on the development of molecular platforms for the preparation of new photosensitizers. The synthesis is practical and scalable thanks to a key organocatalyzed cyclization/oxidation and isomerization sequence. This enables the installation of several strategical structural features, which could prove useful to tweak the physical parameters (such as solubility and photophysics) or click the compound to biological targets.
Photodynamics of Melanin Radicals: Contribution to Photoprotection by Melanin†
- Pages: 866-868
- First Published: 01 December 2022
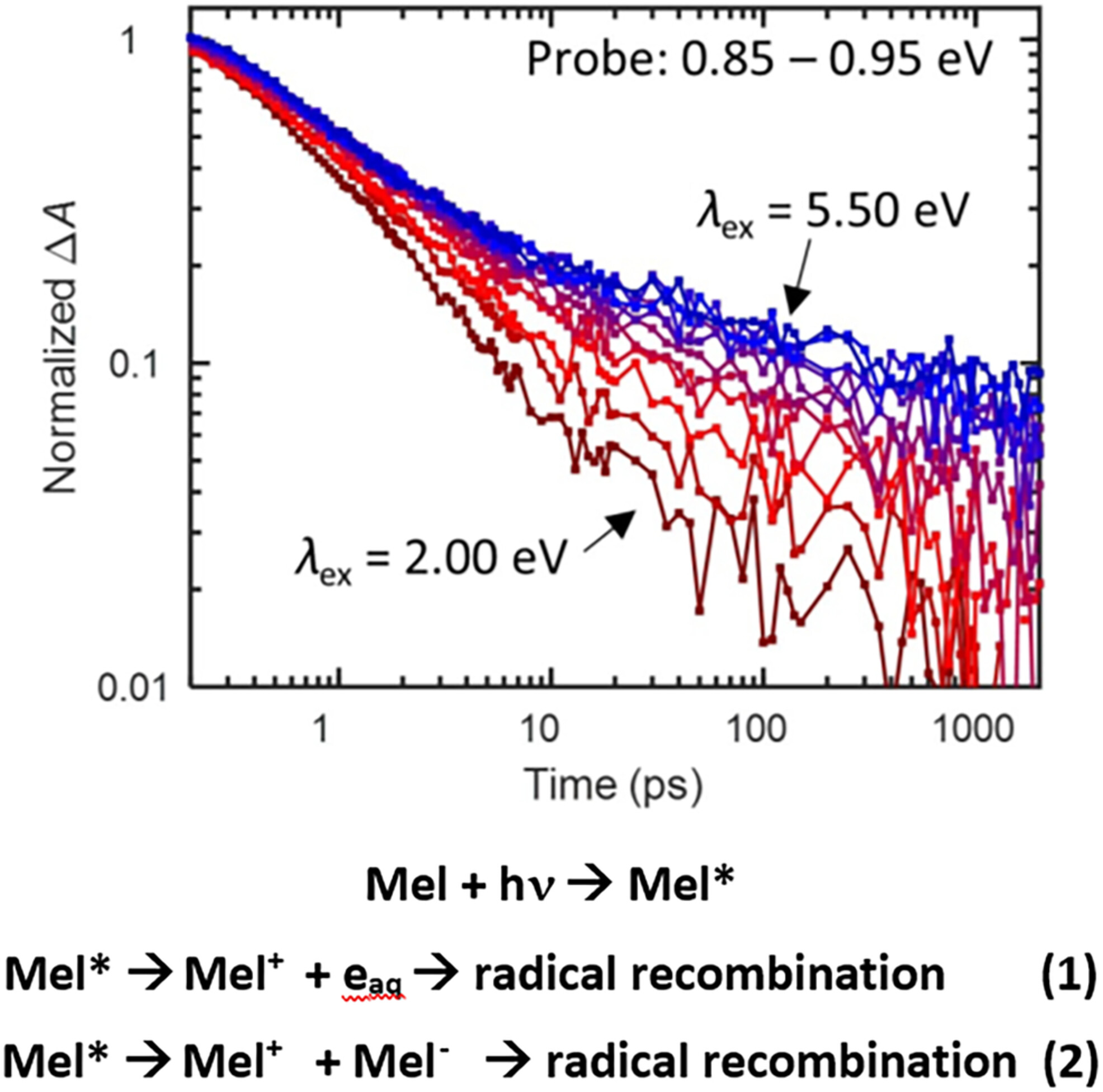
Photoexcitation of melanin with photons of different energies leads to the ultrafast formation of melanin radicals via ionization (1) and charge separation (2) mechanisms (scheme). Although most excited states form melanin radicals possibly in <1 ps, few radicals persist beyond the nanosecond time scale due to very efficient radical recombination (figure). The results suggest a new paradigm in which the ubiquitous ultrafast excited state deactivation seen in melanins comes about through the recombination of charges or neutral radicals that are created promptly by photoexcitation.
Trichloroisocyanuric Acid, A Swimming Pool Disinfectant: New Developments and Role in UV-Induced Skin Inflammation†
- Pages: 869-871
- First Published: 25 August 2022
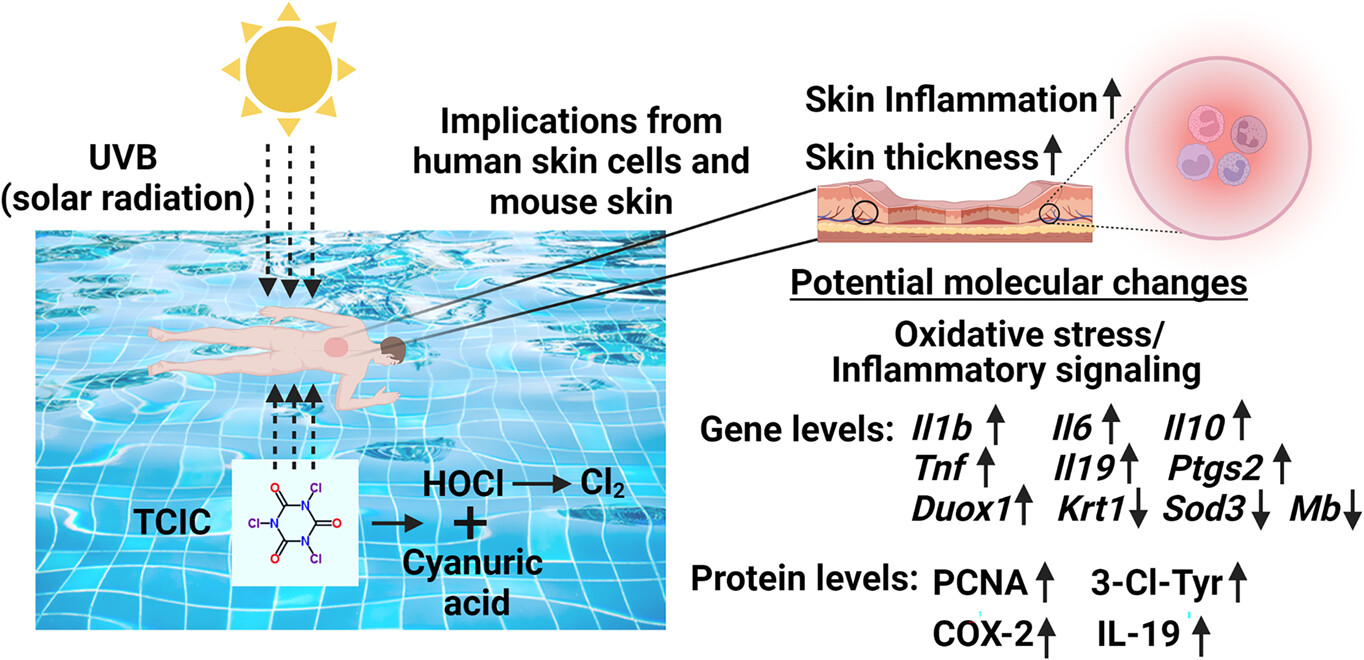
This highlight article discusses the work of Snell et al. that showed the potential effects of a commonly used swimming pool and drinking water disinfectant trichloroisocyanuric acid (TCIC) combined with ultraviolet (UV) radiation on the skin. Based on experiments conducted on an organotypic model of human epidermis and SKH-1 mouse skin, it could be postulated that topical treatment of TCIC followed by UV exposure may enhance human skin thickness and UV-induced inflammation by increasing the expression of certain inflammatory genes and proteins.
Nanoformulation of Lipophilic Osmium Photosensitizers in Liposomes and Micelles as a General Strategy for Improving Reproducibility and Reducing Quenching†
- Pages: 872-873
- First Published: 01 January 2023
Therapeutic Implications of UVB Irradiation in Cancer by Enhancing Anti-Tumor Immunity†
- Pages: 874-877
- First Published: 24 September 2022
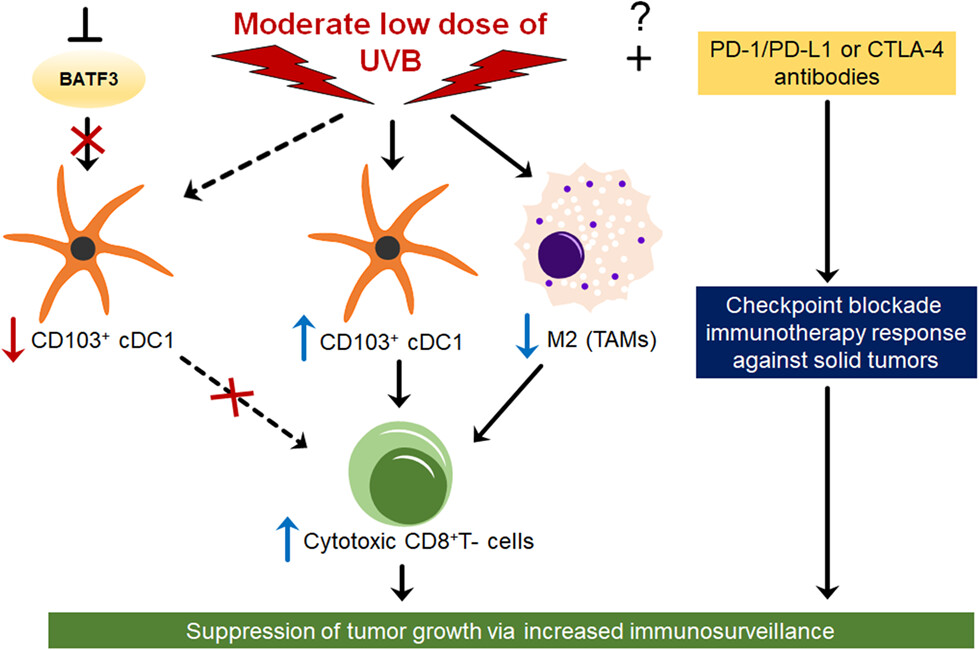
Enhanced anti-tumor immunity by a moderate dose of UVB irradiation and possible future direction to explore if the moderate dose of UVB irradiation can enhance checkpoint blockade immunotherapy response against solid tumors. The moderate low dose of UVB irradiation decreases infiltration of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) and increases CD103+ conventional dendritic (cDC) cells, which results in enhanced infiltration of cytotoxic CD8+ T cells. However, deletion of transcription factor Batf3 reverses this effect. Future studies can be developed by combining a moderate dose of UVB irradiation along with checkpoint blockade antibodies (PD-L1/PD-1 or CTLA-4) to enhance immunotherapy response against solid tumors.