Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Editorial
Research Articles
Visible light-Driven AgBr/AgCl@MIL-101(Fe) Composites For Removal of Organic Contaminant From Wastewater
- Pages: 4-13
- First Published: 26 November 2019
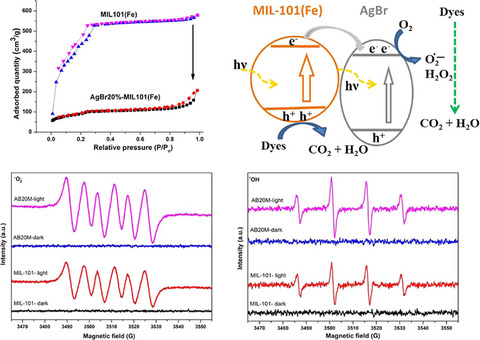
Herein, silver bromide loading on MIL-101(Fe) formed mesopores on the MOF material, enhancing the adsorption ability of the material. Additionally, the formation of AgBr-MIL-101(Fe) interface enabled to lengthen photon-induced charges lifetime. Consequently, the photodegradation efficiency of organic dyes by AgBr@MIL-101(Fe) increased when irradiated. Superoxide () and hydroxyl () radicals play a vital role for the photodegradation of dyes, confirmed by ESR spectra of MIL-101(Fe) and AB20M composite under light irradiation. The higher intensity of characteristic peaks of these radicals for AgBr@MIL-101(Fe) again proved the better photocatalytic ability of the composite than that of MIL-101(Fe).
Fast and Efficient Method to Obtain Tagitinin F by Photocyclization of Tagitinin C
- Pages: 14-20
- First Published: 10 August 2019
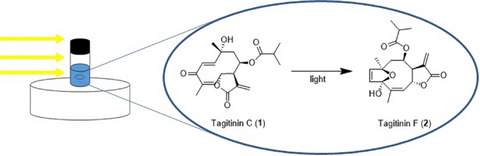
Compound 2 has high pharmacological potential, but it is not easy to obtain, while compound 1 is easily obtained from a widespread plant, Tithonia diversifolia. Among different reaction conditions monitored, one was found that allowed the cyclization of 1 into 2 in <15 min in a photo-dependent reaction. Scaling-up the photocyclization of the pure compound 1 into 2 demonstrated 100% yield, and the isolation of 2 from a UV-irradiated extract was eight-fold higher than the quantity isolated from the non-UV-irradiated extract.
A Dual Emissive Coumarin–urea Derivative with an Electron-withdrawing Substituent in the Presence of Acetate Anion
- Pages: 21-27
- First Published: 27 September 2019
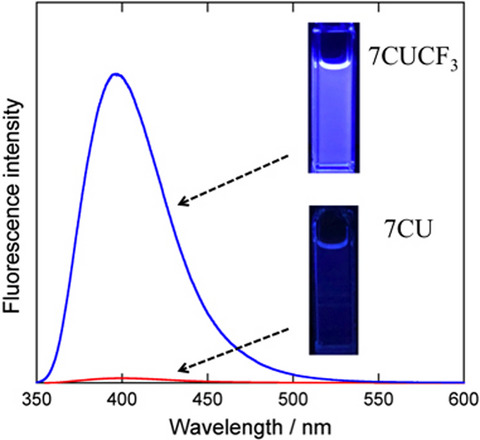
Coumarin–urea derivatives showed significant differences in tautomer formation depending on the positions of a urea moiety substituted on the coumarin ring in the presence of acetate ion. Furthermore, the substitution of a CF3 group resulted in a remarkable improvement of its fluorescence quantum yield. These findings will contribute to new molecular design of highly fluorescent anion sensors.
Mechanistic Studies on the Salicylate-Catalyzed Peroxyoxalate Chemiluminescence in Aqueous Medium
- Pages: 28-36
- First Published: 16 November 2019
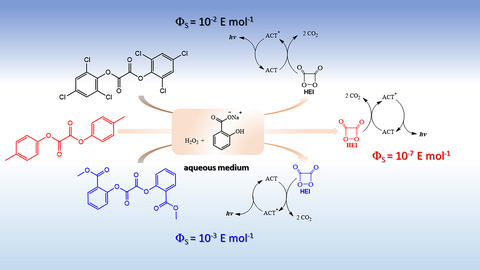
The peroxyoxalate chemiluminescence (PO-CL), principle of “light sticks” and widely used in analytical and bioanalytical assays, is a highly efficient chemiexcitation system in anhydrous conditions, however, in aqueous medium its efficiency is much lower. A kinetic study of the PO-CL in aqueous medium using different oxalate esters, including an ‘ambientally friendly’ derivative, leads to reproducible results and quantum yields of up to 0.1 %, considered significantly high for the aqueous medium.
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone and Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate are Involved in the Control of Shark Bioluminescence
- Pages: 37-45
- First Published: 23 August 2019

Luminous sharks use hormonal control to regulate bioluminescence: melatonin triggers light emission and α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone reduces ongoing luminescence. Interestingly, these hormones are known as regulators of skin pigment movements in vertebrates. Another hormone, the adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), also members of the skin pigmentation regulators, is here tested on the light emission; moreover, the effect of hormonal treatments on the light organ cAMP concentrations was also investigated. Results show that (1) ACTH has an inhibitory effect and (2) cAMP modulation occurs during luminescence. This research reveals analogy between skin pigment migration and luminescence control in two shark families.
Second Rhagophthalmid Luciferase Cloned from Chinese Glow-worm Menghuoius giganteus (Rhagophthalmidae: Elateroidea)
- Pages: 46-54
- First Published: 03 October 2019
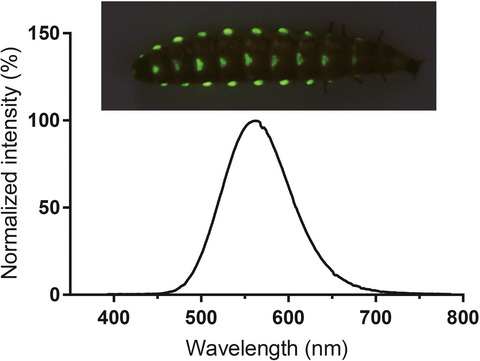
The pH-insensitive beetle luciferases cloned from Rhagophthalmidae. However, the Rhagophthalmids luciferase was cloned from only one species Rhagophthalmus ohbai. In this study, we cloned the luciferase gene from one Chinese glowworm Menghuoius giganteus in Rhagophthalmidae. The luciferase includes 546 deduced amino acids with the highest sequence identity of 90.4% to that of R. ohbai. The luciferase possesses significant luminescence activity at pH 7.8, and its KM for d-luciferin and ATP are 2.2 and 53 μm, respectively. It shows the highest activity at 10°C. It is pH-insensitive with the maximum emission spectrum of 560 nm at pH 7.8.
Analog Retinal Redshifts Visible Absorption of QuasAr Transmembrane Voltage Sensors into Near-infrared
- Pages: 55-66
- First Published: 25 September 2019
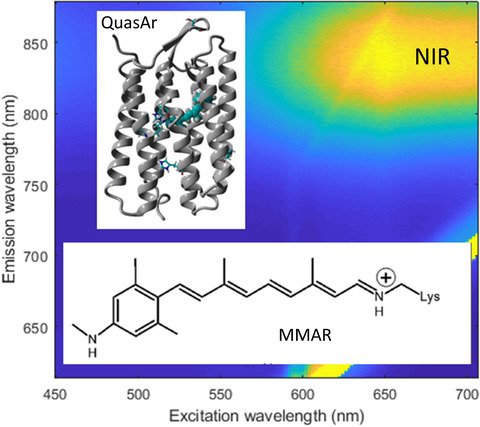
QuasAr1 and QuasAr2, mutants of archaerhodopsin-3, are used in optogenetic applications as fluorescent transmembrane voltage sensors. The native A1 retinal chromophore was substituted with a synthetic retinal analog MMAR containing a methylamino modified dimethylphenyl ring. The absorption, excitation and emission spectra were shifted from the visible to the near-IR spectral region. FT-Raman reveals information about the isomeric configuration of the MMAR chromophore in QuasArs.
Dibenzothiophene Sulfone Derivatives as Plasma Membrane Dyes
- Pages: 67-73
- First Published: 12 November 2019
The fluorescent capacity of dibenzothiophene 5,5-dioxide (DBTOO) was exploited to generate a fluorescent microscopy stain. Through the addition of lipophilic substituents to the DBTOO backbone, a fluorophore with a marked affinity for the plasma membrane of HELA cells was developed. Utilizing a standard DAPI filter set, the plasma membrane of HELA cells was illuminated during imaging. Co-staining with a known plasma membrane dye confirmed the locality of the new DBTOO stains. Pertinent photochemical properties were characterized and reported.
The Glucosamine-derivative NAPA Suppresses MAPK Activation and Restores Collagen Deposition in Human Diploid Fibroblasts Challenged with Environmental Levels of UVB
- Pages: 74-82
- First Published: 26 November 2019
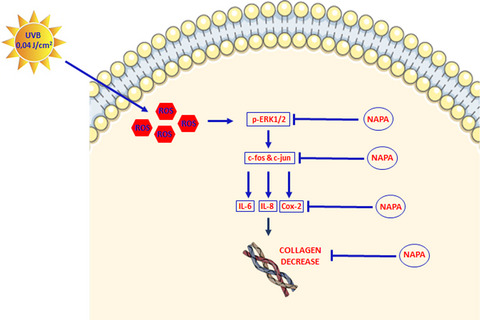
Human primary fibroblast were irradiated with 0.04 J cm−2 UVB dose, which resulted a mild dosage as shown by ROS production measurement. This environmental UVB dose induced activation of MAP kinase ERK 1/2, the stimulation of c-fos and at lower extent of c-jun, and in turn AP-1-dependent up-regulation of IL-6, IL-8, Cox-2 and suppression of collagen type I expression. Pretreatment of fibroblasto with glucosamine-derivative NAPA was able to suppress the increase of IL-6 and IL-8 via the inhibition of MAP kinase ERK phosphorylation and to attenuates the collagen type I decrease induced by the UVBs.
Opsin3 Downregulation Induces Apoptosis of Human Epidermal Melanocytes via Mitochondrial Pathway
- Pages: 83-93
- First Published: 15 November 2019
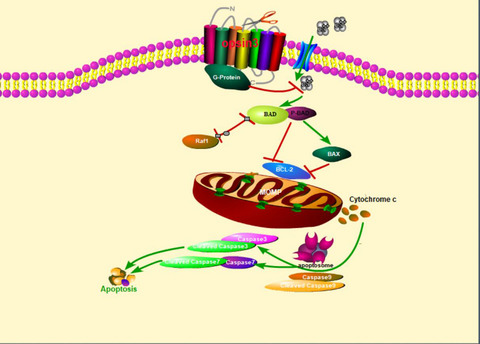
Opsin3 (OPN3) is a key signal responsible for cell survival through a calcium-dependent G protein-coupled signaling and mitochondrial pathway. Our research shows that OPN3 knockdown by RNAi-OPN3 in human epidermal melanocytes leads to apoptosis. Furthermore, the knockdown of OPN3 in human epidermal melanocytes results in a decrease in intracellular calcium levels and then activation of downstream cell signaling pathway.
Wavelength- and Tissue-dependent Variations in the Mutagenicity of Cyclobutane Pyrimidine Dimers in Mouse Skin
- Pages: 94-104
- First Published: 28 August 2019
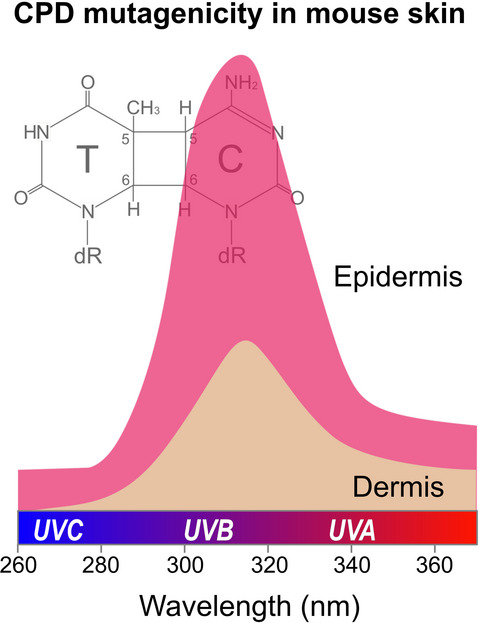
Although the efficiency of cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer (CPD) formation is a main determinant of UVR mutagenicity in mouse skin, the wavelength-dependent variation in the qualitative characteristics of CPD molecules also affects the mutagenic consequences of UVR insults, as shown by the molecular mutagenicity of a CPD molecule, which exhibits a peak at approximately 313 nm. In addition, the CPD mutagenicity in the epidermis is always two- to three-fold higher than that in the dermis irrespective of the wavelength.
ATR Kinase Activity Limits Mutagenesis and Promotes the Clonogenic Survival of Quiescent Human Keratinocytes Exposed to UVB Radiation
- Pages: 105-112
- First Published: 25 September 2019
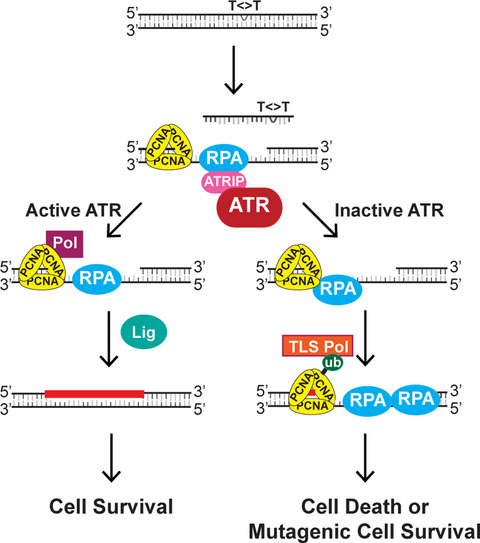
ATR is activated following the removal of UV photoproducts (T<>T) from the genome in quiescent keratinocytes. In the absence of ATR kinase signaling, the gap filling process is abrogated and leads to increased PCNA mono-ubiquitination and RPA-coated single-stranded DNA. These events are then associated with increased mutagenesis and reduced survival.
Protective Effects of Ginseng Proteins on Photoaging of Mouse Fibroblasts Induced by UVA
- Pages: 113-123
- First Published: 23 August 2019

UVA can penetrate the dermis and cause functional damage to dermis fibroblasts that lead to photoaging. Ginseng is a widely used traditional Chinese medicine against skin aging. However, its effects on skin photoaging induced by UVA are not clear. In this study, we show that ginseng proteins separated from ginseng roots have protective effects on UVA-induced photoaging of fibroblasts and the underlying molecular mechanisms. This is the first study to show that ginseng proteins can resist UVA induced antifibroblast photoaging and can improve fibroblast proliferation, contraction and other functions by inhibiting DNA damage and collagen degradation caused by ROS.
Asiatic Acid Glucosamine Salt Alleviates Ultraviolet B-induced Photoaging of Human Dermal Fibroblasts and Nude Mouse Skin
- Pages: 124-138
- First Published: 04 September 2019
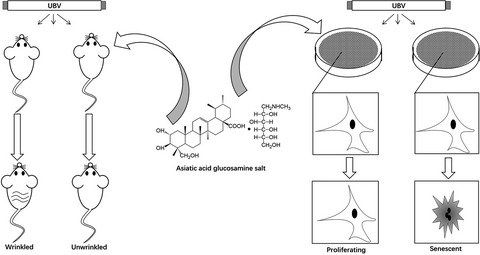
Asiatic acid is an herb extract with wide therapeutic effects including anti-inflammation, anti-fibrosis, anti-oxidant and anti-cancer. However, its chemical structure leads to its extremely low water solubility and bioavailability. When modified by linking its structure to a glucosamine salt, it become a water-soluble drug with high bioavailability and spontaneously form a hydrogel when dissolved in water at high concentration (>30 mg mL−1), which renders it a perfect topical drug for various dermatological diseases. As tested, this modified drug potently rescued UVB-induced wrinkles formation in nude mouse skin and inhibited UVB-induced photoaging of human dermal fibroblasts.
Analyzing the Synergistic Effects of Antioxidants in Combating Photoaging Using Model Nematode, Caenorhabditis elegans
- Pages: 139-147
- First Published: 25 September 2019
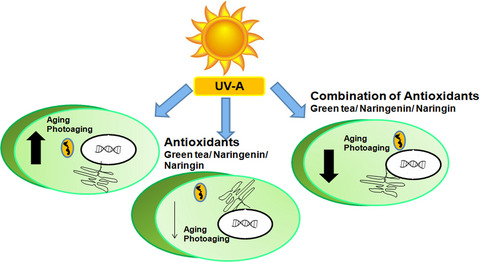
Schematic representation showing the initiation of aging and photoaging process inside the cells exposed to UV-A. Treating the cells with antioxidants has reduced the level of aging and photoaging. Further, the combination of selective antioxidants could reduce the level of aging and photoaging in a greater manner than that of the individual effects.
Pharmacokinetics and Tissue Distribution of DVDMS-2 in Tumor-bearing Mice
- Pages: 148-155
- First Published: 01 October 2019
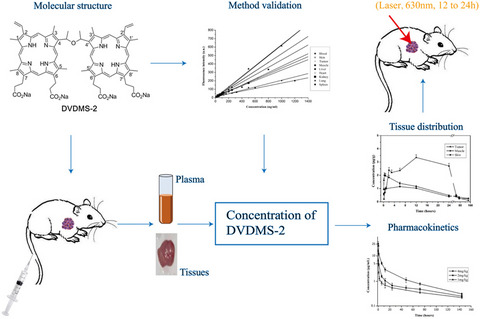
DVDMS-2 is a novel candidate for photodynamic therapy of tumors. In this study, a rapid, reproducible, sensitive and specific method with good linearity was established for DVDMS-2 quantification. The pharmacokinetics of DVDMS-2 in tumor-bearing mice conformed to a two-compartment model. DVDMS-2 accumulated in tumor tissue to a greater extent than adjacent tissues (skin, muscle) and sustained a relatively high-level concentration 12 to 24 h following administration, which may be the optimal treatment time point. Moreover, DVDMS-2 eliminated at a rapid rate in tumor-bearing mice, suggesting that DVDMS-2 may have few side effects. This may be beneficial in future clinical study.
Photoinactivation Sensitivity of Staphylococcus carnosus to Visible-light Irradiation as a Function of Wavelength
- Pages: 156-169
- First Published: 25 September 2019
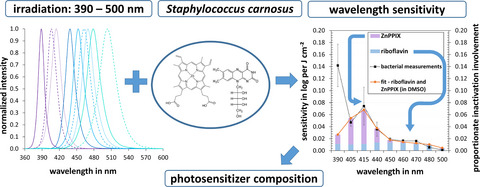
Approach of applying LEDs in a broad range but spectrally resolved (left) on a bacterial strain, to get knowledge about its endogenous photosensitizers (middle). Absorption spectra of possibly involved photosensitizers are measured and variably combined, while the mathematical calculation of a fit with the measured action spectrum of bacterial inactivation carves out the best match (right). The calculated factors indicate to which extent a certain photosensitizer contributes to the measured bactericidal effect. In this investigation, we derived flavins and zinc protoporphyrin IX most relevant for the photosensitizer composition of S. carnosus between 405 and 500 nm.
Disinfection of Cariogenic Pathogens in Planktonic Lifestyle, Biofilm and Carious Dentine with Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy
- Pages: 170-177
- First Published: 04 September 2019
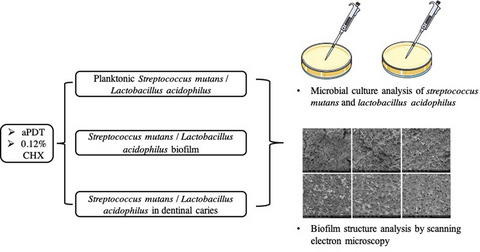
We compared the antibacterial effects of antimicrobial photodynamic therapy (aPDT) and 0.12% chlorhexidine (CHX) on Streptococcus mutans and Lactobacillus acidophilus in planktonic lifestyle, biofilm and carious dentine. Samples were treated with 0.1 mg mL−1 toluidine blue O followed by irradiation with a light emission diode (λ − 635 ± 10 nm; 500 mW; 31.5 J cm−2; 60 s) and 0.12% CHX (60 s), respectively. Microbial culture analysis showed that aPDT achieved comparable antibacterial effects with 0.12% CHX against Lactobacillus acidophilus and showed greater bactericidal potential against Streptococcus mutans biofilm. Photosensitizer and light parameters need further optimization to eradicate Streptococcus mutans in dentine caries.
Effect of High Intensity Blue Light on Fusobacterium nucleatum Membrane Integrity
- Pages: 178-181
- First Published: 13 August 2019
Oral malodor is a common and disturbing condition affecting some 25% of adult population. In most cases the malodor results from the activity of proteolytic oral bacteria. In previous studies we've shown that high intensity blue light is effective against malodor producing bacteria and that this effect is mediated by the production of oxygen radicals. In the present study we tested the effect of blue light against malodor producing bacteria Fusobacterium nucleatum to determine the target site for this phototoxic effect. Taken together, results of the present study suggest that the main damage is caused to the bacterial cell membrane.
Photobiomodulation Enhances Cisplatin Cytotoxicity in a Culture Model with Oral Cell Lineages
- Pages: 182-190
- First Published: 19 August 2019
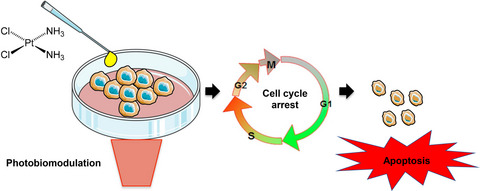
Drawbacks related to cisplatin failure may be associated with the cell energy metabolism. Photobiomodulation is known to transiently increase ROS production and to promote ATP synthesis. In this study, we investigated whether photobiomodulation can potentiate the effects of cisplatin on keratinocytes and cancer cells. Results suggest that cells treated with cisplatin in combination with photobiomodulation presented more cell cycle arrest and died mostly by apoptosis. Photobiomodulation may potentiate the effects of cisplatin, leading to increased drug cytotoxicity and enhanced cell death.
Effect of Photobiomodulation on Repairing Pressure Ulcers in Adult and Elderly Patients: A Systematic Review
- Pages: 191-199
- First Published: 24 September 2019
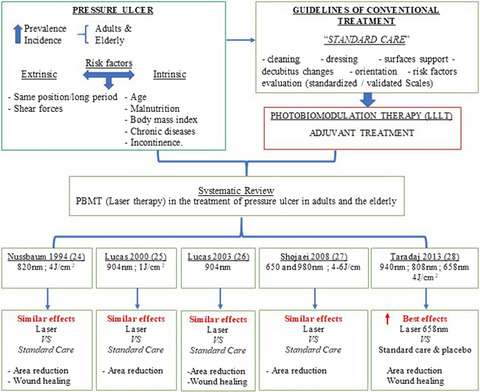
Pressure ulcers are highly prevalent among adult and elderly patients where risk factors vary. In addition to guidelines to the conventional treatment, some auxiliary therapies such as photobiomodulation have shown promising results in wound healing. In this systematic review, only 5 papers were selected according to the eligibility criteria of this research. It was observed that PBMT red wavelength, similar to standard care, promoted tissue repair with a reduced lesion area.
Photobiomodulation Therapy for Attenuating the Dystrophic Phenotype of Mdx Mice
- Pages: 200-207
- First Published: 16 November 2019
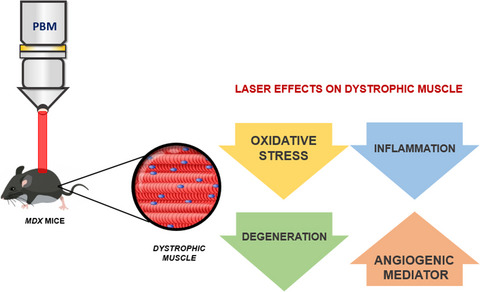
The photobiomodulation (PBM; Aluminum Gallium Arsenide diode, 830 nm wavelengths) was applied on the dystrophic quadriceps muscle of mdx mice, the experimental model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, during the acute phase of dystrophy disease. PBM attenuated the dystrophic phenotype of mdx mice, reducing the degenerative, inflammatory and oxidative stress markers. At the same time, the PBM promoted the increase of angiogenesis mediator.
Long-wavelength Ultraviolet A1 and Visible Light Photoprotection: A Multimodality Assessment of Dose and Response
- Pages: 208-214
- First Published: 29 August 2019
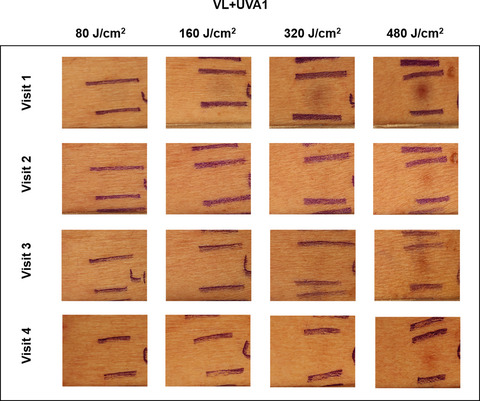
Human skin is exposed to visible light (VL; 400–700 nm) and long-wavelength ultraviolet A1 (UVA1) radiation (370–400 nm) after the application of organic broad-spectrum sunscreens. The biologic effects of these wavelengths have been demonstrated; however, a dose–response has not been investigated. Threshold doses of VL+UVA1 (370–700 nm) resulting in biologic responses were calculated. Results indicate that approximately 2 h of sun exposure, which equates to an approximate VL+UVA1 dose of 400 J cm−2, is capable of inducing inflammation, immediate erythema and delayed tanning. These findings reinforce the need of photoprotection beyond the UV range.





