Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Invited Reviews
Methods of Assessment of the Corneas of the Eyes Laboratory Rabbits Exposed to Solar Ultraviolet-B Radiation
- Pages: 467-479
- First Published: 03 October 2018
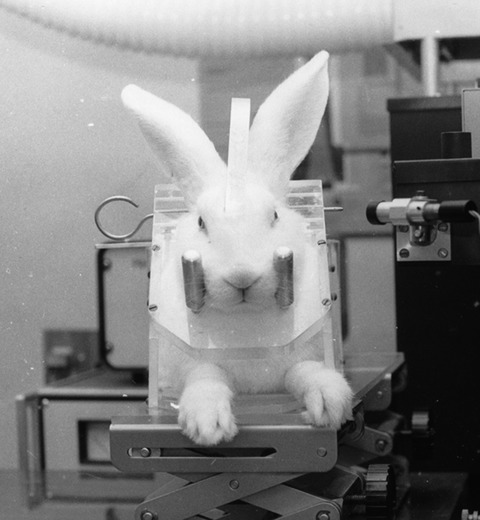
The albino rabbit has been used for over 100 years to assess the acute effects of ultraviolet-B radiation on the eye, especially the cornea. Undertaking such research requires special consideration of how to actually expose the eyes to the UV to be able to define the dose delivered. Having irradiated the eye, then a range of specialized methods have been developed to allow investigators to assess the corneal damage that can be produced both in the living animal and on corneal tissue samples obtained by dissecting them from the eye.
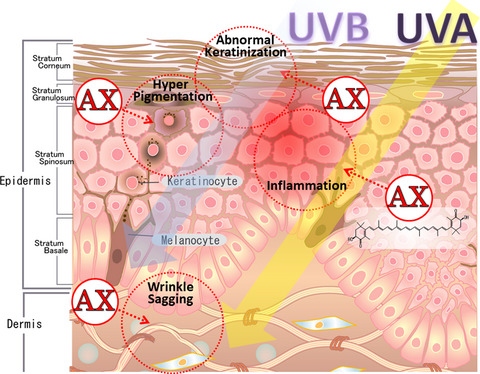
Intracellular Signaling Mechanisms Involved in the Biological Effects of the Xanthophyll Carotenoid Astaxanthin to Prevent the Photo-aging of the Skin in a Reactive Oxygen Species Depletion-independent Manner: The Key Role of Mitogen and Stress-activated Protein Kinase 1
- Pages: 480-489
- First Published: 13 October 2018
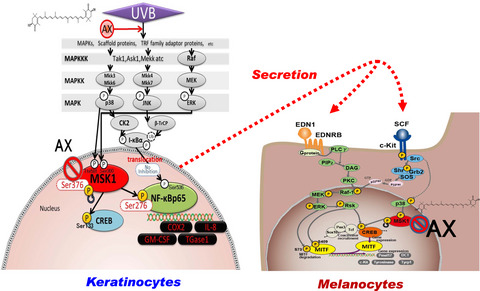
Intracellular signaling mechanisms involved in the biological effects of the xanthophyll carotenoid astaxanthin to prevent the photo-aging of the skin occur in a reactive oxygen species depletion-independent manner, the targeted signaling factor of which is located at mitogen and stress-activated protein kinase 1 in both human keratinocytes and human melanocytes.
The Xanthophyll Carotenoid Astaxanthin has Distinct Biological Effects to Prevent the Photoaging of the Skin Even by its Postirradiation Treatment
- Pages: 490-500
- First Published: 19 October 2018
Research Articles
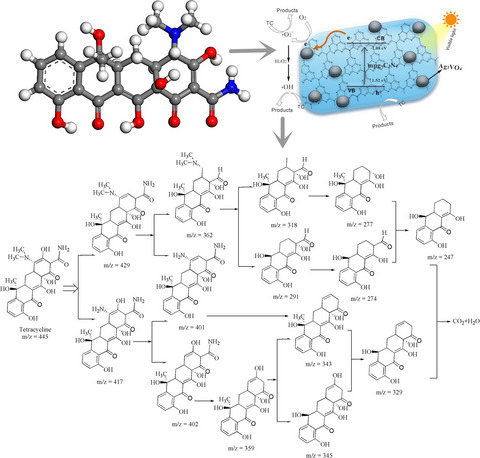
Tetracycline Removal Under Solar Illumination Over Ag3VO4/mpg-C3N4 Heterojunction Photocatalysts
- Pages: 501-511
- First Published: 13 August 2018
Ultrasound-assisted Synthesis of Ag-ZnS/rGO and its Utilization in Photocatalytic Degradation of Tetracycline Under Visible Light Irradiation
- Pages: 512-521
- First Published: 14 August 2018
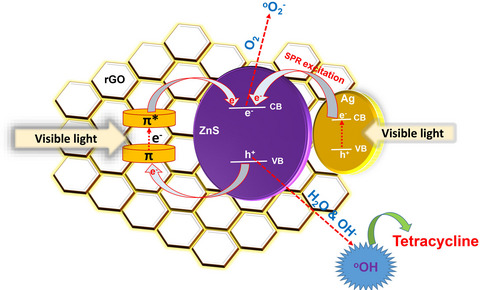
Silver, zinc sulfide, and reduced graphene oxide (Ag-ZnS/rGO) nanocomposite was synthesized through an ultrasound-assisted co-precipitation method and its photocatalytic efficiency was evaluated by considering the degradation of Tetracycline (TC) under visible light. The study of the mechanism of the photocatalytic process disclosed that the synergistic role of surface plasmon resonance (SPR) induced by Ag nanoparticles and p-type semiconductor feature of rGO leads to ZnS semiconductor stimulation in the visible light region.
Silver-Doped TiO2-Coated Cotton Fabric as an Effective Photocatalytic System for Dye Decolorization in UV and Visible Light
- Pages: 522-531
- First Published: 05 September 2018
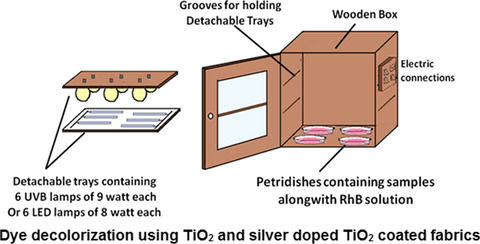
In situ deposition of TiO2 and silver-doped TiO2 on cotton fabric has been carried out without using any binder. Silver-doped TiO2 coating on coated cotton fabric samples can be used repeatedly for the purpose of dye decolorization. Enhanced rates of dye decolorization could be achieved using silver-doped TiO2-coated fabric under both UV and visible light, and the mechanisms of the same have been discussed.
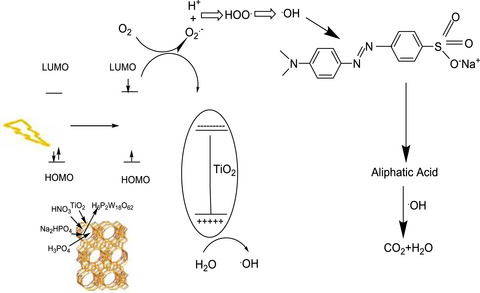
Photocatalytic Performance of H6P2W18O62/TiO2 Nanocomposite Encapsulated into Beta Zeolite under UV Irradiation in the Degradation of Methyl Orange
- Pages: 532-542
- First Published: 17 September 2018
Role of Ser65, His148 and Thr203 in the Organic Solvent-dependent Spectral Shift in Green Fluorescent Protein
- Pages: 543-555
- First Published: 21 September 2018
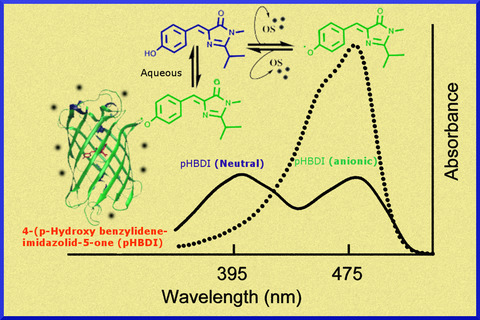
Absorption spectra of GFP are displayed in the presence of aqueous and polar organic solvents. The equilibrium between neutral (395 nm) and anionic (475 nm) chromophore (p-hydroxybenzylidene imidazolidin-5-one) species under aqueous environment is altered toward anionic population in the organic solvent environment.
Coumarin-based Fluorescent Probes for Selectively Targeting and Imaging the Endoplasmic Reticulum in Mammalian Cells
- Pages: 556-562
- First Published: 29 July 2018
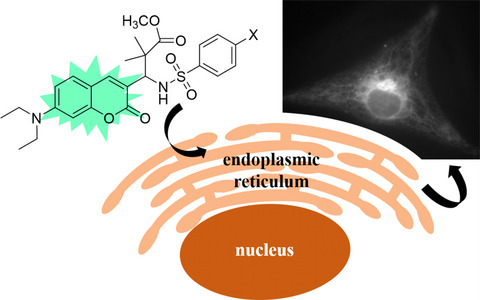
This article reports the synthesis and characterization of two coumarin-based compounds containing sulfonamide side groups and their application as fluorescent imaging probes selective for the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) of live and fixed mammalian cells. They have a negligible toxicity at imaging concentrations. When excited with 400 nm light, these probes have a narrower emission profile than commercially available 400-nm-excitable ER-targeting probes, and are therefore better suited for multicolor imaging experiments with yellow and red emitting imaging probes.
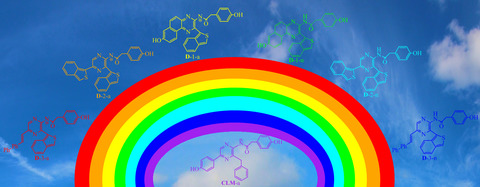
Photoluminescence Rainbow from Coelenteramide—A Theoretical Study
- Pages: 563-571
- First Published: 30 July 2018
Heteropogon contortus BL-1 (Pilli Grass) and Elevated UV-B Radiation: The Role of Growth, Physiological, and Biochemical Traits in Determining Forage Productivity and Quality
- Pages: 572-580
- First Published: 01 August 2018
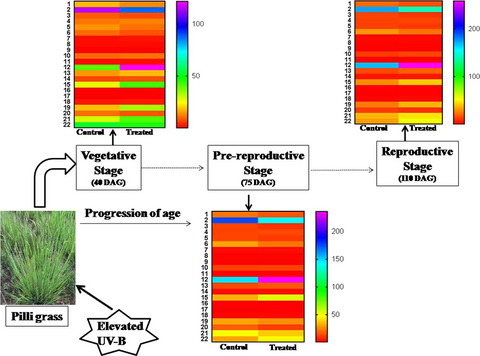
Heteropogon contortus BL-1 (Pilli grass) responses to elevated UV-B (eUV-B) were depended on ambient UV-B and plant age. Under eUV-B, plants developed array of strategies to deal with imposed stress as the age progressed. Most of the variations were observed at vegetative and prereproductive stages. Tannin, phenol, and protein contents increased under eUV-B at all growth stages thus developed resistance but also affected the palatability. 1-22 represent root length, plant height, number of leaves, leaf area, number of tillers, total biomass, MDA, chlorophyll, carotenoids, phenolics, ascorbic acid, tannin, protein, APX, CAT, GR, POX, SOD, sucrose, reducing sugar, total sugar, and starch.
3D Bioprinting with UVA1 Radiation and Photoinitiator Irgacure 2959: Can the ASTM Standard L929 Cells Predict Human Stem Cell Cytotoxicity?
- Pages: 581-586
- First Published: 29 September 2018

3D bioprinting often involves human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSC) that are differentiated into the desired cells to replace body parts like ears. UVA1 radiation (370 ± 5 nm) is used to excite the photoinitiator Irgacure 2959 to create free radicals that photocrosslink hydrogels to make scaffolds for structural support. We questioned if L929 mouse fibroblast cells used in the American Society for Testing Materials standard cytotoxicity assays (F895&F813) can predict the viability of hMSC after UVA1 alone and in combination with Irgacure 2959. We found L929 cannot be used to accurately predict the viability of hMSC after these specific 3D bioprinting conditions.
Inhibitory Effect of Lupeol on MMPs Expression using Aged Fibroblast through Repeated UVA Irradiation
- Pages: 587-594
- First Published: 26 September 2018
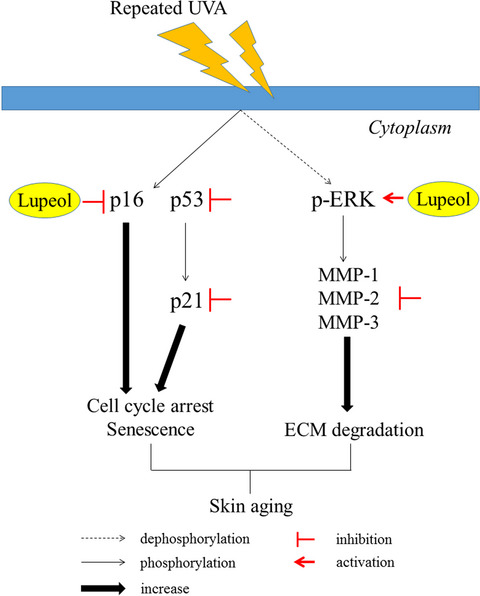
Repeated UVA exposure affects cell cycle associated proteins and MMPs expression. Lupeol degrades the expression of p-p53, p21, p16 and inhibited SA-β-galactosidase activities in senescent fibroblast. Lupeol downregulates MMPs (MMP-1, -2, -3) expression in senescent fibroblast. Lupeol decreases MMPs expression through only the phosphorylation of p-ERK in the MAPK pathway.
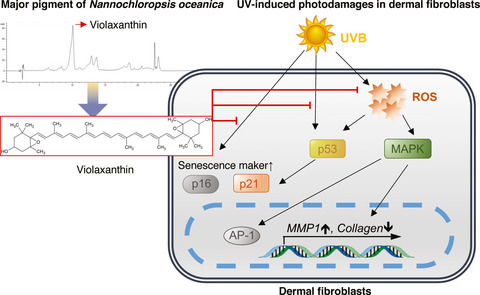
The Protective Effect of Violaxanthin from Nannochloropsis oceanica against Ultraviolet B-Induced Damage in Normal Human Dermal Fibroblasts
- Pages: 595-604
- First Published: 28 September 2018
Protective Effect of Baicalin Against TLR4-mediated UVA-induced Skin Inflammation
- Pages: 605-611
- First Published: 23 September 2018
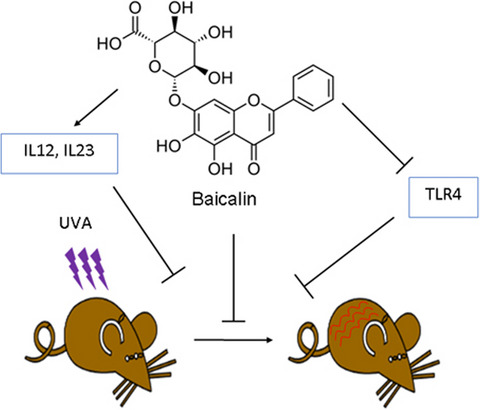
Our results demonstrate the protective effect of baicalin treatment against UVA-induced oxidative damage and inflammation in mice skin via upregulation of IL-12 and IL-23 cytokines. These effects are likely mediated via inhibition of TLR4 pathway, which may serve as a target for prevention against skin inflammation by baicalin.
Tranexamic Acid Ameliorates Nonmelanoma Skin Cancer Induced by Long-term Ultraviolet A Irradiation
- Pages: 612-617
- First Published: 29 September 2018
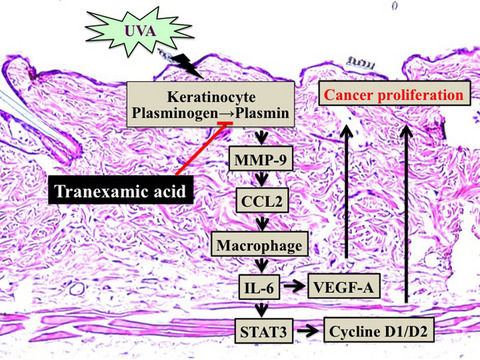
This experiment indicated that the nonmelanoma skin cancer induced by DMBA + UVA long-term irradiation is ameliorated by tranexamic acid through regulation of the plasmin/macrophage/IL-6/STAT3/cyclin D signal transmission pathway. In addition, this ameliorative effect against skin cancer may be mediated via inhibition of the IL-6-induced expression of VEGF-A. From these things, Administration of tranexamic acid, a safe and inexpensive agent, may thus represent an effective treatment for the prevention of skin cancer induced by long-term UV exposure.
Microbiological Decontamination of Water: Improving the Solar Disinfection Technique (SODIS) with the Use of Nontoxic Vital Dye Methylene Blue
- Pages: 618-626
- First Published: 13 August 2018

Data of global horizontal irradiation from World Databank/Solargis™ merged with the global population map. World regions with low solar irradiation (beige areas) represent regions with poor solar radiation (daily sum < 4.4 kWh m−2), while red areas represent areas with relevant solar radiation (daily sum ≥4.4 kWh m−2). The number of people living under poorly irradiated areas was estimated using the Population Explore™ software to be nearly 3 billion people. Considering that northern United States, Canada and Europe contain highly developed access to drinking water, it means that nearly half of this contingent, that is, ~ 1.5 billion people, would benefit from a process as MB-SODIS worldwide.
Antibacterial Effectiveness of Rice Water (Starch)-Capped Silver Nanoparticles Fabricated Rapidly in the Presence of Sunlight
- Pages: 627-634
- First Published: 30 August 2018
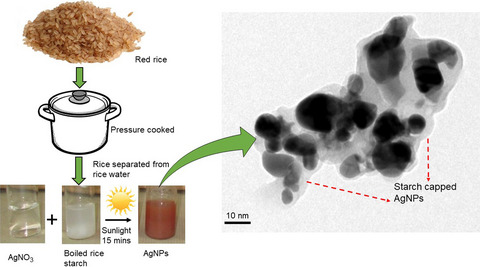
An eco-friendly, cost-effective and rapid synthesis of AgNPs was done using rice water (starch) as reducing agent in the presence of sunlight irradiation. The starch-capped AgNPs were characterized by various techniques and found highly efficient in inhibiting two foodborne bacterial pathogens, Salmonella Typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus.
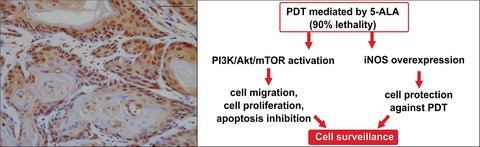
Photodynamic Therapy Mediated by 5-aminolevulinic Acid Promotes the Upregulation and Modifies the Intracellular Expression of Surveillance Proteins in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Pages: 635-643
- First Published: 29 September 2018
Combination of Natural Extracts and Photobiomodulation in Keratinocytes Subjected to UVA Radiation
- Pages: 644-649
- First Published: 29 September 2018
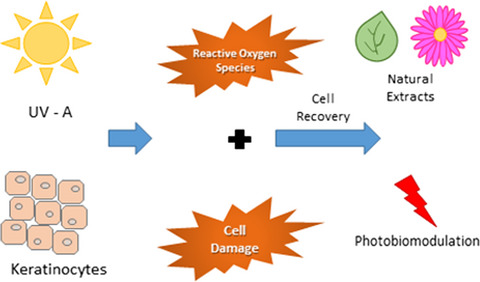
Natural extracts with antioxidant properties can minimize the effects of photoaging by inactivating reactive oxygen species. Photobiomodulation (PBM) has proven to be a useful tool for the modulation of cell metabolism. Here, we investigate the associations of antioxidants with PBM with the aim of promoting skin rejuvenation, after the exposure of keratinocytes to UVA radiation.
A Pilot Observational Study of Environmental Summertime Health Risk Behavior in Central Brisbane, Queensland: Opportunities to Raise Sun Protection Awareness in Australia's Sunshine State
- Pages: 650-655
- First Published: 07 September 2018

Sun-protective behaviours and mobile phone use of urban Queenslanders during a midweek noon time hourly period were observed on a summer's day in central, Brisbane, Australia. Our findings suggest that mobile phones provide an under-utilized opportunity for delivering tailored skin cancer prevention messaging to young people and suggest that a sizeable proportion of funding for mass media public awareness campaigns should be directed towards this approach in favor of traditional electronic media outlets.
Method Article
Solar Ultraviolet Radiation Exposure Proxy-estimated by Sky View Fish-eye Photography—Potentials and Limitations from an Exploratory Correlation Study
- Pages: 656-661
- First Published: 29 September 2018

Solar ultraviolet radiation (UVR) exposure under shade structures may be estimated by sky view fish-eye photography and calculation of percentage of free sky “Sky View Factor” (SVF)—given a global solar UV-irradiance or exposure value for unobstructed sky conditions. SVF and measured solar UVR exposure correlate. Splitting sky view images into a south- and a north-half and weighting the south-half higher improves the estimate. Potentials and limitations of sky view fish-eye photography and calculation of the SVF as a proxy to estimate solar UVR exposure in shade settings are investigated using controlled situations.
Special Issue Research Article
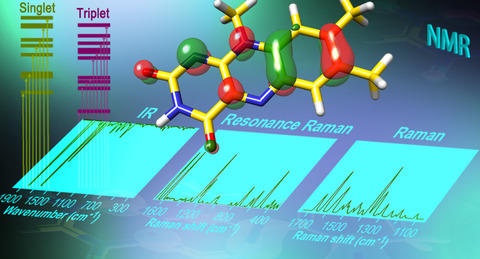
Spectroscopic Properties of Lumiflavin: A Quantum Chemical Study
- Pages: 662-674
- First Published: 26 September 2018