Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Special Issue Honoring Professor Hasan Mukhtar
Special Issue Invited Review
Type I and Type II Photosensitized Oxidation Reactions: Guidelines and Mechanistic Pathways
- Pages: 912-919
- First Published: 13 January 2017
Special Issue Invited Reviews
Damaging Effects of Ultraviolet Radiation on the Cornea
- Pages: 920-929
- First Published: 09 December 2016
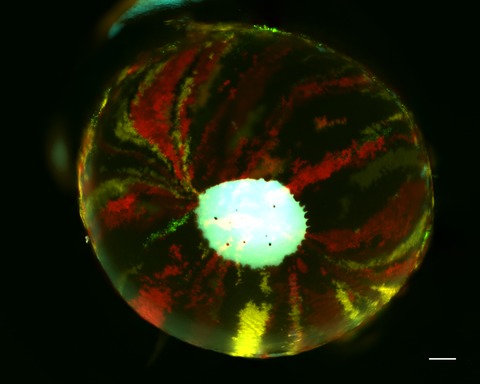
The clarity and structural integrity of the cornea is essential for proper vision. It is highly exposed to sunlight and therefore susceptible to ultraviolet radiation (UVR)-induced damage. We have recently used a mouse model containing fluorescent probes in stem cells in the cornea. A single low dose of UVB provoked an increase in the epithelial progeny of the stem cells in the limbus being forced centripetally towards the center of the cornea, creating a spoke like appearance of the labeled progeny growing toward the center of the cornea. This review highlights the damaging effects of UVR on the cornea.
Crosstalk Among UV-Induced Inflammatory Mediators, DNA Damage and Epigenetic Regulators Facilitates Suppression of the Immune System
- Pages: 930-936
- First Published: 09 December 2016
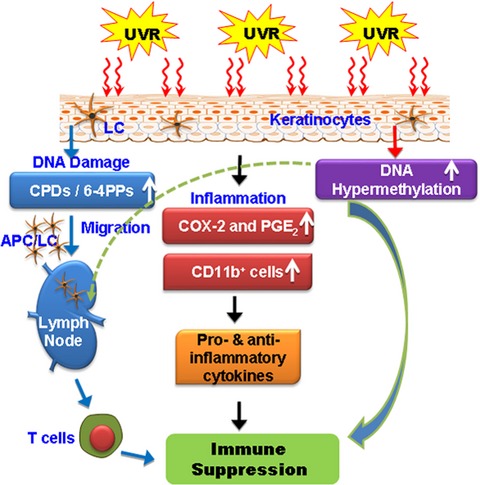
Crosstalk among UV radiation-induced inflammatory mediators, DNA damage and epigenetic regulators results in photo-immunosuppression. UVB radiation-induced photodamage initiates migration of antigen-presenting cells from skin to regional lymph nodes, where they present antigen to T cells in an unusual way. UVB-induced inflammatory mediators and DNA damage affect epigenetic regulators and all together play crucial roles in suppression of immune system in UV radiation-exposed mouse skin. This suppression of immune system is implicated in skin cancer risk.
UVB-generated Microvesicle Particles: A Novel Pathway by Which a Skin-specific Stimulus Could Exert Systemic Effects
- Pages: 937-942
- First Published: 31 December 2016

UVB generates microvesicle particles through involvement of the lipid mediator platelet-activating factor (PAF). The cartoon depicts theoretical pathway by which UVB-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) which generate PAF agonists that then trigger microvesicle particle release. This cartoon also suggests potential targets by which this pathway can be modulated.
Autophagy in UV Damage Response
- Pages: 943-955
- First Published: 09 December 2016
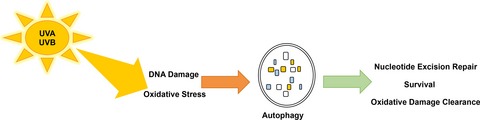
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation exposure has a number of effects on skin cells, including DNA damage, oxidative stress and apoptosis. Recent evidence has shown that autophagy is also activated by UV to mediate the complex response to UV-induced stress. This review investigates the current understanding of the role of autophagy in UV response and UV-induced disease, as well as the implications of autophagy modulation in the treatment or prevention of skin cancer.
Phytochemicals for the Prevention of Photocarcinogenesis
- Pages: 956-974
- First Published: 07 January 2017
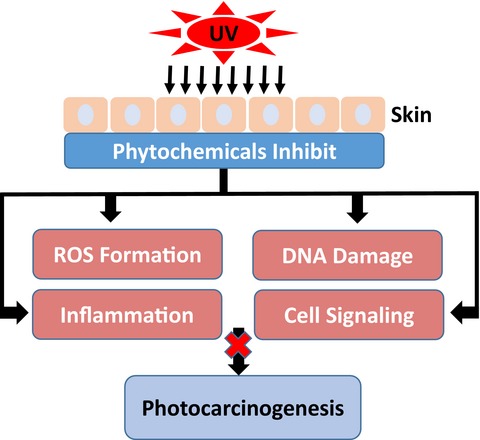
Ultraviolet (UV) exposure is the main cause of human skin cancer due to its damaging effects on skin cells. Chemoprevention prevents or delays the development of skin cancer through the use of phytochemicals. Phytochemicals impede the damaging effects of UV radiation and may lead to inhibition of photocarcinogenesis.
Melanoma Chemoprevention: Current Status and Future Prospects
- Pages: 975-989
- First Published: 15 March 2017

Exposure to ultraviolet radiation is a leading cause of skin cancers, including melanoma. Current preventive strategies and therapies are not sufficient to reduce incidence or mortality associated with melanoma. Therefore, it is necessary to explore new therapeutic, as well as chemopreventive strategies for melanoma management. Here, we discuss studies aimed at chemoprevention of melanoma. To date, limited clinical studies have been done in the field of melanoma chemoprevention, and no agent has so far been approved, for clinical use. However, encouraging results from preclinical studies support further exploration and clinical trials to identify novel agents for melanoma prevention in humans.
Special Issue Research Articles
The B6-vitamer Pyridoxal is a Sensitizer of UVA-induced Genotoxic Stress in Human Primary Keratinocytes and Reconstructed Epidermis
- Pages: 990-998
- First Published: 13 January 2017
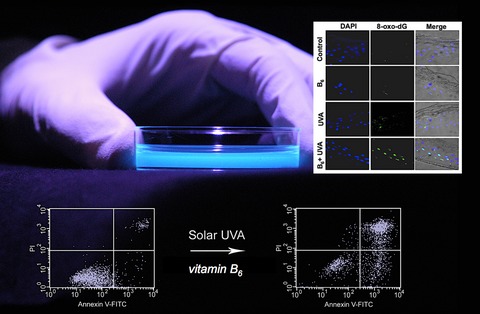
UVA-driven photooxidative stress in human skin may originate from excitation of specific endogenous chromophores acting as photosensitizers. Here, evidence is presented suggesting that the B6-vitamer pyridoxal is a sensitizer of genotoxic stress in human adult primary keratinocytes. In human reconstructed epidermis, pyridoxal pre-incubation followed by UVA exposure caused genomic oxidative base damage (8-oxo-dG), procaspase 3 cleavage and TUNEL positivity, consistent with UVA-driven photooxidative damage that may be relevant to human skin exposed to high concentrations of B6-vitamers.
Silibinin Treatment Inhibits the Growth of Hedgehog Inhibitor-Resistant Basal Cell Carcinoma Cells via Targeting EGFR-MAPK-Akt and Hedgehog Signaling
- Pages: 999-1007
- First Published: 25 January 2017
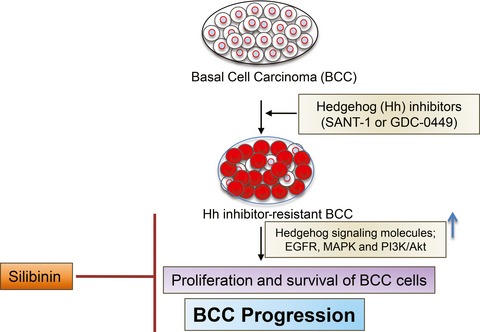
In this study, we evaluated the efficacy of a natural agent silibinin to overcome resistance against hedgehog inhibitors (Sant-1 or GDC-0449) in basal cell carcinoma (BCC) cells. The silibinin treatment strongly inhibited the cell growth and induced death in ASZ001, ASZ001-Sant-1-resistant and ASZ001-GDC-0449-resistant BCC cells. Colony-forming ability of the hedgehog inhibitor-resistant BCC cells was completely inhibited with silibinin treatment. Mechanistic studies revealed that silibinin inhibits EGFR-MAPK-Akt and hedgehog signaling in resistant BCC cells. Silibinin treatment also targeted the key cell death-associated molecules in the resistant BCC cells.
Skin Exposure to Ultraviolet B Rapidly Activates Systemic Neuroendocrine and Immunosuppressive Responses
- Pages: 1008-1015
- First Published: 26 September 2016
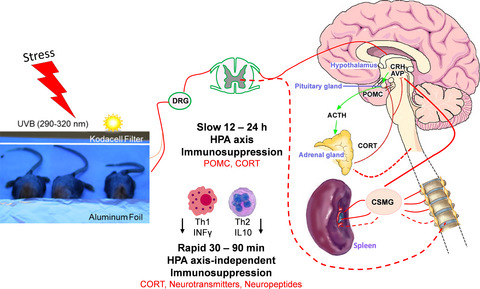
Possible neuroendocrine pathways involved in spleenic immunosuppressive action evoked by exposure of murine skin to ultraviolet B (UVB) radiation. UVB-induced afferent neural signals activate the central HPA axis resulting in pituitary proopiomelanocortin-derived ACTH and adrenal corticosterone release to plasma. Slower immunosuppressive action, takes 12–24 h (upper part). UVB-induced afferent neuronal signals affect CNS and directly activate adrenal gland (CORT, neurotransmitters) and spleen (neurotransmitters, neuropeptides). Rapid immunosuppression, 30–90 min (lower part).
Naproxen Inhibits UVB-induced Basal Cell and Squamous Cell Carcinoma Development in Ptch1+/−/SKH-1 Hairless Mice
- Pages: 1016-1024
- First Published: 22 March 2017
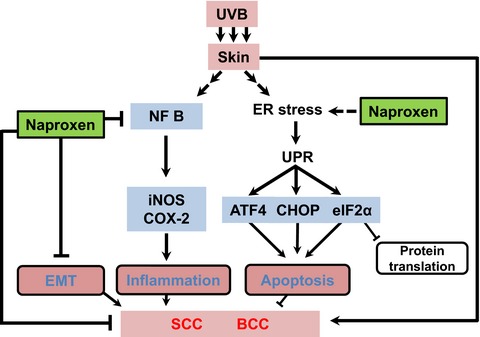
Cancer chemoprevention efficacy of naproxen against UVB-induced cutaneous neoplasm. Naproxen treatment reduces UVB-induced basal cell carcinoma (BCC) and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) development in Ptch1+/−/SKH-1 hairless mice. It inhibits tumor cell proliferation, NFκB-mediated inflammatory responses, epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) and induces apoptosis. The mechanism involves enhancing unfolded protein response signaling (UPR)-related proteins eIF2α, ATF4, and CHOP. Abrogating expression of CHOP diminishes these effects of naproxen on tumor cells.
Ultraviolet Radiation-Induced Downregulation of SERCA2 Mediates Activation of NLRP3 Inflammasome in Basal Cell Carcinoma
- Pages: 1025-1033
- First Published: 25 January 2017
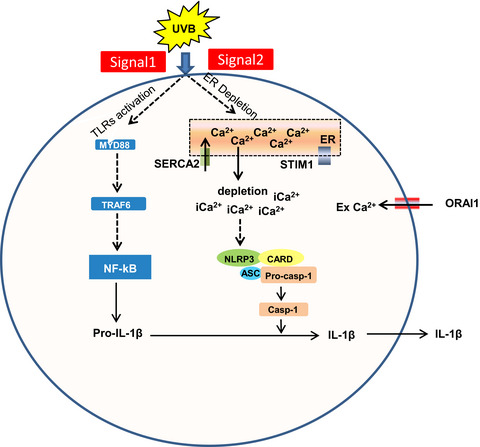
Critical role for Ca2+ mobilization in activation of the nucleotide-binding domain, leucine-rich-repeat-containing family, pyrin domain-containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome. Ultraviolet (UV) B exposure blocks Ca2+ mobilization by downregulating the expression of sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA2), a component of store-operated Ca2+ entry (SOCE) that leads to activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome.
Research Articles
Novel Bi2WO6-coupled Fe3O4 Magnetic Photocatalysts: Preparation, Characterization and Photodegradation of Tetracycline Hydrochloride
- Pages: 1034-1042
- First Published: 15 February 2017
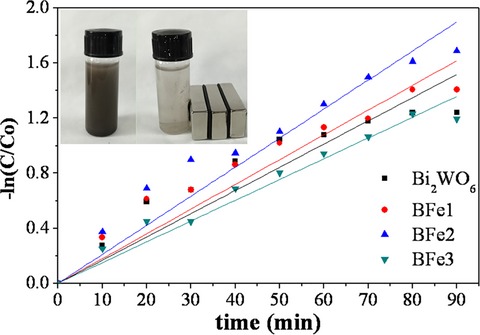
Novel Bi2WO6-coupled Fe3O4 magnetic photocatalysts with excellent and stable photocatalytic activity for degrading tetracycline hydrochloride and RhB were successfully synthesized via a facile solvothermal route with sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate. The results indicated that introduction of Fe3O4 not only provided magnetism for separating the as-prepared magnetic photocatalysts from the solution, but also enhanced photocatalytic activity for degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride. In addition, appropriated Fe3O4 can improve nanospheres morphology and visible-light response.
Elucidation of Binding Mechanism of Photodynamic Therapeutic Agent Toluidine Blue O with Chicken Egg White Lysozyme by Spectroscopic and Molecular Dynamics Studies
- Pages: 1043-1056
- First Published: 01 March 2017

Toluidine blue O (TBO) is a cationic phenothiazine dye, used as potential antitumor drug in photodynamic therapy. The binding mechanism of TBO with lysozyme is studied by multispectroscopic, molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation methods. The results from steady state emission and time-resolved fluorescence spectral studies unambiguously helped us to conclude the prevalence of static quenching mechanism in lysozyme–TBO system. UV–vis absorption, circular dichroism and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic techniques have been utilized to unravel TBO-induced secondary and tertiary conformational changes in lysozyme. The molecular docking studies of lysozyme–TBO system substantiated the findings of site marker experiment.
FRET in a Synthetic Flavin- and Bilin-binding Protein
- Pages: 1057-1062
- First Published: 05 January 2017
Antigenotoxic Effect Against Ultraviolet Radiation-induced DNA Damage of the Essential Oils from Lippia Species
- Pages: 1063-1072
- First Published: 08 February 2017
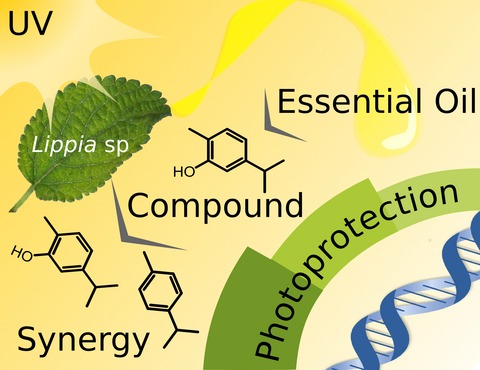
The essential oils (EO) of six Colombian Lippia species were evaluated for antigenotoxicity against ultraviolet radiation. Results showed that EO from Lippia alba, Lippia micromera and Lippia origanoides have antigenotoxic effects. This effect was linked to the major constituents the EO such as citral, carvacrol, ρ-cymene, geraniol and thymol, which were somewhat soluble in the water fraction of the EO. The antigenotoxicity of these EO constituents was unconnected to their antioxidant activity. Inside the EO, these terpenes act synergistically for its antigenotoxicity, which suggests a combined, more than a single, mode of action for these EO constituents.
Proteomic Analyses of Changes in Synechococcus sp. PCC7942 Following UV-C Stress
- Pages: 1073-1080
- First Published: 25 January 2017
Enhancement of the Efficacy of Photodynamic Inactivation of Candida albicans with the Use of Biogenic Gold Nanoparticles
- Pages: 1081-1090
- First Published: 12 February 2017
UVA Light-mediated Ascorbate Oxidation in Human Lenses
- Pages: 1091-1095
- First Published: 13 January 2017

This study shows that UVA light (320–400 nm) can oxidize human lens ascorbate and decrease glutathione levels. The combined effects are a decline in ascorbate reduction and an increase in the production of α-dicarbonyl compounds. The latter can react with lens proteins to form advanced glycation end products (AGEs) that can cross-link proteins and could contribute to lens aging and cataract formation.
Photo-co-carcinogenesis of Topically Applied Retinyl Palmitate in SKH-1 Hairless Mice
- Pages: 1096-1114
- First Published: 28 January 2017
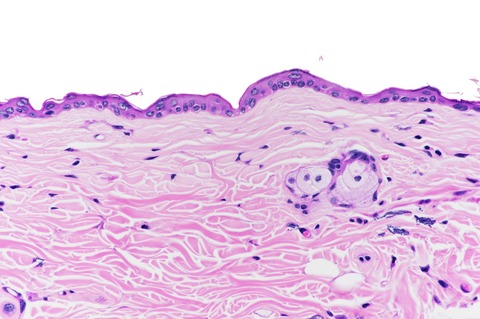
Solar ultraviolet radiation (UVR) is known to induce skin cancers and is also responsible for the premature aging of skin. Certain structural changes associated with skin aging can be reversed or improved with the topical applications of vitamin A and its esters. In this paper, the topical application of retinyl palmitate, a natural ester of vitamin A and a common ingredient in anti-aging skincare products, was shown to enhance the carcinogenic effects of UVR in the skin of hairless mice: earlier skin tumor onsets and increased incidences and multiplicities of neoplasms were observed when compared to control animals.
A Comparison of Dose Metrics to Predict Local Tumor Control for Photofrin-mediated Photodynamic Therapy
- Pages: 1115-1122
- First Published: 13 January 2017
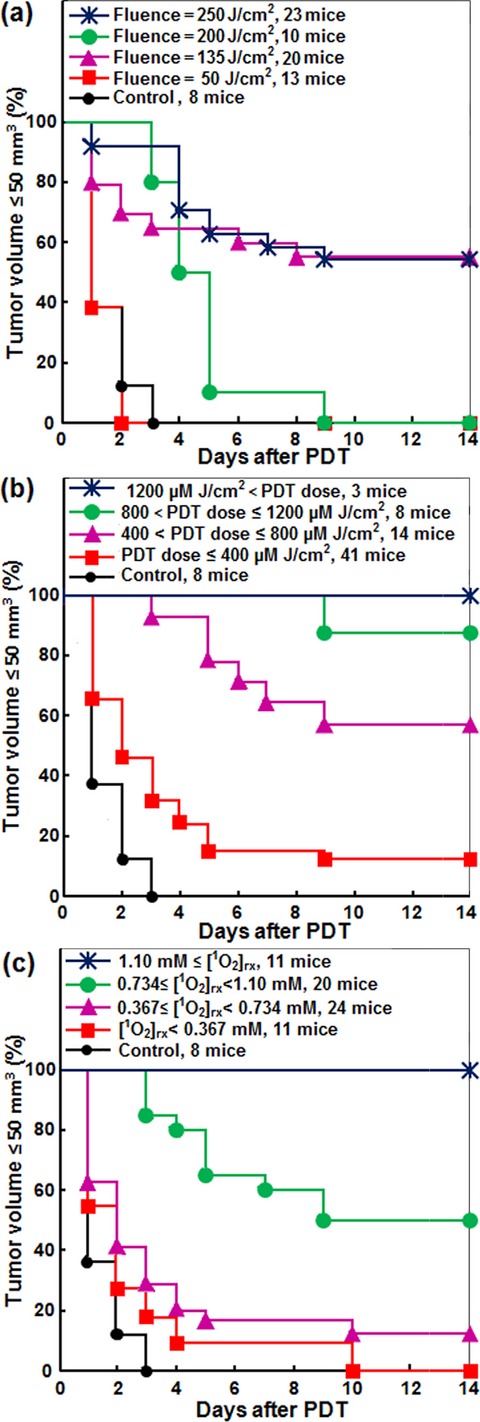
This preclinical study examines light fluence, photodynamic therapy (PDT) dose and “apparent reacted singlet oxygen,” [1O2]rx, to predict local control rate (LCR) for Photofrin-mediated PDT of radiation-induced fibrosarcoma (RIF) tumors. LCR was stratified for different dose metrics for 74 mice (66 + 8 control). Complete tumor control at 14 days was observed for [1O2]rx ≥ 1.1 mm or PDT dose ≥1200 µm J cm−2 but cannot be predicted with fluence alone. LCR increases with increasing [1O2]rx and PDT dose but is not well correlated with fluence. Comparing dosimetric quantities, [1O2]rx outperformed both PDT dose and fluence in predicting tumor response and correlating with LCR.
Schoolyard Shade and Sun Exposure: Assessment of Personal Monitoring During Children's Physical Activity
- Pages: 1123-1132
- First Published: 18 January 2017
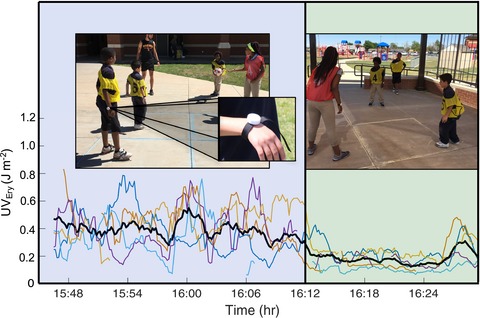
The use of personal UV dosimeters allows for the detection of individual erythemal UV exposures. Results show that substantial benefits can be garnered through focused bioclimatic design of children's recreational space to utilize shade, both natural and artificial, to reduce UV exposures during play, and to extend safe outdoor stays.
Retrospective
Claud S. Rupert (1919–2017): The Father of DNA Repair
- Pages: 1133-1134
- First Published: 17 May 2017