Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Research Articles
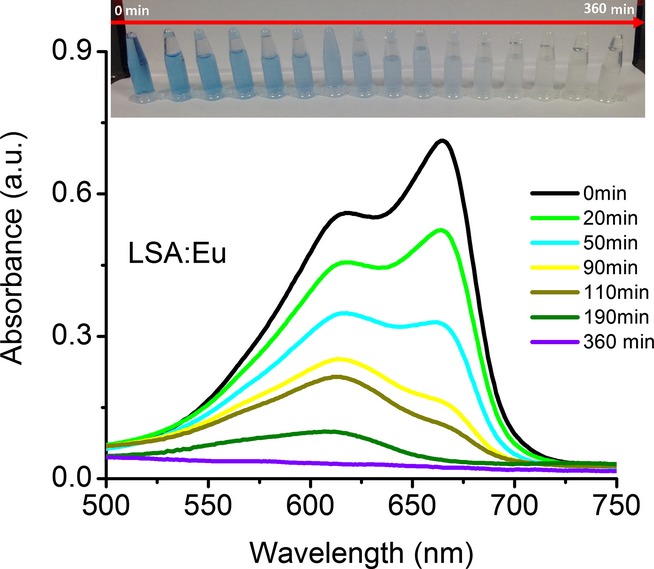
Photocatalytic Activity of LaSr2AlO5:Eu Ceramic Powders
- Pages: 505-509
- First Published: 03 February 2015
One-Pot Synthesis of Cu2O/ZnO Nanoparticles at Present of Folic Acid to Improve UV-Protective Effect of Cotton Fabrics
- Pages: 510-517
- First Published: 12 January 2015
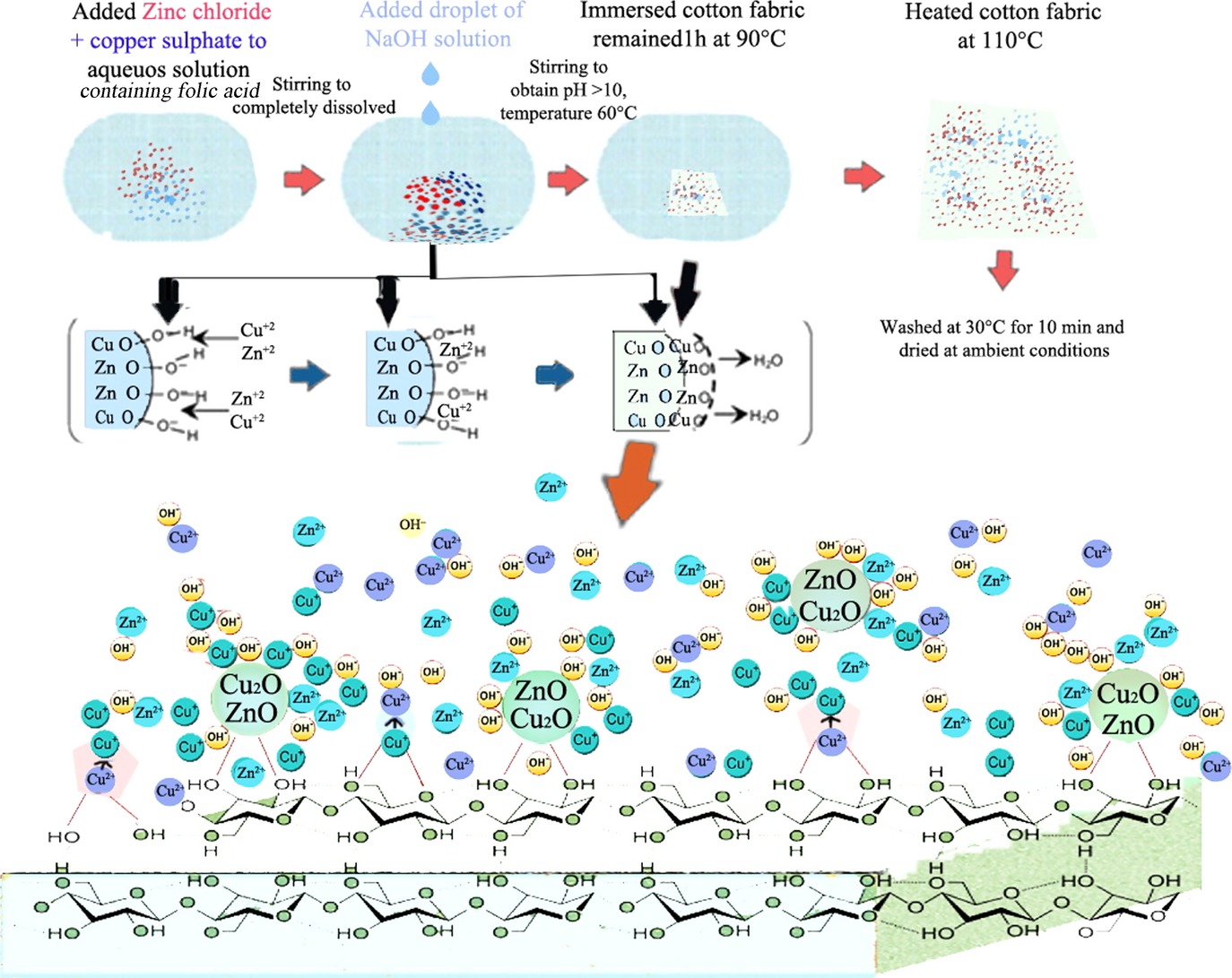
In this work, zinc chloride and copper sulfate have been used as precursors and Cu2O/ZnO nanoparticles have been synthesized in aqueous/alkali media at the presence of cotton fabrics and folic acid. Folic acid, as a biotemplate for synthesis of Cu2O/ZnO, was used to improve the reducing and stabilizing the ability of cotton fabric. Cotton fabric was used as a soft template to control the synthesis of desirable nanostructures with specific size and morphology.
Formulation of Aluminum Chloride Phthalocyanine in Pluronic™ P-123 and F-127 Block Copolymer Micelles: Photophysical properties and Photodynamic Inactivation of Microorganisms
- Pages: 518-525
- First Published: 20 January 2015
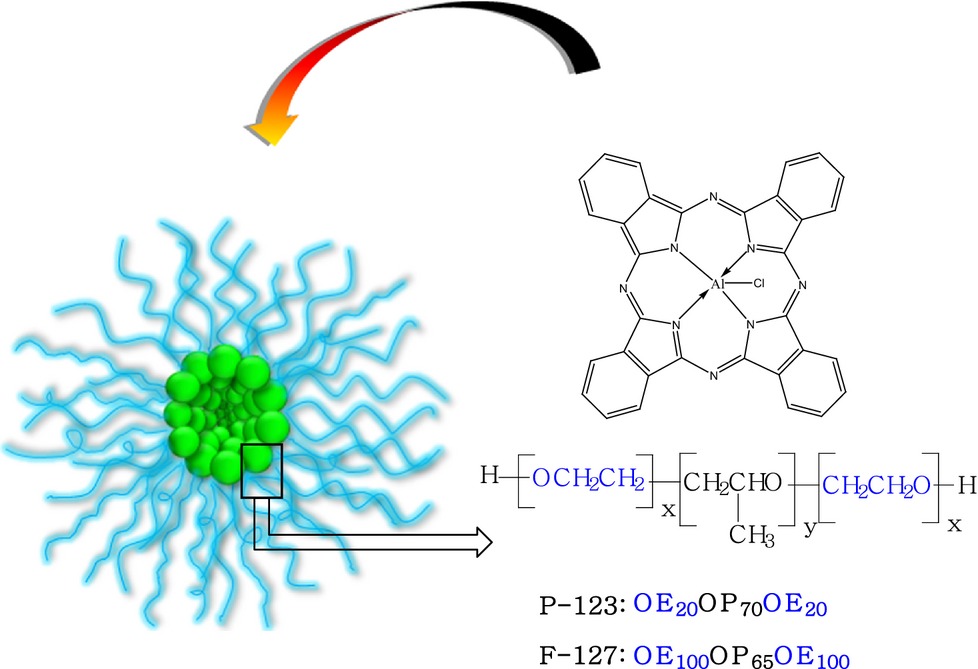
Formulations of aluminum chloride phthalocyanine were prepared in polymeric micelles of pluronic™ surfactants F-127 and P-123 and tested for inactivation of microorganisms. The process of incorporation of AlPcCl on copolymers was effective and the formulation obtained for the system AlPcCl/P-123 had good results against different kind of microorganisms.
Decontamination Efficiency of a DBD Lamp Containing an UV–C Emitting Phosphor
- Pages: 526-532
- First Published: 28 January 2015
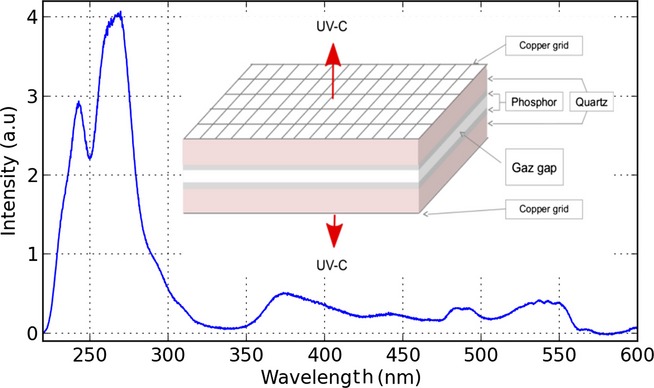
An innovative mercury-free Dielectric Barrier Discharge (DBD) flat lamp has been developed to obtain large spectrum UV-C radiation. The UV-C radiation is produced by a pyrophosphate phosphor doped with Pr3+ (α-Ca2P2O7: Pr2%Na2%) internal coating excited by the 172 nm emission of a Ne-Xe plasma. This work investigates the influence of the plasma parameters on the newly developed UV source energy efficiency and its bactericidal efficiency.
Hiporfin-Mediated Photodynamic Therapy in Preclinical Treatment of Osteosarcoma
- Pages: 533-544
- First Published: 25 January 2015
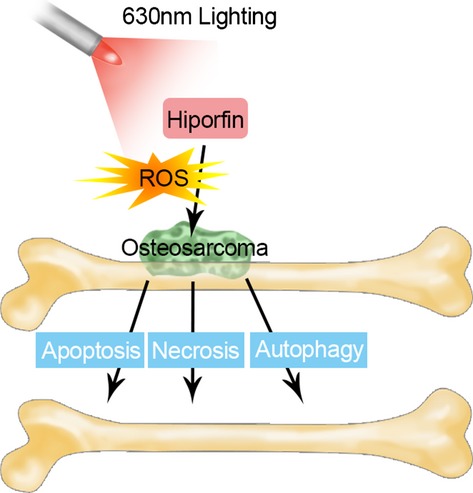
Hiporfin is one kind of photosensitizer that has been approved by Chinese SFDA. In this study, hiporfin was used to see its photodynamic activity in osteosarcoma. After illumination by 630 nm laser, hiporfin killed osteosarcoma cells by increased ROS level and through apoptosis and necroptosis pathways. In vivo study also showed potent tumor eradication. All these provided evidences for the clinical trial of hiporfin on osteosarcoma.
Survey of UV Emissions from Sunbeds in the UK
- Pages: 545-552
- First Published: 28 January 2015

Spectral irradiance of 195 sunbeds in five areas of the United Kingdom was measured in order to assess the radiant doses as increased use of indoor tanning has led to concerns for its impact on the risk of cutaneous cancers. Use of sunbeds for cosmetic purposes should be discouraged, with effective enforcement of the ban on under-18 use, strict control on tanning duration and promotion of information on health risks of sunbed use. Such an integrated approach on safe equipment, safe use and information should reduce the risk of detrimental impact of sunbed use on public health.
Solar Spectral Irradiance and Summary Outputs Using Excel
- Pages: 553-557
- First Published: 21 January 2015

An Excel spreadsheet that calculates solar spectral irradiance between 290–3000 nm on an unshaded, horizontal surface under a cloudless sky at sea level, together with summary outputs such as global UV index, illuminance and percentage of energy in different wavebands. The spreadsheet is easy to use by anyone with an interest in sunlight and solar power irrespective of their background in that just four inputs are required—geographical latitude, month, day of month and time of day.
Evaluation of Photoprotective Potential and Percutaneous Penetration by Photoacoustic Spectroscopy of the Schinus terebinthifolius Raddi Extract
- Pages: 558-566
- First Published: 12 January 2015
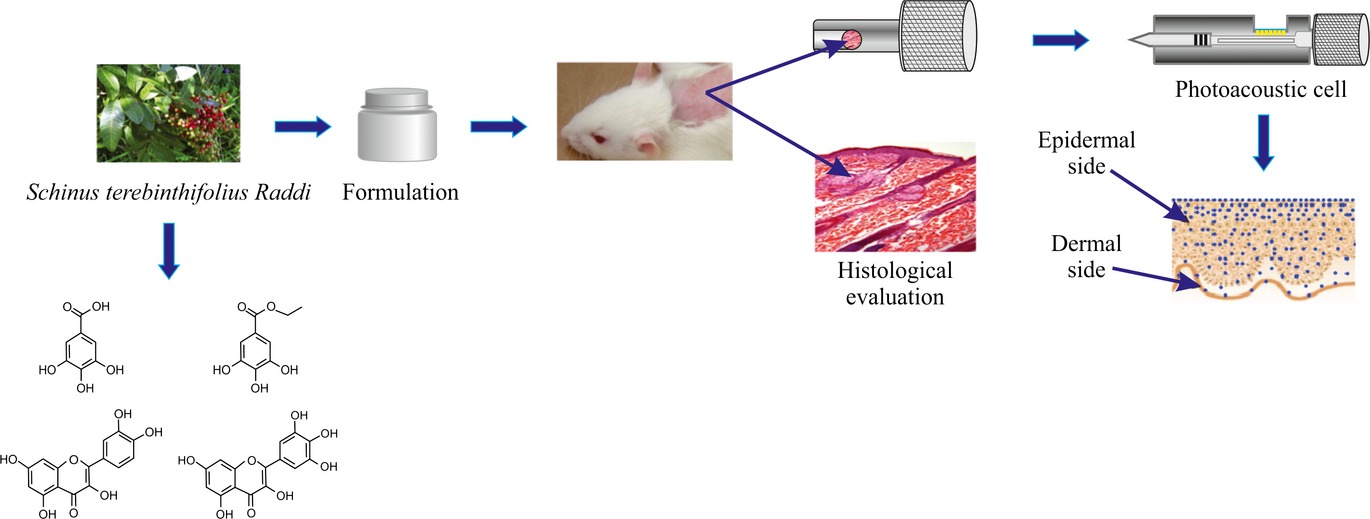
Plant extracts can be incorporated in photoprotective formulations. The crude extract and the fraction containing gallic acid, ethyl gallate and a mixture of flavonoids were obtained from Schinus terebinthifolius leaves. Emulsion and gel formulations containing the crude extract were prepared to evaluate the permeation and the histology of the skin after topical application of the formulations. The photoacoustic spectroscopy measurements confirmed absorption in the UV region and related to the permeation of these formulations. No histopathological changes were detected.
Light Treatment Improves Sleep Quality and Negative Affectiveness in High Arctic Residents During Winter
- Pages: 567-573
- First Published: 09 January 2015

Subjects residing at Canadian Forces Station (CFS) Alert (82° 30′ 00″ N) filled out questionnaires regarding sleep difficulty, psychological well-being and mood and wore Actigraphs to obtain objective sleep data. Saliva was collected prior to and following treatment to measure melatonin and assess melatonin onset. Individuals were given individualized daily light treatment interventions based on their pretreatment salivary melatonin profile. The light treatments were effective in improving sleep quality and reducing negative affect among the participants.
Special Issue Dedicated to the Memory of Michael Kasha
Introduction
Special Issue Research Articles
On the Dual Phosphorescence of Xanthone and Chromone in Glassy Hydrocarbon Hosts
- Pages: 576-585
- First Published: 12 March 2015
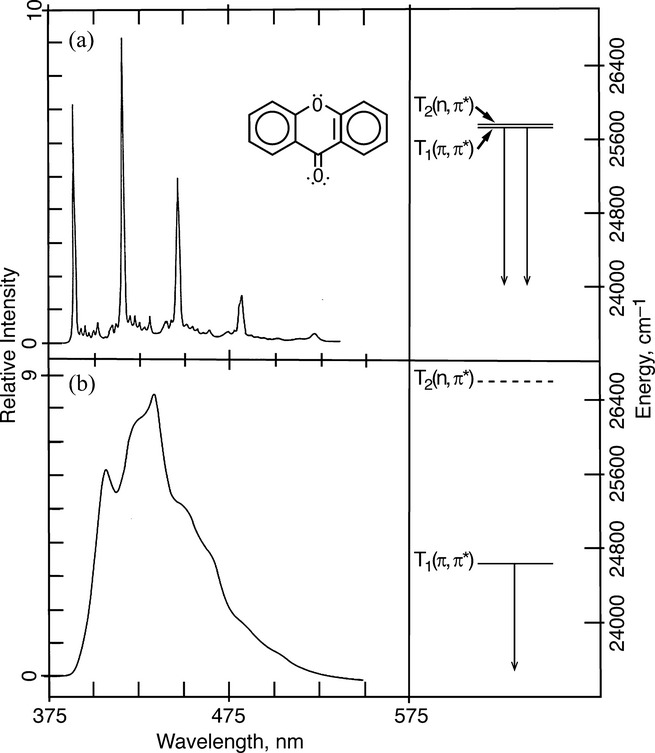
Trace quantities of hydrogen-bonding impurities in otherwise highly purified and dried glassy hydrocarbon matrices at 77 K modify the relative triplet state energy levels, and hence the photophysical properties of two aromatic ketones, xanthone and chromone, to the extent that the intrinsic spectroscopic properties are obscured. The intrinsic spectroscopic properties of each are revealed in multicrystalline n-alkane Shpol'skii matrices, and also in rigorously purified and dried hydrocarbon glasses at 77 K. The extreme sensitivity to substoichiometric quantities of hydrogen-bonding impurities arises from the near-degeneracy of the two lowest-lying triplet states, and the sensitive nature of the n→π* blueshift phenomena to specific hydrogen-bonding interactions.
Absorption and Emission Sensitivity of 2-(2′-Hydroxyphenyl)benzoxazole to Solvents and Impurities
- Pages: 586-598
- First Published: 18 November 2014
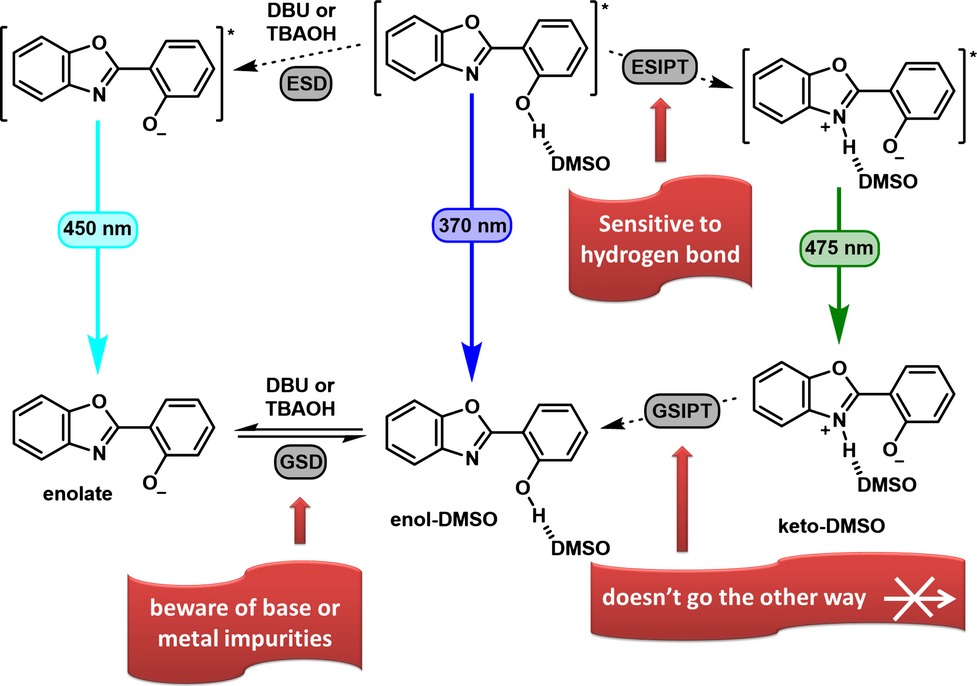
Minor long-wavelength absorption bands of the excited state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT) dye 2-(2′-hydroxyphenyl)benzoxazole (HBO) have been observed in DMSO by us and others. These bands might have been caused by base or metal salt impurities introduced by glass Pasteur pipettes that are equipped with latex rubber bulbs. Without the interference of extraneous bases or metal salts, solvent-mediated deprotonation fails to occur. The propensity of HBO to deprotonation is much higher in DMSO than in less polar solvents. The solvatochromic shifts of HBO suggest that the ESIPT is hindered in polar solvents that are also strong hydrogen bond acceptors.
Electronic and Vibrational Dynamics of Hollow Au Nanocages Embedded in Cu2O Shells
- Pages: 599-606
- First Published: 14 February 2015
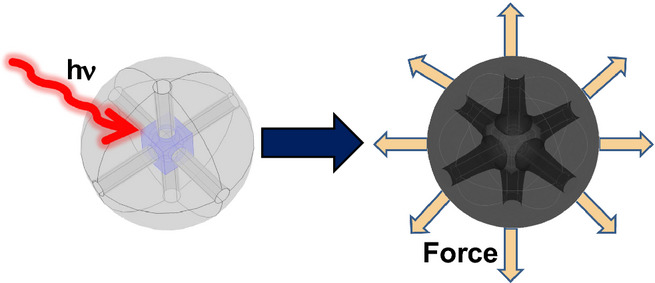
Femtosecond optical excitation of the localized surface plasmon resonance of Au–Cu2O core-shell nanocages creates hot electrons which transfer energy to the Au and Cu2O lattices on picosecond timescales, leading to coherent vibrational motion. Structural mechanics simulations reproduce the dominant lattice vibrational frequency by treating the rapid thermal expansion of the Au nanocage as a force that acts on the Cu2O shell.
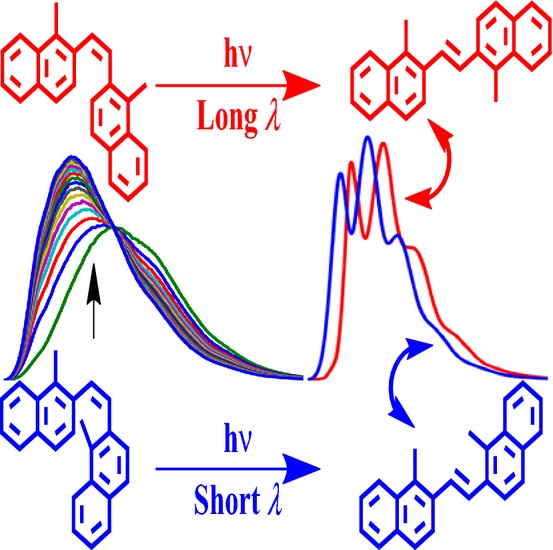
Photoisomerization of cis-1,2-di(1-Methyl-2-naphthyl)ethene at 77 K in Glassy Media
- Pages: 607-615
- First Published: 18 October 2014
Steric and Electronic Factors Associated with the Photoinduced Ligand Exchange of Bidentate Ligands Coordinated to Ru(II)
- Pages: 616-623
- First Published: 18 November 2014
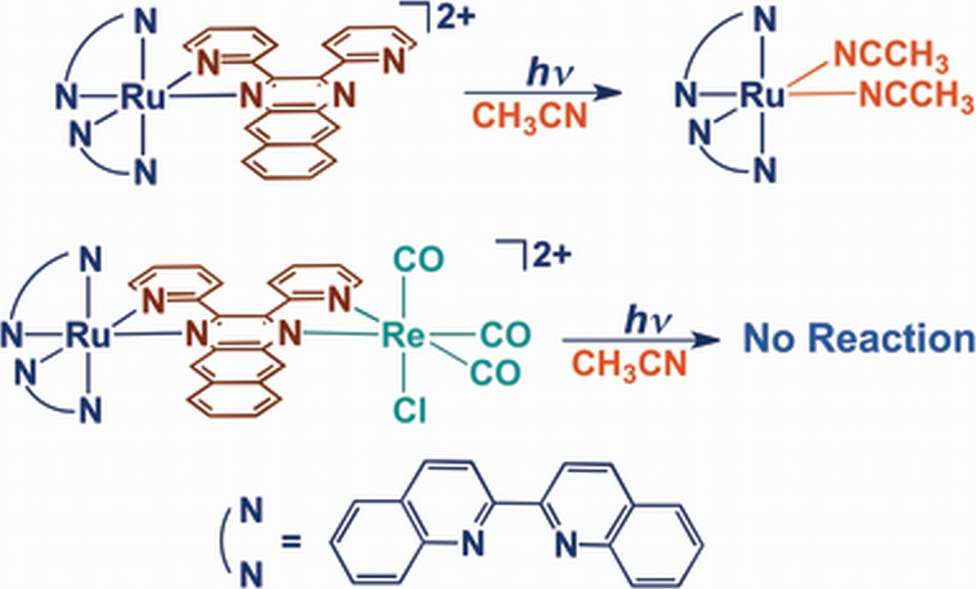
In an effort to create a molecule that can absorb low energy visible or near-infrared light for photochemotherapy (PCT) with easily tunable excited state properties, the new complexes [Ru(biq)2(dpb)](PF6)2 (1, biq = 2,2′-biquinoline, dpb = 2,3-bis(2-pyridyl)benzoquinoxaline) and [(biq)2Ru(dpb)Re(CO)3Cl](PF6)2 (2) were synthesized and characterized. Complex 1 undergoes photoinduced ligand dissociation of the dpb ligand in coordinating solvent in the PCT window, however, the bimetallic complex is photoinert but does absorb lower energy light. The differences in the photophysical properties and the crystal structures of the complexes are discussed and used to explain the differences in photoreactivity.
Transition from Charge-Transfer to Largely Locally Excited Exciplexes, from Structureless to Vibrationally Structured Emissions
- Pages: 624-636
- First Published: 01 November 2014
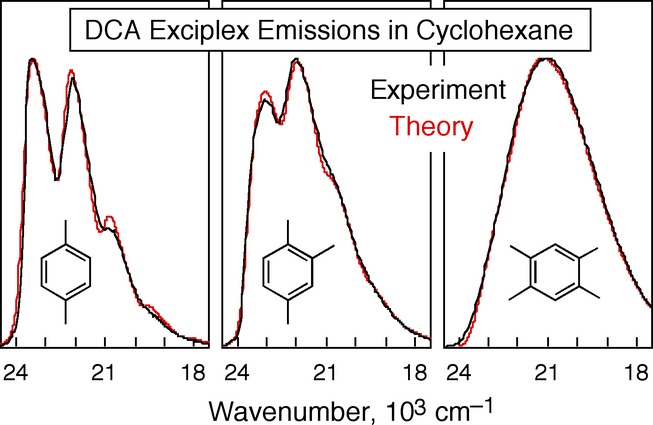
Exciplexes of 9,10-dicyanoanthracene with low oxidation potential (Eox) alkylbenzenes in cyclohexane show structureless emission spectra suggesting ideal charge-transfer (CT) states. With higher Eox donors, vibrational structure emerges. A theoretical model of mixing with a locally excited (LE) state reproduces the spectra and radiative rate constants. The fractional CT character of a highly mixed exciplex varies widely with fluctuations in the microscopic environment and/or librational geometry. Fluctuations favoring the LE (or CT) state contribute more to the blue (or red) side of the overall spectrum. The “ideal CT” appearance of the low-Eox spectra is illusory, resulting instead from several compensating factors.
Improved Spectral Coverage and Fluorescence Quenching in Donor–acceptor Systems Involving Indolo[3-2-b]carbazole and Boron-dipyrromethene or Diketopyrrolopyrrole
- Pages: 637-653
- First Published: 16 February 2015
![Improved Spectral Coverage and Fluorescence Quenching in Donor–acceptor Systems Involving Indolo[3-2-b]carbazole and Boron-dipyrromethene or Diketopyrrolopyrrole](/cms/asset/1554aeba-4e73-457c-a8a4-f8c804e00b57/php12437-toc-0001-m.jpg)
We report synthesis and studies of organic compounds incorporating indolo[3,2-b]-carbazole (ICZ), and 4,4-difluoro-4-bora-3a,4a-diaza-s-indacene (BODIPY) or diketopyrrolopyrrole (DPP). The spectroscopic studies suggest stronger interaction between ICZ and BODIPY in both ground and excited states as well as more efficient energy transfer from ICZ to BODIPY, compared to those of the ICZ-DPP compound, which could be related to the unfavorable orientation of the transition dipoles of ICZ and DPP chromophores. Furthermore, in a solid film of the ICZ–π–BODIPY triad an aggregate of the triad molecules was observed, resulting in a redshift of the absorption maximum (~100 nm) relative to a solution.
A New Series of Fluorescent Indicators for Super Acids
- Pages: 654-659
- First Published: 07 August 2014
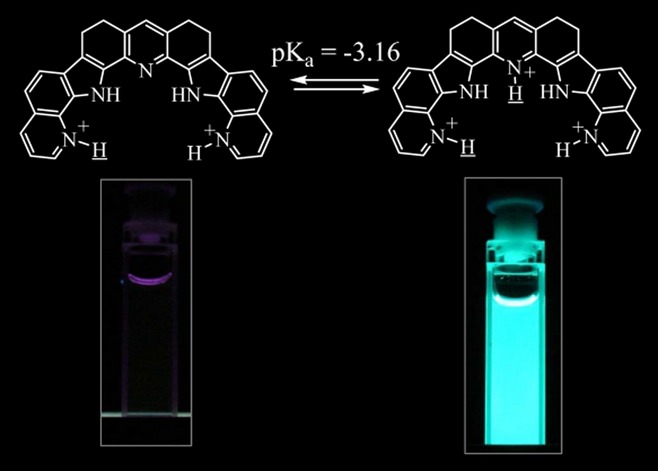
A new series of fluorescent indicators are developed for sensing super acids. The fluorescence intensity switches from the nonemissive state (the diprotonated form) to the intense emissive state (the triprotonated form) with pKa as low as −3.16. This super acid indicator with the highly emissive intensity, great chemical stability and excitation/emission wavelengths in the visible region may find potential applications in industry.
Steady-State Spectroscopy of the 2-(N-methylacetimidoyl)-1-naphthol Molecule
- Pages: 660-671
- First Published: 04 March 2015
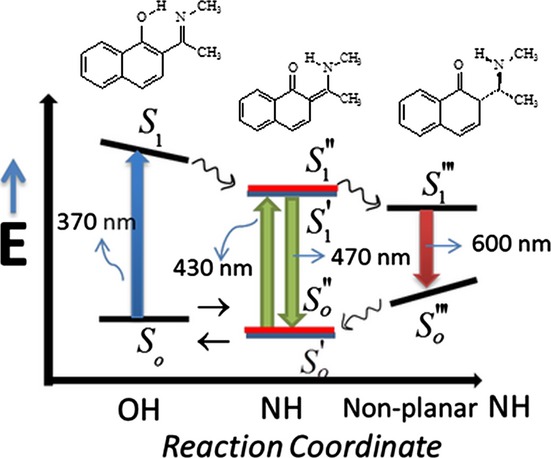
The steady-state spectroscopy of 2-(N-methylacetimidoyl)-1-naphthol reveals composite absorption and emission spectra from 298 to 193 K in hexane. The S0 state absorption can be assigned to the sum of three molecular structures in chemical equilibrium: the OH normal tautomer and two NH proton transfer tautomers. On photoexcitation of the OH tautomer the excited state intramolecular proton transfer is undergone, and the corresponding NH emission is monitored at 470 nm. On photoexcitation of the NH tautomers the previous emission is monitored in addition to another emission at 600 nm, which is ascribed to intramolecular hydrogen-bonded (IHB) nonplanar NH tautomers generated from the IHB planar NH tautomers.
Electron Spin Exchange in Linked Phenothiazine–Viologen Charge Transfer Complexes Incorporated in “Through-Ring” (Rotaxane) α-Cyclodextrins
- Pages: 672-677
- First Published: 16 February 2015
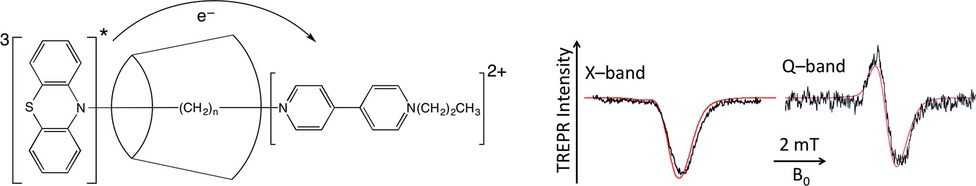
Photoexcitation of covalently bound phenothiazine donors with methylviologen acceptors separated by C8, C10 and C12 alkane chain spacers incorporated in a “through-ring” (rotaxane) fashion to α-cyclodextrin hosts leads to biradicaloid charge-separated states that are studied by time-resolved electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy at the X-band and Q-band microwave frequencies. Computer simulation of the spectra using a “static” model for spin-correlated radical pairs allows extraction of the spin exchange interactions, which range from –2 to –1000 Gauss. The results are discussed in terms of through-bond vs through-space electronic coupling mechanisms as a function of donor–acceptor distance.
Photo-Wolff Rearrangement of 2-Diazo-1,2-naphthoquinone: Stern–Volmer Analysis of the Stepwise Reaction Pathway
- Pages: 678-683
- First Published: 05 September 2014
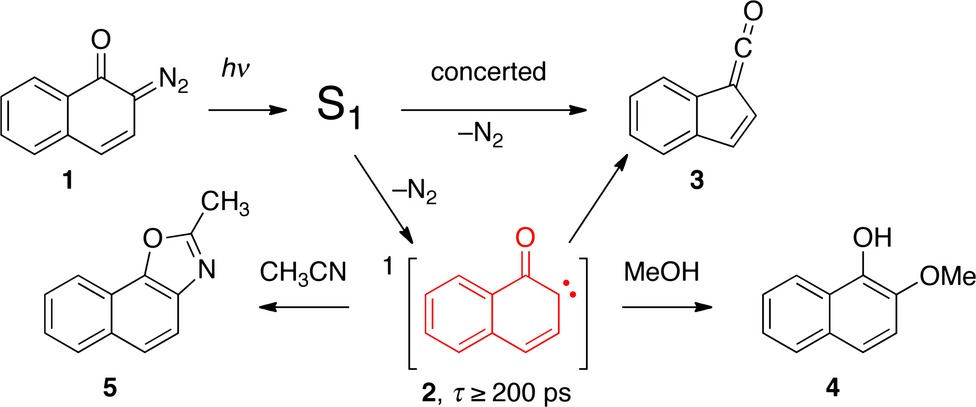
A quantitative assessment of the stepwise versus concerted photodeazotization pathways of 2-diazo-1,2-naphthoquinone (1) forming ketene 3 is provided. Trapping of the carbene intermediate 2 by methanol yields 2-methoxy-1-naphthol (4) in up to 12% yield. [3+2]Cycloaddition of 2 and acetonitrile yielding 2-methylnaphth[2,1-d]oxazole (5) was also observed. The lifetime of the thermalized carbene 2 is at least 200 ps. A comparison of the yields of 5 formed upon photolysis and upon thermolysis of 1 in acetonitrile provides evidence that a substantial part of the hot nascent carbene 2 formed photolytically rearranges to the ketene 3 during its vibrational relaxation (hot ground-state reaction).
Utilization of PARAFAC-Modeled Excitation-Emission Matrix (EEM) Fluorescence Spectroscopy to Identify Biogeochemical Processing of Dissolved Organic Matter in a Northern Peatland
- Pages: 684-695
- First Published: 12 March 2015
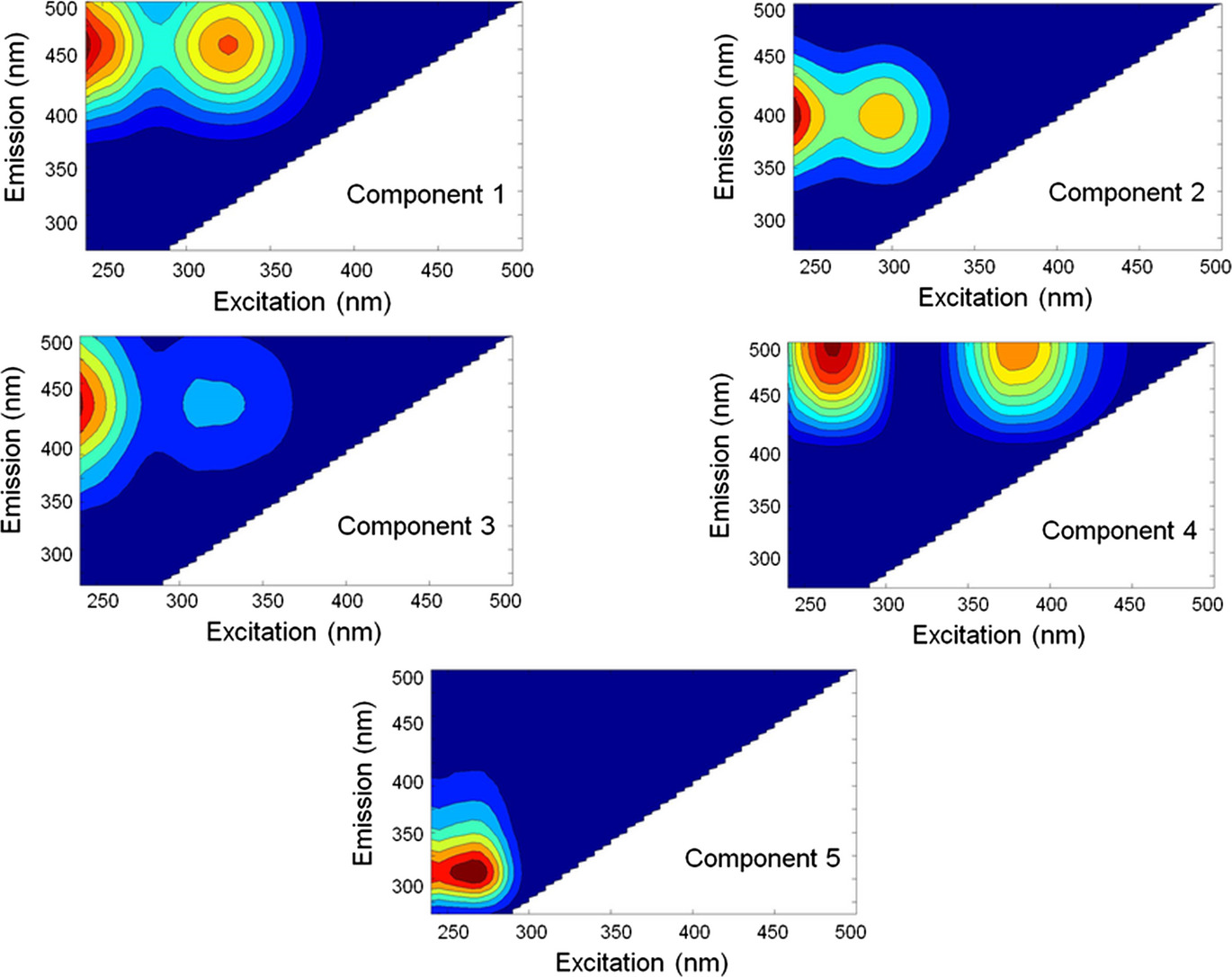
Spectral characteristics of five components of Dissolved Organic Matter (DOM) in Glacial Lake Agassiz peatland porewaters identified by PARAFAC modeling of EEM fluorescence spectra. Color contours reflect intensities expressed in Quinine Sulfate Equivalent (QSE) units; blue low, red high. The relative loadings of these components to total fluorescence vary as a function of peat type and depth, and appear to be a function of the quality of the DOM and the active microbial community present.
Comparison of Templating Abilities of Urea and Thioruea During Photodimerization of Bipyridylethyelene and Stilbazole Crystals
- Pages: 696-704
- First Published: 28 September 2014
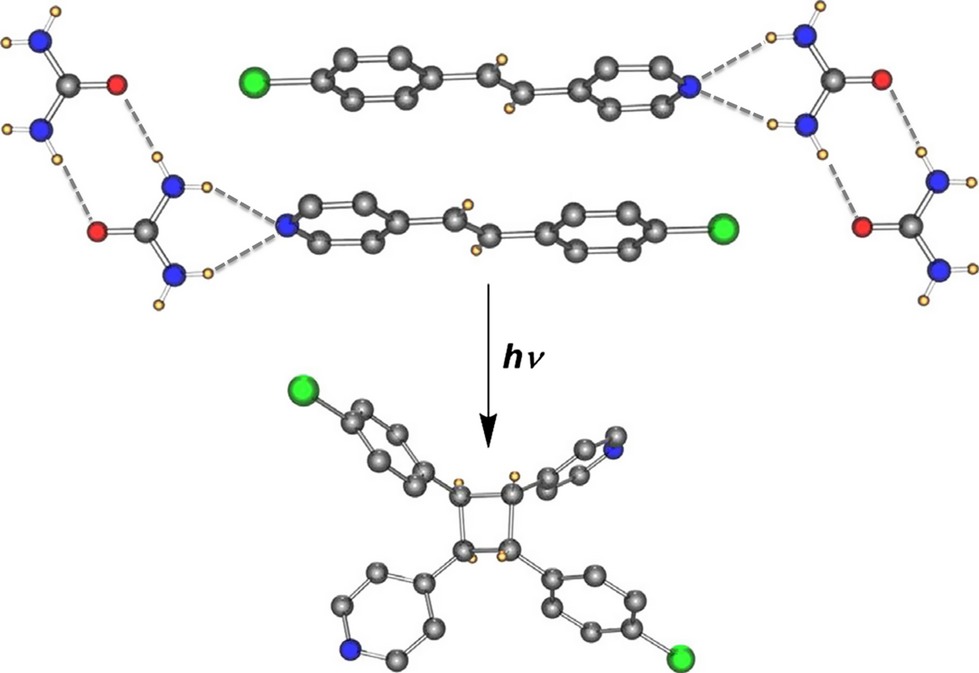
Templating properties of urea in solid-state photodimerization of stilbazoles and bispyridylethylenes have been established through a study that combined photochemistry and X-ray crystallography. The templating ability of urea derives from its ability to form hydrogen bond with itself and with coguests stilbazoles and bispyridylethylenes. At this stage, it is not easy to predict when urea will and when will not function as a template.
Following Oxygen Consumption in Singlet Oxygen Reactions via Changes in Sensitizer Phosphorescence
- Pages: 705-713
- First Published: 04 November 2014
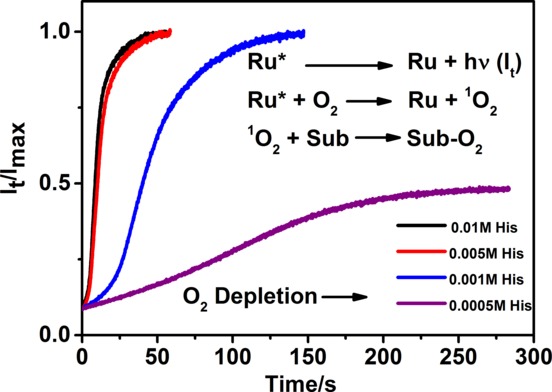
Photolysis of a Ruthenium-pyrene complex in oxygenated aqueous solutions results in efficient sensitization of singlet oxygen. In the presence of substrates, large increases in the orange luminescence of the Ruthenium-pyrene complex are observed as dissolved oxygen reacts with the substrate. Luminescence intensity changes allow determination of rate constants for singlet oxygen reaction with substrates.
o-Amino Analogs of Green Fluorescence Protein Chromophore: Photoisomerization, Photodimerization and Aggregation-induced Emission
- Pages: 714-722
- First Published: 27 October 2014
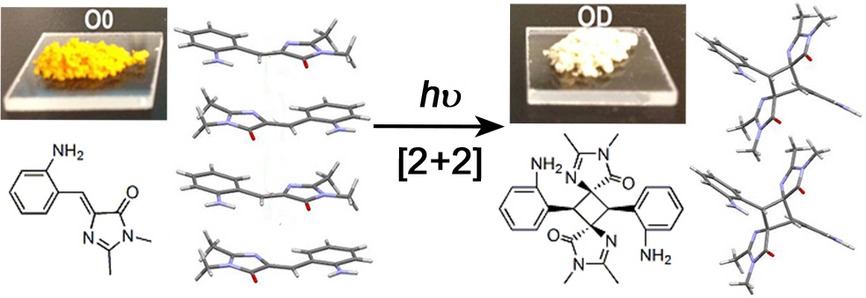
The GFP-like chromophore O0 undergoes solid-state [2 + 2] photodimerization to form a head-to-tail syn-oriented photodimer OD that is confirmed by X-ray crystallography. The excited-state “meta-ortho effect” of the amino analogs of GFP chromophore in solutions and aggregates is also established and discussed.
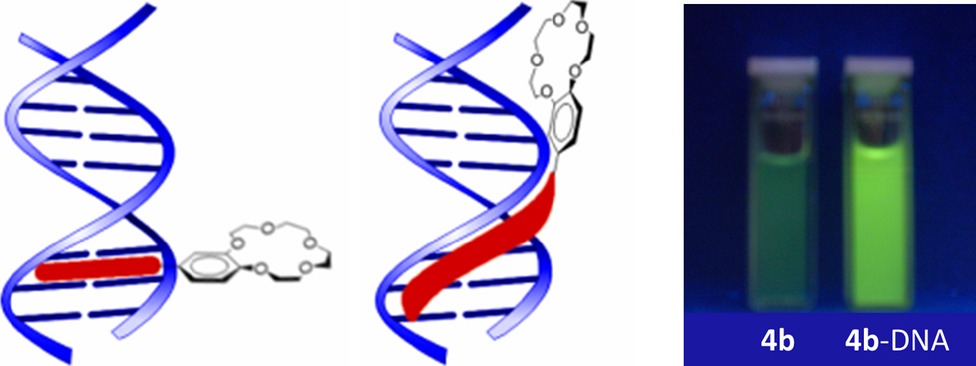
Interaction of Crown Ether-Annelated Styryl Dyes with Double-Stranded DNA
- Pages: 723-731
- First Published: 18 December 2014
Nanometal Surface Energy Transfer Optical Ruler for Measuring a Human Telomere Structure
- Pages: 732-738
- First Published: 22 January 2015

Through the use of optical quenching of a molecular dye (DY680) by a gold nanoparticle appended to DNA, the conformation of the Hybrid-2 conformer in telomeric DNA sequence was measured. The results clearly demonstrate the versatility of nanometal surface energy transfer (NSET) molecular rulers for measuring biopolymer structures, allowing mapping of the structure and no evidence of nonspecific interactions between the gold and DNA sequence which would lead to perturbation of the folding landscape.
Electronic Interactions of Michler's Ketone with DNA Bases in Synthetic Hairpins
- Pages: 739-747
- First Published: 08 October 2014
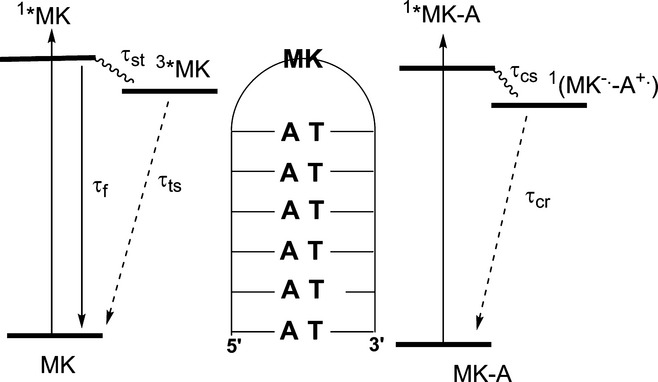
The behavior of DNA conjugates having Michler's ketone hairpin linkers is dependent upon the ground state conformation of the linker. Linkers in which there is little interaction with the adjacent base pair undergo fluorescence and intersystem crossing to form a long-lived triplet state; whereas linkers that are stacked with an adjacent purine base undergo fast, reversible electron transfer.
Opening Enediyne Scissors Wider: pH-Dependent DNA Photocleavage by meta-Diyne Lysine Conjugates
- Pages: 748-758
- First Published: 24 December 2014
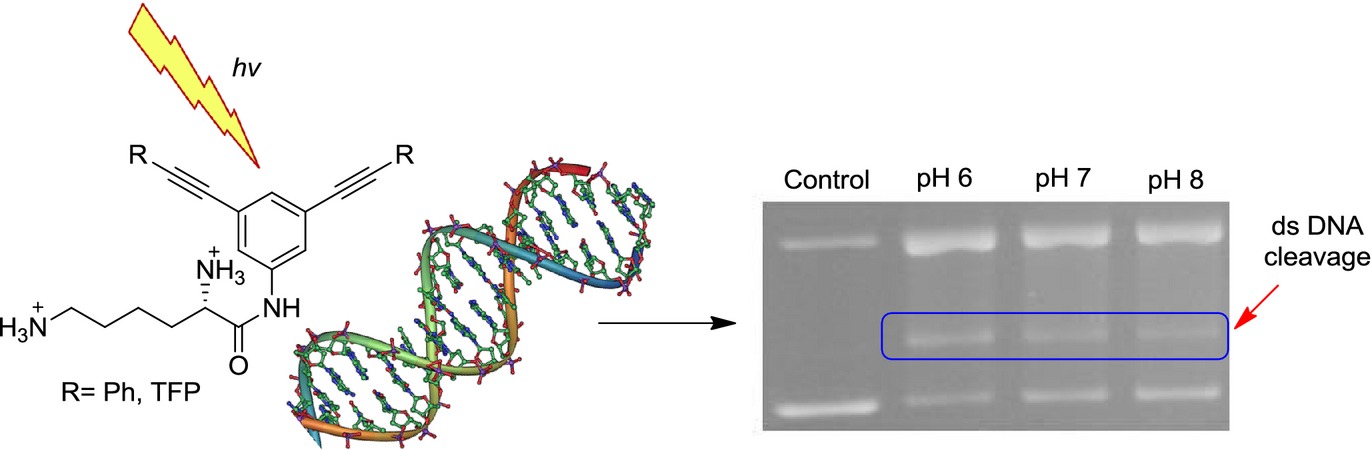
Upon photochemical activation, meta-bis-tetrafluoropyridinylalkyne-lysine conjugates induce pH-dependent DNA ds-photocleavage. Efficiency of DNA damage is strongly enhanced at pH < 7. The observed pH-dependence of the DNA photocleavage activity stems from change in the protonation states of lysine amino groups. The ROS (Reactive Oxygen Species) scavenger experiments suggest that singlet oxygen is partially involved in the DNA damage.
Electronic Excitations in G-quadruplexes Formed by the Human Telomeric Sequence: A Time-Resolved Fluorescence Study
- Pages: 759-765
- First Published: 01 November 2014
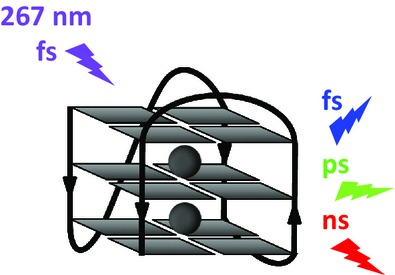
G-quadruplexes formed by folding of the human telomeric sequence d(GGGTTAGGGTTAGGGTTAGGG) in presence of K+ ions are studied by fluorescence spectroscopy from femtosecond to nanosecond domains. Population of exciton states leads to ultrafast energy transfer. Bright excited states with weak charge transfer character emit at the fluorescence maximum and decay between 1 and 100 ps. Charge transfer states with longer lifetime emit at lower energy. Due to the increased rigidity of these monomolecular structures, the persistence of excitations is longer and the contribution of charge transfer states is more pronounced than what is observed for tetramolecular G-quadruplexes.