Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER PICTURE
Outside Front Cover: Plasma Process. Polym. 4/2025
- First Published: 07 April 2025

Outside Front Cover: Plasma Processes and Polymers, a Wiley polymers journal, focuses on the interdisciplinary field of low temperature plasma science.
Our scope encompasses a wide range of topics in the area of plasma sources and plasma-based treatments, including surface modification, plasma polymerization, plasma discharges, plasma medicine, and many other related subjects.
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Effects of Tube Diameter and Gas Flow Rate on the Discharge Dynamics Characteristics and Reactive Species of Nanosecond Pulsed Discharge Plasma in Contact With Water
- First Published: 03 November 2024
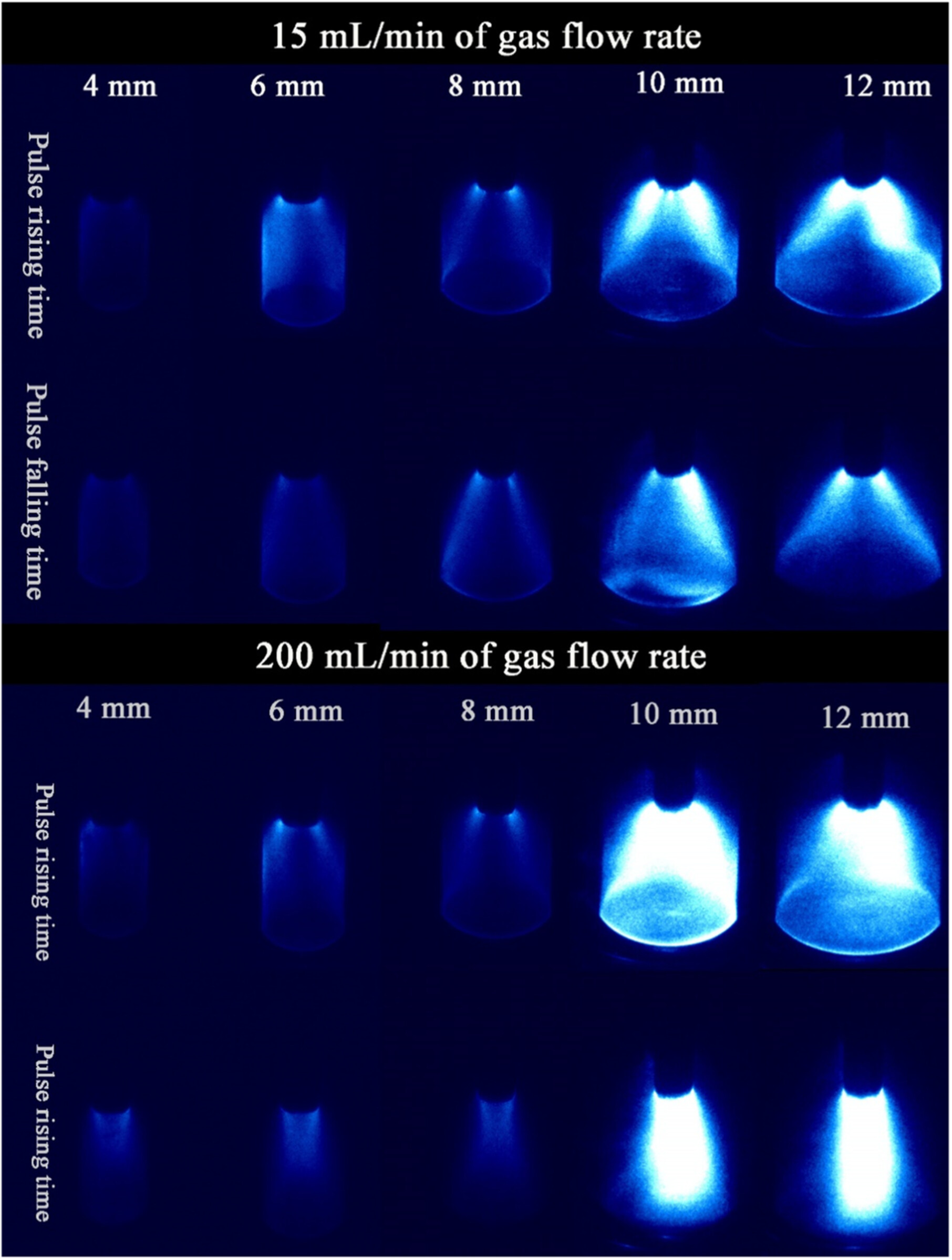
Nanosecond pulsed discharge in contact with the liquid generated in a quartz tube propagates radially to inner surface of the tube during the pulse rising time, contracted toward the axial direction of the quartz tube at pulse falling time.
The discharge diffusive is increased significantly by an appropriate combination of quartz tube diameter and gas flow rate.
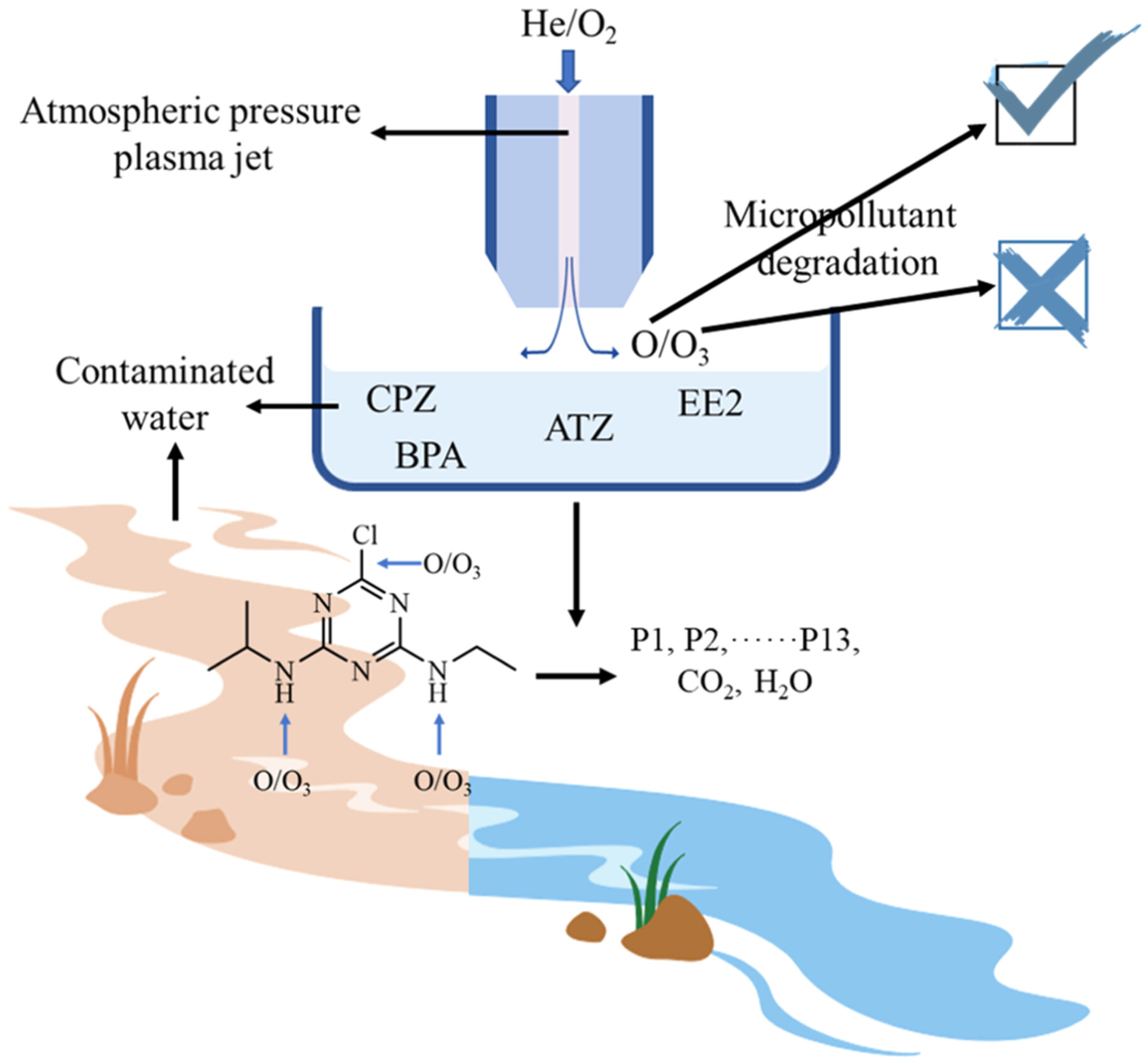
Degradation of Micropollutants in Water by O Atoms Produced by an Atmospheric Pressure He/O2 Plasma Jet
- First Published: 02 December 2024
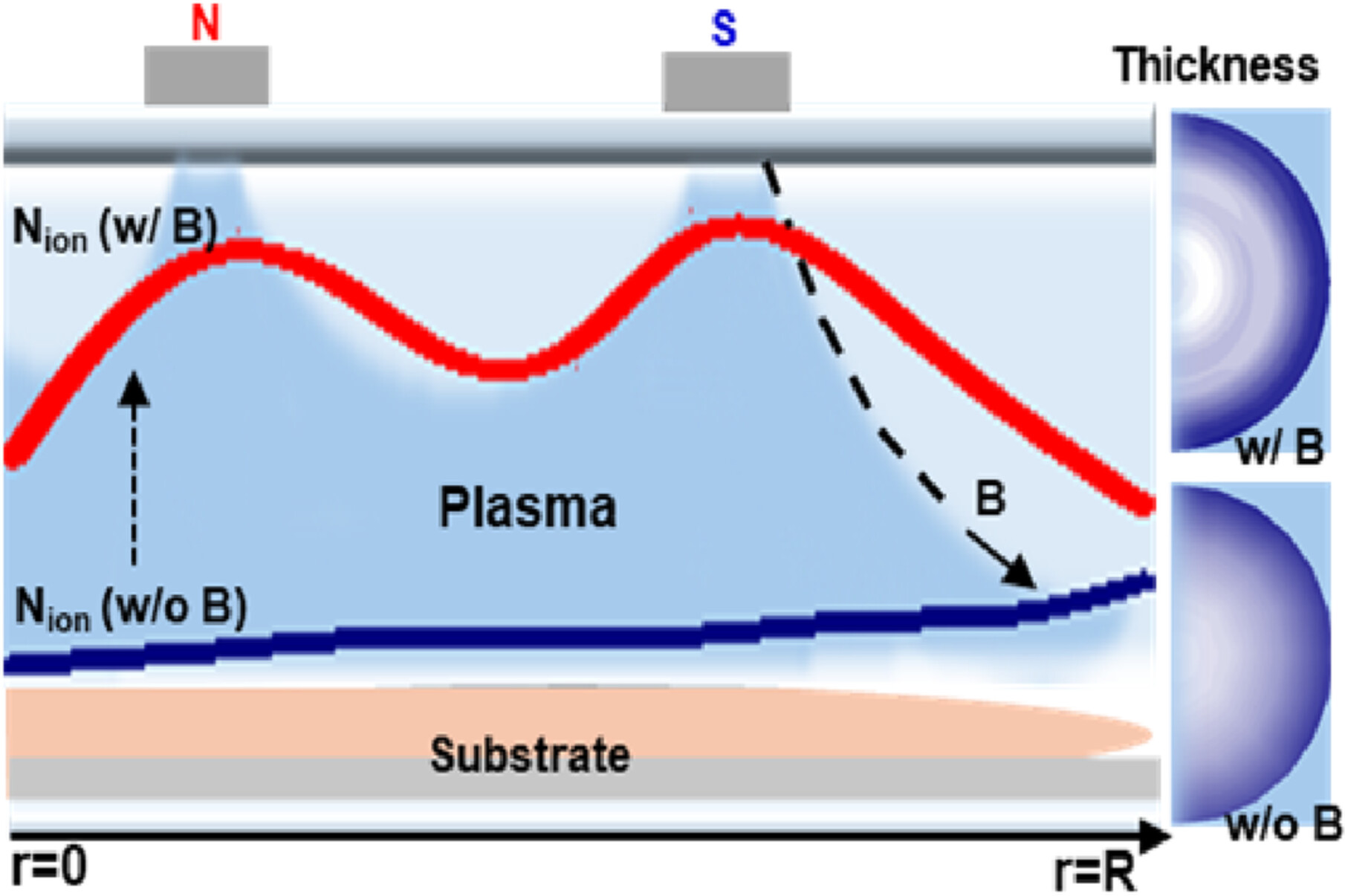
Impact of Inhomogeneous Magnetic Fields on Polymer Deposition in Low-Pressure Capacitively Coupled Ar/C4F8 Plasma
- First Published: 04 December 2024
Surface Passivation of Silicon Nanoparticles Monitored by In Situ FTIR
- First Published: 08 December 2024
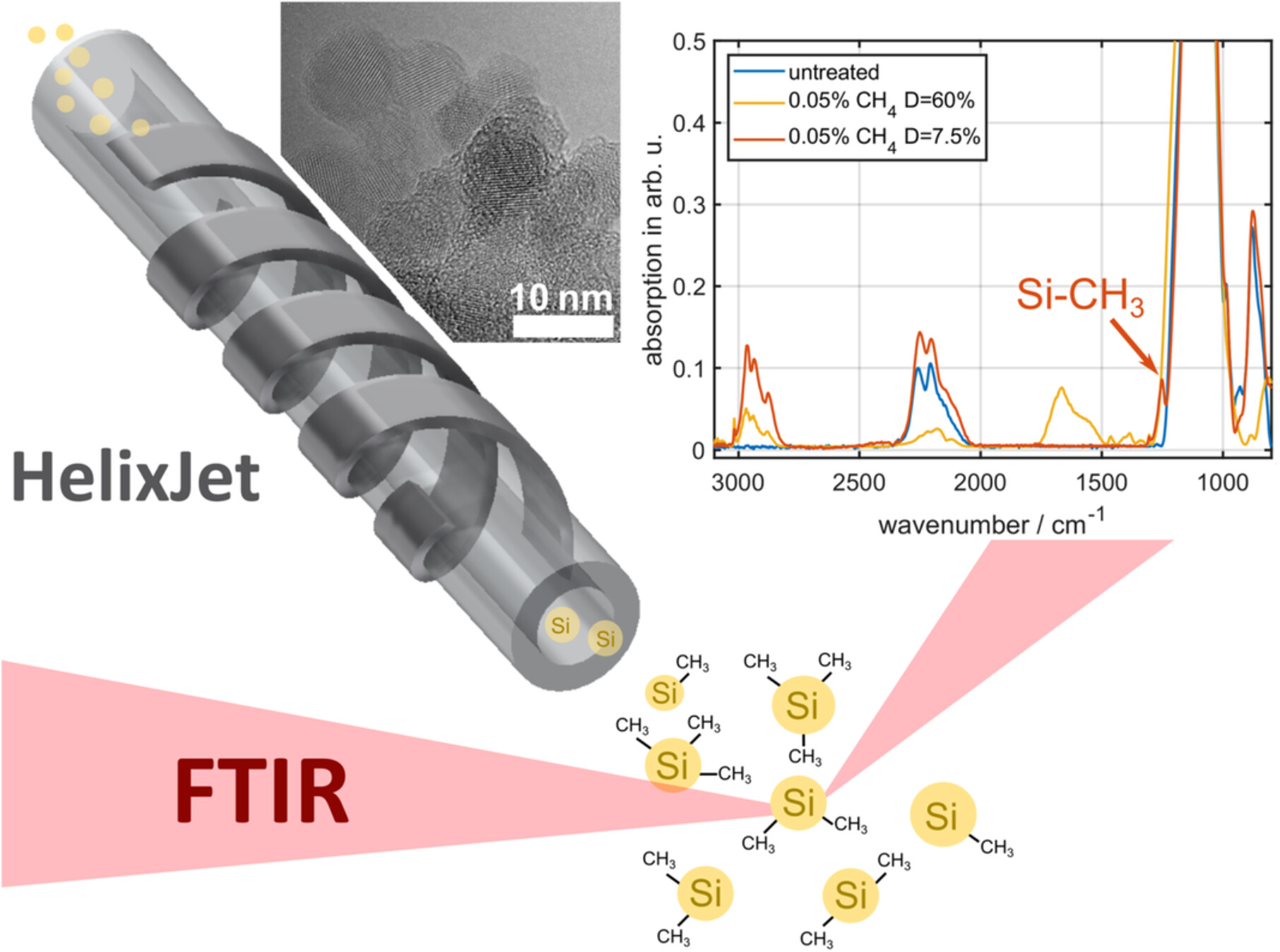
Atmospheric pressure plasmas are a cost-effective alternative to low-pressure systems for the subsequent synthesis and surface passivation of nanocrystals with optical qualities. In this study, we report on a combined system for the synthesis of silicon nanoparticles and their surface passivation using a pulsed methane plasma. The chemical composition of the particles is analyzed in situ using a reflective FTIR setup. Depending on the duty cycle of pulsed methane plasma, methylation on the silicon nanoparticle surface is induced or amorphous carbon growth on the nanoparticles is achieved.
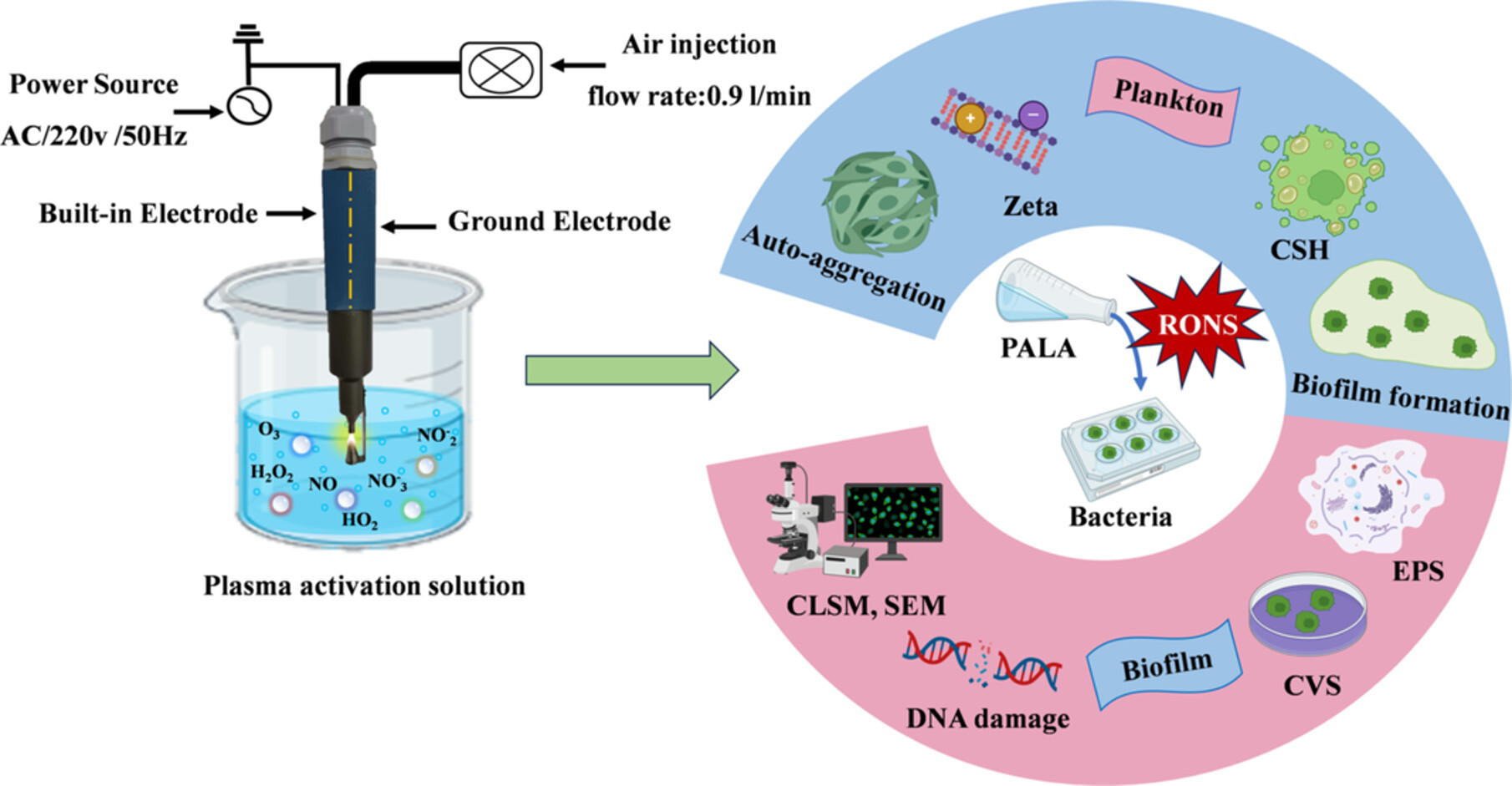
Decontamination Effect of Plasma-Activated Lactic Acid on Biofilm Formation of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa and Listeria Monocytogenes
- First Published: 15 December 2024
Selective Killing of Human Breast Cancer Cells by Plasma-Treated L-Arginine Solution
- First Published: 22 December 2024
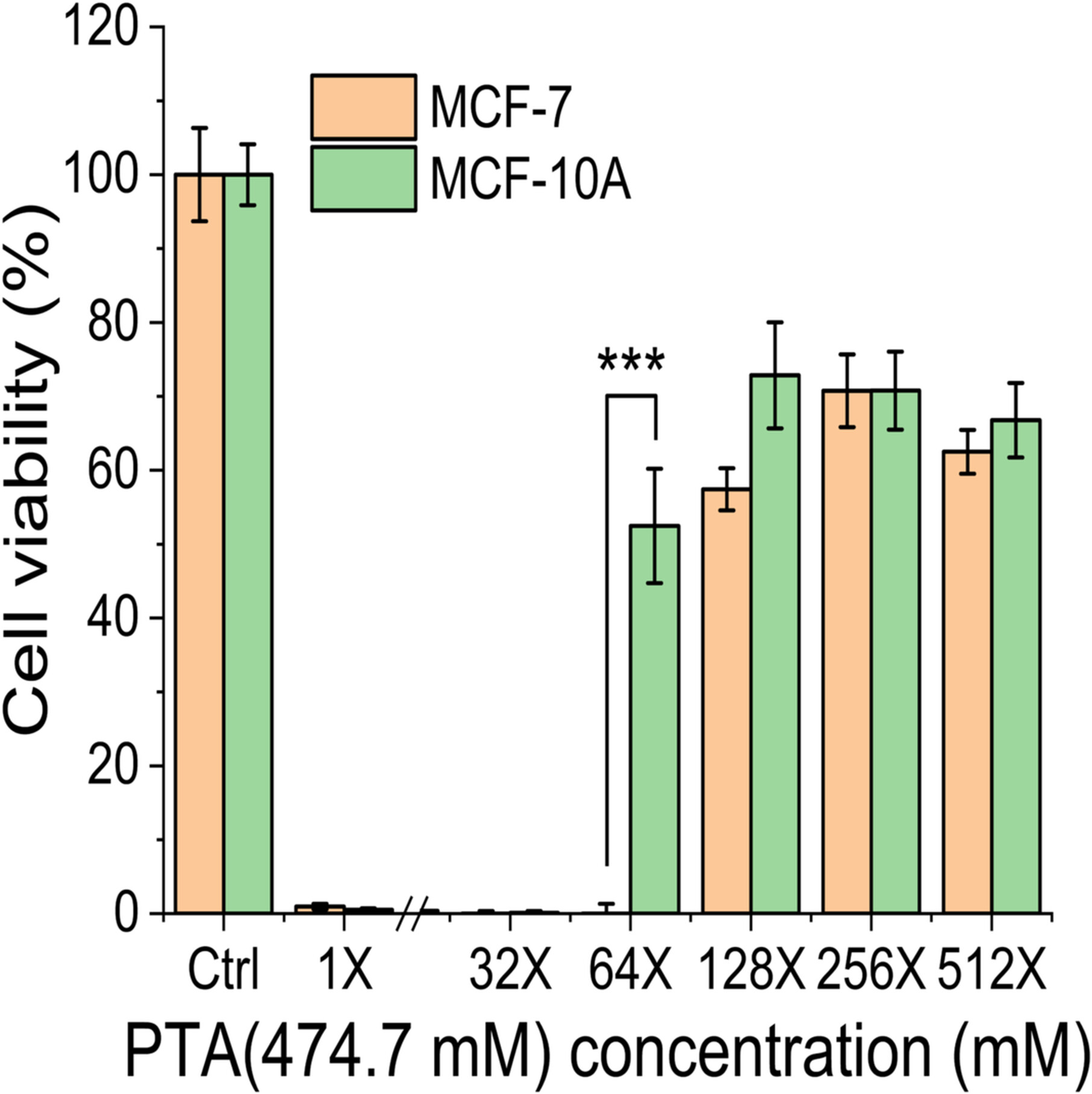
PTA solution showed a selective killing effect on breast cancer MCF-7 cells, and this research studied its mechanism by analyzing the newly formed compounds in PTA and their cytotoxicity. The synergistic and antagonism effects of several identified compounds showed a preliminary result of selective killing effects.
Using Air Plasma-generated High-Valence NOx for Olive Oil Activation to Produce High-Performance Antimicrobial Agents
- First Published: 29 December 2024
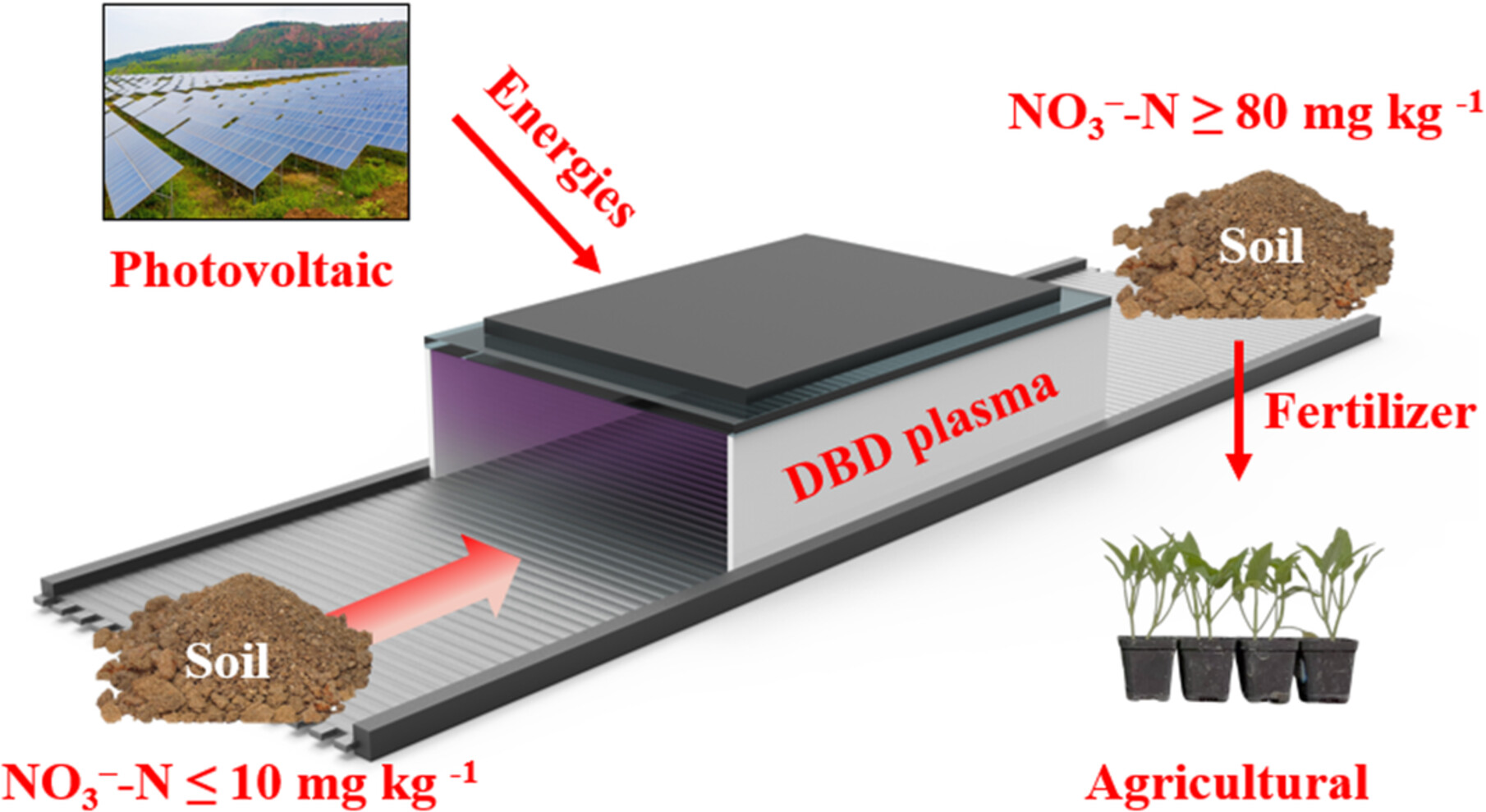
Direct Nitrogen Fixation in Air Over Soil Using Dielectric Barrier Discharge Plasma for Enhanced Plant Growth
- First Published: 30 December 2024
Plasma-Assisted Nitrogen Fixation for Mars: A Simulation Study on in Situ Resource Utilization
- First Published: 30 December 2024
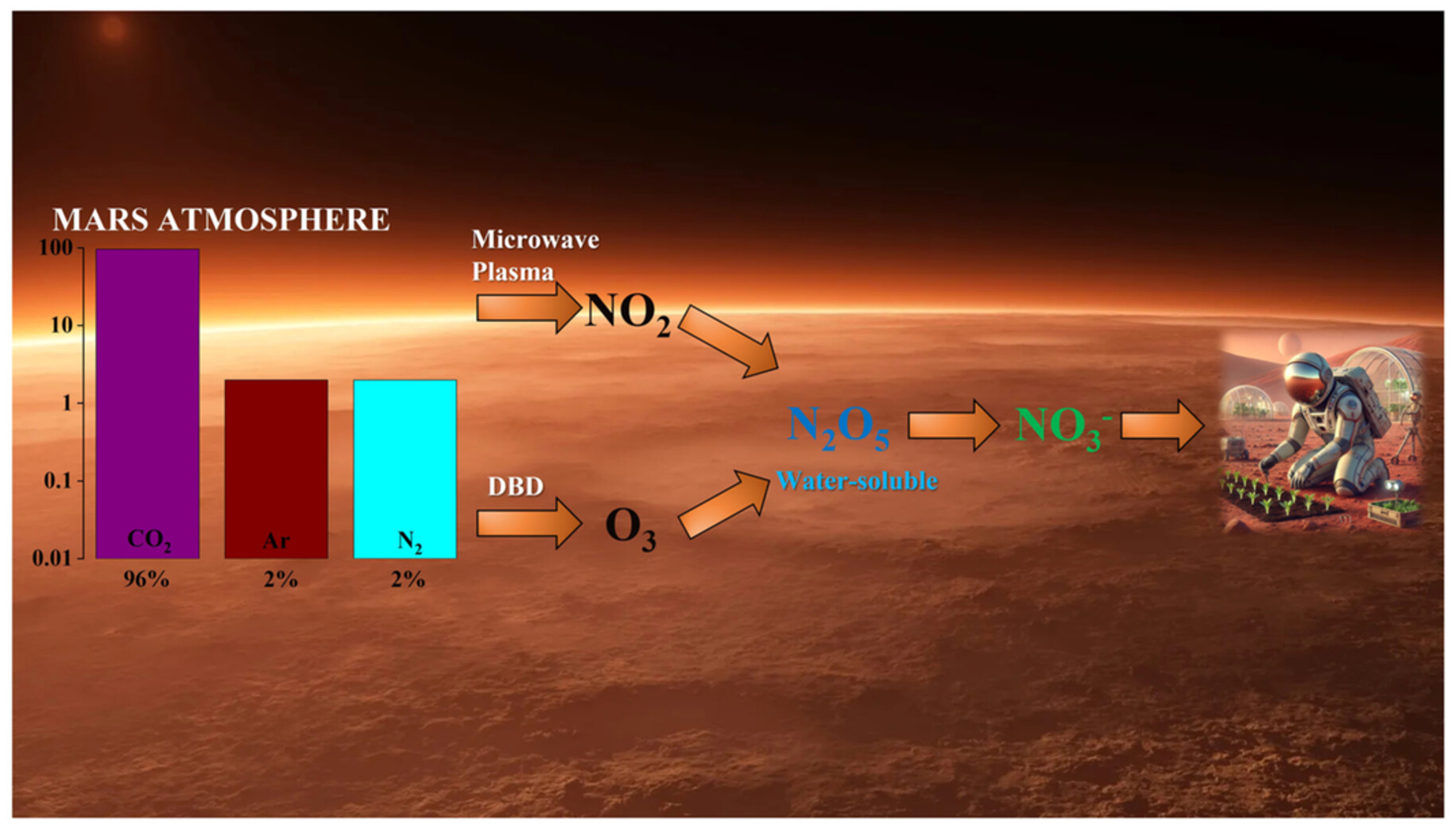
This study examines the simulation methods for nitrogen fixation in the Martian atmosphere using plasma technology. By integrating microwave discharge with dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) techniques, nitrogen and CO2 from the Martian atmosphere are successfully converted into water-soluble nitrogen fertilizer (N₂O₅), suitable for agricultural applications.
Plasma Polymerization of Pentane and Hexane for Antibacterial and Biocompatible Thin Films
- First Published: 30 December 2024
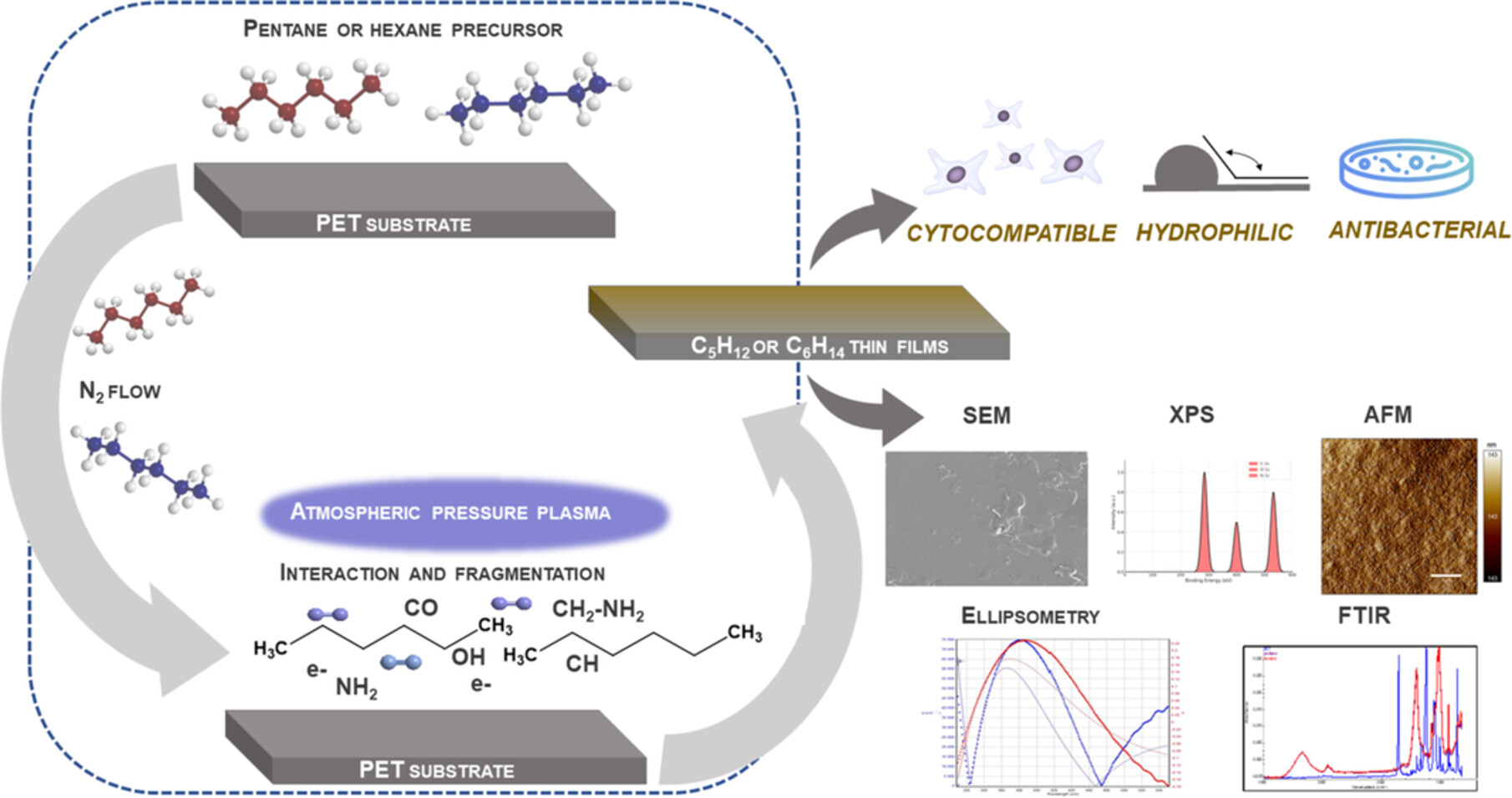
Atmospheric plasma polymerization using pentane and hexane creates antibacterial, biocompatible thin films on PET surfaces. The superhydrophilic coatings, achieved without complex chemicals, provide a scalable solution to prevent bacterial adhesion, making them promising for biomedical applications, especially in medical devices susceptible to biofilm formation.
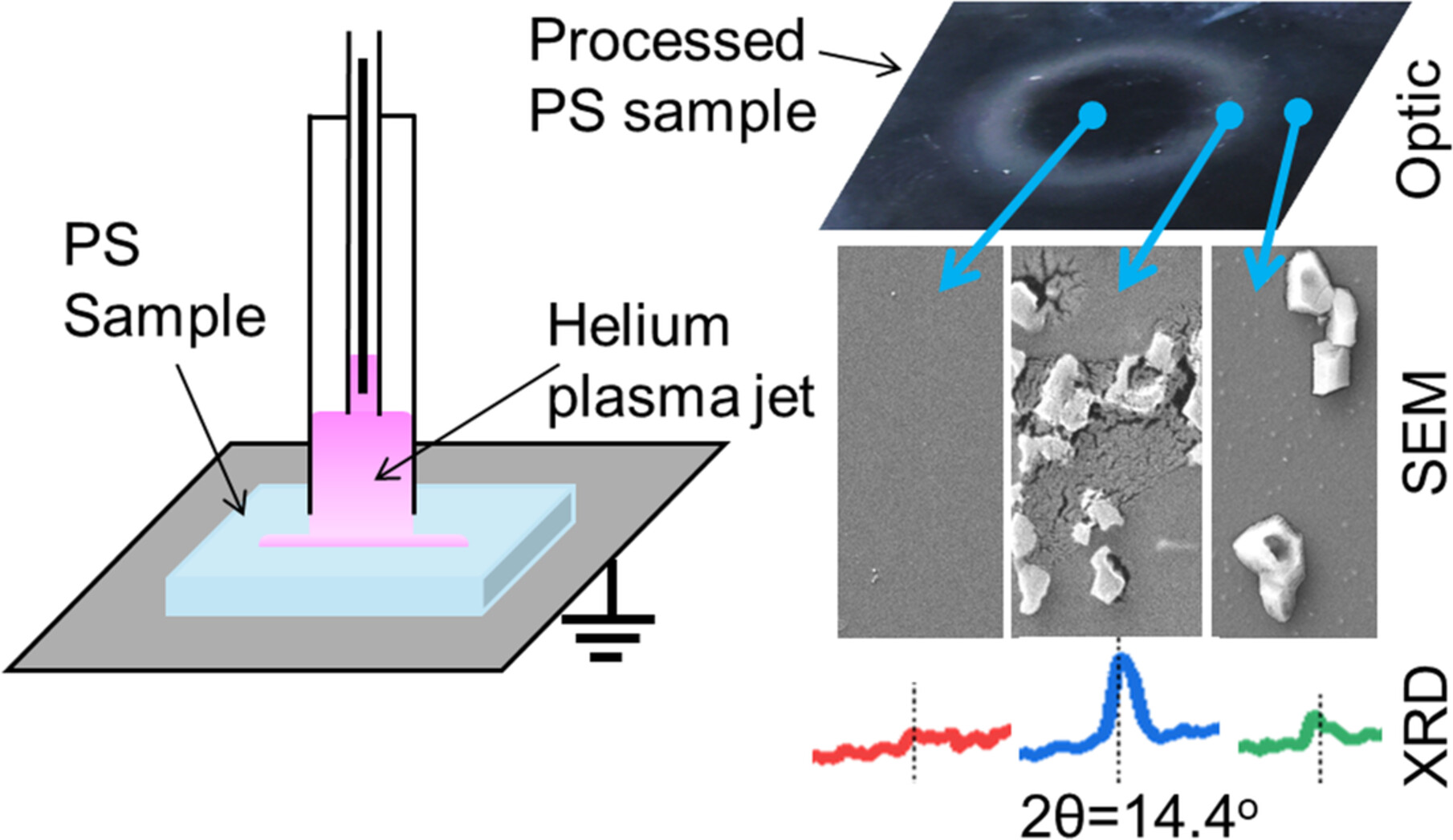
Interaction of an Open-To-Air Helium Plasma Jet, Produced by Sub-Microsecond Discharges, With a Polystyrene Surface
- First Published: 02 January 2025
Reactive Species Production and Colon Cancer Cytotoxicity of an Electrosurgical Cold Argon Plasma Device
- First Published: 05 January 2025
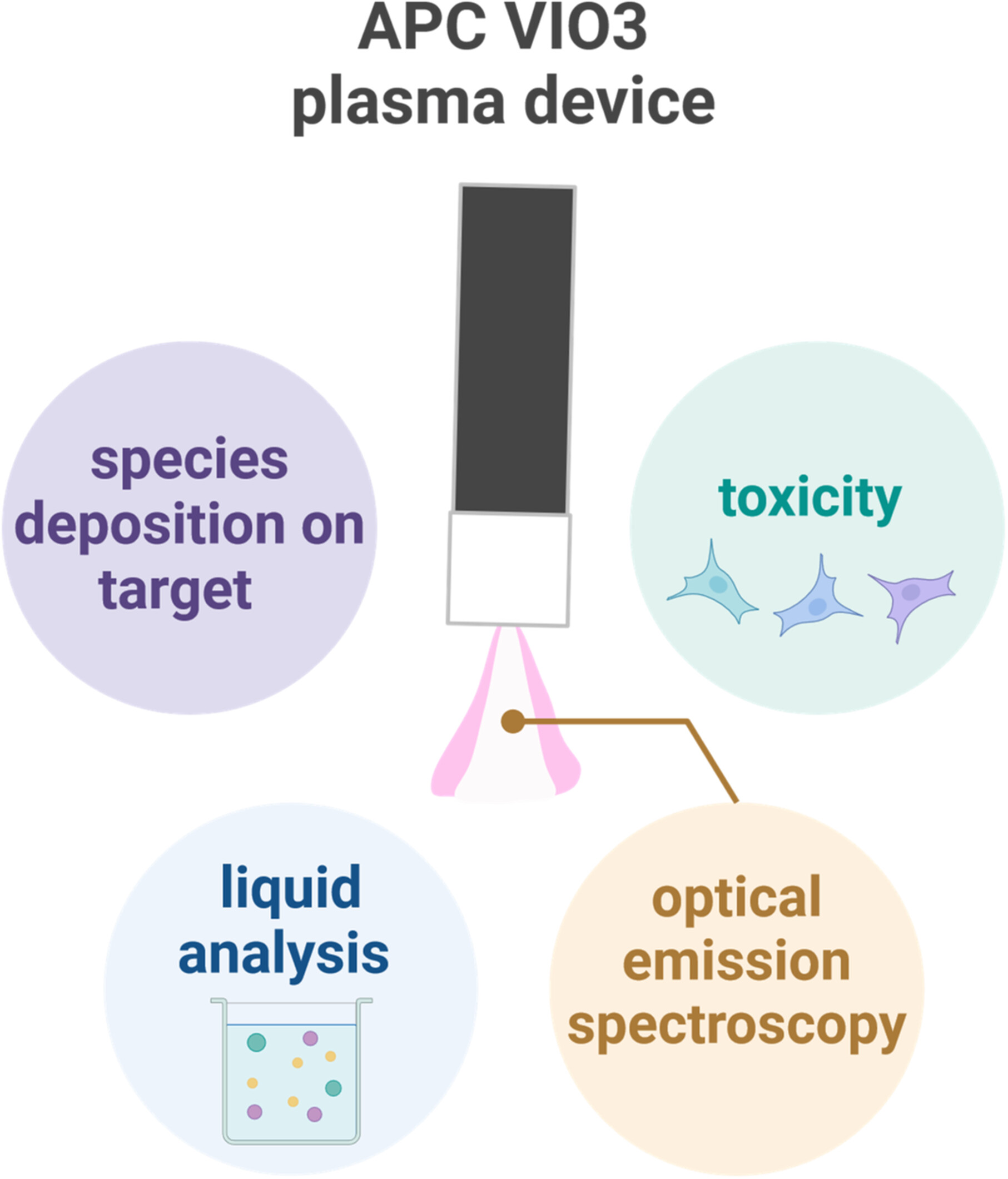
We investigated an electrosurgical argon plasma device with a novel parameter set allowing its operation at lower temperatures. We studied the device's ability to generate reactive species and measured their penetration into hydrogels and human HT29 colon cancer cell toxicity to preliminarily assess the cold mode's potential in gastrointestinal oncology.
Quantitative Measurement of Surface Oxidation of Polypropylene by O Atoms: Increase and Subsequent Decrease in Hydrophilicity Induced by O-Atom Treatment
- First Published: 05 January 2025

Oxidation of polypropylene surfaces by O atoms initially reduces the water contact angle (WCA) on the surface but subsequently causes the WCA to increase. The changes in the WCA reduction and increase rates with respect to the density and flux of O atoms are examined. Their mechanism is also discussed.
Investigation on Plasma Characteristics and In-Flight Spheroidization Boron Carbide Powders in Radio Frequency Inductively Coupled Plasma
- First Published: 06 January 2025
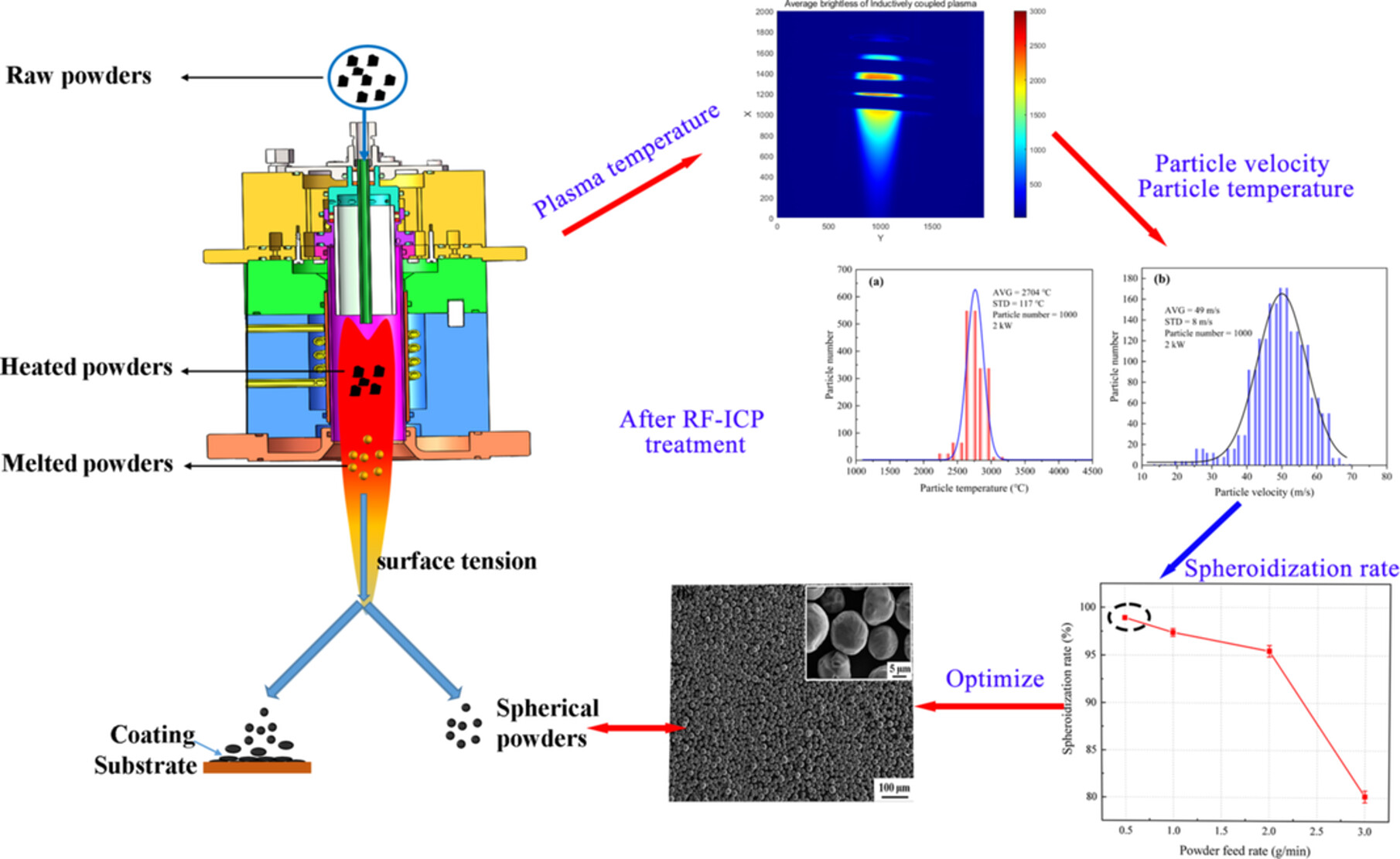
The radio frequency driven inductively coupled plasma (RF-ICP) spheroidizes boron carbide (B4C) powders, enhancing powder sphericity and coating uniformity. The B4C powder after RF-ICP treatment, particularly those with high particle temperatures and particle velocities, demonstrate higher spheroidization rates and better sphericity.
Reactive Molecular Dynamics Simulation on Interaction Mechanisms of Cold Atmospheric Plasma and Phosphatidylcholine in Cell Membrane Structure
- First Published: 04 February 2025
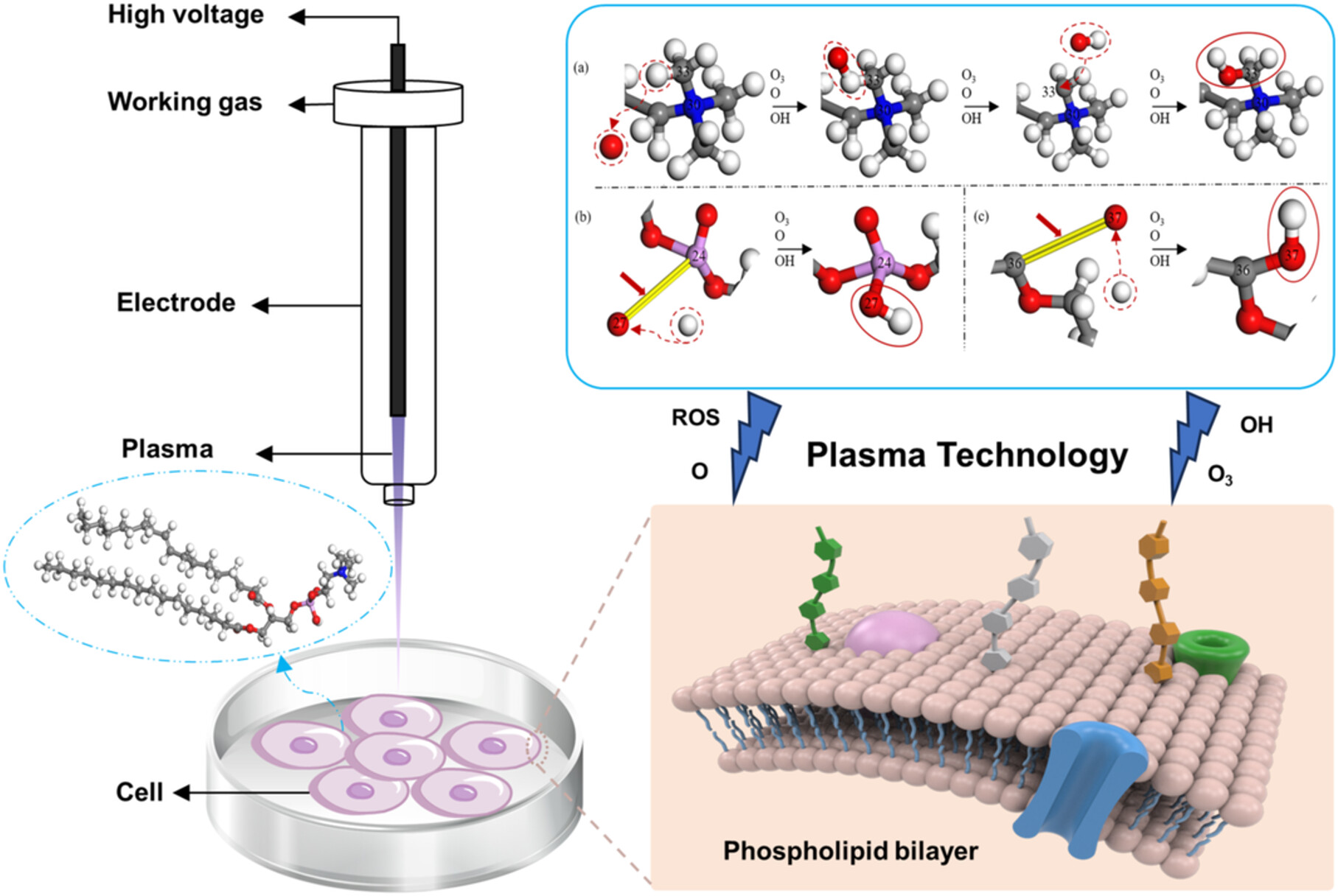
The cell membrane serves as the first line of defense for cancer cells. In this study, the primary constituent of the membrane, phosphatidylcholine (POPC), is used as the reaction model. The lipid oxidative stress interaction mechanism of ROS (specifically O atoms, OH radicals, and O3 molecules) with POPC at the molecular level is investigated by reactive molecular dynamics (MD) simulation. The computational data provide the detailed oxidative process of lipid oxidation of POPC induced by CAP and fundamental insights for optimizing CAP to effectively inactivate cancer cells.