Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Chronic endometritis: Really so relevant in repeated IVF failure?
- First Published: 16 September 2017
REVIEW
Undifferentiated connective tissue diseases and adverse pregnancy outcomes. An undervalued association?
- First Published: 16 September 2017
IMMUNE CELLS AND PREGNANCY
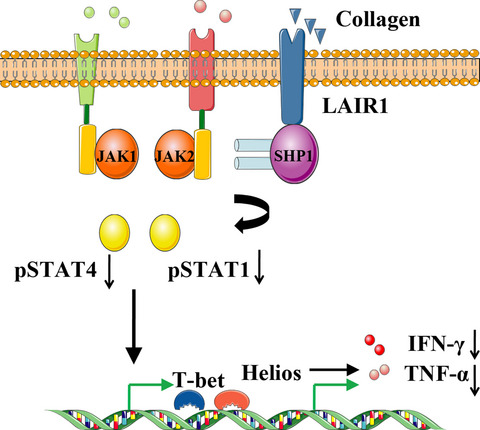
Involvement of the JAK-STAT pathway in collagen regulation of decidual NK cells
- First Published: 04 October 2017
Comparison of the percentages of CD4+ CD25high FOXP3+, CD4+ CD25low FOXP3+, and CD4+ FOXP3+ Tregs, in the umbilical cord blood of babies born to mothers with and without preeclampsia
- First Published: 16 September 2017
Expansion of CD4 phenotype among CD160 receptor-expressing lymphocytes in murine pregnancy
- First Published: 16 September 2017
INFECTION AND REPRODUCTION
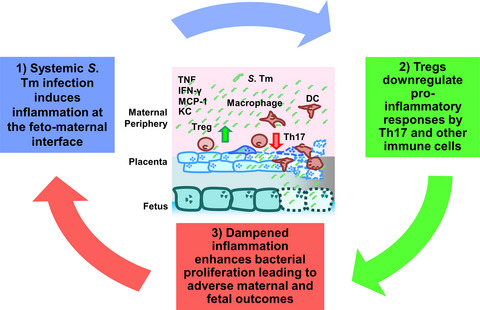
Modulation of Th17 and regulatory T-cell responses during murine pregnancy contributes to increased maternal susceptibility to Salmonella Typhimurium infection
- First Published: 09 October 2017
Chlamydia trachomatis regulates innate immune barrier integrity and mediates cytokine and antimicrobial responses in human uterine ECC-1 epithelial cells
- First Published: 16 September 2017
Distinct peripheral vs mucosal T-cell phenotypes in chlamydia-infected women
- First Published: 26 September 2017
IMMUNOLOGICAL FACTORS IN PREGNANCY
Transcription factor CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-β upregulates microRNA, let-7f-1 in human endocervical cells
- First Published: 16 September 2017
The extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 triggers angiogenesis in human ectopic endometrial implants by inducing angioblast differentiation and proliferation
- First Published: 16 September 2017
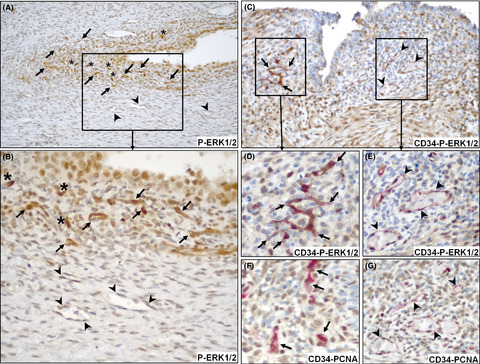
Increased ERK1/2 phosphorylation (P-ERK1/2) is involved in endothelial progenitor cell (angioblast) differentiation and proliferation in endometriosis. Several individual cells (asterisks) and cell clusters of vascular like structures (presumptive vessels; arrows) display the strongest P-ERK1/2 immunoreactivity in the ectopic endometrium, whereas endothelial cells in distal to ectopic tissue (arrowheads) exhibit weak to moderate P-ERK1/2 immunoreactivity (A, B). CD34, an angioblast marker and P-ERK1/2 double immunostaining is seen in ectopic endometrial specimens (C-E) with stronger P-ERK1/2 (brown) immunoreactivity in CD34 immunoreactive (red) endothelial progenitor cells (arrows; C or D) vs. mature vascular endothelial cells (arrowheads in C or E). Representative photomicrographs of CD34 and PCNA double immunostained ectopic endometrial specimens display stronger co-expression of CD34 (red) and PCNA (brown) in endothelial progenitor cells (arrows; F) than in mature vascular endothelial cells (arrowheads; G), indicating proliferative nature of this CD34 immunoreactive angioblasts.
CLINICAL ASPECTS OF REPRODUCTIVE IMMUNOLOGY
Successful treatment with intrauterine delivery of dexamethasone for repeated implantation failure
- First Published: 16 September 2017
IMMUNOGENETICS OF PREGNANCY
A Single Nucleotide Polymorphism of DNA methyltransferase 3B gene is a risk factor for recurrent spontaneous abortion
- First Published: 20 September 2017