Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Specific targeting and noninvasive magnetic resonance imaging of an asthma biomarker in the lung using polyethylene glycol functionalized magnetic nanocarriers
- Pages: 172-183
- First Published: 28 December 2015
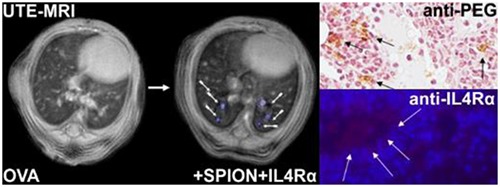
PEG-functionalized anti-IL4Rα-conjugated SPIONs allowed enhanced targeting of IL4Rα asthma biomarker in the lung. Noninvasive free-breathing UTE-MRI allowed monitoring of the developed magnetic nanocarriers, which co-localized with the inflammatory sites. Enhanced targeting to areas rich in IL4Rα positive inflammatory cells was confirmed using histological analyses
MRI monitoring of nanocarrier accumulation and release using Gadolinium-SPIO co-labelled thermosensitive liposomes
- Pages: 184-194
- First Published: 11 January 2016
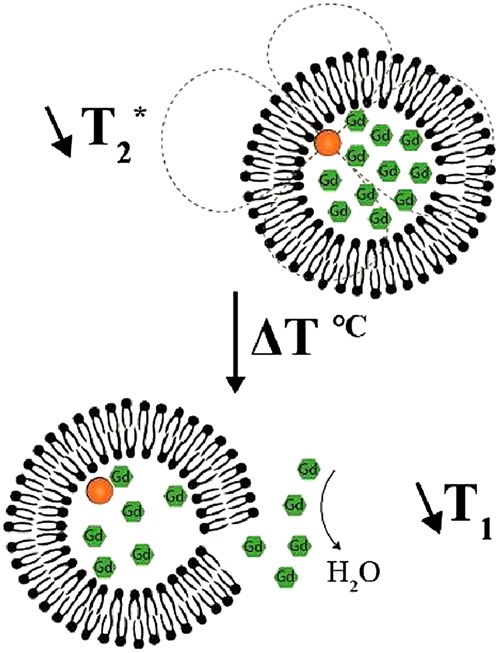
While the T2* shortening effect arising from the encapsulated iron oxide nanoparticles into the nanocarrier allow or detect the presence of thermosensitive liposome carrier, its content release could have been characterized based on the independent T1 or T2 shortening gadolinium release-induced effect.
A method for accurate pH mapping with chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) MRI
- Pages: 195-202
- First Published: 21 December 2015
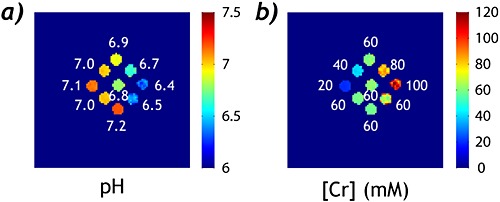
RF power-based ratiometric analysis of spillover effect-corrected inverse CEST asymmetry (PRICEST) provides enhanced pH measurement over the recently proposed RF power-based ratiometric (PRCEST) imaging. The difference between MRI-determined pH (pHMRI) and electrode-measured pH is 0.12±0.13 and 0.04±0.03 for PRCEST and PRICEST imaging, respectively. The derived labile proton ratio linearly scales with creatine concentration, and the exchange rate shows dominantly base-catalyzed relationship with pH, independent of creatine concentration. Hence, PRICEST quantitative CEST MRI augments pH imaging.
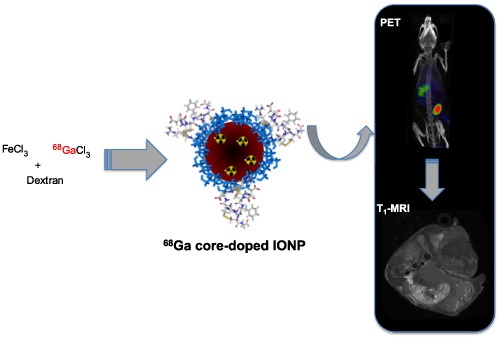
Fast synthesis and bioconjugation of 68Ga core-doped extremely small iron oxide nanoparticles for PET/MR imaging
- Pages: 203-210
- First Published: 08 January 2016
Early detection of colonic dysplasia by magnetic resonance molecular imaging with a contrast agent raised against the colon cancer marker MUC5AC
- Pages: 211-221
- First Published: 14 January 2016
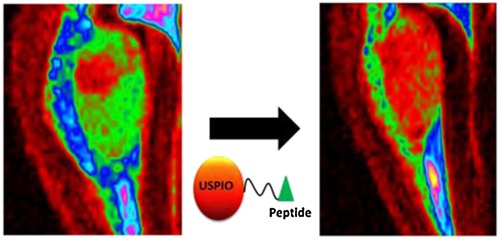
SIRB, sans iron oxide rhodamine B, a novel cross-linked dextran nanoparticle, labels human neuroprogenitor and SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells and serves as a USPIO cell labeling control
- Pages: 222-228
- First Published: 25 January 2016
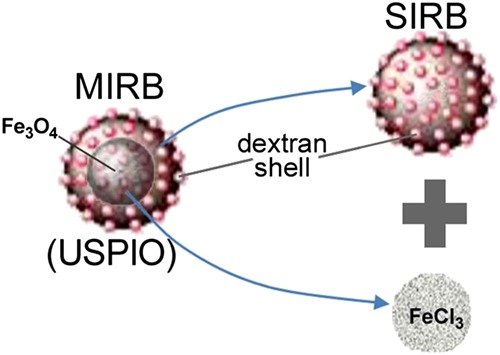
SIRB is a new cross-linked dextran nanoparticle that does not contain Fe3O4. SIRB is designed to provide all of the cell labeling properties of the ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide (USPIO) nanoparticle Molday ION Rhodamine B (MIRB). SIRB possesses a similar size, charge, and cross-linked dextran coating to MIRB. SIRB does not alter cellular viability, proliferation, or differentiation. SIRB can be used to label cells as a control to check the toxicity of the surface coating surrounding the iron oxide core.
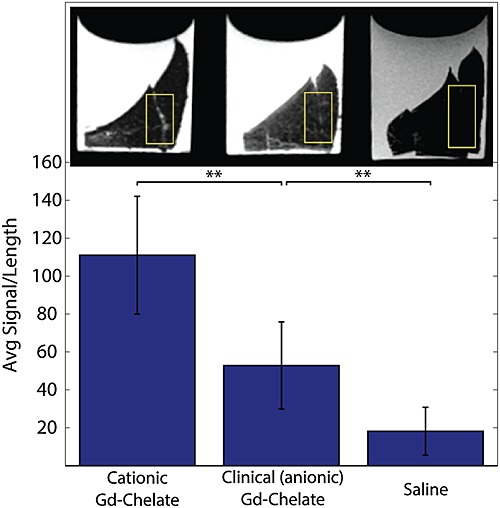
Cationic gadolinium chelate for magnetic resonance imaging of cartilaginous defects
- Pages: 229-235
- First Published: 08 February 2016
Evaluating the effectiveness of transferrin receptor-1 (TfR1) as a magnetic resonance reporter gene
- Pages: 236-244
- First Published: 29 February 2016
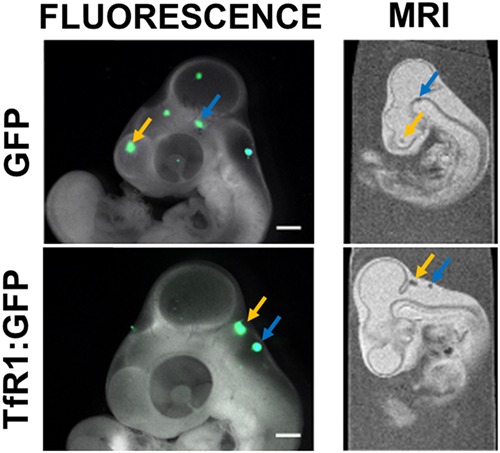
We evaluate transferrin receptor-1 (TfR1) as an MR reporter gene in the model cell line CHO-K1. Although under standard culture conditions iron levels increase significantly on overexpression of this gene, we found that medium supplementation with iron sources results in dramatically higher levels of intracellular iron and MR contrast, irrespective of the reporter. We conclude that TfR1 is not an effective reporter, and that for short-term cell tracking it is sufficient to simply supplement culture medium with ferric citrate.
High signal intensity in dentate nucleus and globus pallidus on unenhanced T1-weighted MR images in three patients with impaired renal function and vascular calcification
- Pages: 245-250
- First Published: 11 January 2016
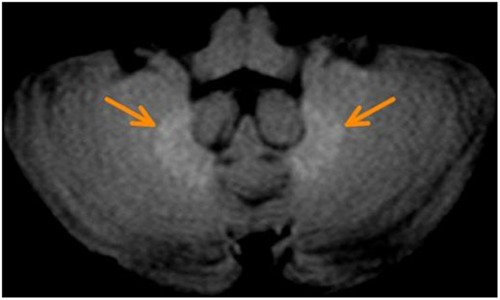
We report on three patients with impaired renal function and vascular calcification (two with confirmed nephrogenic systemic fibrosis) whose unenhanced T1-weighted MRIs showed conspicuous high signal intensity in the dentate nucleus and the globus pallidus after they had been exposed to relatively low doses of linear gadolinium-based contrast agents (0.27, 0.45, and 0.68 mmol/kg). Of note, all three analysed patients suffered from transient signs of neurological disorders of undetermined cause.