Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information - TOC
Issue Information - JIP
Editorial
IJSCN special issue on Ka band and high throughput satellites
- Pages: 459-460
- First Published: 18 February 2016
Special Issue Papers
Towards the Terabit/s satellite – interference issues in the user link
- Pages: 461-482
- First Published: 17 June 2015
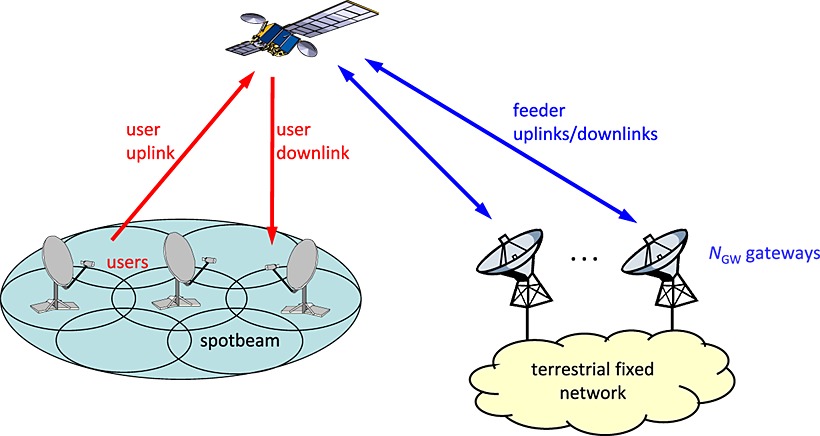
Present high-capacity geostationary satellites provide throughput up to 140 Gb/s (ViaSat-1, EchoStar 17). In order to keep up with the quickly increasing bit rate requirements of new services, future communication satellites must increase their capacity to the terabit/s throughput range. This paper discusses the main interference effects occurring in the user uplinks and downlinks of a multi-beam satellite: co-channel interference, adjacent-channel interference and cross-polarisation interference. Different cluster sizes for the beam pattern and use of dual polarisations are considered.
Ka band enabling technologies for high throughput satellite (HTS) communications
- Pages: 483-501
- First Published: 26 November 2015

Satellite communications are ever evolving by leveraging newer Ka frequency bands, sophisticated payload processing technologies and higher capacity architectures to keep up with an insatiable global thirst for real-time connectivity in our un-plugged world. These developments have resulted in a newer class of overhead wireless communication known as high throughput satellites (HTS). While a foundational corner stone for enhanced HTS is the migration to Ka-band, application of advanced technologies is enabling the creation of a newer class of HTS. With the potential of exceeding total throughput of 100's of Gbps, this paper explores some of the adaptive, agile and infrastructure technologies that will make the next generation of HTS possible.
Architectures for next generation high throughput satellite systems
- Pages: 523-546
- First Published: 27 January 2016
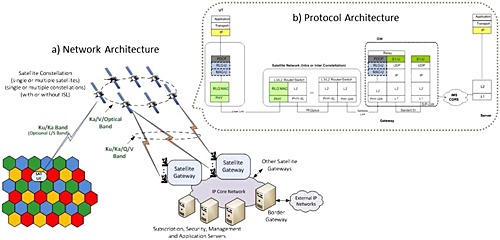
This paper presents a model to estimate aggregate system capacity as a function of radio band, available spectrum, spot beams, waveforms, and payload capability comprising antenna size, power, and digital/analog connectivity across various links and availability objectives for next-generation high throughput satellite systems. This paper presents architectural building blocks for next-generation high throughput satellite systems using low earth, medium earth, and geosynchronous orbit satellite constellations, with and without onboard processing and inter-satellite links. This paper describes a system implementation approach using industry standards such as DVB-S2X and 4G LTE.
Performance, cost analysis, and ground segment design of ultra high throughput multi-spot beam satellite networks applying different capacity enhancing techniques
- Pages: 547-573
- First Published: 01 March 2016
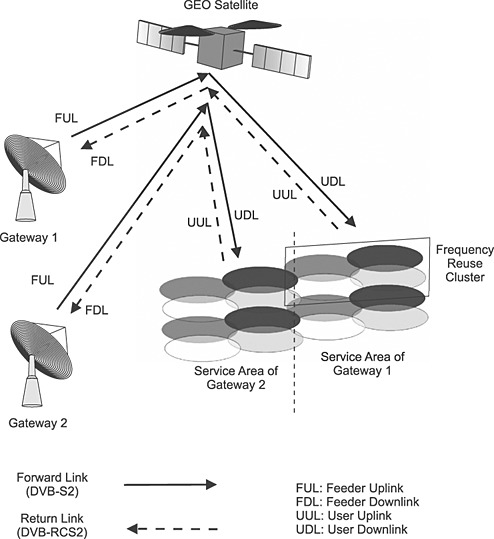
The present paper identifies and analyzes ground segment capacity-enhancing techniques for ultra-high-throughput multi-spot beam satellite networks operating in Q/V-band in the feeder link and in Ka-band in the user link. The impact of several capacity-enhancing techniques on system performance is analyzed using a realistic time step-based system simulator. Their impact on the ground segment costs is also analyzed.
From S-band mobile interactive multimedia to fixed satellite interactive multimedia: making satellite interactivity affordable at Ku-band and Ka-band
- Pages: 575-601
- First Published: 03 November 2015
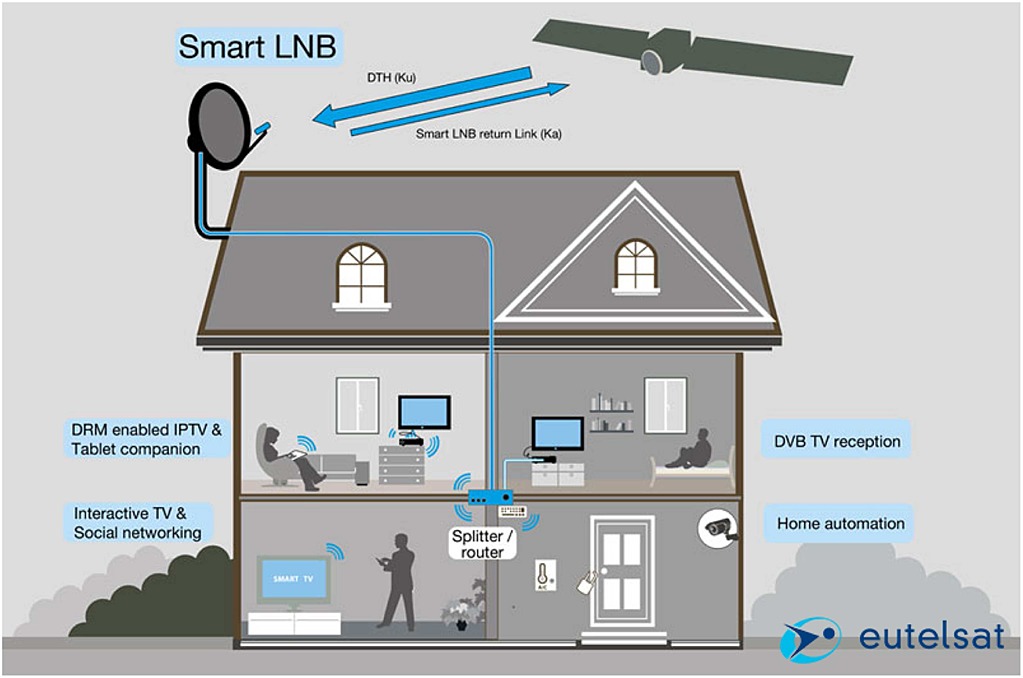
The figure shows a typical user terminal implementing fixed interactive multimedia services (F-SIM). The Smart low noise block (LNB) provides Internet protocol (IP) connectivity to the users' network. The user is able to get access to interactive multi-media systems exploiting the F-SIM protocols and a small dish. All radio frequency and baseband processing functions are integrated in the outdoor unit (ODU), which communicates with an indoor unit (IDU) via a normal coaxial cable.





