Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Characteristics of tissue temperature during ablation with THERMOCOOL SMARTTOUCH SF versus TactiCath versus QDOT MICRO catheters (Qmode and Qmode+): An in vivo porcine study
- Pages: 7-15
- First Published: 05 October 2023
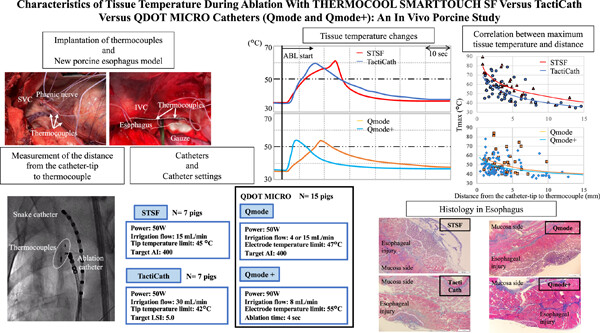
We aimed to investigate differences in tissue temperature characteristics during radiofrequency ablation using three catheters, commonly employed in the 50 W high-power short-duration (HPSD) setting and a 90 W/4 s very HPSD setting catheter. We identified temperature variations across the four ablation settings and their association with collateral damage, including injuries to the esophagus and phrenic nerve. These findings provide valuable insights into the safety and effectiveness of RF ablation across various settings.
Comparison of transseptal puncture using a dedicated RF wire versus a mechanical needle with and without electrification in an animal model
- Pages: 16-24
- First Published: 27 October 2023
Comparison of the effect of ethanol infusion into the vein of Marshall between with and without collateral veins
- Pages: 25-34
- First Published: 27 October 2023
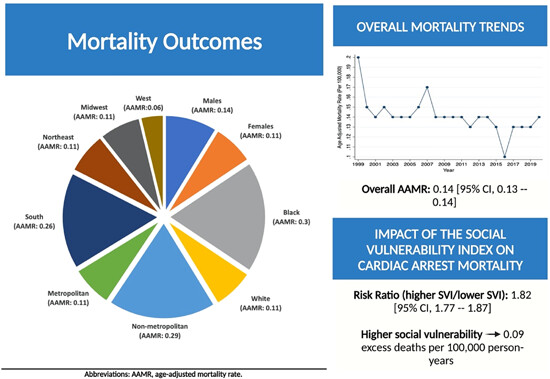
Mortality trends, disparities, and social vulnerability in cardiac arrest mortality in the young: A cross-sectional analysis
- Pages: 35-43
- First Published: 03 November 2023
Impact of intracardiac echocardiography versus transesophageal echocardiography guidance on left atrial appendage occlusion procedures: A meta-analysis
- Pages: 44-57
- First Published: 05 November 2023
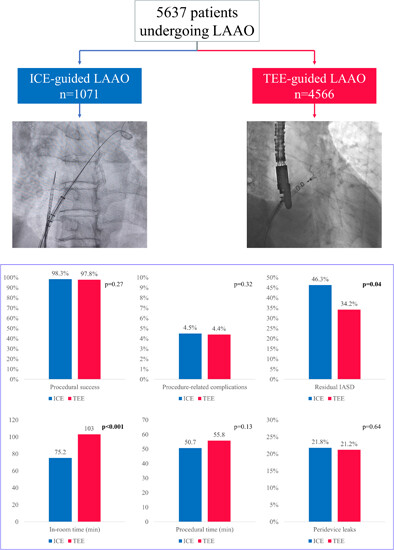
In this meta-analysis, left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO) using intracardiac echocardiography (ICE) guidance resulted in a similar procedural safety and efficacy as transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) guidance. ICE-guidance resulted in shorter in-room time, without significant differences in procedural and fluoroscopy time. During follow-up, there was no difference in peri-device leaks, with a significantly higher risk of residual interatrial septal defects in the ICE-guided group.
EDITORIAL
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Lower contact force predicts right pulmonary vein carina breakthrough after ablation index-guided pulmonary vein isolation using high-power short-duration
- Pages: 60-68
- First Published: 27 October 2023
The impact of early cryoballoon ablation on clinical outcome in patients with atrial fibrillation: From the Korean cryoballoon ablation registry
- Pages: 69-77
- First Published: 05 November 2023
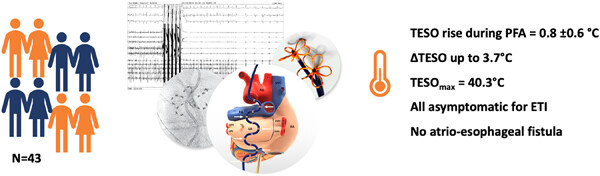
Impact of pulsed field ablation on intraluminal esophageal temperature
- Pages: 78-85
- First Published: 09 November 2023
Pulsed-field ablation does not induce esophageal and periesophageal injury—A new esophageal safety paradigm in catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation
- Pages: 86-93
- First Published: 17 November 2023
EDITORIAL
Have the cake and eat it too: PFA, a case of a technological miracle?
- Pages: 94-96
- First Published: 30 November 2023
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Clinical outcomes and predictors of delayed echocardiographic response to cardiac resynchronization therapy
- Pages: 97-110
- First Published: 27 October 2023
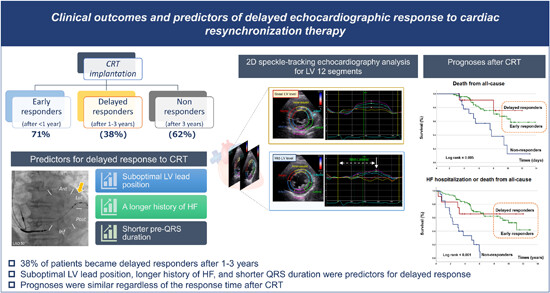
A total of 38% of patients who did not exhibit an echocardiographic response 1 year after CRT implantation experienced a positive response after 3 years. Delayed responders had a similar prognosis of all-cause death and HF hospitalization rates as early responders. Predictors of delayed response compared with early response were a longer duration from initial HF hospitalization to CRT, the non-exact concordant LV lead location to the latest mechanical activation site, and shorter pre-QRS duration.
Initial clinical experience of atrial fibrillation ablation guided by a cryoballoon-compatible, magnetic-based circular catheter
- Pages: 111-119
- First Published: 14 November 2023
Left bundle branch pacing versus left ventricular septal pacing as a primary procedural endpoint during left bundle branch area pacing: Evaluation of two different implant strategies
- Pages: 120-129
- First Published: 14 November 2023
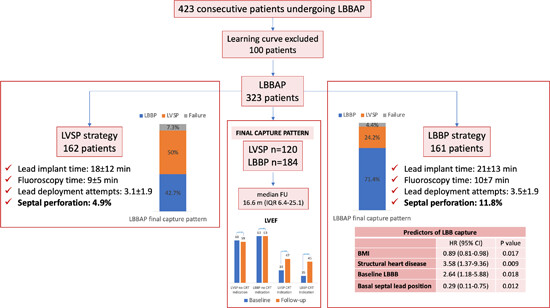
During LBBAP, a strategy aiming to obtain LBB capture in every patient compared to a strategy accepting LVSP as a primary endpoint resulted in comparable implant parameters but higher rates of septal perforation. Patients with proven LBB capture showed a significantly narrow paced QRS but comparable LVEF changes to LVSP.
Catheter ablation of typical atrial flutter improves cardiac chamber size and function
- Pages: 130-135
- First Published: 17 November 2023
High-power short-duration versus low-power long-duration ablation for pulmonary vein isolation: A substudy of the AWARE randomized controlled trial
- Pages: 136-145
- First Published: 21 November 2023
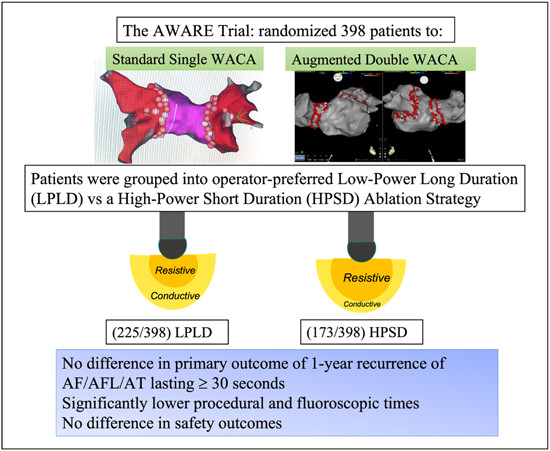
In this large substudy of the AWARE Trial, a high-power short-duration (HPSD) radiofrequency ablation strategy was found to be similarly effective as a low-power long-duration strategy with no difference in time to first recurrence of any AF lasting ≥30 s. Procedural were substantially reduced with HPSD ablation with no significant difference in overall complication rates.
Cardiac resynchronization using fusion pacing during exercise
- Pages: 146-154
- First Published: 27 October 2023
Left atrial strain is a good predictor of atrio-ventricular synchrony in leadless pacemaker pacing
- Pages: 155-161
- First Published: 27 November 2023
Pulsed-field versus cryoballoon ablation for atrial fibrillation—Impact of energy source on sedation and analgesia requirement
- Pages: 162-170
- First Published: 27 November 2023
Clinical impact of left atrial remodeling pattern in patients with atrial fibrillation: Comparison of volumetric, electrical, and combined remodeling
- Pages: 171-181
- First Published: 29 November 2023
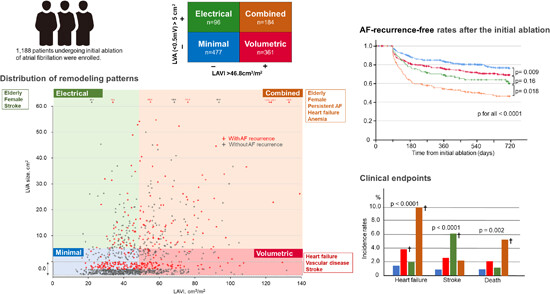
This study included 1188 patients who underwent initial ablation for atrial fibrillation (AF). Patients were divided into four groups by low-voltage area (LVA)-presence and left atrial volume index (LAVI). The distribution of LVA size and LAVI, and clinical characteristics of each group are shown. AF recurrence rates and clinical outcomes are compared between groups.
Comparison of electrogram characteristics in persistent atrial fibrillation
- Pages: 182-197
- First Published: 29 November 2023
Acute procedural efficacy and safety of a novel expandable diameter cryoballoon in atrial fibrillation ablation: Early results from a multicenter ablation registry
- Pages: 198-205
- First Published: 01 December 2023
REVIEW
Cardiac stereotactic radiation therapy for refractory ventricular arrhythmias in patients with left ventricular assist devices
- Pages: 206-213
- First Published: 29 November 2023