Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Articles of Public Interest
Critical Review
Alcohol and Opioid Use, Co-Use, and Chronic Pain in the Context of the Opioid Epidemic: A Critical Review
- Pages: 478-488
- First Published: 04 January 2018
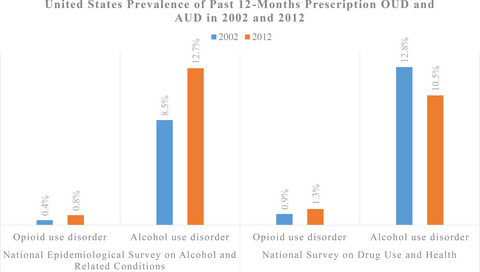
The increase in opioid use and overdose in the United States has been called an “opioid epidemic.” Alcohol use increases the risk of opioid overdose and given the prevalence of alcohol use disorder far exceeds the rate of opioid use disorder, research on the interactions between alcohol and opioids, as well as treatment of the comorbid disorders is desperately needed.
Commentary
Biochemistry, Pharmacology, Physiology and Metabolism
Impact of Moderate Alcohol Discontinuation on Insulin Action and Secretion in Latinos With and Without Hepatitis C
- Pages: 492-499
- First Published: 08 December 2017
Phosphatidylethanol Levels Among Incarcerated Women: The Influence of Pre-incarceration Alcohol Consumption and Length of Abstinence
- Pages: 500-507
- First Published: 27 December 2017
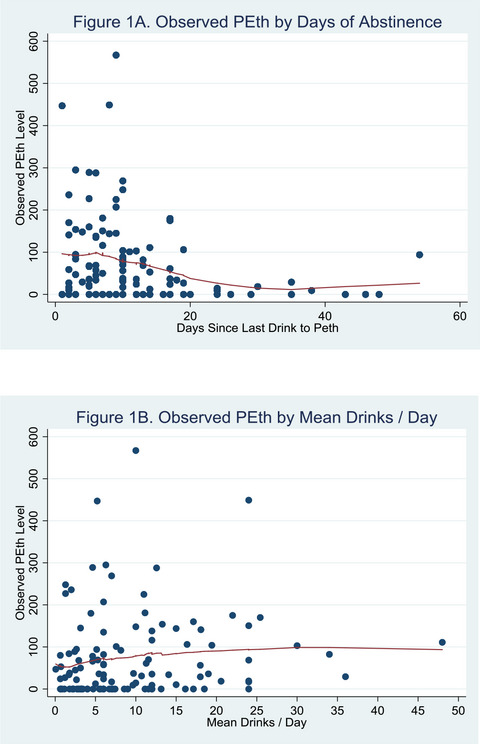
Data from 116 recently incarcerated, alcohol use-disordered women show that the number of days since last alcoholic drink and number of drinks per day prior to incarceration were associated with Phosphatidylethanol (PEth) detectability after a period of abstinence, but only days since last drink was associated with PEth level in blood. Results demonstrate the practicality of PEth as an alcohol biomarker among women in the criminal justice system, and highlight which alcohol use factors are most pertinent to PEth elimination.
Human and Animal Genetics
Associations Between MAOA-uVNTR Genotype, Maltreatment, MAOA Methylation, and Alcohol Consumption in Young Adult Males
- Pages: 508-519
- First Published: 09 December 2017
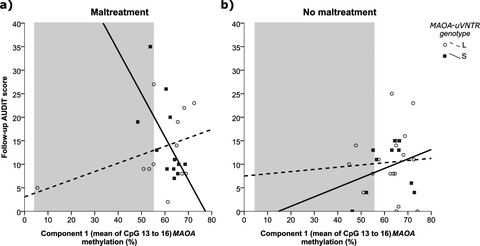
The present study demonstrated that MAOA methylation moderates the association of alcohol consumption with the interaction between MAOA-uVNTR genotype and maltreatment in a sample of adolescents seeking treatment for substance misuse. Carriers of the S allele, who experienced maltreatment and displayed lower intronic MAOA methylation levels, reported higher AUDIT score, in contrast to L allele carriers. The present findings suggest MAOA methylation as a putative molecular mechanism which intertwines life experiences and constitutive factors, and ultimately can influence mental health.
Polygenic Risk Score Prediction of Alcohol Dependence Symptoms Across Population-Based and Clinically Ascertained Samples
- Pages: 520-530
- First Published: 05 February 2018
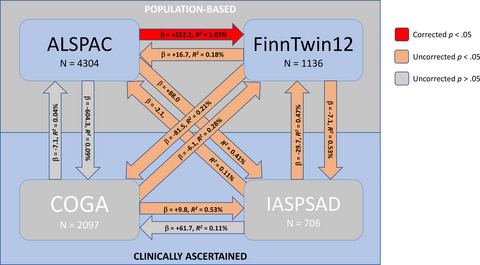
Gene identification efforts for alcohol use disorders are made more complicated by heterogeneity – the existence of different genes and etiological pathways influencing their development between individuals. Using genome-wide polygenic risk score methods, we found a lack of overlap in genetic influences on alcohol dependence symptoms between independent samples from epidemiological population-based studies versus studies of clinically-ascertained families densely affected with alcoholism. Mechanisms underlying alcohol use disorders may differ between these groups, indicating caution when combining them for research or inference.
Pathology, Immunology and Development
Investigating the Relationships Between Alcohol Consumption, Cannabis Use, and Circulating Cytokines: A Preliminary Analysis
- Pages: 531-539
- First Published: 29 December 2017
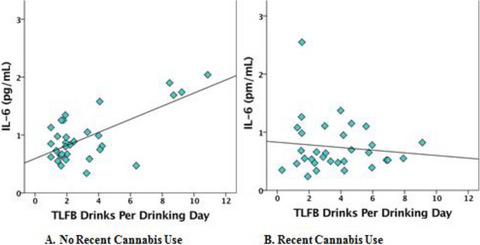
We demonstrate that cannabis moderates the positive association between alcohol consumption and inflammatory markers in blood. Specifically, we observed a positive relationship between alcohol consumption and IL-6 (a circulating marker of inflammation) in human subjects who had not used cannabis in the past 90 days, but no such relationship in those who had consumed cannabis in the past 90 days. Findings suggest that cannabinoids, which are thought to have anti-inflammatory effects, may confer protection from inflammation associated with alcohol use.
Neuroscience
Effects of Withdrawal from Chronic Intermittent Ethanol Exposure on Sleep Characteristics of Female and Male Mice
- Pages: 540-550
- First Published: 19 December 2017
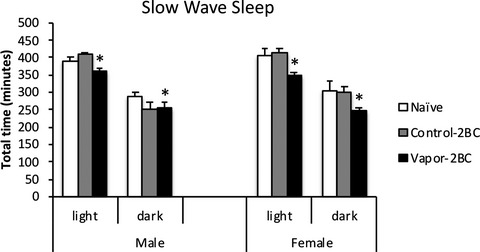
In addition to escalation of ethanol drinking associated with chronic intermittent ethanol vapor exposure, male and female C57BL/6J mice showed altered sleep characteristics. This figure shows decreased sleep quantity and we also observed a reduction in delta power during sleep, consistent with reduced sleep quality. There were subtle sex differences in sleep latencies and episode features. Because sleep disturbances are considered so important in continued ethanol drinking and relapse, this model will be of great importance in examining possible treatments.
Epidimiology, Diagnosis and Comorbidity
Heavy Episodic Drinking Trajectories Among Underage Young Adult Women: The Role of Feminine Norms
- Pages: 551-560
- First Published: 07 February 2018
Predictors of Longitudinal Trajectories of Alcohol Consumption in People with HIV
- Pages: 561-570
- First Published: 19 December 2017
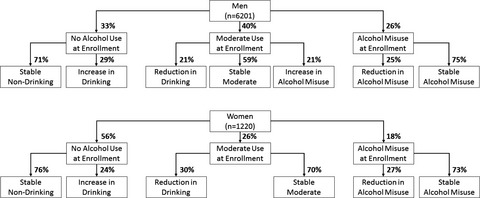
Alcohol consumption trajectories are heterogeneous among People With HIV and range from people with stable use, who tend to have lower levels of other risk behaviors, to those whose consumption patterns vary, and have a higher prevalence of risk behaviors and other comorbidities. With the increased life expectancy of People With HIV, the potential for increased alcohol-related morbidity and mortality has grown and highlights the need to integrate routine screening and interventions for alcohol misuse into HIV primary care.
Behavior, Treatment and Prevention
Co-Administration of Low-Dose Naltrexone and Bupropion Reduces Alcohol Drinking in Alcohol-Preferring (P) Rats
- Pages: 571-577
- First Published: 09 December 2017
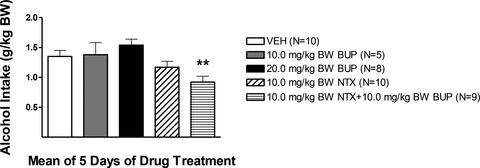
This study examined whether a low dose of naltrexone or bupropion which are ineffective in decreasing alcohol drinking when administered alone, can decrease alcohol drinking when administered in combination (NTX + BUP). Rats selectively bred for high voluntary alcohol drinking (alcohol-preferring, P rats) were treated with NTX or BUP alone, or in combination, every day for 5 days prior to daily scheduled access to alcohol. Combining low, ineffective doses of NTX and BUP results in a medication that effectively reduces alcohol drinking.
Spatial Epidemiology of Alcohol- and Drug-Related Health Problems Among Northern Plains American Indians: Nebraska and South Dakota, 2007 to 2012
- Pages: 578-588
- First Published: 30 January 2018
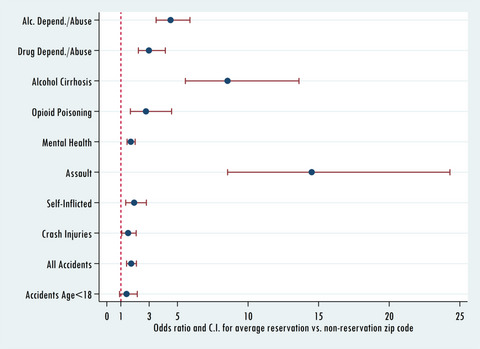
American Indian (AI) reservation areas in South Dakota and Nebraska experienced elevated hospitalization rates for many health problems previously linked to substance abuse. Holding other area characteristics constant, zip codes with average percent AI among reservations (67.7%) were predicted to have uniformly higher substance-related hospitalization rates than they would with average non-reservation percent AI (1.5%). This difference was well-supported for 9 of 10 outcomes (as indicated by 95% credible intervals). A complex set of factors help to explain these differences.
Brief Exposures to the Taste of Ethanol (EtOH) and Quinine Promote Subsequent Acceptance of EtOH in a Paradigm that Minimizes Postingestive Consequences
- Pages: 589-602
- First Published: 14 December 2017
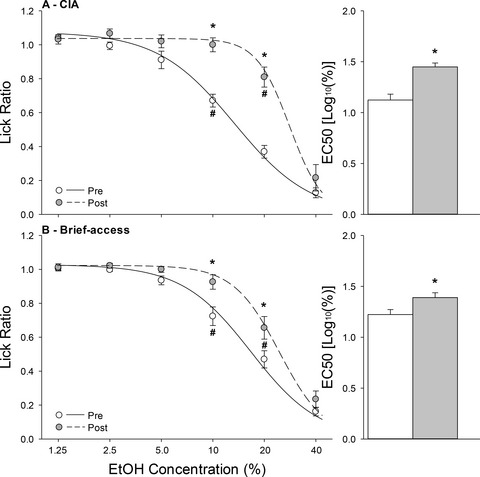
Repeated presentations of ethanol increased the acceptance of its taste. Exposure to ethanol in a brief-access licking paradigm, designed to minimize any postingestive consequences, resulted in a lateral shift in the concentration response function of randomly presented ethanol concentrations. More extensive ethanol consumption in a chronic-intermittent access paradigm resulted in an even larger shift in the acceptance of the taste of ethanol. The increase in taste acceptance following brief-access exposure robustly increased free-access ethanol consumption, relative to naïve rats.
Sleep Characteristics and Behavioral Problems Among Children of Alcoholics and Controls
- Pages: 603-612
- First Published: 19 December 2017
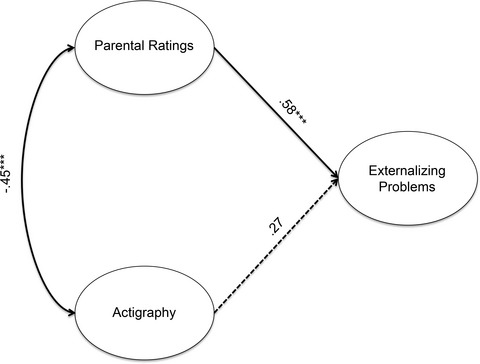
We compared multiple measures of sleep and the relationships between sleep and behavioral problems in children of alcoholics and controls. One hundred and fifteen children aged 8 to 12 participated in this study. Sleep difficulties and duration appear to be a general risk factor for behavioral problems in both COAs and non-COAs, yet the relationships between specific sleep parameters and behavioral problems appear to be different between the 2 groups.
Pharmacogenetic Effects of Naltrexone in Individuals of East Asian Descent: Human Laboratory Findings from a Randomized Trial
- Pages: 613-623
- First Published: 19 December 2017
Effect of Gabapentin on Sleep and Event-Related Oscillations (EROs) in Rats Exposed to Chronic Intermittent Ethanol Vapor and Protracted Withdrawal
- Pages: 624-633
- First Published: 29 December 2017
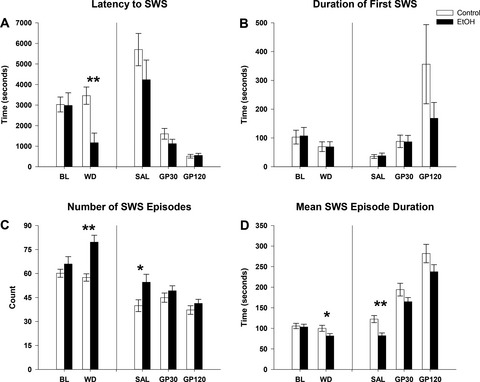
Chronic intermittent alcohol vapor exposure, in adult rats, produces a long-lasting fragmentation of slow wave sleep (SWS) and an increase in the beta EEG frequency bands. Gabapentin was found to produce a dose dependent reduction in SWS sleep fragmentation and a decrease in the latency to the first SWS episode suggesting that gabapentin could eliminate some of the enduring brain effects of chronic alcohol exposure.
Effects of Initiating Abstinence from Alcohol on Daily Craving and Negative Affect: Results from a Pharmacotherapy Clinical Trial
- Pages: 634-645
- First Published: 29 December 2017
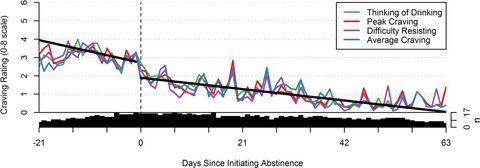
Patients with alcohol use disorder (AUD) may worry that initiating abstinence will intensify their cravings and negative affect. We examined changes in daily craving and negative affect before and after patients initiated abstinence from alcohol during a pharmacotherapy clinical trial. Initiating abstinence was associated with immediate (same-day) reductions in craving, followed by continued, gradual reductions in craving and negative affect after that. Results provide more precise insight into the timing and magnitude of change in clinically important AUD treatment outcomes.
Comparison of Characteristics of Female Drivers with Single and Multiple DUI Convictions
- Pages: 646-653
- First Published: 13 February 2018






