Maturing out of alcohol and cannabis co-use: A test of patterns and personality predictors
Corresponding Author
Jack T. Waddell
Department of Psychology, Arizona State University, Tempe, Arizona, USA
Correspondence
Jack T. Waddell, Department of Psychology, Arizona State University, 900 S McAllister, Tempe, AZ 85287-1104, USA.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorJustin Jager
Department of Psychology, Arizona State University, Tempe, Arizona, USA
Search for more papers by this authorLaurie Chassin
Department of Psychology, Arizona State University, Tempe, Arizona, USA
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Jack T. Waddell
Department of Psychology, Arizona State University, Tempe, Arizona, USA
Correspondence
Jack T. Waddell, Department of Psychology, Arizona State University, 900 S McAllister, Tempe, AZ 85287-1104, USA.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorJustin Jager
Department of Psychology, Arizona State University, Tempe, Arizona, USA
Search for more papers by this authorLaurie Chassin
Department of Psychology, Arizona State University, Tempe, Arizona, USA
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
Objective
Reductions in substance involvement into adulthood are thought to represent a normative maturing out of substance use. However, patterns and predictors of maturing out of alcohol and cannabis co-use remain largely unstudied. Therefore, the current study tested developmental trajectories of alcohol and cannabis use from late adolescence into adulthood and whether late adolescent personality traits predicted trajectory class membership.
Methods
Data come from a longitudinal study of family history of alcohol disorder (N = 458). Age bands were created to model trajectories of drinking quantity, negative alcohol consequences, and cannabis use frequency from late adolescence (age 18–22) to young adulthood (age 23–28) and adulthood (age 29–36). Participants reported on their sensation seeking, conscientiousness, and neuroticism during late adolescence and their typical drinking quantity, negative alcohol consequences, and cannabis use frequency at each age band.
Results
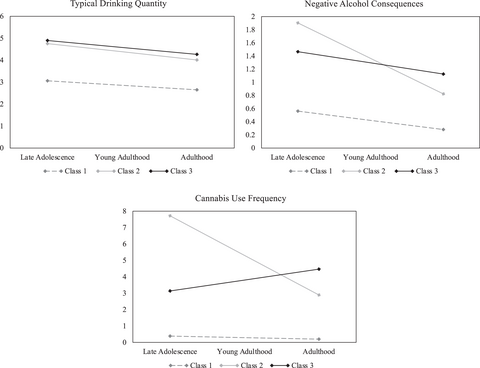
Three trajectory classes were derived from an initial Parallel Process Growth Mixture Model: (1) low-risk maturing out of alcohol-only use, (2) high-risk maturing out of co-use, and (3) high-risk switchers who increased their cannabis use into adulthood. Late adolescent sensation seeking was associated with higher odds of being in both co-use trajectories, whereas a lack of conscientiousness was associated with higher odds of being a co-use switcher.
Conclusions
We identified heterogeneity in trajectories of co-use, which suggests that a lack of maturing out of alcohol involvement may be accompanied by increased cannabis use. Moreover, late adolescent personality traits may predispose individuals toward riskier developmental trajectories of substance use into adulthood.
Graphical Abstract
Three trajectory classes of alcohol and cannabis use from late adolescence into adulthood consisted of low-risk maturing out of alcohol-only use, high-risk maturing out of co-use, and high-risk switchers who increase cannabis use. Late adolescent sensation seeking was associated with higher odds of being in both co-use trajectories, whereas a lack of conscientiousness was associated with higher odds of being a co-use switcher. Interventions may benefit from targeting personality to deter against riskier developmental trajectories of alcohol and cannabis co-use.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| acer14898-sup-0001-Supinfo.docxWord 2007 document , 17 KB |
Appendix S1 |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
REFERENCES
- American Psychiatric Association. (1980) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 3rd edition. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association.
- Andreason, N.C., Endicott, J., Spitzer, R.L. & Winokur, G. (1977) The family history method in affective illness: reliability and validity. Archives of General Psychiatry, 34, 1229–1235.
- Arnett, J.J. (2000) Emerging adulthood: a theory of development from the late teens through the twenties. The American Psychologist, 55, 469–480.
- Arria, A.M., Caldeira, K.M., Bugbee, B.A., Vincent, K.B. & O'Grady, K.E. (2016) Marijuana use trajectories during college predict health outcomes nine years post-matriculation. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 159, 158–165.
- Arterberry, B.J., Treloar, H. & McCarthy, D.M. (2017) Empirical profiles of alcohol and marijuana use, drugged driving, and risk perceptions. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, 78, 889–899.
- Ashenhurst, J.R., Harden, K.P., Corbin, W.R. & Fromme, K. (2015) Trajectories of binge drinking and personality change across emerging adulthood. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 29, 978–991.
- Asparouhov, T. & Muthén, B. (2014) Auxiliary variables in mixture modeling: using the BCH method in Mplus to estimate a distal outcome model and an arbitrary secondary model. Mplus Web Notes, 21, 1–22.
- Bailey, A.J., Farmer, E.J. & Finn, P.R. (2019) Patterns of polysubstance use and simultaneous co-use in high risk young adults. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 205, 107656.
- Bolck, A., Croon, M. & Hagenaars, J. (2004) Estimating latent structure models with categorical variables: one-step versus three-step estimators. Political Analysis, 12, 3–27.
- Brook, J.S., Lee, J.Y., Brown, E.N., Finch, S.J. & Brook, D.W. (2011) Developmental trajectories of marijuana use from adolescence to adulthood: personality and social role outcomes. Psychological Reports, 108, 339–357.
- Chassin, L., Barrera, M., Bech, K. & Kossak-Fuller, J. (1992) Recruiting a community sample of adolescent children of alcoholics: a comparison of three subject sources. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 53, 316–319.
- Chassin, L., Flora, D. & King, K.M. (2004) Trajectories of alcohol and drug use and dependence from adolescence to adulthood: the effects of familial alcoholism and personality. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 113, 483–498.
- Chiu, V., Leung, J., Hall, W., Stjepanović, D. & Degenhardt, L. (2021) Public health impacts to date of the legalisation of medical and recreational cannabis use in the USA. Neuropharmacology, 193, 108610.
- Conrod, P.J. (2016) Personality-targeted interventions for substance use and misuse. Current Addiction Reports, 3, 426–436.
- Conrod, P.J., Castellanos-Ryan, N. & Mackie, C. (2011) Long-term effects of a personality-targeted intervention to reduce alcohol use in adolescents. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 79, 296–306.
- Coskunpinar, A., Dir, A.L. & Cyders, M.A. (2013) Multidimensionality in impulsivity and alcohol use: a meta-analysis using the UPPS model of impulsivity. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research, 37, 1441–1450.
- Costa, P.T. & McCrae, R.R. (1992) Normal personality assessment in clinical practice: the NEO personality inventory. Psychological Assessment, 4, 5–13.
- Cyders, M.A. & Smith, G.T. (2008) Emotion-based dispositions to rash action: positive and negative urgency. Psychological Bulletin, 134, 807–828.
- D'Amico, E.J., Parast, L., Meredith, L.S., Ewing, B.A., Shadel, W.G. & Stein, B.D. (2016) Screening in primary care: what is the best way to identify at-risk youth for substance use? Pediatrics, 6, 138.
- Dawson, D.A., Grant, B.F., Stinson, F.S. & Chou, P.S. (2006) Maturing out of alcohol dependence: the impact of transitional life events. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 67, 195–203.
- Dick, D.M., Smith, G., Olausson, P., Mitchell, S.H., Leeman, R.F., O'Malley, S.S. et al. (2010) Understanding the construct of impulsivity and its relationship to alcohol use disorders. Addiction Biology, 15, 217–226.
- Grant, B.F., Chou, S.P., Saha, T.D., Pickering, R.P., Kerridge, B.T., Ruan, W.J. et al. (2017) Prevalence of 12-month alcohol use, high-risk drinking, and DSM-IV alcohol use disorder in the United States, 2001–2002 to 2012–2013: results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on alcohol and related conditions. JAMA Psychiatry, 74, 911–923.
- Gray, K.M., Watson, N.L. & Christie, D.K. (2009) Challenges in quantifying marijuana use. The American Journal on Addictions, 18(2), 178–179. https://doi.org/10.1080/10550490902772579
- Green, K.M., Musci, R.J., Johnson, R.M., Matson, P.A., Reboussin, B.A. & Ialongo, N.S. (2016) Outcomes associated with adolescent marijuana and alcohol use among urban young adults: a prospective study. Addictive Behaviors, 53, 155–160.
- Gunn, R.L., Aston, E.R. & Metrik, J. (2022) Patterns of cannabis and alcohol co-use: substitution versus complementary effects. Alcohol Research: Current Reviews, 42, 04.
- Gunn, R.L., Norris, A.L., Sokolovsky, A., Micalizzi, L., Merrill, J.E. & Barnett, N.P. (2018) Marijuana use is associated with alcohol use and consequences across the first 2 years of college. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 32, 885–894.
- Gunn, R., Jackson, K., Borsari, B. & Metrik, J. (2019) A longitudinal examination of daily patterns of cannabis and alcohol co-use among medicinal and recreational veteran cannabis users. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 205, 107661.
- Hasin, D.S. (2018) US epidemiology of cannabis use and associated problems. Neuropsychopharmacology, 43, 195–212.
- Hasin, D.S., Kerridge, B.T., Saha, T.D., Huang, B., Pickering, R. & Smith, S.M. (2016) Prevalence and correlates of DSM-5 cannabis use disorder, 2012-2013: findings from the National Epidemiologic Survey on alcohol and related conditions-III. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 173, 588–599.
- Hindocha, C., Norberg, M.M. & Tomko, R.L. (2018) Solving the problem of cannabis quantification. The Lancet Psychiatry, 5(4), e8. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2215-0366(18)30088-9
- Johnston, L.D., O'Malley, P.M., Miech, R.A., Bachman, J.G. & Schulenberg, J.E. (2016) Monitoring the Future national survey results on drug use, 1975-2015: overview, key findings on adolescent drug use. Ann Arbor: Institute for Social Research.
- Jung, T. & Wickrama, K.A. (2008) An introduction to latent class growth analysis and growth mixture modeling. Social and Personality Psychology Compass, 2, 302–317.
10.1111/j.1751-9004.2007.00054.x Google Scholar
- Kearns, N.T., Gunn, R.L., Stevens, A.K., Berey, B.L. & Metrik, J. (2022) Longitudinal associations between impulsivity and alcohol and cannabis use frequency, quantity, and problems among military veterans. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors Advanced Online Publication.
- King, K.M., Littlefield, A.K., McCabe, C.J., Mills, K.L., Flournoy, J. & Chassin, L. (2018) Longitudinal modeling in developmental neuroimaging research: common challenges, and solutions from developmental psychology. Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience, 33, 54–72.
- Lee, M.R. & Sher, K.J. (2018) “Maturing out” of binge and problem drinking. Alcohol Research: Current Reviews, 39, 31–42.
- Lee, M.R., Chassin, L. & Villalta, I.K. (2013) Maturing out of alcohol involvement: transitions in latent drinking statuses from late adolescence to adulthood. Development and Psychopathology, 25, 1137–1153.
- Lejuez, C.W., Magidson, J.F., Mitchel, S.H., Sinha, R., Stevens, M.C. & De Wit, H. (2010) Behavioral and biological indicators of impulsivity in the development of alcohol use, problems, and disorders. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research, 34, 1334–1345.
- Linden-Carmichael, A.N., Stamates, A.L. & Lau-Barraco, C. (2019) Simultaneous use of alcohol and marijuana: patterns and individual differences. Substance Use & Misuse, 54, 2156–2166.
- Littlefield, A.K., Sher, K.J. & Wood, P.K. (2009) Is “maturing out” of problematic alcohol involvement related to personality change? Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 118, 360–374.
- Littlefield, A.K., Sher, K.J. & Wood, P.K. (2010) Do changes in drinking motives mediate the relation between personality change and “maturing out” of problem drinking? Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 119, 93–105.
- Littlefield, A.K., Vergés, A., Wood, P.K. & Sher, K.J. (2012) Transactional models between personality and alcohol involvement: a further examination. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 121(3), 778–783.
- Maggs, J.L. & Schulenberg, J.E. (2004) Trajectories of alcohol use during the transition to adulthood. Alcohol Research & Health, 28, 195–201.
- Magid, V., MacLean, M.G. & Colder, C.R. (2007) Differentiating between sensation seeking and impulsivity through their mediated relations with alcohol use and problems. Addictive Behaviors, 32, 2046–2061.
- McCabe, S.E., Arterberry, B.J., Dickinson, K., Evans-Polce, R.J., Ford, J.A., Ryan, J.E. et al. (2021) Assessment of changes in alcohol and marijuana abstinence, co-use, and use disorders among US young adults from 2002 to 2018. JAMA Pediatrics, 175, 64–72.
- Meier, M.H., Caspi, A., Knodt, A., Hall, W., Ambler, A., Harrington, H. et al. (2022) Long-term cannabis use and cognitive reserves and hippocampal volume in midlife. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 179, 362–374.
- Merrill, J.E., Carpenter, R.W., Boyle, H.K., Haikalis, M., Jackson, K.M., Miranda, R. et al. (2021) Do alcohol-related consequences and how they are evaluated predict consumption during and days until the next drinking event? Psychology of Addictive Behaviors Advanced Online Publication.
- Midanik, L.T., Tam, T.W. & Weisner, C. (2007) Concurrent and simultaneous drug and alcohol use: results of the 2000 National Alcohol Survey. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 90, 72–80.
- Moeller, F.G., Barratt, E.S., Dougherty, D.M., Schmitz, J.M. & Swann, A.C. (2001) Psychiatric aspects of impulsivity. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 158, 1783–1793.
- Muthén, B. & Muthén, L.K. (2000) Integrating person-centered and variable-centered analyses: growth mixture modeling with latent trajectory classes. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research, 24, 882–891.
- National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA). (2020) What is the scope of marijuana use in the United States?
- Nylund, K.L., Asparouhov, T. & Muthén, B.O. (2007) Deciding on the number of classes in latent class analysis and growth mixture modeling: a Monte Carlo simulation study. Structural Equation Modeling, 14, 535–545.
- O'Malley, P.M. (2004) Maturing out of problematic alcohol use. Alcohol Research & Health, 28, 202–204.
- Patrick, M.E., Kloska, D.D., Terry-McElrath, Y.M., Lee, C.M., O'Malley, P.M. & Johnston, L.D. (2018) Patterns of simultaneous and concurrent alcohol and marijuana use among adolescents. The American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse, 44, 441–451.
- Patrick, M.E., Terry-McElrath, Y.M., Le, C.M. & Schulenber, J.E. (2019) Simultaneous alcohol and marijuana use among underage young adults in the United States. Addictive Behaviors, 88, 77–81.
- Patton, D.V. (2020) A history of United States cannabis law. Journal of Law and Health, 34, 1.
- Quinn, P.D. & Harden, K.P. (2013) Differential changes in impulsivity and sensation seeking and the escalation of substance use from adolescence to early adulthood. Development and Psychopathology, 25, 223–239.
- Quinn, P.D., Stappenbeck, C.A. & Fromme, K. (2011) Collegiate heavy drinking prospectively predicts change in sensation seeking and impulsivity. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 120, 543–556.
- Risso, C., Boniface, S., Subbaraman, M.S. & Englund, A. (2020) Does cannabis complement or substitute alcohol consumption? A systematic review of human and animal studies. Journal of Psychopharmacology, 34(9), 938–954.
- Robins, L.N., Helzer, J.E., Croughan, J. & Ratcliff, K.S. (1981) National Institute of Mental Health diagnostic interview schedule: its history, characteristics, and validity. Archives of General Psychiatry, 38, 381–389.
- Smith, G.T. & Cyders, M.A. (2016) Integrating affect and impulsivity: the role of positive and negative urgency in substance use risk. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 163, S3–S12.
- Staff, J., Schulenberg, J.E., Maslowsky, J., Bachman, J.G., O'Malley, P.M., Maggs, J.L. et al. (2010) Substance use changes and social role transitions: proximal developmental effects on ongoing trajectories from late adolescence through early adulthood. Development and Psychopathology, 22, 917–932.
- Subbaraman, M.S., Metrik, J., Patterson, D. & Swift, R. (2017) Cannabis use during treatment for alcohol use disorders predicts alcohol treatment outcomes. Addiction, 112, 685–694.
- Thompson, K., Holley, M., Sturgess, C. & Leadbeater, B. (2021) Co-use of alcohol and cannabis: longitudinal associations with mental health outcomes in young adulthood. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18, 3652.
- Tucker, J.S., Rodriguez, A., Davis, J.P., Klein, D.J. & D'Amico, E.J. (2021) Simultaneous trajectories of alcohol and cannabis use from adolescence to emerging adulthood: associations with role transitions and functional outcomes. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 35, 628–637.
- VanderVeen, J.D., Hershberger, A.R. & Cyders, M.A. (2016) UPPS-P model impulsivity and marijuana use behaviors in adolescents: a meta-analysis. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 168, 181–190.
- Vergés, A., Jackson, K.M., Bucholz, K.K., Grant, J.D., Trull, T.J., Wood, P.K. et al. (2012) Deconstructing the age-prevalence curve of alcohol dependence: why “maturing out” is only a small piece of the puzzle. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 121, 511–523.
- Waddell, J.T. (2021) Between-and within-group effects of alcohol and cannabis co-use on AUD/CUD in the NSDUH 2002–2019. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 225, 108768.
- Waddell, J.T., Blake, A.J. & Chassin, L. (2021a) Relations between impulsive personality traits, alcohol and cannabis co-use, and negative alcohol consequences: a test of cognitive and behavioral mediators. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 225, 108780.
- Waddell, J.T., Corbin, W.R. & Leeman, R.F. (2021b) Differential effects of UPPS-P impulsivity on subjective alcohol response and craving: an experimental test of acquired preparedness. Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacology Advanced Online Publication.
- Waddell, J.T., Sternberg, A., Grimm, K.J. & Chassin, L. (2021c) Do alcohol consequences serve as teachable moments? A test of between-and within-person reciprocal effects from college age to adulthood. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, 82, 647–658.
- Waddell, J.T., Gunn, R.L., Corbin, W.R., Borsari, B. & Metrik, J. (2021d) Drinking less on cannabis use days: the moderating role of UPPS-P impulsive personality traits. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors Advanced Online Publication.
- Waddell, J.T., Sternberg, A., Bui, L., Ruof, A.R., Blake, A.J., Grimm, K.J. et al. (2021e) Relations between child temperament and adolescent negative urgency in a high-risk sample. Journal of Research in Personality, 90, 104056.
- Waddell, J.T., Elam, K.K. & Chassin, L. (2022) Multidimensional impulsive personality traits mediate the effect of parent substance use disorder on adolescent alcohol and cannabis use. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 51, 1–13.
- Wardell, J.D., Egerton, G.A. & Read, J.P. (2020) Does cannabis use predict more severe types of alcohol consequences? Longitudinal associations in a 3-year study of college students. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research, 44, 1141–1150.
- Waddell, J.T. & Marszalek, J.M. (2022) Indirect and direct effects of simultaneous alcohol and cannabis use on alcohol hangovers. Addictive Behaviors, 134, 107420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2022.107420
- White, H.R., Beardslee, J. & Pardini, D. (2017) Early predictors of maturing out of marijuana use among young men. Addictive Behaviors, 65, 56–62.
- Whiteside, S.P. & Lynam, D.R. (2001) The five factor model and impulsivity: using a structural model of personality to understand impulsivity. Personality and Individual Differences, 30, 669–689.
- Windle, M. (2020) Maturing out of alcohol use in young adulthood: latent class growth trajectories and concurrent young adult correlates. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research, 44, 532–540.
- Zakhari, S. & Li, T.K. (2007) Determinants of alcohol use and abuse: impact of quantity and frequency patterns on liver disease. Hepatology, 46(6), 2032–2203.
- Zarrett, N. & Eccles, J. (2006) The passage to adulthood: challenges of late adolescence. New Directions for Youth Development, 111, 13–28.
- Zuckerman, M. (2007) Sensation seeking and risky behavior. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
10.1037/11555-000 Google Scholar
- Zuckerman, M., Kuhlman, D.M., Joireman, J., Teta, P. & Kraft, M. (1993) A comparison of three structural models for personality: the big three, the big five, and the alternative five. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 65, 757–768.