Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER PICTURE
Cover Picture: Materials and Corrosion. 9/2022
- Page: 1339
- First Published: September 2022
MASTHEAD
Masthead: Materials and Corrosion. 9/2022
- Page: 1341
- First Published: September 2022
CONTENTS
Contents: Materials and Corrosion. 9/2022
- Pages: 1342-1345
- First Published: September 2022
ARTICLES
Influence of Al and Fe additions on metal dusting of NiCr alloys
- Pages: 1346-1358
- First Published: 23 March 2022
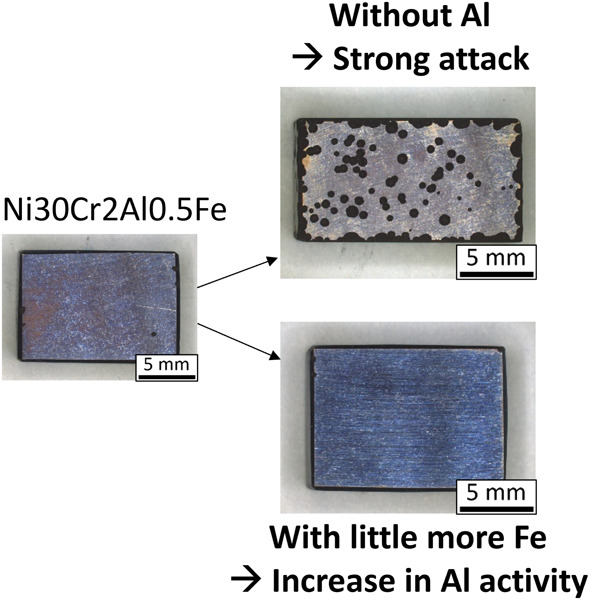
Model Ni-based alloys with compositions derived from Alloy 699 XA were studied in aggressive metal dusting conditions. Their metal dusting resistance was compared to the commercial alloys 699 XA and 602 CA. The alloys with the highest tested chromium (30 wt%) and aluminum (2–3 wt%) contents were the most resistant against metal dusting attacks.
Insights into the oxidation behavior of Ni–25Cr–10Fe–xSi (x = 1, 2, 3, 4 wt%) alloys at 1000°C in ambient air
- Pages: 1359-1368
- First Published: 02 May 2022
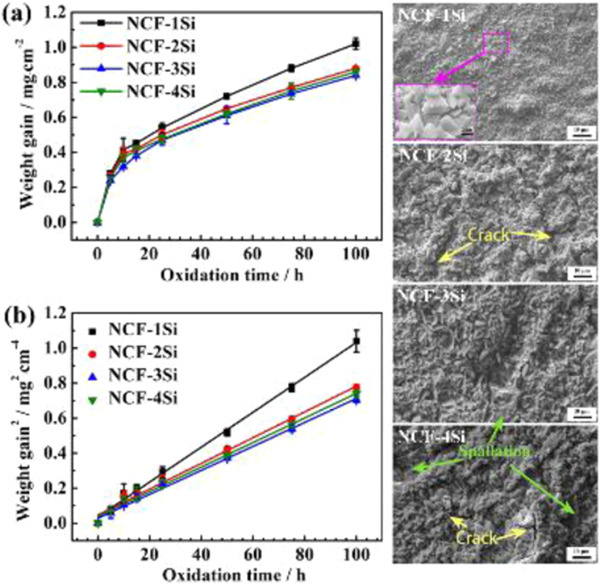
The effect of Si on the oxidation resistance of the Ni–25Cr–10Fe alloys was investigated by scanning electron microscopy, Raman spectroscopy, and Thermo-Calc software. The results show that 3 wt% is a reasonable value for the addition of Si and that the distribution of silica plays a key role in the stability of the oxide scales.
Long-term low-temperature hot corrosion of PTA welded René 41 superalloy under marine-like conditions
- Pages: 1369-1382
- First Published: 03 May 2022
The long-term, low-temperature hot-corrosion behavior of a plasma transferred arc-welded René 41 superalloy under marine-like conditions is investigated in this study. After a combination of energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction analyses, a reaction mechanism is derived in association with thermodynamic calculations. Furthermore, the differences between cyclic and isothermal studies are compared and discussed.
Effect of Ce addition on the high-temperature oxidation resistance of Mg–Gd alloys
- Pages: 1383-1392
- First Published: 09 May 2022
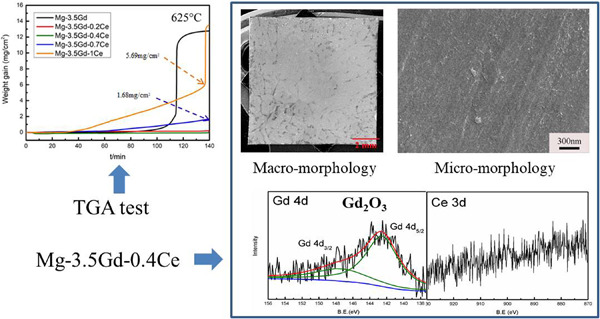
The oxidation resistance of the Mg–3.5Gd–xCe alloys was compared between 550°C and 650°C. Microalloying with Ce is beneficial for improving the oxidation resistance of the Mg–3.5Gd alloy. The Ce addition deteriorates the oxidation resistance when its content exceeds 0.7 wt%. Gd2O3 and MgO were detected in the oxide films of the Mg–3.5Gd–0.2Ce and Mg–3.5Gd–0.4Ce alloys.
Effect of high-temperature, high-pressure, and acidic conditions on the structure and properties of high-performance fibers
- Pages: 1393-1404
- First Published: 02 May 2022
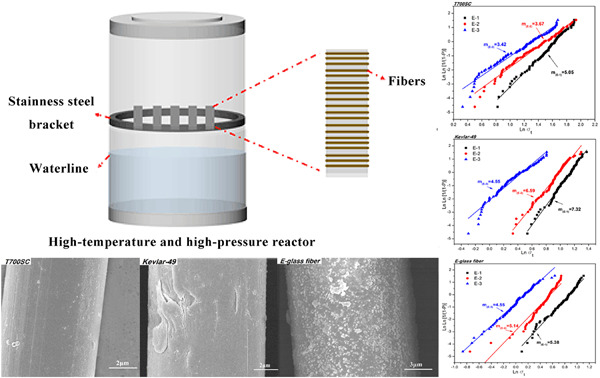
The corrosion behavior of carbon, aramid, and glass fibers in different corrosive environments is investigated. Corrosion under a high-temperature and high-pressure H2S/CO2 environment results in more serious damage to the high-performance fiber structures, where the tensile strength retention of carbon, aramid, and glass fibers is 70.28%, 49.66%, and 48.18%, respectively.
Study on the microstructure and corrosion behavior of CoCrNi MEA annealed at different temperatures in Na2CO3/NaHCO3 solution
- Pages: 1405-1419
- First Published: 21 March 2022
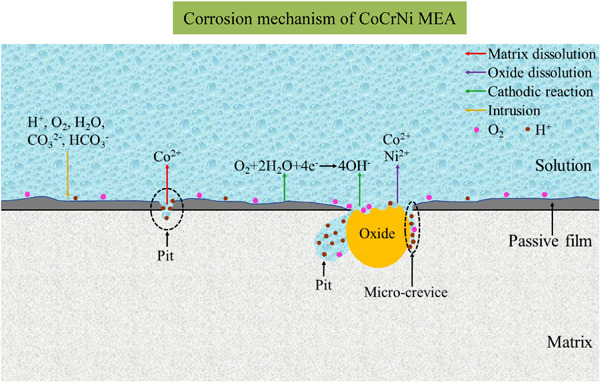
The effect of different annealing temperatures on the corrosion behavior of CoCrNi medium entropy alloy (MEA) was investigated in an alkaline soil simulation solution. The results show the corrosion resistance of the MEA gradually increases with increasing annealing temperature. The corrosion behavior of the MEA is correlated with grain size, oxide inclusions, and surface passive film.
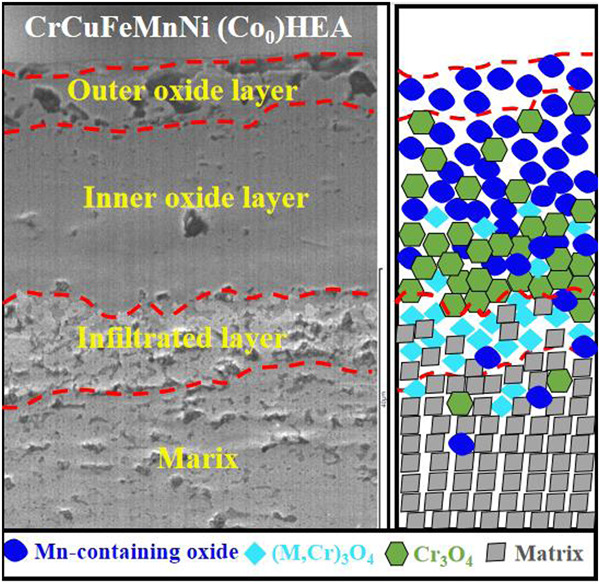
Microstructure and atmospheric oxidation behavior of CrCuFeMnNiCox high-entropy alloys fabricated by vacuum hot-press sintering
- Pages: 1420-1429
- First Published: 09 May 2022
Enhanced corrosion and wear properties of H13 steel with Co-based alloy coating prepared by laser cladding
- Pages: 1430-1443
- First Published: 25 March 2022
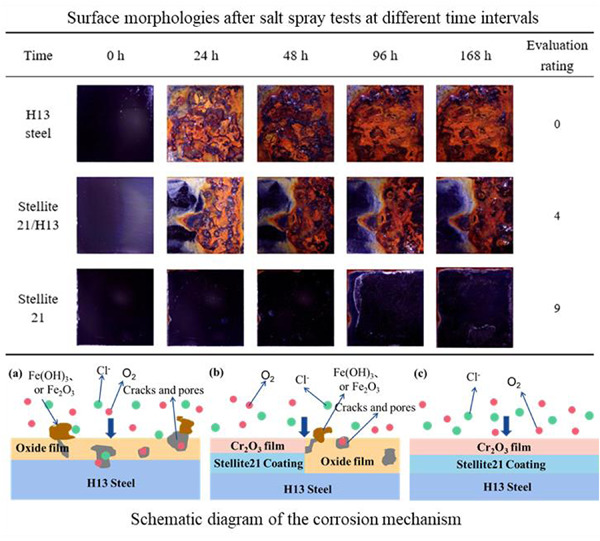
The microstructural evolution, microhardness, corrosion, and wear properties of laser-cladding Co-based alloy coating on H13 steel were investigated in this study. The coating exhibited better wear resistance than the substrate. Both the electrochemical corrosion test and salt spray test proved the enhanced corrosion resistance of H13 steel with a Co-based coating.
Preparation of two-dimensional boron nitride-layered double hydroxide hybrid to reinforce the corrosion protection of the epoxy coating
- Pages: 1444-1458
- First Published: 22 March 2022
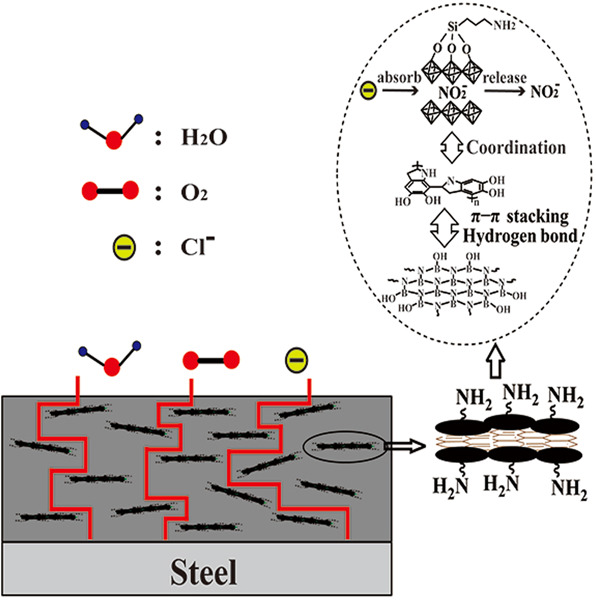
DBNs-aminated layered double hydroxide (ALDH) with epoxy was coated on Q215 steel to form a composite epoxy coating. The electrochemical impedance spectroscopy test and brine immersion test were used to characterize the anticorrosion performance of the composite epoxy coating. The result revealed that the DBNs-ALDH reinforced the anticorrosion performance of the epoxy coating.
What happens when a Pb–Sn coating deposited on low carbon steel is exposed in an HCl-polluted wet environment? Development of a corrosion mechanism
- Pages: 1459-1473
- First Published: 20 May 2022
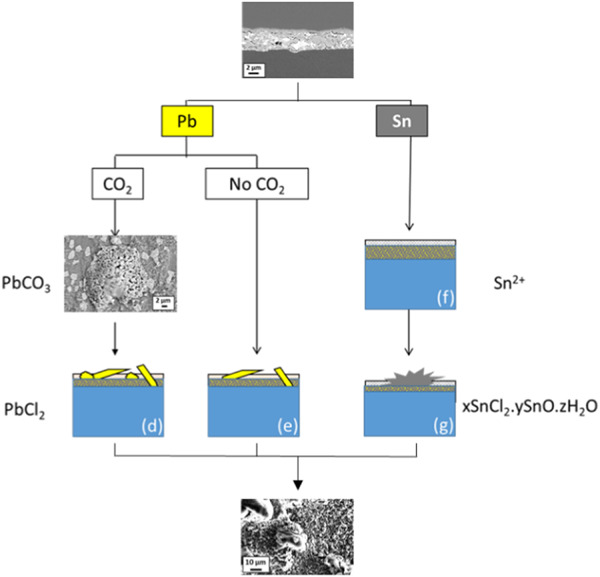
The purpose of this article is to establish a global corrosion mechanism when a Pb–Sn coating deposited on low carbon steel is corroded in an HCl-polluted wet environment. The successive stages of the process are shown by specifying each step and focusing on each element. The consequences of this corrosion phenomenon are analyzed and solutions are proposed to minimize its impact.
Marine atmospheric corrosion of carbon steel in the tropical microclimate of Port Louis
- Pages: 1474-1489
- First Published: 21 March 2022
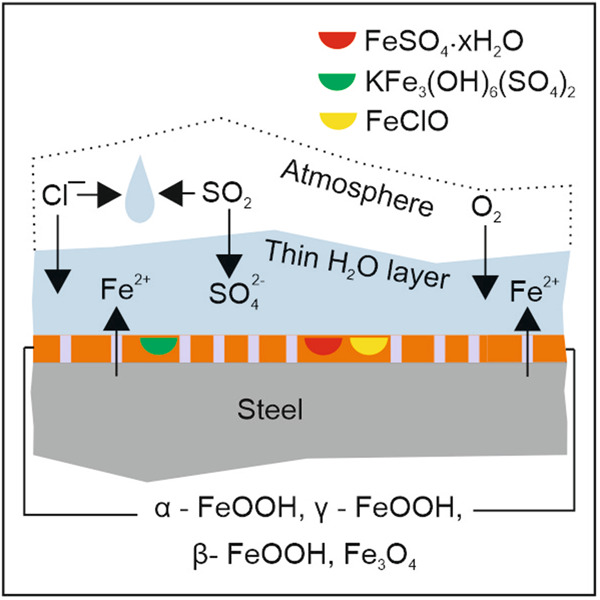
This study helps to understand the corrosion kinetics of carbon steel and to determine any association between the environment and the rust content in a corrosion layer formed in a marine atmosphere in which airborne salinity is low. The results show that marine atmospheric corrosion rate is also dependent on factors other than airborne salinity while the formation of akaganeite, magnetite and other insoluble compounds at the coastal sites is sparse.
Investigation of 3-(phenylsulfinyl)indoles self-assembled monolayer for the inhibition of iron corrosion in acidic media
- Pages: 1490-1504
- First Published: 04 May 2022
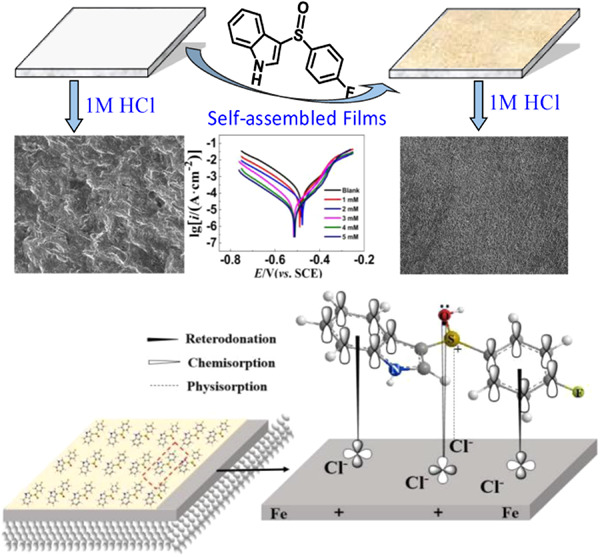
Indole-sulfoxides are synthesized in water as a green reaction medium. Indole ring and sulfoxide have strong charge electrophilic/nucleophilic activity to interact with metal atoms and form self-assembly film on the iron surface. The self-assembly films protect the metal surface by interaction of chemical and physical adsorption.
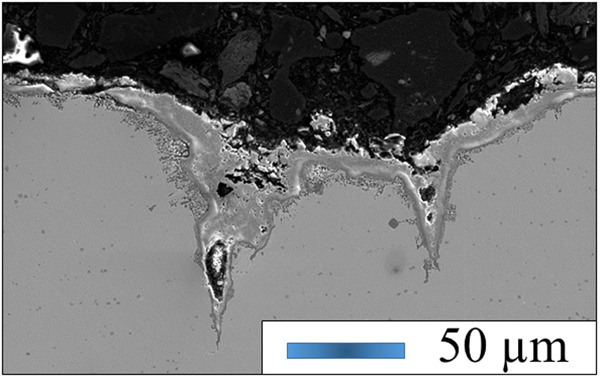
Intergranular corrosion effect on fatigue behavior of dissimilar 6005A-5083 aluminum alloys weld joints
- Pages: 1505-1518
- First Published: 05 May 2022

The effect of intergranular corrosion defect depth on the fatigue properties of 6005A-5083 welded joints was studied by soaking in different corrosion solutions for a fixed time. The results show that when the intergranular corrosion defect is larger than 248 μm, the corrosion defect dominates the fatigue expansion process, and the fracture occurs at the 5083 base metal position, which is mainly due to the stress concentration generated by corrosion defects under cyclic stress.