Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Picture: Crystal Research and Technology 12'2014
- First Published: 12 December 2014
Issue Information
Issue Information: Crystal Research and Technology 12'2014
- First Published: 12 December 2014
Contents
Contents: Crystal Research and Technology 12'2014
- Pages: A63-A66
- First Published: 12 December 2014
Original Papers
Preeminent visible-light photocatalytic activity over BiOBr–BiVO4 heterojunctions
- Pages: 933-938
- First Published: 04 December 2014
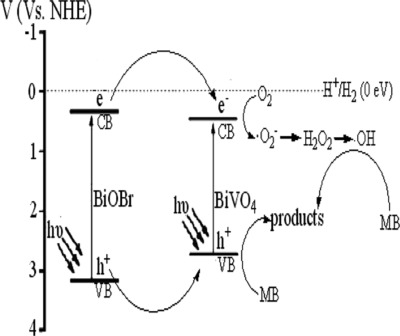
In this work, we prepared for the first time a class of novel heterojunctions of BiOBr–BiVO4 fabricated by depositing BiOBr nanoflakes onto the surface of BiVO4. The optimum photocatalytic activity of the 0.925BiOBr–0.075BiVO4 heterojunction was almost 14 and 144 times as high as those of individual BiOBr and BiVO4 in visible-light degradation of methylene blue. Photogenerated holes of BiVO4 would play a dominant role in the photocatalytic system.
The growth and spectral analysis of mixed crystal of Yb-doped Lu0.5Y0.5PO4 mixed crystals
- Pages: 939-942
- First Published: 25 November 2014
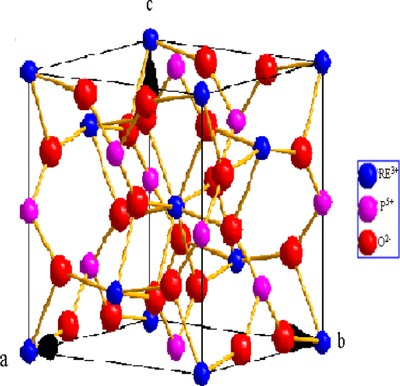
A new kind of 5 at% Yb-doped Lu0.5Y0.5PO4 crystals were firstly grown by spontaneously nucleated high-temperature solution method using lead pyrophosphate (Pb2P2O7) as the solvent. The X-ray powder diffraction (XRPD) patterns recorded at room temperature showed the crystals possessed tetragonal xenotime structure. The polarized absorption spectra and the fluorescence spectra of Yb:LuxY1-xPO4 were measured at room temperature, respectively. The results show that Yb:LuxY1-xPO4 mixed crystal...
Crystal growth, quality characterization and THz properties of DAST crystals
- Pages: 943-947
- First Published: 03 December 2014
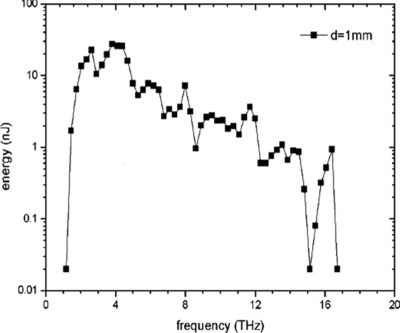
DAST crystal is a kind of promising candidate for the generation and detection of terahertz wave. High-quality DAST crystals were grown by slope nucleation method, and widely tunable terahertz waves ranging from 1.16 to 16.71 THz were generated from 1 mm-thick DAST crystal using the optical parametric oscillator. It was obtained that the THz output energy was 27.4 nJ (peak power of 2.74 W).
Engineering ZnO nanowire surfaces via a chemical method
- Pages: 948-952
- First Published: 28 July 2014

Porous nanowires with large surface area are advantageous for device applications. However, the synthesis of this kind of nanostructure has rarely been reported. In this paper, quasi-aligned ZnO nanowire arrays with porous surfaces were successfully fabricated via a facile chemical method. Time-dependent experiments have also been carried out to better understand the formation process of porous structure on the nanowire surface.
CIS and CIGS nanomaterials prepared by solvothermal method and their spectral properties
- Pages: 953-958
- First Published: 10 December 2014
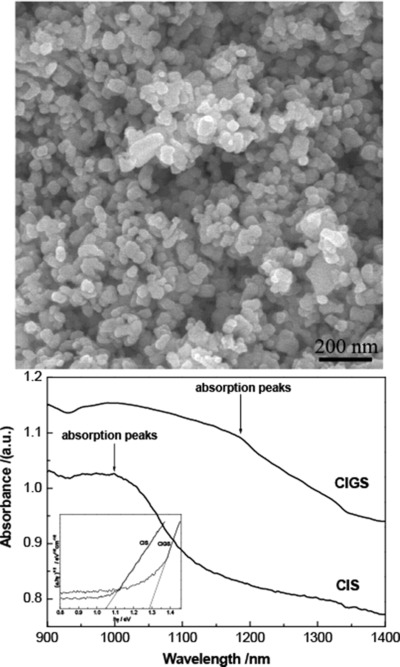
Here a simple solvothermal technique was adopted to synthesize uniform CIS and CIGS nanomaterials. The influence of surfactant, temperature, Ga amount on the structure, morphology, phase and spectral properties was analyzed. The results show that CIS and CIGS nanomaterials can be obtained at 200 °C. PVP-30 can greatly improve the dispersion of nanoparticles. UV-vis-NIR spectra show that the absorption peak and absorption edge of CIGS obviously shift to a lower energy compared with CIS.
The effects of solvent and microwave on the preparation of Magnesium Oxide Precursor
- Pages: 959-964
- First Published: 13 November 2014
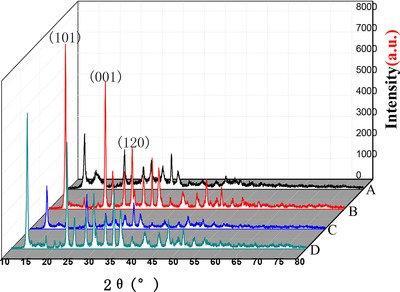
Four methods including hydrothermal method, glycol-hydrothermal method, microwave-hydrothermal method and glycol-microwave-hydrothermal method were used to prepare magnesium oxide precursor by the reaction of MgSO4·7H2O with (NH4)2CO3. The glycol-hydrothermal method can create high quality Magnesium Oxide precursor with a high degree of crystallinity, high purity, high aspect ratio, smooth surface, and good dispersibility.
Structural and mechanical properties of KН2PО4 single crystals with embedded nanoparticles and organic molecules
- Pages: 965-974
- First Published: 10 November 2014
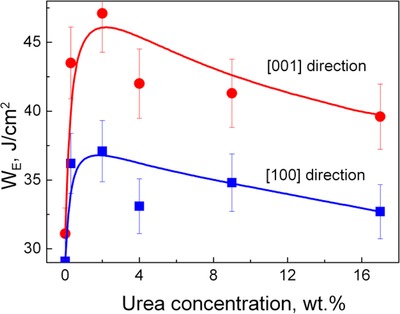
The manuscript is devoted to the microstructure – strength relationship of KDP crystals containing organic molecules and the ones with incorporated TiO2 nanoparticles. It is found that differences in the structure formation mechanism result in the opposite influence of the additives on the mechanical properties and the laser damage threshold of KDP crystal.
Hydrothermal syntheses of silver phosphate nanostructures and their photocatalytic performance for organic pollutant degradation
- Pages: 975-981
- First Published: 03 December 2014
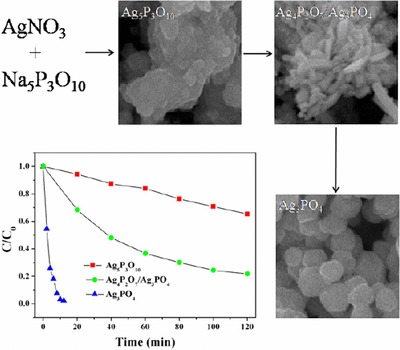
A facile hydrothermal method for the syntheses of Ag5P3O10, Ag4P2O7/Ag3PO4 and Ag3PO4 nanostructures was developed. The photocatalytic activities were evaluated by the degradation of organic pollutants under simulated sunlight irradiation. The photocatalytic mechanism was systematically investigated.
Graphene oxide used as a surfactant to induce the flower-like ZnO microstructures: growth mechanism and enhanced photocatalytic properties
- Pages: 982-989
- First Published: 10 December 2014

Graphene oxide was used as a temple to induce the formation of flower-like ZnO microparticals compared with classical surfactants. The flower-like ZnO microparticals were gained by calcining zinc hydroxide carbonate. The photocatalytic activity of the flower-like ZnO microparticals was evaluated by photo degradation reaction of rhodamine B (RhB) which was better than ZnO microparticals formed in the CTAB and BS-12.






