Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Macromol. Rapid Commun. 19/2009
- First Published: 22 September 2009

Front Cover: Electrohydrodynamic co-jetting can result in microfibers with defined compartments. Here, the selective surface modification of bicompartmental microfibers is reported. This novel technology has the potential to address a so-far unmet requirement of tissue engineering: how to pattern cells in a three-dimensional scaffold framework. Further details can be found in the article by S. Mandal, S. Bhaskar, and J. Lahann* on page 1638.
Contents
Feature Article
Hairy Core–Shell Nanoparticles via RAFT: Where are the Opportunities and Where are the Problems and Challenges?
- Pages: 1603-1624
- First Published: 22 September 2009
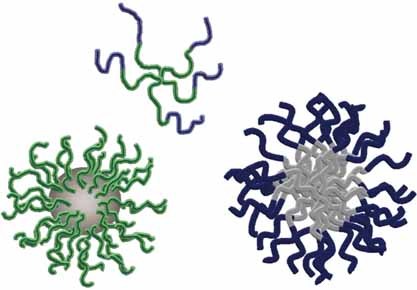
Hairy core–shell nanoparticles, which include (crosslinked) micelles, unimolecular micelles such as star polymers with block structures in each arm and surface grafted nanoparticles such as inorganic particles can be prepared using the versatile RAFT process. The underlying concepts are explained, but the approaches are also critically discussed regarding their feasibility. The advantages are contrasted to the problems occurring from dealing with a radical process.
Communications
On the Quantitative Click Conjugation of Molecular Weight Distributions: What Can Theoretically Be Expected?
- Pages: 1625-1631
- First Published: 22 September 2009
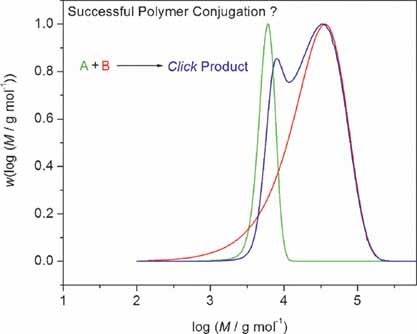
The assessment of the success of block copolymer formation via quantitative click conjugation is often carried out via inspection of the SEC distribution, w(log M) versus log M), of the initial polymers and the coupling product. The present theoretical investigation demonstrates that the inspection of the shape of the SEC distribution is—in many cases—a poor guide for assessing the success of the conjugation.
Three-Dimensional Polycaprolactone Hierarchical Scaffolds Supplemented with Natural Biomaterials to Enhance Mesenchymal Stem Cell Proliferation
- Pages: 1632-1637
- First Published: 22 September 2009
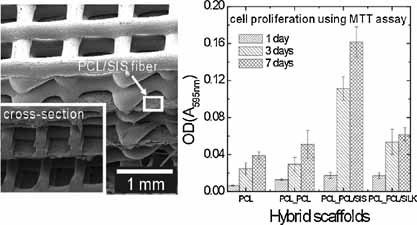
3-D hierarchical scaffolds were fabricated by a 3-D plotting system and an electrospinning process. To improve the cellular behaviour on the hierarchical 3-D scaffold, two natural materials, small intestine submucosa (SIS) and silk fibroin, were electrospun with PCL. The bone marrow-derived rat mesenchymal stem cells exhibited an incredible increase in cell proliferation on the 3-D hierarchical scaffold containing natural biomaterials.
Micropatterned Fiber Scaffolds for Spatially Controlled Cell Adhesion
- Pages: 1638-1644
- First Published: 22 September 2009
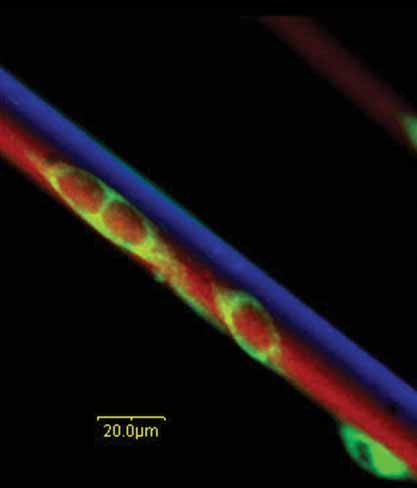
The fabrication of novel bicompartmental microfiber scaffolds for spatially guided cell adhesion is demonstrated. These scaffolds are prepared via electrohydrodynamic co-spinning of biodegradable PLGA polymers, followed by selective patterning with a cell-adhesion ligand via Huisgen heterocycloaddition on one compartment only. Mamalian cells cultured on these scaffolds are found to adhere specifically onto the compartment containing the immobilized ligand, as shown in the figure.
Combinatorial Energy Transfer between an End-Capped Conjugated Polyelectrolyte and Chromophore-Labeled PNA for Strand-Specific DNA Detection
- Pages: 1645-1650
- First Published: 22 September 2009
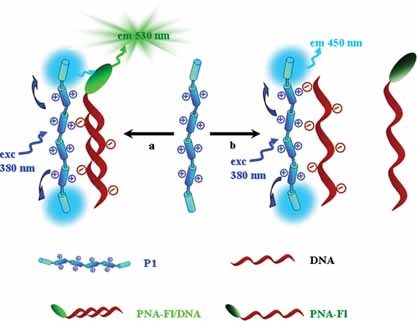
Towards a more sensitive DNA assay. A novel end-capping approach is reported to synthesize light harvesting water soluble conjugated polyfluorene (P1). By offering efficient intra and intermolecular energy transfer from fluorene backbone to low energy end-capper anthracene sites, end-capped polymer P1 improves the signal output for fluorescein appended to peptide nucleic acid/DNA duplex than that for uncapped P2 via FRET.
Glucosamine Hydrochloride Functionalized Water-Soluble Conjugated Polyfluorene: Synthesis, Characterization, and Interactions with DNA
- Pages: 1651-1655
- First Published: 22 September 2009
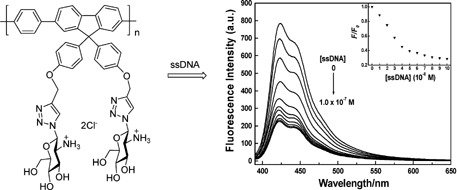
Glucosamine hydrochloride functionalized water-soluble conjugated polyfluorene was synthesized through Cu(I)-catalyzed azide/alkyne “click” ligation and Suzuki coupling polymerization. Grafting glucosamine hydrochloride to the side chains of the conjugated polymers cannot only improve water-solubility and biocompatibility of the polymers, but also provide positively charged ammonium binding sites for conjugated polymers with artificial or natural polyanions.
Damping Behavior of the Aggregation–Disaggregation Self-Oscillation of a Polymer Chain
- Pages: 1656-1662
- First Published: 22 September 2009
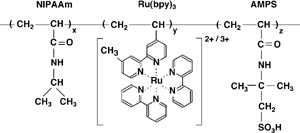
The effect of the initial concentration of the substrates of the Belousov–Zhabotinsky (BZ) reaction and the effect of temperature on the autonomous aggregation–disaggreagtion self-oscillation of a polymer chain has been studied. The initial concentration of the BZ substrates and the temperature exert an influence on the waveform and the period of the self-oscillation. The development of a novel self-oscillating polymer system and the discovery of novel self-oscillating behavior may lead to a wide variety of non-linear phenomena and may inspire experimental and theoretical consideration.
Polyaniline “Nanotube” Self-Assembly: The Stage of Granular Agglomeration on Nanorod Templates
- Pages: 1663-1668
- First Published: 22 September 2009

A critical stage of PANI “nanotube” self-assembly, namely the granular agglomeration or growth onto nanorod templates, is identified and controlled. When the synthesis pH is held above 2.5, smooth insulating nanorods exhibiting hydrogen bonding and containing phenazine structures are produced, while below pH 2.5, small 15–30 nm granular PANI nanoparticles agglomerate or grow onto the available nanorod surface, coinciding with an increase in conductivity of the resulting structures of three orders of magnitude.
pH Tailoring Electrical and Mechanical Behavior of Polymer–Clay–Nanotube Aerogels
- Pages: 1669-1673
- First Published: 22 September 2009
Poly(acrylic acid) provides a means of tailoring the electrical conductivity and mechanical behavior of an aerogel by altering pH during processing. The aerogel shown here, prepared from a pH 3 aqueous mixture containing 2.5 wt.-% PAA, 5 wt.-% clay, and 0.05 wt.-% SWNT, has a compressive modulus of 462 kPa and conductivity of 1.67 × 10−6 S · cm−1.
Controlling Orientation and Functionalization in Thin Films of Block Copolymers
- Pages: 1674-1678
- First Published: 22 September 2009
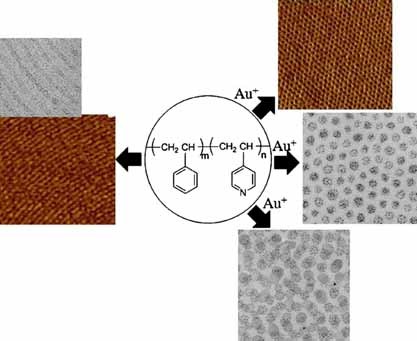
Controlling orientation and functionalization with a high degree of order is difficult to achieve, and each has typically been done in a separate process. Here, a simple but very useful route to accomplish both in a single procedure is provided. In addition, this method enables the tailoring of film morphology through changes of the phase behavior in solution.
Synthesis of CdSe–Poly(N-vinylcarbazole) Nanocomposite by Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization for Potential Optoelectronic Applications
- Pages: 1679-1683
- First Published: 22 September 2009
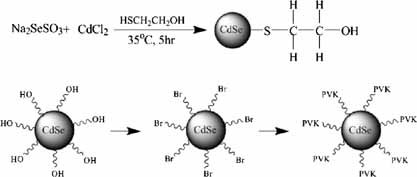
A cheaper and greener non-TOP-based approach is employed for the synthesis of thiol-capped CdSe nanocrystals through a wet chemical route, and then ATRP of N-vinylcarbazole is carried out on the functionalized CdSe nanocrystal surfaces to obtain the CdSePVK nanocomposite. The basic structural characterizations and optical properties of thiol-capped CdSe nanoparticles and CdSePVK nanocomposites are presented.
Back Cover
Macromol. Rapid Commun. 19/2009
- First Published: 22 September 2009

Back Cover: Towards a more sensitive DNA assay: a novel end-capping approach is reported to synthesize light-harvesting cationic conjugated polyfluorene. By offering efficient intra- and intermolecular energy transfer from fluorene backbone to end-capper anthracene, it enhances the sensitivity of a DNA assay over the uncapped version via FRET. Further details can be found in the article by S. K. Dishari, K.-Y. Pu, and B. Liu* on page 1645.






