Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
(Ann. Phys. 7/2024)
- First Published: 08 July 2024
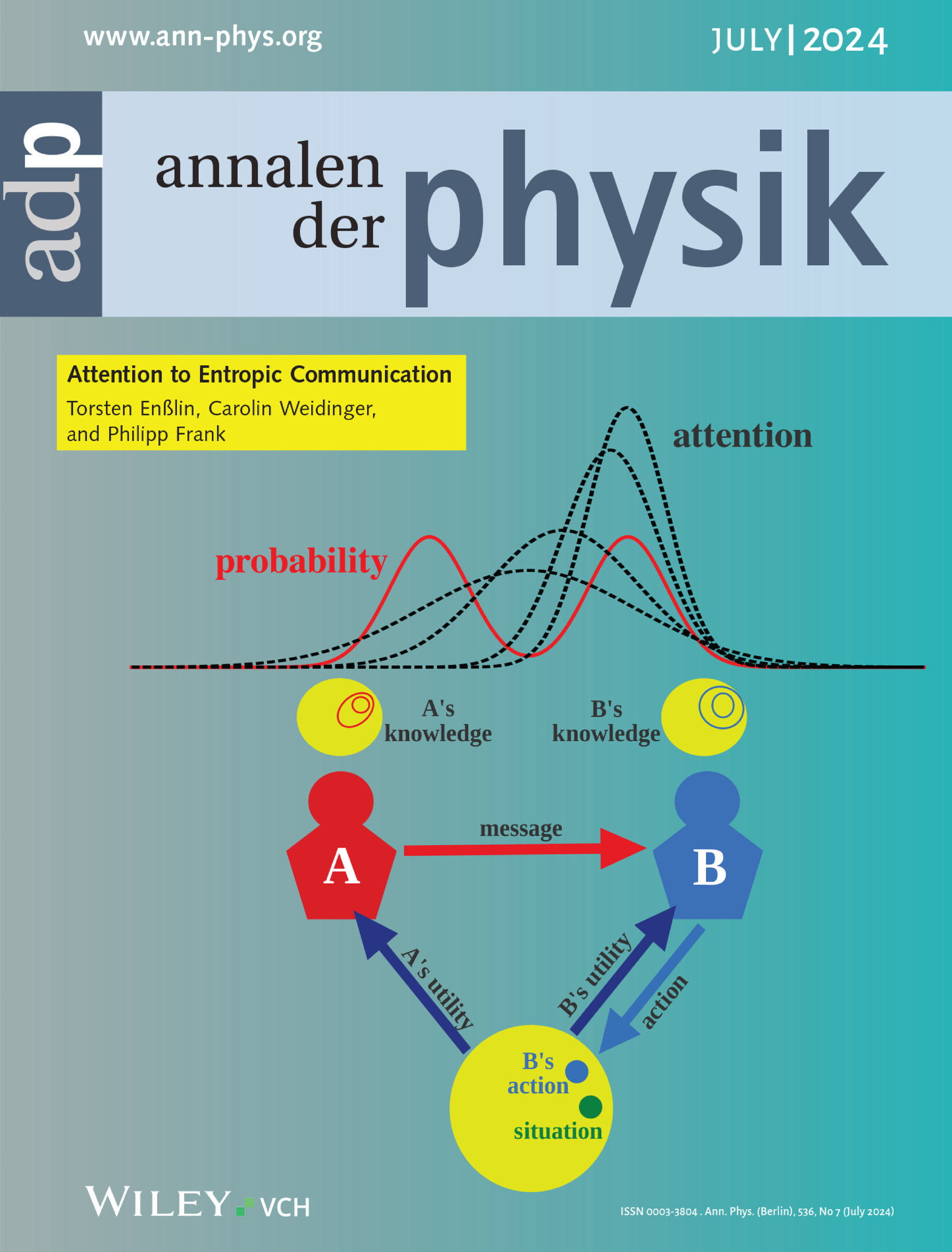
Attention to Entropic Communication
Attention focuses limited cognitive resources on essential information and therefore plays a central role in natural and artificial intelligence. Relative attention entropy allows to focus approximate probability functions on their most relevant parts. In the top image, the attention guided approximation of a double peaked probability density by a Gaussian focuses on the more relevant peak. Bottom: Attention emerges as importance-weighted probability in utility-conscious communication. For further information, see article number 2300334 by Torsten Enßlin and co-workers
Masthead
Perspective
Improving on Complexity: Ideas for Enhancing Quantitative Modeling of Climate Mobility
- First Published: 30 May 2024

In this paper ways are proposed for quantitative research to better address the complexity of climate mobility. First technical suggestions are presented to improve upon migration models and highlight promising developments. Then it is argued that quantitative methods can broaden the scope of research inquiries by examining how climate mitigation and adaptation influences mobility, and assessing how mobility itself impacts vulnerability.
Review
Spin Transport in High-Field Superconductors
- First Published: 25 May 2024
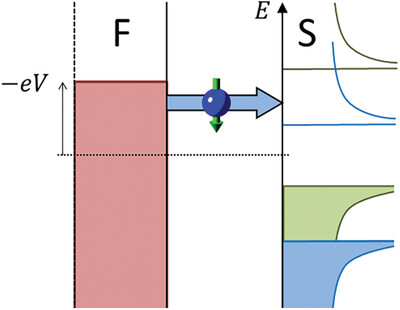
High-field superconductors are characterized by a spin splitting of the density of states. Efficient spin injection and long-range coupled spin and heat transport are possible in the energy window of the spin splitting. In hybrid structures with ferromagnets, large thermoelectric effects appear. Experimental progress, open questions and application perspectives are reviewed.
Research Articles
Attention to Entropic Communication
- First Published: 17 April 2024
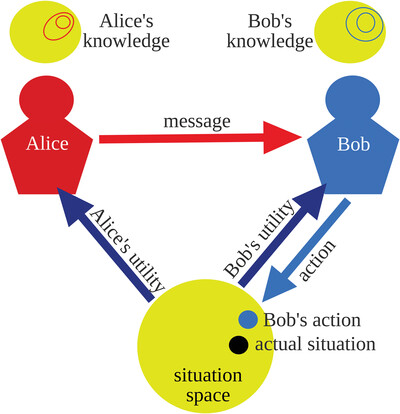
For artificial and natural intelligence, the concept of attention is very relevant. Here, a probabilistic concept of attention and its entropy is introduced, which allows to construct communication that primarily transmits relevant information. The attention concept is motivated by the analysis of an asymmetric communication scenario. Its entropy is derived from axioms.
Optomechanical Coupling Optimization in Engineered Nanocavities
- First Published: 17 April 2024
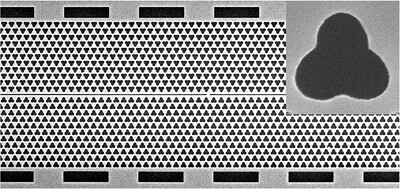
Brownian motion of nano-objects is a source of dissipation and dephasing for many processes, particularly the ones related to the interaction between light and matter. However, motional degrees of freedom can also be exploited to control the interaction with the nanoworld. Here, an optimized platform is presented to control optomechanical interaction in the GHz frequency range with high efficiency.
The Propagation Dynamics of the Symmetric Pearcey Gaussian Beam in the Kerr Medium
- First Published: 08 March 2024
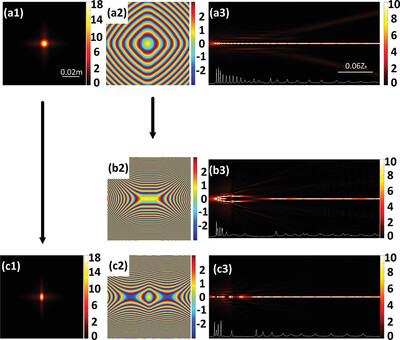
In this paper, symmetric Pearcey Gaussian beams (SPGBs) are studied in a Kerr medium. By varying the initial input power, we investigate the auto focusing ability of the beams and find a clear restrictive relationship between the breath-like structure and the initial input power. The critical collapse power when SPGBs change from discrete beams to regular breath-like structure is investigated. Finally, the transmission of SPGBs under different phase modulation when SPGBs are affected by astigmatic, the whole beam is rotated, and the angle of rotation can be controlled is discussed.
Polyadic Opinion Formation: The Adaptive Voter Model on a Hypergraph
- First Published: 27 March 2024
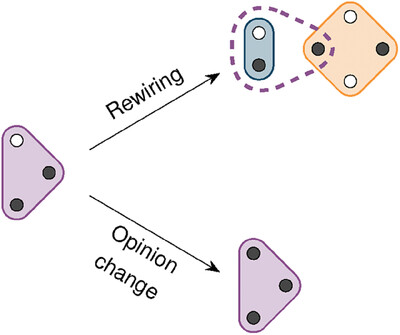
This study extends the adaptive voter model to hypergraphs to investigate how peer pressure affects collective decision-making. If groups always follow the majority, the network rapidly splits into disconnected communities. Conversely, if individuals adopt opinions proportionally to their representation in the group, the network reaches a stable state, maintaining connections between individuals with different opinions.
Analytic Continuation of Multipoint Correlation Functions
- First Published: 01 May 2024
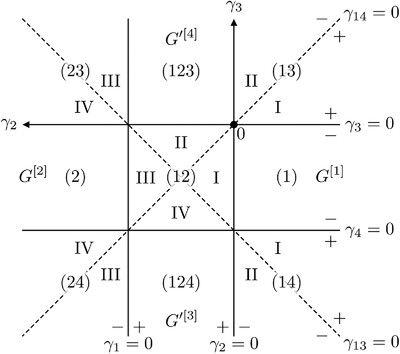
This article explains how multipoint correlators in the imaginary-frequency Matsubara formalism (MF) can be analytically continued to the real-frequency Keldysh formalism (KF). The physical information in both types of correlators is fully encoded in partial spectral functions (PSFs). We analytically extract PSFs from MF correlators and give explicit formulas for the MF-to-KF analytic continuation of two-, three-, and four-point correlators.
Exotic Topological Magnetic States in Thin Co/Pd Ferromagnetic Films
- First Published: 13 March 2024
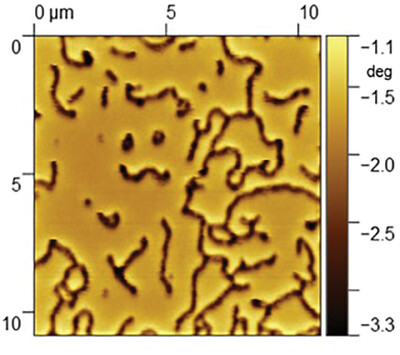
The magnetic properties and micromagnetic structure of Co/Pd multilayer films with different bilayer thicknesses, but with the same ratio Co versus Pd are studied. A number of micromagnetic features in the films are revealed, such as skyrmions, 360° domain walls, skyrmioniums and the combination of them.
Antimatter Gravity and the Results of the ALPHA-g Experiment
- First Published: 18 April 2024
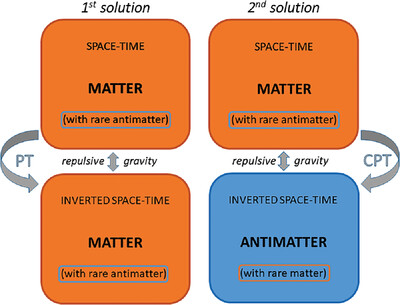
The recent results of the ALPHA-g experiment, which show gravitational attraction between antihydrogen atoms and the Earth, seem to undermine the success of repulsive-gravity models in the cosmological field. Analyzing the theory of CPT gravity, two solutions are found that are consistent with the experimental results, while preserving the large-scale gravitational repulsion.
Electron Odd-Pearcey Gaussian Beams Propagating In a Constant Magnetic Field
- First Published: 16 April 2024
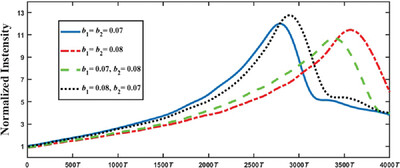
The paper presents the introduction of a novel type of electron beams. The electron beams exhibit remarkable auto-focusing characteristic, and the focal length can be controlled by adjusting certain parameters. Additionally, in a constant magnetic field, the electron beams exhibit intriguing properties, notably the dual auto-focusing property, which sets them apart from other known electron beams.
Exact Functional Integration of Radial and Complex Slave-Boson Fields: Thermodynamics and Dynamics of the Two-Site Extended Hubbard Model
- First Published: 16 May 2024
Slave boson approaches have been applied to numerous strongly correlated electronic systems, in particular in order to unravel their potential functionalities. Nonetheless, proofs that these functional integral representations systematically reproduce the exact solutions are still missing, especially in the case of the popular Kotliar and Ruckenstein representation. This paper fills this gap in the case of the extended Hubbard Model.
Improving the Performance of Cooling and Entanglement in a Double Cavity Optomechanical System Assisted by the Quantum Coherent Feedback
- First Published: 09 May 2024
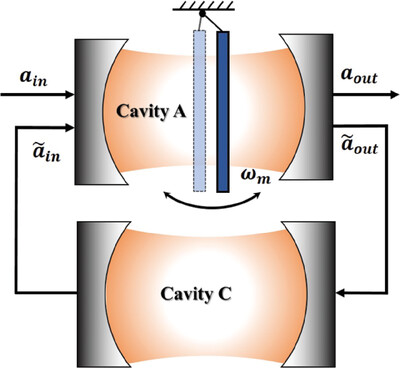
In this work, a theoretical scheme is proposed for improving the performance of cooling and entanglement. The physical model is based on a double cavity optomechanical system assisted by the field-mediated coherent feedback. This scheme can go beyond the resolved sideband and may provide a new path for the optomechanical manipulation involving the low-frequency mechanical resonator.
Semiquantum Key Distribution Using Initial States in Only One Basis Without the Classical User Measuring
- First Published: 23 May 2024
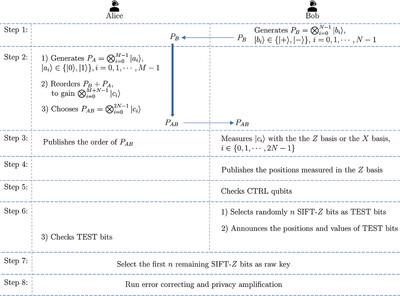
A semiquantum key distribution protocol, which prepares initial states in only one basis and removes the classical user's measurement, is proposed. The protocol is secure against the attack, where the ancilla particles are independent in the forward and backward channels but the unitary operations are same for each round. This work inspires to achieve quantum superiority with minimal quantum resources.





