Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
(Ann. Phys. 10/2023)
- First Published: 20 October 2023
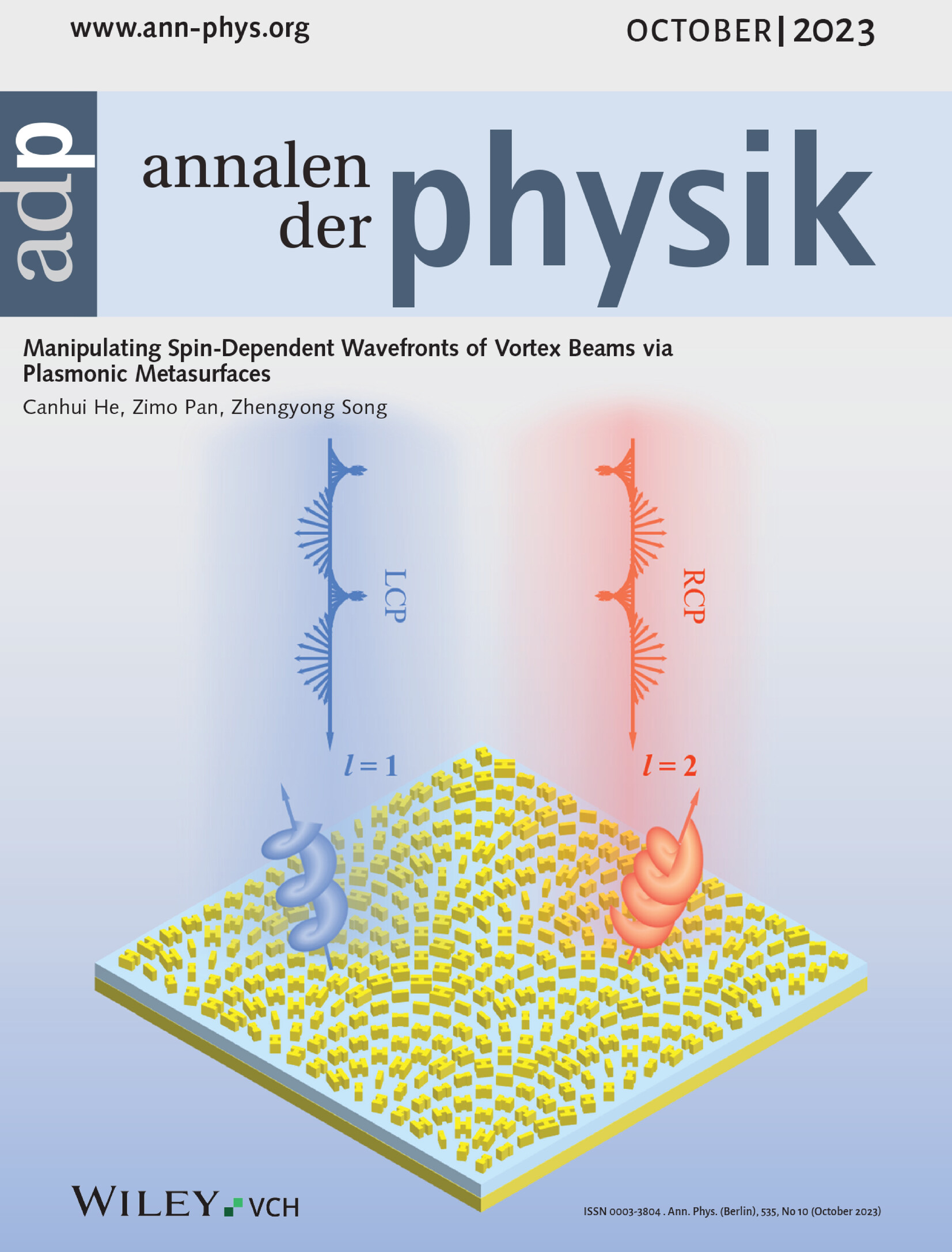
Spin-Dependent Wavefronts
In article number 2300235, Canhui He, Zimo Pan, and Zhengyong Song propose reflective plasmonic metasurfaces for manipulating spin-dependent wavefronts of vortex beams in the visible band. Spin-locked limitation of geometric phase is released by combining propagating phase and geometric phase, thereby providing a practical approach for independently tailoring circularly polarized wavefronts in a single metasurface.
Masthead
Review
Plasma Photocathodes
- First Published: 17 September 2023
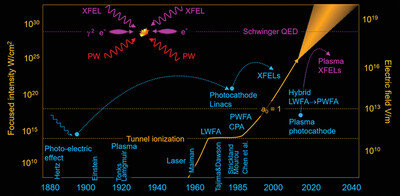
This paper reviews progress and prospects of plasma photocathodes, which are an emerging pathway toward ultrabright electron beams from plasma wakefield accelerators. They are theorized for over a decade, but recently a first realization has demonstrated proof-of-concept at SLAC. The review describes how this is achieved, and outlines identified improvements that will further develop this technology.
Research Articles
Controlled-NOT Gate Based on the Rydberg States of Surface Electrons
- First Published: 04 September 2023
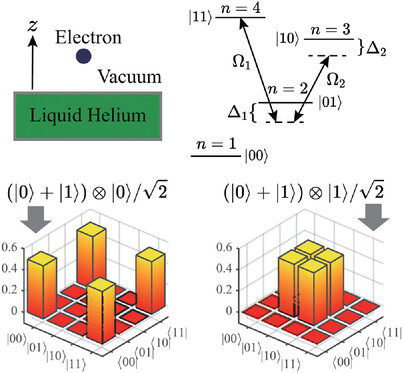
A theoretical controlled-NOT gate scheme encoding a two-qubit system on the four-level Rydberg structure of a surface electron is proposed. The dark state in the electromagnetically induced transparency effect is exploited to increase the robustness against dissipation. The gate fidelity is 0.9989 with experimentally achievable parameters.
Controlling the Trajectory of Swallowtail Gaussian Beams in Dynamic Parabolic Potentials
- First Published: 04 September 2023
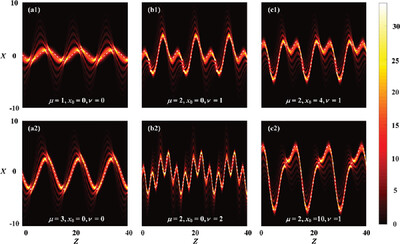
Swallowtail Gaussian beams propagate and reverse periodically in a medium with dynamic parabolic potential. According to the detailed analysis and numerical results for different parabolic potentials, the intensity of the beams, the focal position, and the acceleration trajectory can be effectively controlled by the potential. In addition, 2D Swallowtail Gaussian beams exhibit similar focusing properties.
Prediction of Interesting Ferromagnetism in Janus Semiconducting Cr2AsP Monolayer
- First Published: 14 September 2023
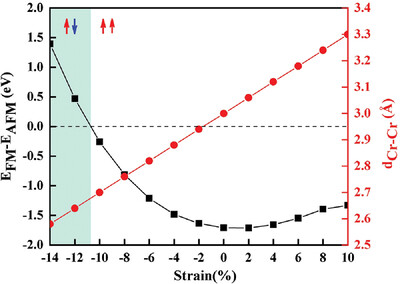
The Janus Cr2AsP monolayer is proven to be an intrinsic ferromagnetic semiconductor with an exchange splitting bandgap of 0.15 eV at the PBE+U level. Concentration-dependent Se doping, such as Cr2AsSexP (x = 0.25, 0.50, 0.75), can regulate Cr2AsP from ferromagnetic semiconductor to ferromagnetic half-metallicity. These charming properties render the Janus Cr2AsP monolayer with great potential for applications in spintronic devices.
Infrared Absorber Leveling in Ultra-Wideband by Using Hybrid Plasmonic Structure
- First Published: 15 September 2023
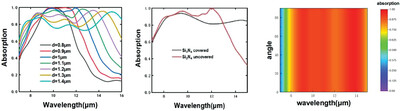
In this paper, a periodic triangular resonant unit is proposed as a broadband, efficient, ultra-thin metal-insulator-metal (MIM) infrared absorber made of metal Ti/Ge/Ti. The field amplitude equations are built for a system on dipole–a waveguide cavity to find and prove the essence of plasma absorption leveling. This is created by the effects of quantum coherence due to mode combination in a waveguide cavity.
Probe Response of an Optomechanical System with Optomechanical Coupling Modulated Periodically
- First Published: 15 September 2023
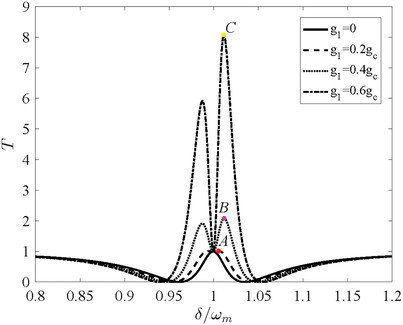
Periodic external action proves to be an effective method for modifying the performance of a cavity optomechanical system. This paper investigates the probe response of a cavity optomechanical system with periodic modulation of the optomechanical coupling. A significant amplification, rather than absorption in the conventional optomechanically induced transparency schemes, near the transparent point is observed due to periodic modulation.
Quantum Zeno and Anti-Zeno Effects in the Dynamics of Non-Degenerate Hyper-Raman Processes Coupled to Two Linear Waveguides
- First Published: 15 September 2023
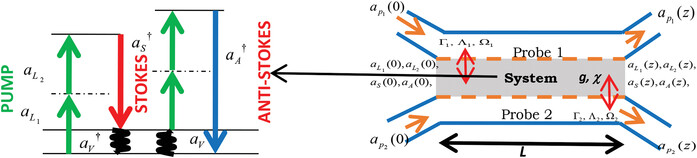
Quantum Zeno (anti-Zeno) effects are investigated with the help of two probes interacting with a system undergoing the hyper-Raman process. Each probe mode interacts with one of the pump, Stokes, and anti-Stokes modes at a time. The results demonstrate that the quantum Zeno (anti-Zeno) effects are closely associated with the phase matching (mismatching).
High-Frequency Gravitational Waves in Electromagnetic Waveguides
- First Published: 15 September 2023
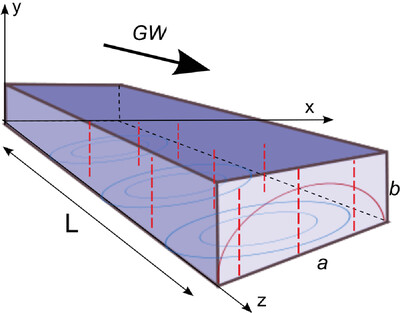
The interaction between a high-frequency gravitational wave and an electromagnetic wave in a waveguide is discussed in the linearized theory. It is shown that a gravitational wave, having the same frequency as the electromagnetic wave, gives rise to a Second Harmonic Generation effect, exciting a frequency-doubled electromagnetic mode in the waveguide. An estimate of such effect is presented.
Optical Non-Reciprocity in Coupled Resonators by Detailed Balance
- First Published: 17 September 2023
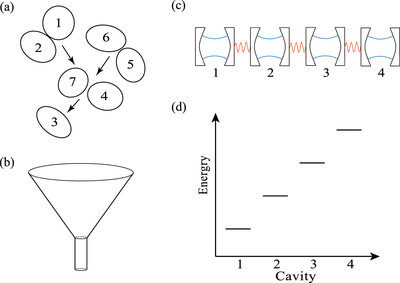
Inspired by photosynthetic energy transfer process, a method of realizing non-reciprocal optical transmission in an array of coupled resonators is theoretically proposed. The optical nonreciprocity arises from the frequency gradient and the interaction with the environment, which is similar to photosynthetic energy transfer. Detailed balance is used to describe these findings.
Speakable and Unspeakable in Quantum Measurements
- First Published: 17 September 2023
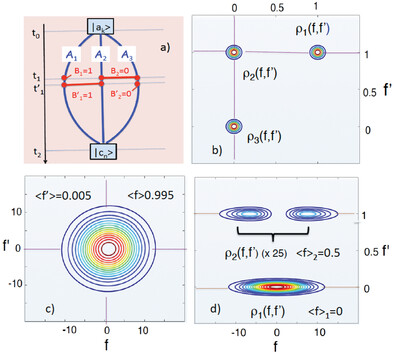
Feynman famously warned against looking for the “machinery behind the law” governing quantum behavior. More recently, several authors claimed progress in describing the properties of a weakly perturbed quantum system. Some of their claims are indeed spectacular, some outright paradoxical. Have they succeeded where Feynman failed? Or have they gone down the “blind alley” he reserved for such endeavors?
Manipulating Spin-Dependent Wavefronts of Vortex Beams via Plasmonic Metasurfaces
- First Published: 19 September 2023
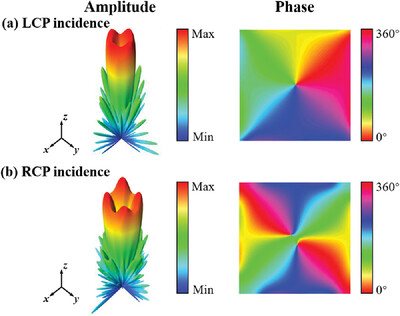
Through tuning the dimension and rotation angle of H-shaped meta-atoms to combine propagating phase and geometric phase, a three-bit meta-atom library is established for circularly polarized waves. Three reflective plasmonic metasurfaces are presented for manipulating spin-dependent wavefronts of vortex beams in the visible band.
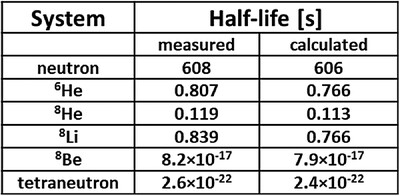
Ab Initio Thermodynamics Calculation of Beta Decay Rates
- First Published: 19 September 2023
All-Dielectric Multichannel Terahertz Metasurface Empowering Independent Wavefront Manipulation
- First Published: 19 September 2023
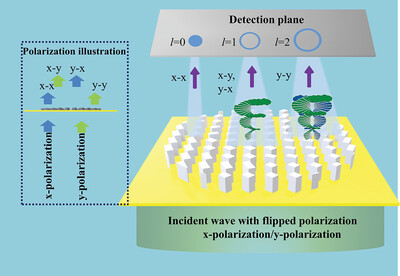
In this work, one transmission-mode, multichannel all-silicon metasurface platform that can implement functionalities separately in two orthogonally polarized output fields under linearly polarized incidences is proposed, which can effectively promote the design flexibility. For proof-of-principle experimental exhibitions, a monolayer metasurface composed of silicon pillars is designed, fabricated, and characterized to demonstrate the ability of multi-dimensional light field control, such as polarization-switchable focusing beam.
Control of Correlation Using Confinement in Case of Quantum System
- First Published: 19 September 2023
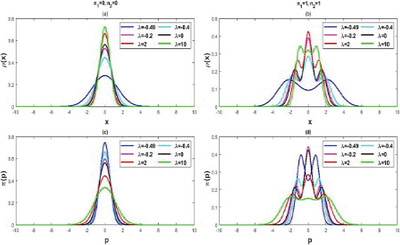
The effect of spatial confinement on correlation, Shannon entropy, and mutual information on two interacting particles is studied in detail. Upon imposing confinement on the system, these measures for all states demonstrate a dependence on both inter-particle interaction strength λ and confining length L. In the case of strong spatial confinement, λ hardly plays any role.
Propagation Characteristics of a Partially Coherent Gaussian Schell-model Array Vortex Beam in the Joint Turbulence Effect of a Jet Engine and Atmosphere
- First Published: 19 September 2023
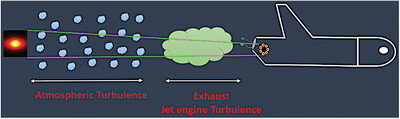
The propagation characteristics of the Gaussian Schell-model array vortex beam across joint turbulence of jet engine exhaust and the atmosphere is investigated. The results show that, the beam spreads faster with a larger propagation distance, lower spatial coherence, and high-strength turbulence. Furthermore, it is more influenced when its propagation is near the jet engine exhaust.