Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
(Ann. Phys. 1/2023)
- First Published: 16 January 2023

Nonlinear Optics
Spherical MoS2 nanoparticles are synthesized using ordered 3D mesoporous silica as hard templates, as described by Lei Zhang and co-workers in article number 2200378. The uniform morphology of the nanoparticles mimics an isotropy-like medium for generating a polarization-dependent third-order nonlinear optical response with suppression of second-harmonic generation. Typical spherical MoS2 nanoparticles and the frequency-conversion process are shown in the cover image.
Masthead
Editorial
Annalen der Physik – Wiley's Physics Forum and Center of Excellence
- First Published: 16 January 2023
Perspective
Then & Now
Rudolph Clausius (1822–1888) and His Concept of Mathematical Physics
- First Published: 11 December 2022

Rudolph Clausius is well known as a pioneer of the mechanical theory of heat (1857) and as the creator of the concept of entropy (1865), often called the discoverer of the second law of thermodynamics (1850). This paper focuses on his concept of mathematical physics, that has influenced modern physics far beyond the field of thermodynamics.
Research Articles
Third-Order Nonlinear Effect and Polarization-Dependent Modulation Using Spherical-Like MoS2 Nanoparticles
- First Published: 31 October 2022
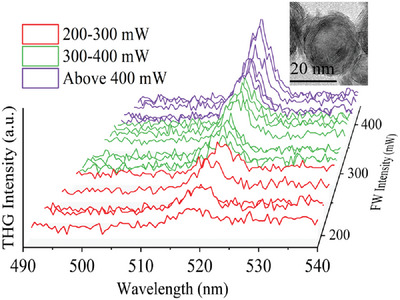
Spherical MoS2 nanoparticles (NPs) are synthesized utilizing ordered 3D mesoporous silica (EP-FDU-12) as hard templates. The independent third harmonic generation (THG) is detected in artificial spherical-like MoS2 NPs and the polarization-dependent is observed between pump fundamental wave and THG. The uniformity morphology of NPs mimics an isotropy-like medium for suppressing second harmonic generation and isolating third-order nonlinear optical response.
Phase Covariant Channel: Quantum Speed Limit of Evolution
- First Published: 21 November 2022
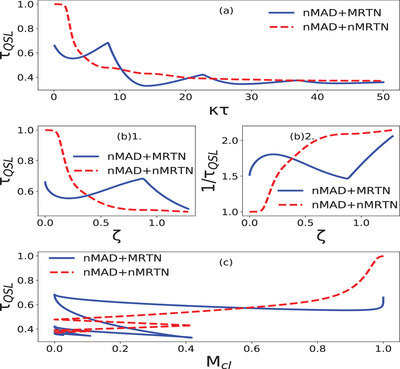
The phase-covariant map describes the physical processes involving absorption, emission and pure dephasing. To investigate the effect of phase covariant maps on quantum speed limit time , they consider the maps under various combinations of the above processes and investigate the dependence of on quantum memory (ζ). For absorption-free phase covariant maps, both CP-(in)divisible, (non)-Markovian dephasing are taken into account. The role of coherence-mixedness balance on the speed limit time is checked in the presence of both vacuum and finite temperature effects. For the initial maximal coherent state, they show that the presence of a CP-indivisible non-Markovian dephasing map does not always speed up the quantum evolution. They also investigate the rate at which Holevo's information changes and the action quantum speed of evolution for specific cases of the phase covariant map.
Regular Electric Field in Electromagnetic Coupled to a Scalar Field
- First Published: 20 November 2022
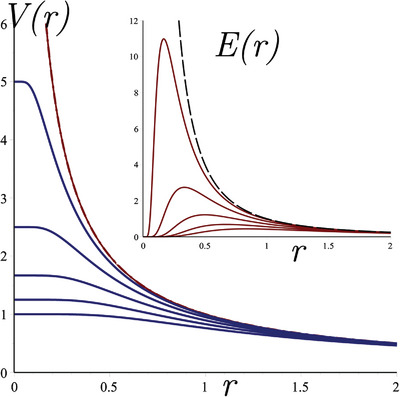
In the framework of nonminimally coupled electromagnetic and scalar fields in flat spacetime, the existence of non-singular electric fields is proved for an electric monopole. A formalism is introduced upon which the coupled regular-electric and scalar fields are obtained. For a given regular electric field this formalism implies two supersymmetric coupling functions corresponding to a scalar and a phantom field.
Enhancement of Non-Gaussianity and Nonclassicality of Photon-Added Displaced Fock State: A Quantitative Approach
- First Published: 20 November 2022
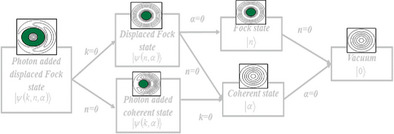
A quantitative analysis of non-Gaussian and nonclassical aspects of photon added displaced Fock state is performed using a number of measures, like Wigner–Yanese skew information, entanglement potential, Wigner logarithmic negativity, and relative entropy of non-Gaussianity. Robustness of the negativity of the Wigner function over different noise channels is also studied.
Optical Nonlinearity of Emerging ZrS2 and HfS2 Semiconductors
- First Published: 13 December 2022
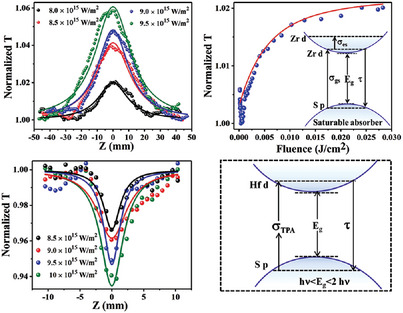
ZrS2 and HfS2 films are prepared by chemical vapor deposition. Saturable absorption happens in ZrS2 due to the larger ground state absorption than that of excited state. Reverse saturable absorption appears in HfS2 due to the two-photon absorption. The figure of merit values of ZrS2 and HfS2 are much larger than graphene at the wavelength of 800 nm.
Magnetoelectric-Field Electrodynamics: Search for Magnetoelectric Point Scatterers
- First Published: 13 December 2022
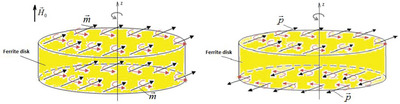
Mesoscopic structures with electric and magnetic dipole-carrying excitations behave like point scatterers with their inherent magnetoelectricity. The magnetoelectric resonance effect arises from the coupling of electrostatic and magnetostatic oscillations. We have the combined effects of magnetic dipole precession in a bias magnetic field along with electric quadrupole precession in an electric field gradient.
Transmission Reflection Integrated Programmable Metasurface for Real-Time Beam Control and High Efficiency Transmission Polarization Conversion
- First Published: 14 December 2022
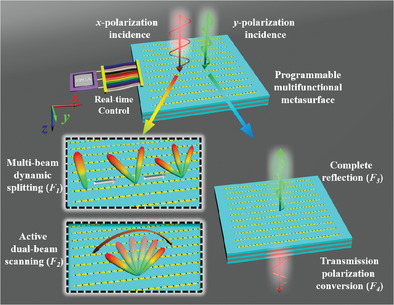
A schematic model of the proposed transmission-reflection-integrated programmable coding multifunctional metasurface which can implement multiple independent functionalities at the same frequency band, including multibeam dynamic splitting, active dual-beam scanning, complete reflection, and transmission polarization conversion is shown in the table of contents.
Collective Behavior in Quantum Interference: A Supplementary Superposition Principle
- First Published: 14 December 2022
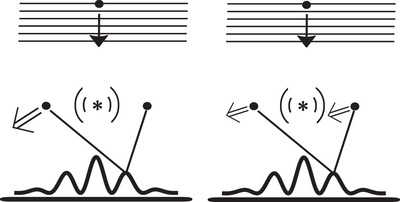
Quantum physics is based on the superposition of amplitudes. Interactions occur only along the path associated with each amplitude. This is challenged to include collective interactions along a given path and shown to be a viable alternative to the standard superposition principle in systems with more than two bodies.
Fast Generation of 2N-Photon Fock States using Shortcuts to Adiabaticity and Ultrastrong Light–Matter Coupling
- First Published: 14 December 2022
Enhanced Charging in Common Environments Compared to Independent Environments for Two-Level Systems
- First Published: 14 December 2022
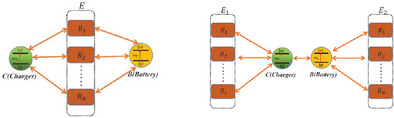
Compared with a quantum battery and a charger in their own independent environment, the charging performance for a quantum battery and a charger in common environments can be achieved by increasing the number of environments and setting appropriate coupling strength between the system and the environment.
Universal Global Cloning of Continuous Variables Entanglement
- First Published: 14 December 2022
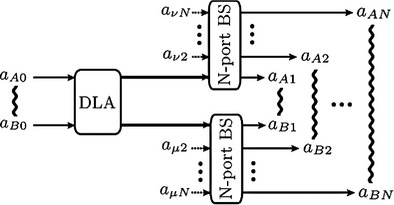
In this paper, a 1-to-N universal global entanglement cloning machine (UGECM), which is composed of only single deterministic linear amplifiers and two N-port beam splitters, is proposed. It is demonstrated that the entanglement replicas of this UGECM are of high fidelity and inseparability preservation. Such a UGECM may find its new applications in quantum entanglement broadcasting.
Broadband Plasmon-Induced Transparency to a Electromagnetically Induced Absorption Conversion Metastructure Based on Germanium
- First Published: 14 December 2022
Interactions of Localized Wave Structures on Periodic Backgrounds for the Coupled Lakshmanan–Porsezian–Daniel Equations in Birefringent Optical Fibers
- First Published: 14 December 2022
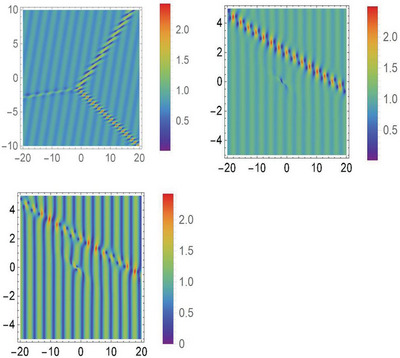
Localized waves on periodic backgrounds are constructed by using the matrix analysis and SU(2) transformation for the coupled Lakshmanan–Porsezian–Daniel equations. Moreover, interactions and dynamic behaviors of these localized waves are shown. The results may be applicable to the relevant experimental investigations in optical fibers, fluid dynamics and other media.
Quantum-Error-Rejection for Hyperentanglement Transmission without Calibrated Reference Frames
- First Published: 14 December 2022
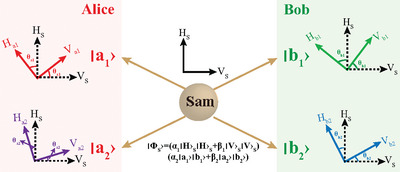
In this paper, a spatial-polarization hyperentanglement transmission scheme with misalignment reference frames between the communication parties is proposed. By implementing the scheme, the decoherence effect caused by the misalignment of the reference frames between the communication parties can be completely suppressed, and the success probability of the scheme can theoretically reach 100%.
Particle Spin Described by Quantum Hamilton Equations
- First Published: 14 December 2022
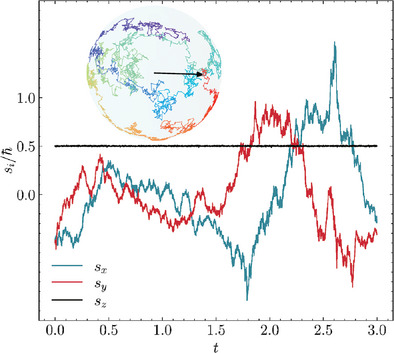
The quantum generalization of the classical Hamilton equations is derived for spinning particles in Nelson's stochastic mechanics. The solutions of these equations for a particle in a homogeneous magnetic field lead to a stochastically spinning particle with the well-known quantized expectation values.
High-Fidelity and Low-Cost Hyperparallel Quantum Gates for Photon Systems via Λ-Type Systems
- First Published: 14 December 2022
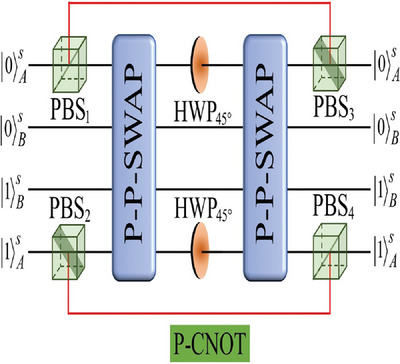
Assisted by a three-level Λ-type atom, an underlying polarization–polarization swap (P-P-SWAP) quantum gate is constructed with near-unit fidelity. Moreover, the hyper-controlled-not and hyper-controlled-controlled-not gates are implemented perfectly with 2 and 4 P-P-SWAP gates, respectively, both of which are high fidelity in practical conditions and can work efficiently with a relatively lower-Q factor.
Gravitational Redshift Induces Quantum Interference
- First Published: 14 December 2022
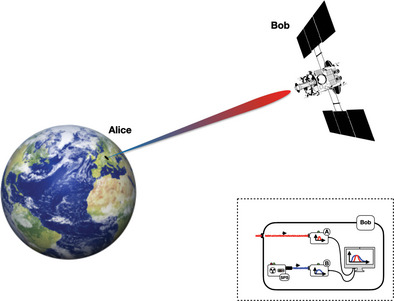
Gravitational redshift is shown to act as a quantum channel on the quantum state of propagating photons. The transformation induced is known in quantum optics as mode-mixing, which shifts excitations between field modes. This opens the possibility of generating nonclassical states of light through propagation in a gravitational field, and testing the predictions of quantum field theory in curved spacetime.