Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW ARTICLES
Human age reversal: Fact or fiction?
- First Published: 02 July 2022
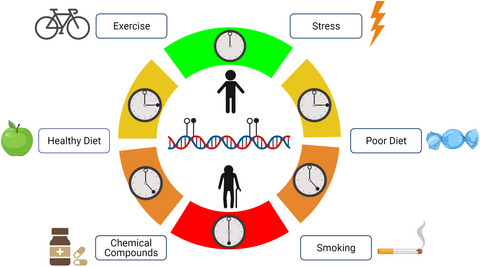
Aging is concomitant with a slew of molecular changes, including significant shifts in the epigenome. These age-related alterations can be used to construct aging clocks, which are computational models thought to predict biological age. The delta between predicted biological age and chronological age correlates with disease burden, mortality, and health. A growing body of evidence indicates that aging clocks are sensitive to health-promoting (left) and deleterious (right) interventions.
Age-related thymic involution: Mechanisms and functional impact
- First Published: 12 July 2022
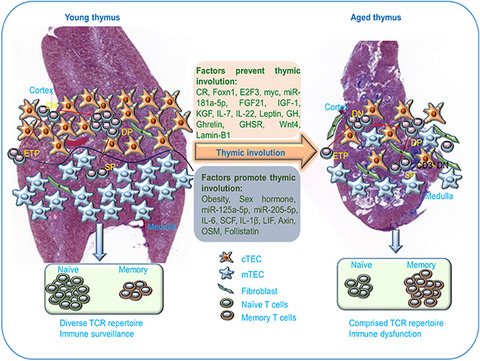
Age-related thymic involution has many negative impacts on immune function including reduced pathogen resistance, high autoimmunity incidence, and attenuated tumor immunosurveillance. This review summarizes the current understanding of how age impacts thymic development and function, as well as the mechanisms underlying age-related thymic involution, particularly TEC transcriptional profile changes during thymic aging.
ORIGINAL PAPER
Effects of cerebral amyloid angiopathy on the brain vasculome
- First Published: 18 July 2022
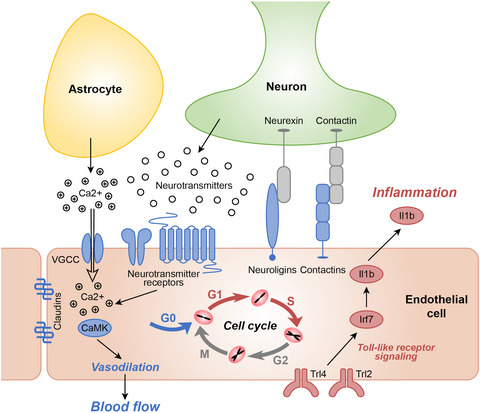
Vascular Aβ accumulation disrupts neurovascular coupling, induces erroneous cell cycle reactivation, and promotes inflammation in cerebral endothelium. These alterations can result in cerebrovascular dysfunction and contribute to the vascular pathology of cerebral amyloid angiopathy and Alzheimer's disease.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
DAF-2/insulin IGF-1 receptor regulates motility during aging by integrating opposite signaling from muscle and neuronal tissues
- First Published: 08 July 2022
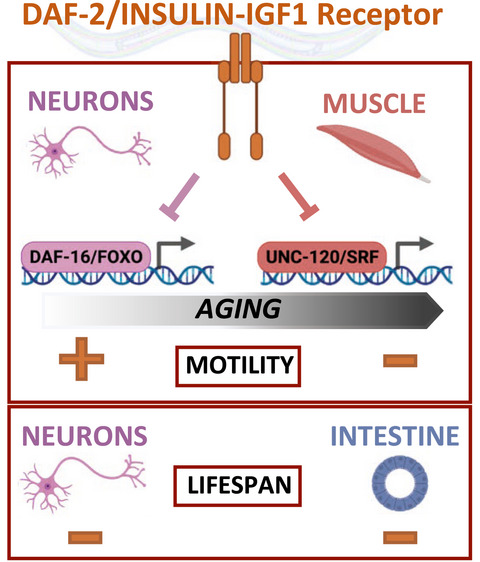
In C. elegans, age-associated regulation of motility by the DAF-2/insulin-IGF-1 receptor is determined by the sequential and opposing impact of neurons and muscle and can be dissociated from the lifespan phenotype. Intestinal and neuronal DAF-2 activities modulate lifespan, whereas muscle DAF-2 does not. Neuronal DAF-2 promotes motility in early adulthood through inhibition of DAF-16/FOXO, whereas muscle DAF-2 decreases motility in middle age through inactivation of UNC-120/SRF.
Urolithin A improves mitochondrial health, reduces cartilage degeneration, and alleviates pain in osteoarthritis
- First Published: 01 July 2022
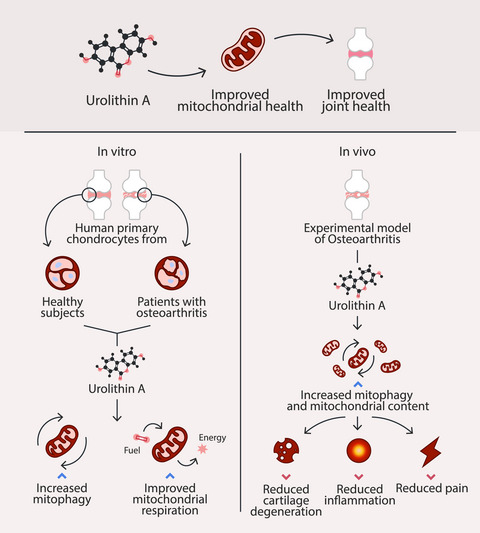
Mitochondrial dysfunction is a hallmark of joint aging and osteoarthritis (OA). Here, we show that the natural compound Urolithin A (UA) improves mitophagy and mitochondrial function in human cartilage cells from healthy donors and OA patients. In an in vivo model of OA, UA improves joint mitochondrial health, reduces inflammation, and protects against OA-associated cartilage degeneration and pain, indicating the potential of UA to promote joint function and mobility during aging and in OA patients.
A partial reduction of VDAC1 enhances mitophagy, autophagy, synaptic activities in a transgenic Tau mouse model
- First Published: 07 July 2022
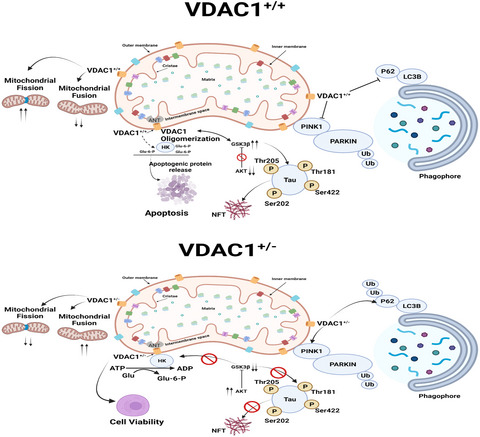
Schematic overview of VDAC1+/+ and VDAC1+/− model: Working model for the regulation of mitophagy, mitochondrial dynamics, mitochondrial biogenesis, VDAC1, and Hexokinase interaction, and VDAC1 and P-Tau interaction. In VDAC1+/+, (i) dissociation of hexokinase (HK) results in a “closed” VDAC configuration that prevents adenine nucleotide exchange and uncouples intra and extramitochondrial metabolism, (ii) shifts the equilibrium to the VDAC1 oligomeric state, mediating the release of apoptogenic proteins and leading to apoptosis, (iii) Elevated GSK3β activity is a key event in phosphorylation of Tau and synaptic pathology in AD. GSK3β is proposed to activate VDAC1 phosphorylation, ultimately leading to mitochondrial dysfunction and synaptic damage in AD, (iv) Defective mitophagy, (v) increased mitochondrial fission and decreased mitochondrial fusion. In VDAC1+/− (i) VDAC1 and ANT reportedly interact directly when complexed with HK, an arrangement that facilitates mitochondrial contact site formation and metabolite exchange, (ii) decreased GSK3β and P-Tau activity, and (iii) PINK1 recruits PARKIN from the cytoplasm to mitochondrial outer membrane. After PARKIN has been recruited to mitochondria, activated PARKIN ubiquitinates proteins in the mitochondrial outer membrane VDAC to facilitate mitophagy. PARKIN-mediated ubiquitination recruits autophagy adapter protein p62, and these proteins interact with LC3B. LC3B participates in the formation of an autophagosome, which is fated for lysosomal destruction to clear out damaged mitochondrion, (iv) decreased mitochondrial fission and increased mitochondrial fusion.
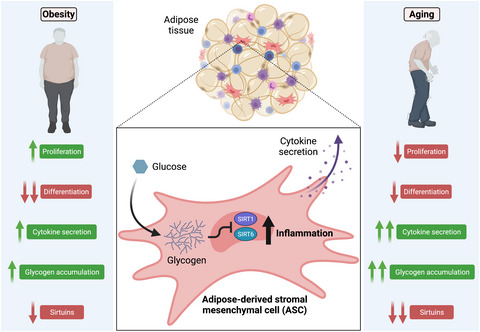
Glycogen accumulation in adipocyte precursors from elderly and obese subjects triggers inflammation via SIRT1/6 signaling
- First Published: 10 July 2022
Faster cytotoxicity with age: Increased perforin and granzyme levels in cytotoxic CD8+ T cells boost cancer cell elimination
- First Published: 11 July 2022
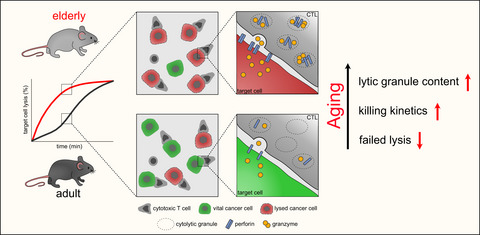
Immunosenescence is associated with decreased T cell numbers and impaired functionality of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL). Surprisingly, we find that, despite immunosenescence, CTL efficiency against cancer cells increases with age, if similar CTL numbers or individual cells are compared. Elevated perforin and granzyme levels turn CTLs of elderly mice into ultimate killers, highlighting the importance of distinguishing cell intrinsic alterations from microenvironmental changes in elderly individuals.
Vitamin D supplementation worsens Alzheimer's progression: Animal model and human cohort studies
- First Published: 12 July 2022
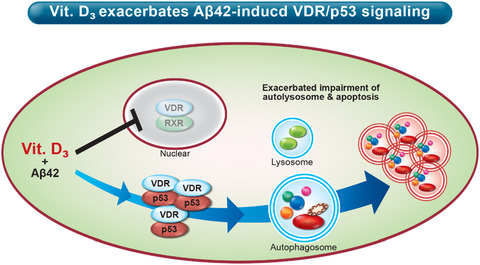
We studied whether it is beneficial to supplement vitamin D to APP/PS1 mice and humans. The animal studies show vitamin D deficiency is an early disease outcome and supplementation of vitamin D worsens AD brain pathology via enhancing VDR/p53 complex to impair autophagosome. Nationwide longitudinal cohort studies also suggest long-term vitamin D supplementation is associated with higher risk of dementia in dementia-free older adults and higher mortality in dementia individuals. Our results caution against prolonged use of vitamin D by AD patients and older adults.
seRNA PAM controls skeletal muscle satellite cell proliferation and aging through trans regulation of Timp2 expression synergistically with Ddx5
- First Published: 18 July 2022
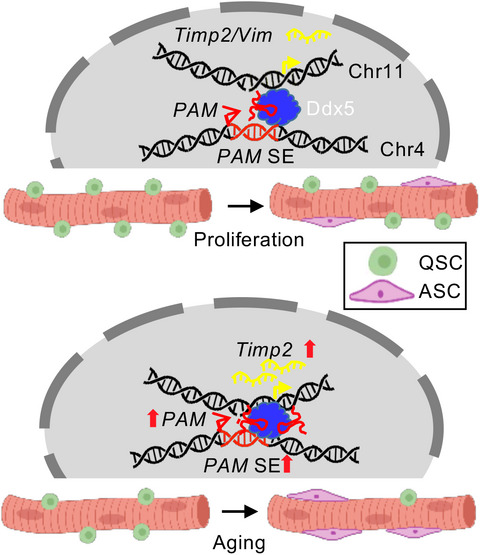
Muscle satellite cells (SCs) are indispensable for muscle regeneration and lncRNAs play important roles in regulating SC activities. Here, we characterize the function of lncRNA PAM in SC. We show that PAM promotes SCs proliferation by binding with Ddx5 to facilitate the chromatin interaction between PAM residing super enhancer (SE) and target loci, Timp2 and Vim. In aging mice, the activity of PAM SE is elevated to enhance the transcription of Timp2, which potentially modulates extracellular matrix (ECM) components in aging muscle.
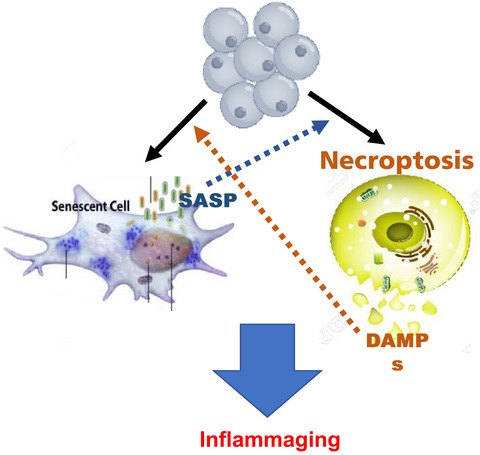
Senolytic treatment reduces cell senescence and necroptosis in Sod1 knockout mice that is associated with reduced inflammation and hepatocellular carcinoma
- First Published: 23 July 2022
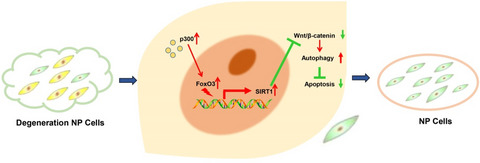
p300 arrests intervertebral disc degeneration by regulating the FOXO3/Sirt1/Wnt/β-catenin axis
- First Published: 30 July 2022
p38α-MAPK-deficient myeloid cells ameliorate symptoms and pathology of APP-transgenic Alzheimer's disease mice
- First Published: 31 July 2022
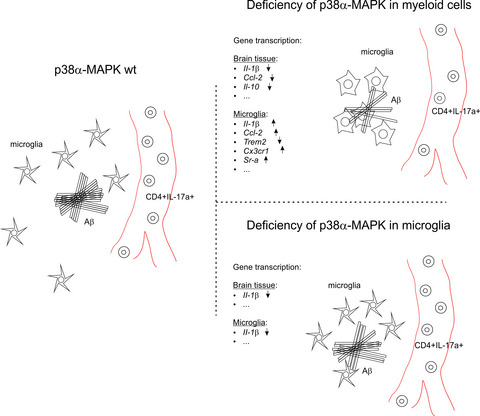
Deficiency of p38α-MAPK in myeloid cells, but not only in microglia, efficiently attenuates cerebral Aβ and improves cognitive function in APP-transgenic Alzheimer's disease mice. As possible mechanisms, p38α-MAPK-deficient myeloid cells decrease peripheral IL-17a-expressing CD4-positive cells and increase inflammatory activation and Aβ internalization in microglia.
Sirt1 overexpression improves senescence-associated pulmonary fibrosis induced by vitamin D deficiency through downregulating IL-11 transcription
- First Published: 30 July 2022
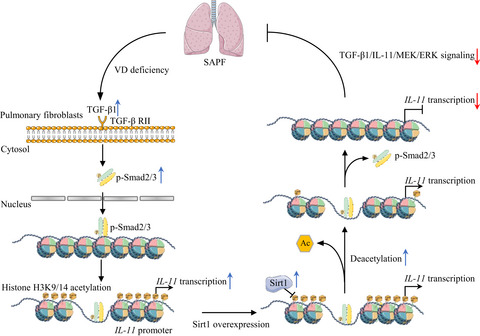
Pulmonary Sirt1 and serum vitamin D (VD) decrease with physiological aging, activating TGF-β1/IL-11/MEK/ERK (TIME) signaling and promoting senescence-associated pulmonary fibrosis (SAPF). Sirt1 overexpression ameliorates SAPF in VD-deficient mice through downregulating IL-11 transcribed by Smad2 via deacetylating H3K9/14ac mainly at the region from −871 to −724 of IL-11 promoter, and subsequently inhibiting TIME signaling in pulmonary fibroblasts. This signal in aging fibroblasts could be a therapeutic target for preventing physiologically VD deficiency-induced SAPF.
SHORT COMMUNICATION
Integrity of hypothalamic–pituitary-testicular axis in exceptional longevity
- First Published: 29 June 2022
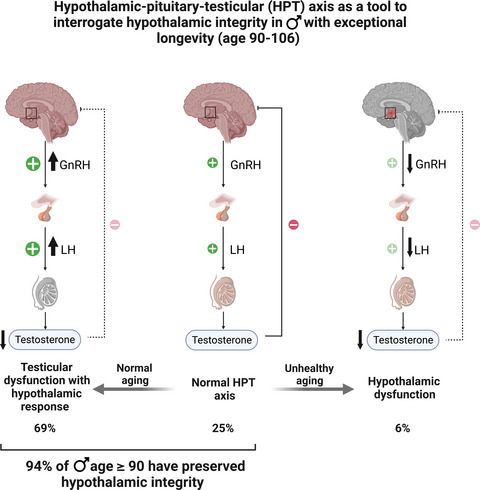
The hypothalamus is increasingly being recognized as a key player in longevity. Hypothalamic integrity in men with longevity can be inferred from the function of the hypothalamic-pituitary-testicular (HPT) axis. We herein found that the majority of nonagenarian and centenarian men have preserved hypothalamic regulation of the HPT axis.