Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Issue Information
- Pages: 1433-1434
- First Published: August 2022

Front cover image:
A flavonoid O-methyltransferase (GhOMT1) in Gossypium hirsutum is found to play a critical role in anthocyanidin methylation. Deficiency of GhOMT blocks the anthocyanidins methylation, increases anthocyanidins accumulation and enhances PAs biosynthesis in fibers of NCCs. The multi-colored cotton fibers were selectively bred from the progeny of the empurpled mutant of GhOMT1 deficiency crossed with NCCs. This work broadens our understanding on mechanisms of plant color formation and open up huge possibilities to achieve cotton fibers with new colors. Cover illustration refers to the article in this issue (Ke et al., 1546–1560).
Brief Communication
iSoybean: A database for the mutational fingerprints of soybean
- Pages: 1435-1437
- First Published: 17 May 2022
FLOURY ENDOSPERM20 encoding SHMT4 is required for rice endosperm development
- Pages: 1438-1440
- First Published: 20 May 2022
EARLY MORNING FLOWERING1 (EMF1) regulates the floret opening time by mediating lodicule cell wall formation in rice
- Pages: 1441-1443
- First Published: 30 May 2022
Enhancing the accumulation of eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid in transgenic Camelina through the CRISPR-Cas9 inactivation of the competing FAE1 pathway
- Pages: 1444-1446
- First Published: 20 June 2022
Review Article
m6A-mediated regulation of crop development and stress responses
- Pages: 1447-1455
- First Published: 18 February 2022
Research Articles
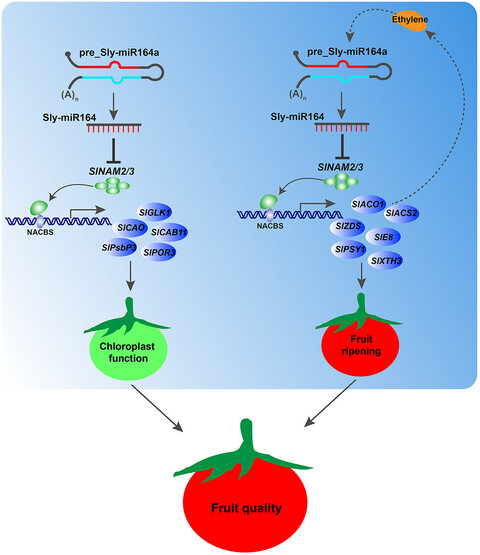
SlMIR164A regulates fruit ripening and quality by controlling SlNAM2 and SlNAM3 in tomato
- Pages: 1456-1469
- First Published: 11 April 2022
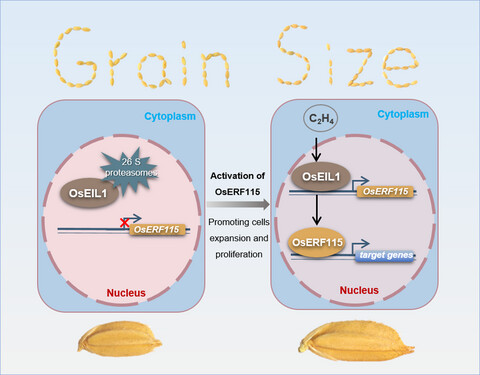
The OsEIL1-OsERF115-target gene regulatory module controls grain size and weight in rice
- Pages: 1470-1486
- First Published: 11 April 2022
Riboflavin integrates cellular energetics and cell cycle to regulate maize seed development
- Pages: 1487-1501
- First Published: 14 April 2022
R gene triplication confers European fodder turnip with improved clubroot resistance
- Pages: 1502-1517
- First Published: 21 April 2022
Overexpression of cytoplasmic C4 Flaveria bidentis carbonic anhydrase in C3 Arabidopsis thaliana increases amino acids, photosynthetic potential, and biomass
- Pages: 1518-1532
- First Published: 25 April 2022
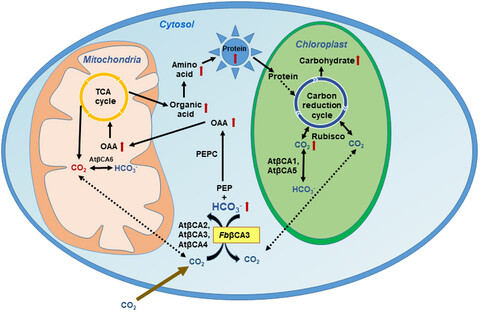
The cytosolic FbβCA3 having low Km for CO2 increase the hydration of CO2. The dashed arrows indicate the diffusion of CO2 within the cytosol and the organells. FbβCA3 overexpression increased the flux of the carboxylic acid to the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA) in mitochondria to play an an ansplerotic role to synthesize higher amounts of total amino acids and proteins that contribute to increase photosynthetic efficiency and biomass (OAA - oxaloacetic acid; PEP - phoshoenol pyruvate; PEPC - phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase; TCA cycle - tri carboxylic acid cycle).
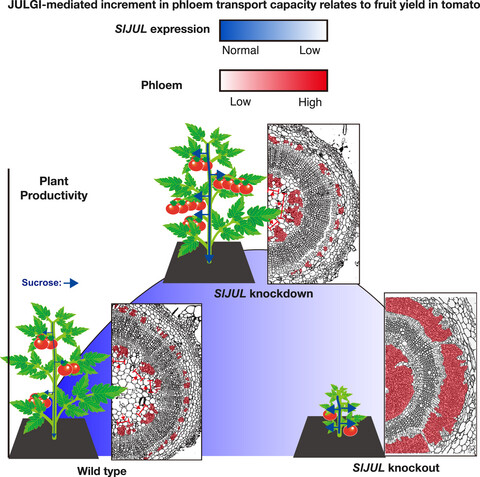
JULGI-mediated increment in phloem transport capacity relates to fruit yield in tomato
- Pages: 1533-1545
- First Published: 28 April 2022
Function deficiency of GhOMT1 causes anthocyanidins over-accumulation and diversifies fibre colours in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum)
- Pages: 1546-1560
- First Published: 03 May 2022
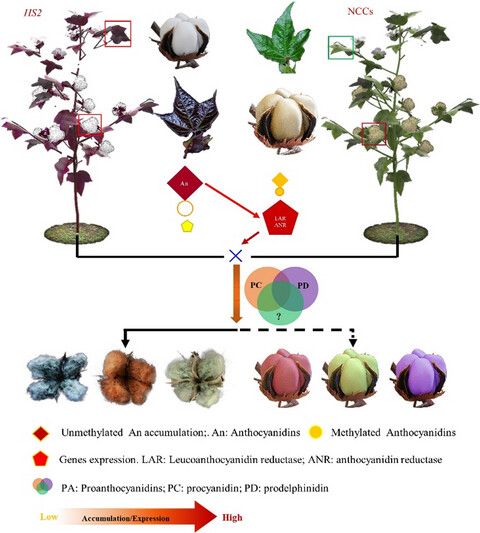
A putative flavonoid O-methyltransferase (GhOMT1) in Gossypium hirsutum is found to play a critical role in anthocyanidin methylation. Deficiency of GhOMT1 blocks the anthocyanidins methylation, increases anthocyanidins accumulation and enhances PAs biosynthesis in fibres of NCCs which broaden our understanding on mechanisms of plant colour formation and open up huge possibilities to achieve cotton fibres with new colours.
Two high hierarchical regulators, PuMYB40 and PuWRKY75, control the low phosphorus driven adventitious root formation in Populus ussuriensis
- Pages: 1561-1577
- First Published: 05 May 2022
Custom-made design of metabolite composition in N. benthamiana leaves using CRISPR activators
- Pages: 1578-1590
- First Published: 05 May 2022
Natural variation of HTH5 from wild rice, Oryza rufipogon Griff., is involved in conferring high-temperature tolerance at the heading stage
- Pages: 1591-1605
- First Published: 05 May 2022
GmTDN1 improves wheat yields by inducing dual tolerance to both drought and low-N stress
- Pages: 1606-1621
- First Published: 05 May 2022
Application of developmental regulators to improve in planta or in vitro transformation in plants
- Pages: 1622-1635
- First Published: 06 May 2022