Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH REPORT
Stimulus-Induced Gamma Sources Reduce in Power but Not in Spatial Extent With Healthy Aging in Human EEG
- First Published: 14 May 2025
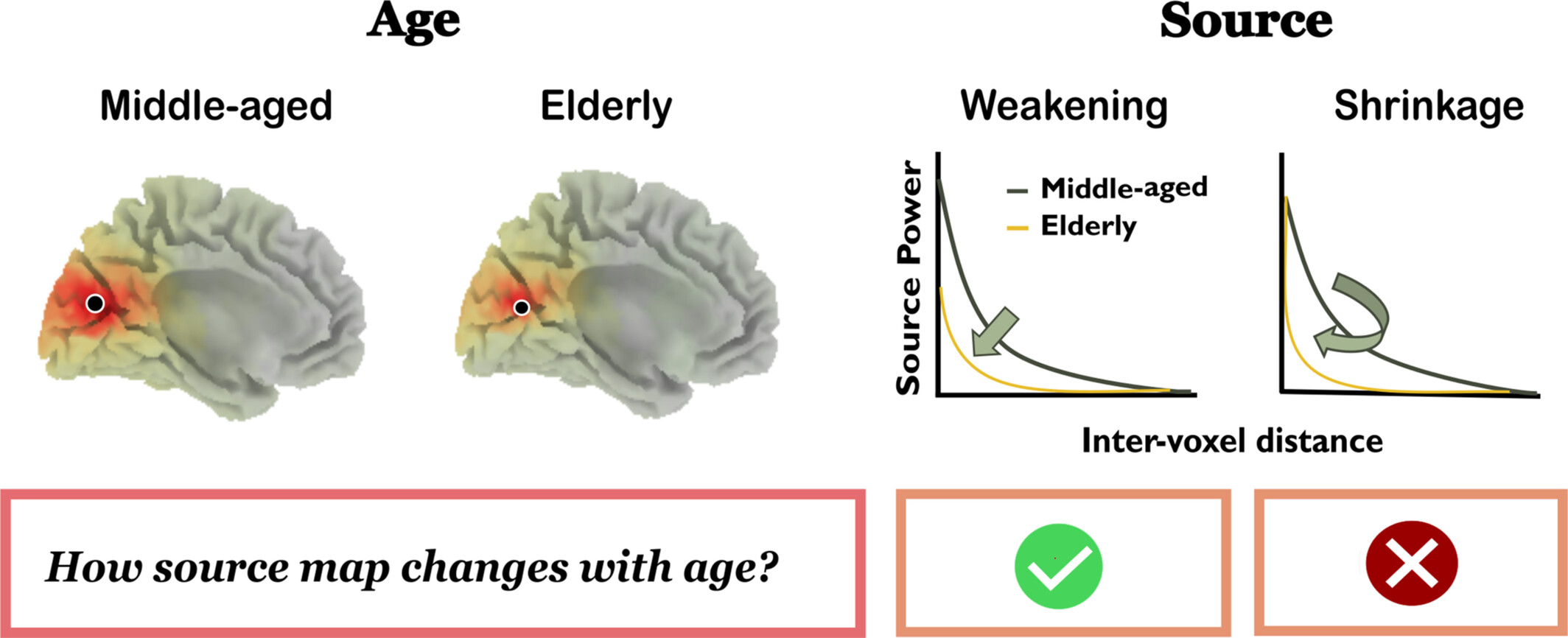
Gamma oscillations elicited by visual gratings decline with healthy aging and Alzheimer's disease. To determine whether reduced gamma activity reflects diminished source magnitude or shrinkage, we reconstructed gamma sources and modeled their spatial distribution as an exponential decay from the seed voxel. Our findings reveal a significant reduction in gamma source magnitude without spatial shrinkage, offering valuable insights into the neural mechanisms underlying healthy aging.
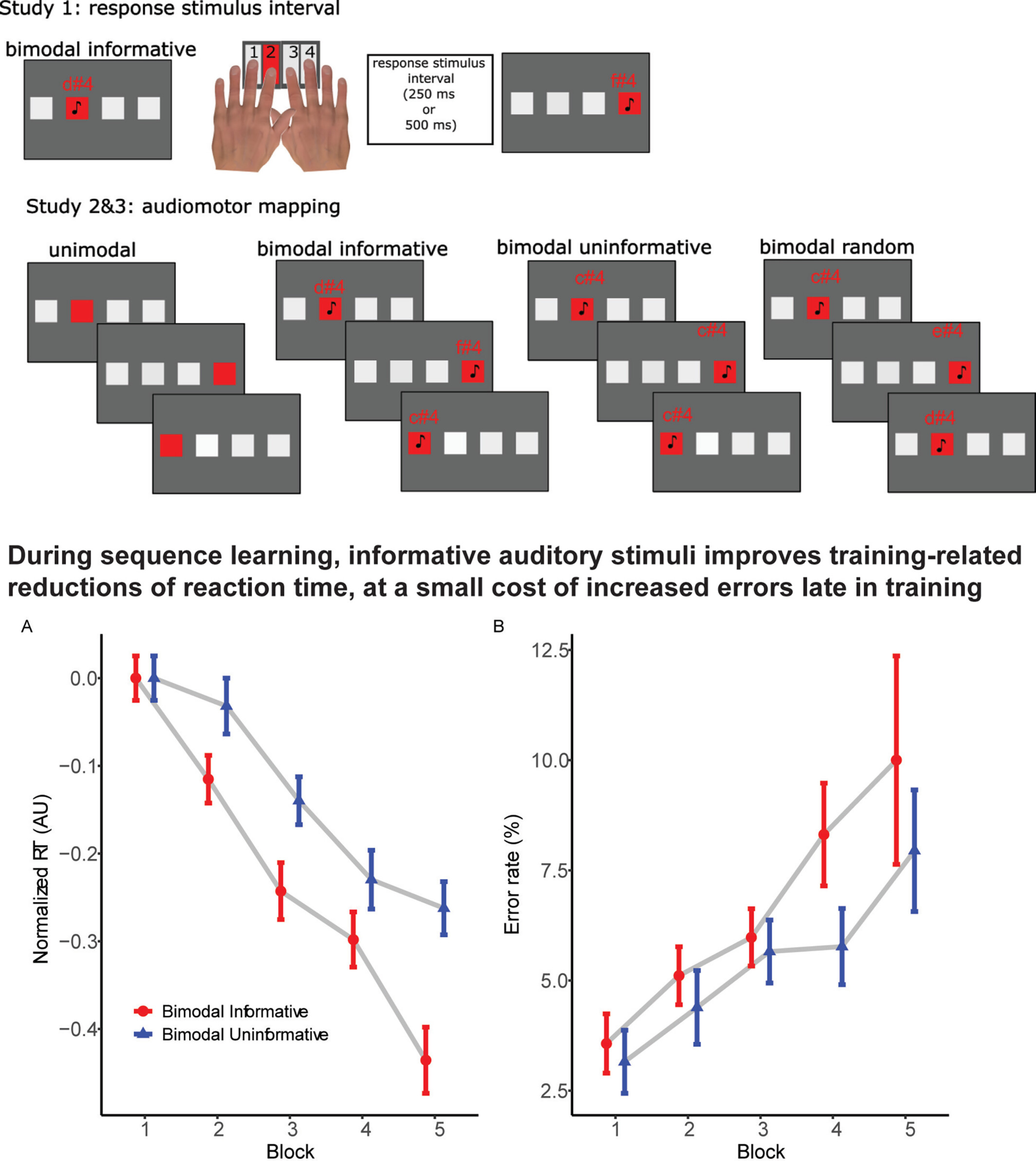
Informative Auditory Cues Enhance Motor Sequence Learning
- Pages: 1-10
- First Published: 21 May 2025
Gestational Valproate Exposure Induces Tissue-Specific Transcriptomic Changes in the Neonatal Brain and Choroid Plexus in a Rat Model of Epilepsy, GAERS
- First Published: 14 May 2025
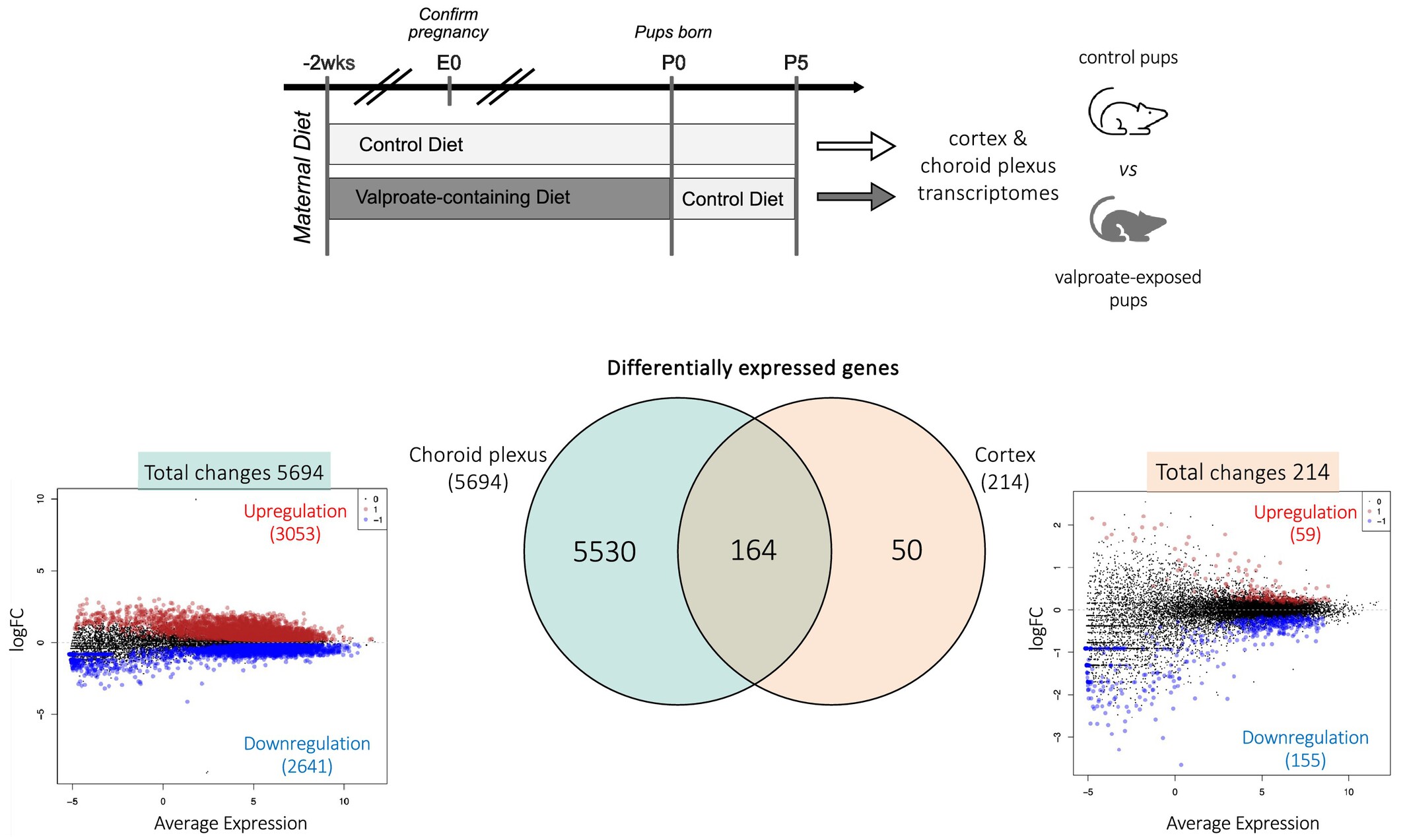
This study used a rat model of absence epilepsy, Genetic Absence Epilepsy Rat from Strasbourg (GAERS), to investigate the effects of gestational valproate exposure on early postnatal brain cortex and lateral choroid plexus transcriptomes. Results showed distinct differential gene expression patterns between the two tissues, with substantially more genes affected in the choroid plexus. Numerous genes involved in the normal functioning of the choroid plexus were dysregulated, potentially revealing additional targets related to the developmental neurotoxicity of valproate.
EDITORIAL
SPECIAL ISSUE ARTICLE
The Neuronal Basis of Mismatch Negativity (MMN) and Its Clinical Applications
Age-Related Differences in Neural Correlates of Auditory Spatial Change Detection in Real and Virtual Environments
- First Published: 15 May 2025
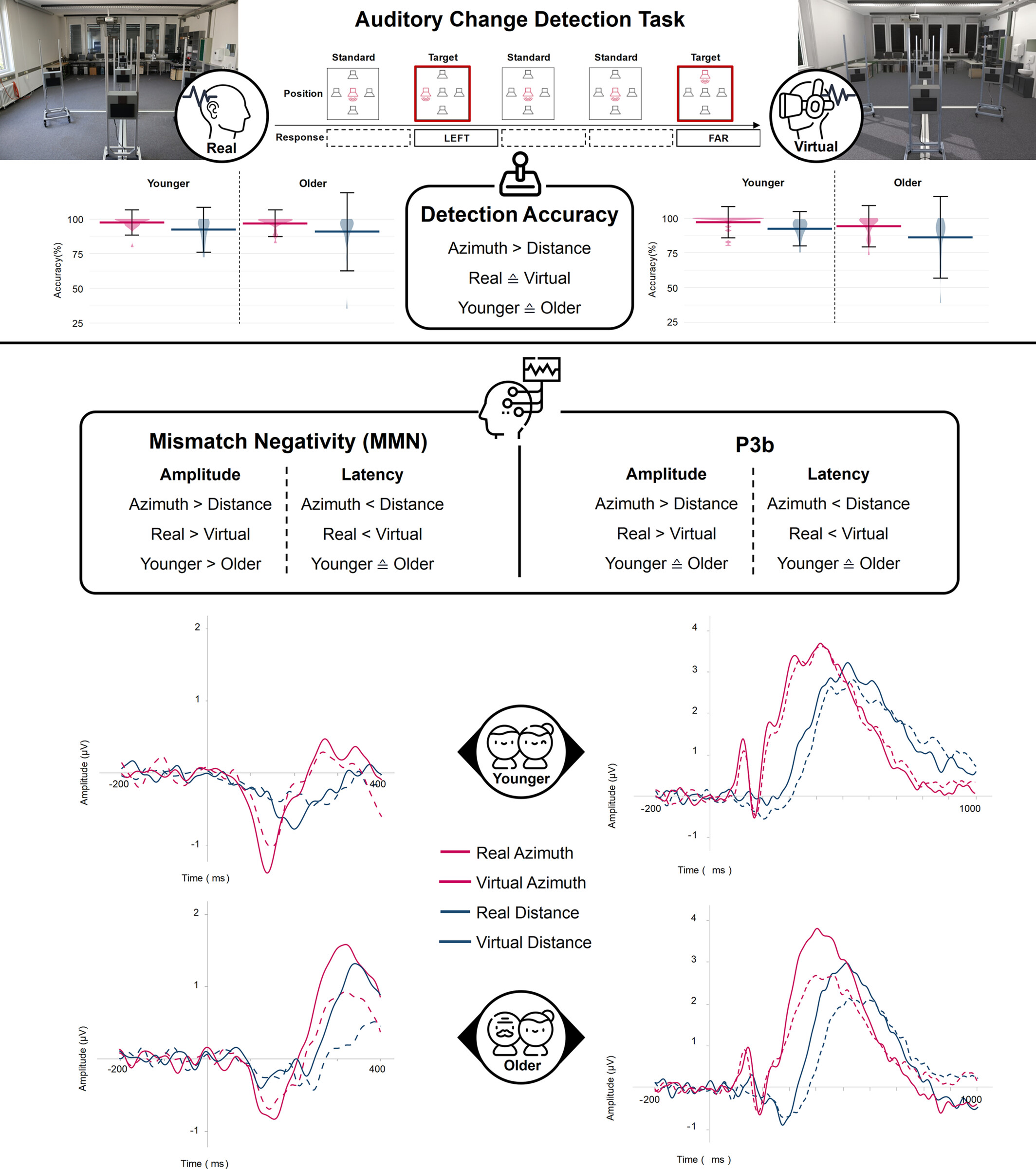
We examined auditory change detection in real and virtual environments across two age groups using behavioral measures and event-related potentials. Participants responded to changes in distance and azimuth from a central reference loudspeaker. Results underscore the potential of audiovisual virtual environments as a research tool for exploring auditory processing and associated neural mechanisms.
REVIEW ARTICLE
Nano-Chaperones: Bridging Therapeutics for Amyloid Aggregation in Alzheimer's Disease and Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus
- First Published: 19 May 2025
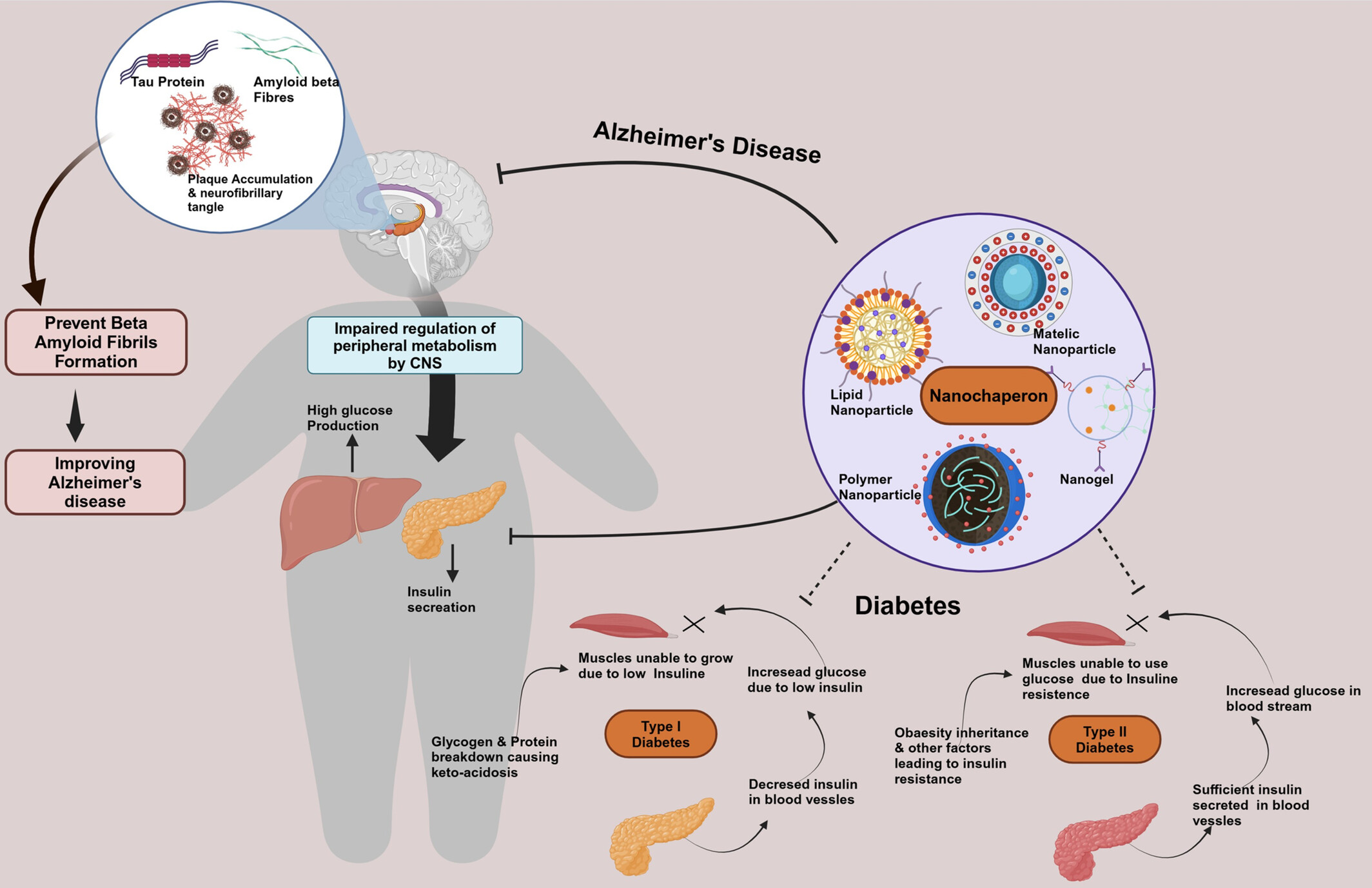
AD is linked to the accumulation of amyloid beta and tau proteins, which disrupts the central nervous system's control over peripheral metabolism. This disruption impacts insulin production and glucose balance, playing a role in the onset of both Type 1 and Type-2 diabetes. Nano-chaperones, including lipid, polymer, and metallic nanoparticles, as well as nanogels, present promising therapeutic options to address metabolic imbalances and lessen amyloid buildup, thereby enhancing outcomes in both AD and diabetes.
SPECIAL ISSUE ARTICLE
The Relevance of a Philosophical Toolkit to Advance Neuroscience
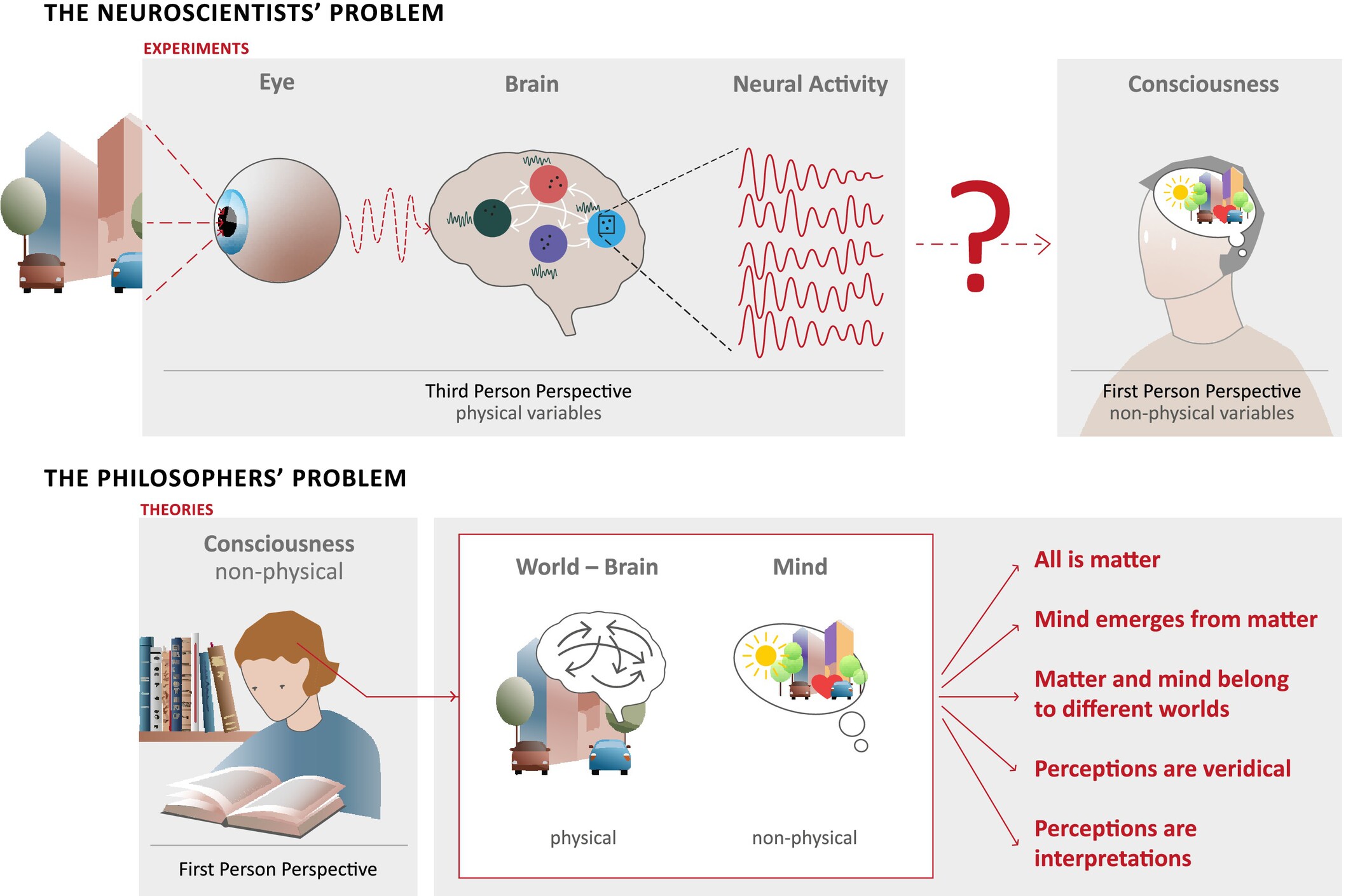
The Mind–Matter Dichotomy: A Persistent Challenge for Neuroscientific and Philosophical Theories
- First Published: 19 May 2025
CORRECTION
RESEARCH REPORT
Intraperitoneal Single Injection of Dexamethasone Leads to Region-Specific Changes in the Profile of Neuron-Specific Proteins in the Rat Brain
- First Published: 25 May 2025
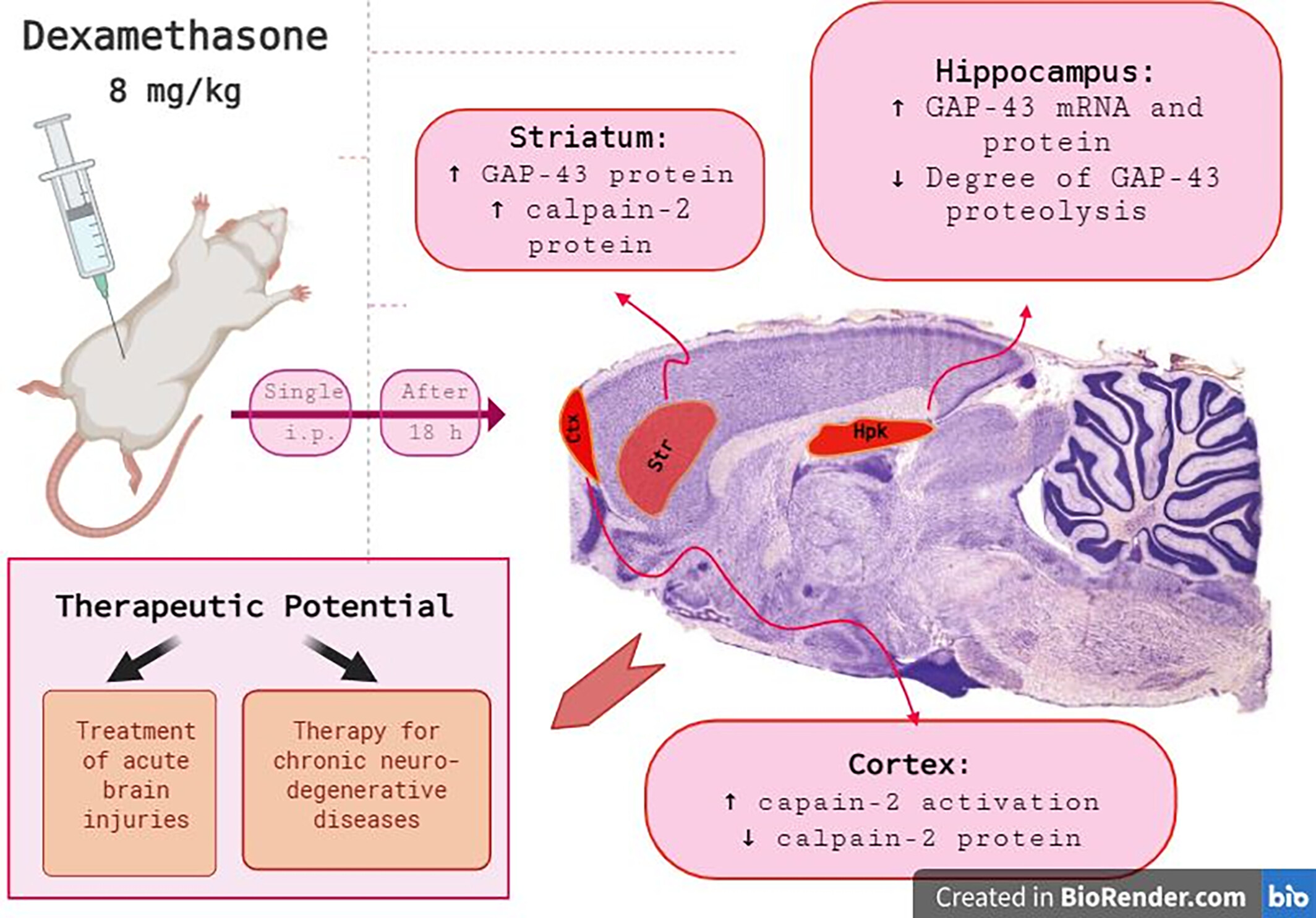
Dexamethasone (DEX) injection with an 8-mg/kg intraperitoneal dose stimulates GAP-43 mRNA and protein production in the rat hippocampus and only GAP-43 protein level in the striatum. Also, DEX administration increases calpain-2 protein production in the striatum, but decreases it in the prefrontal cortex. The activation of calpain-2 is observed only in the prefrontal cortex, but it should be noted that degree of cleavage of GAP-43 by calpain-2 decreases in the hippocampus. These findings suggest DEX's potential therapeutic application in stimulating regenerative processes for both acute brain injuries and chronic neurodegenerative conditions through enhanced production of crucial proteins like GAP-43, tyrosine hydroxylase, and calpains.
TECHNICAL NOTE
BSD: A Bayesian Framework for Parametric Models of Neural Spectra
- First Published: 26 May 2025
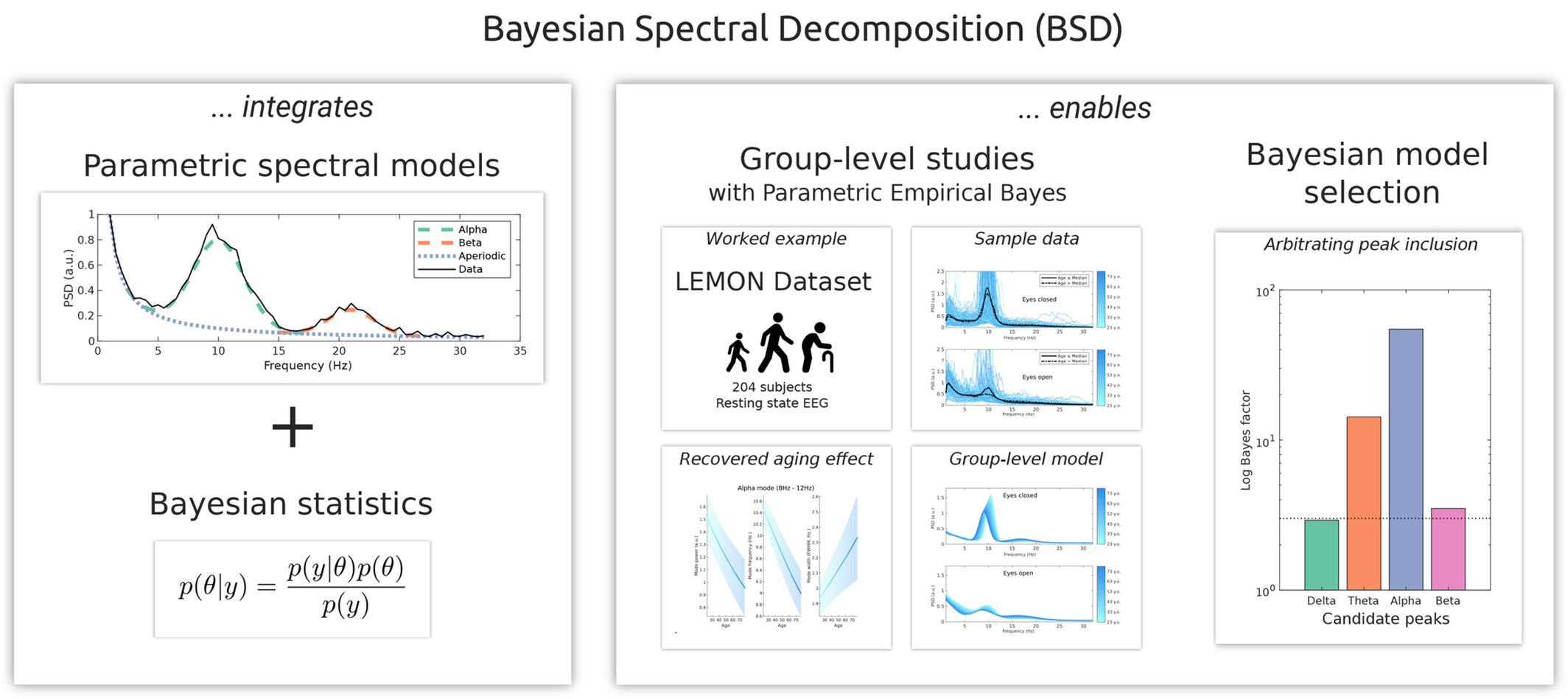
We introduce Bayesian spectral decomposition (BSD): By performing Bayesian inversion of parametric models of neural spectral power, BSD enables straightforward group-level analysis of spectral content and robust detection of spectral peaks. We demonstrate how BSD reveals the ageing effect on the spectral content of resting state occipital EEG signals.
RESEARCH REPORT
Left Ventral Caudate Functional Connectivity Mediates the Relationship Between Habitual Responding and Alcohol Use
- First Published: 26 May 2025
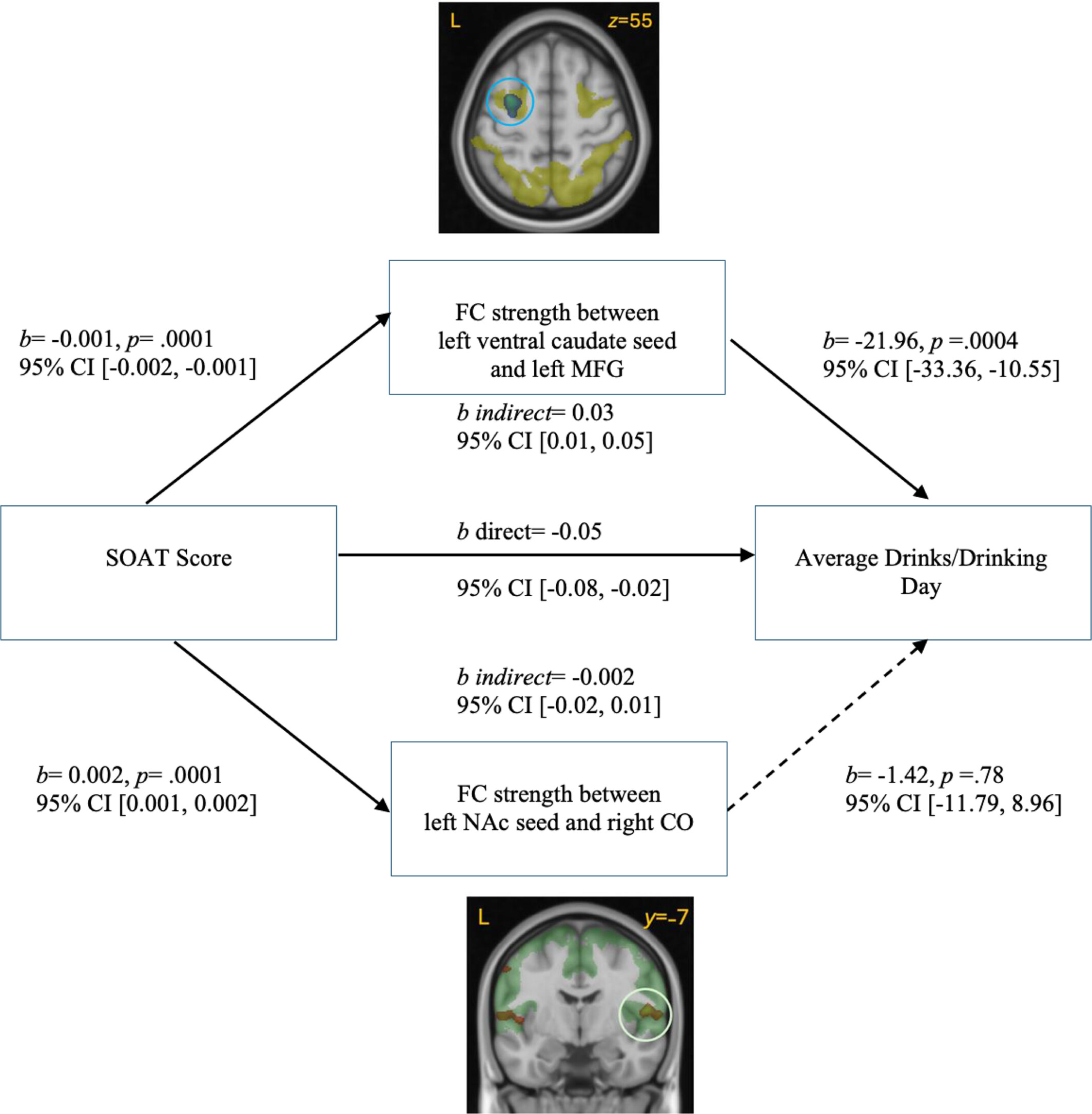
Resting state functional connectivity (FC) between the left ventral caudate and the left middle frontal gyrus (MFG) correlated negatively, while FC between the left nucleus accumbens (NAc) and the right central operculum (CO) correlated positively, with Slips of Action Task (SOAT) score. The relationship between SOAT and average drinks per drinking day was significantly mediated by FC strength of the left ventral caudate and left MFG. A similar trend with cumulative work for alcohol fell short of significance. Solid arrow indicates a significant association. Dashed arrow indicates nonsignificant association.