Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIALS
Peering deeper into asthmatic lungs
- Pages: 1037-1038
- First Published: 19 June 2019
See related Article
Nasal high-flow therapy: Established roles and emerging opportunities
- Pages: 1039-1041
- First Published: 05 September 2019
Special delivery: Engineered endothelial cells for pulmonary arterial hypertension
- Pages: 1042-1043
- First Published: 19 August 2019
See related Article
Signals and signposts: Biomarkers in IPF and PAH at the crossroads of clinical relevance
- Pages: 1044-1045
- First Published: 05 September 2019
COMMENTARIES
Implementation of evidence into practice: The key to improving patient outcomes
- Pages: 1046-1048
- First Published: 01 July 2019
Major contributions by and the future scope of cohort studies to advance respiratory and sleep medicine
- Pages: 1049-1050
- First Published: 26 July 2019
INVITED REVIEW SERIES
Paediatric and Adult Bronchiectasis
Moving forward: Bronchiectasis and chronic suppurative lung disease in children and adults in the 21st century
- Pages: 1051-1052
- First Published: 19 August 2019
Find the whole series here
Pathophysiology, causes and genetics of paediatric and adult bronchiectasis
- Pages: 1053-1062
- First Published: 25 February 2019
Paediatric and adult bronchiectasis: Specific management with coexisting asthma, COPD, rheumatological disease and inflammatory bowel disease
- Pages: 1063-1072
- First Published: 20 June 2019
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Asthma and Allergy
Quantitative assessment of airway remodelling and response to allergen in asthma
- Pages: 1073-1080
- First Published: 07 March 2019
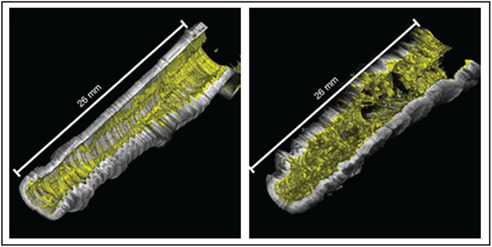
Endobronchial optical coherence tomography is used to investigate the microstructural features of airway in allergic individuals with and without asthma, before and after allergen challenge. Quantification of these features reveals significant differences between the asthmatic and non-asthmatic airways both at baseline and in response to allergen.
See related Editorial
COPD
Nasal high-flow therapy compared with non-invasive ventilation in COPD patients with chronic respiratory failure: A randomized controlled cross-over trial
- Pages: 1081-1087
- First Published: 13 May 2019

Non-invasive ventilation (NIV) reduces transcutaneous partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PtCO2) more than nasal high-flow (NHF) therapy in hypercapnic COPD, but NHF is better tolerated.
See related Editorial
Nasal high flow does not improve exercise tolerance in COPD patients recovering from acute exacerbation: A randomized crossover study
- Pages: 1088-1094
- First Published: 06 August 2019
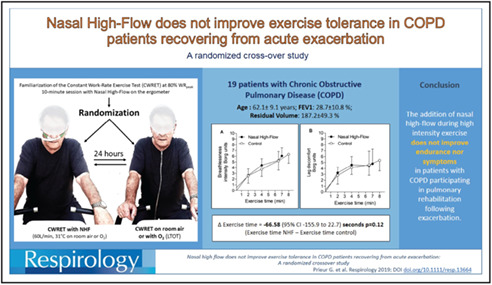
The addition of nasal high flow during high-intensity exercise does not improve endurance in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease participating in pulmonary rehabilitation following exacerbation.
See related Editorial
Pulmonary Vascular Disease
BMPR2-expressing bone marrow-derived endothelial-like progenitor cells alleviate pulmonary arterial hypertension in vivo
- Pages: 1095-1103
- First Published: 12 April 2019
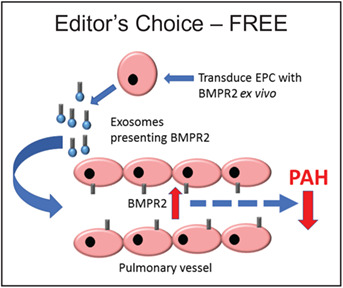
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is causally linked to reduced bone morphogenetic protein receptor type 2 (BMPR2) expression. Endothelial progenitor cells engineered to overexpress BMPR2 are therapeutic in the rat monocrotaline PAH model, despite short retention time in the lungs. This approach may have clinical potential.
See related Editorial
Osteopontin lung gene expression is a marker of disease severity in pulmonary arterial hypertension
- Pages: 1104-1110
- First Published: 08 April 2019
Osteopontin (OPN), a pleiotropic cytokine, was identified among the top five upregulated genes in the lung explants from patients with Group I pulmonary arterial hypertension, compared to normal controls. Its expression correlated strongly to haemodynamic severity. Ingenuity pathway analysis showed the involvement of OPN in functions and networks relevant to vascular remodelling.
See related Editorial
Analysis by proteomics reveals unique circulatory proteins in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- Pages: 1111-1114
- First Published: 08 August 2019
This study utilized a combination of non-targeted discovery proteomics with targeted quantitation by mass spectrometry of soluble plasma biomarkers to identify potentially important molecules and pathways in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). Five proteins were identified to be differentially expressed in IPF compared to healthy controls.
See related Editorial










-1652674259.png)

