Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Picture: Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 7∕2017
- First Published: 03 July 2017

Structural analysis of phosphatidylcholine using a thin layer chromatography-based method
Guiwei Tan, Yinggang Tian, Min Addy, Yanling Cheng, Qinglong Xie, Bo Zhang, Yuhuan Liu, Paul Chen, and Roger Ruan
The cover shows a new method to directly perform enzymatic hydrolysis reaction on a TLC plate. With a connection between two-dimensional chromatography and in situ enzymatichydrolysis, a TLC plate can play following roles: a separation tool, an enzymatic reaction carrier and an non-destructive identification tool. GC-MS chromatograms of fatty acids released from different positions of PC are attached as well.
Back Cover
Back Cover: Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 7∕2017
- First Published: 03 July 2017

The use of ATR-FTIR spectroscopy to measure changes in the oxirane content and iodine value of vegetable oils during epoxidation
Mohammad Hossein Tavassoli-Kafrani, Frederik R. van de Voort, and Jonathan M. Curtis
Monitoring changes in iodine value (IV) and oxirane oxygen content during the epoxidation of vegetable oils by ATR-FTIR.
Editorial Board
Contents
Review Articles
Nutritional composition, extraction, and utilization of wheat germ oil: A review
- First Published: 24 December 2016
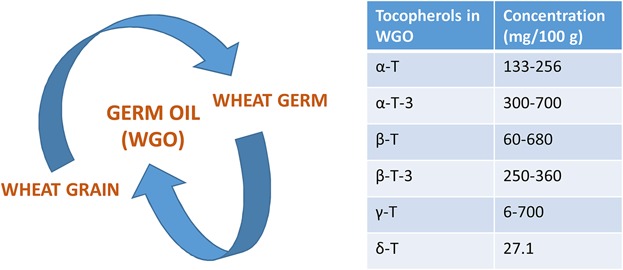
Wheat germ oil is a valuable by-product from wheat grain which is a good source of important nutraceuticals such as α- and β-tocopherol. Extraction of this oil from wheat germ is important for the effective utilization of its various potential nutraceuticals that have reported health benefits. This review also explains detailed chemical composition, processing, functional activities, and potential utilization of wheat germ oil.
Nanoemulsions for food fortification with lipophilic vitamins: Production challenges, stability, and bioavailability
- First Published: 07 January 2017
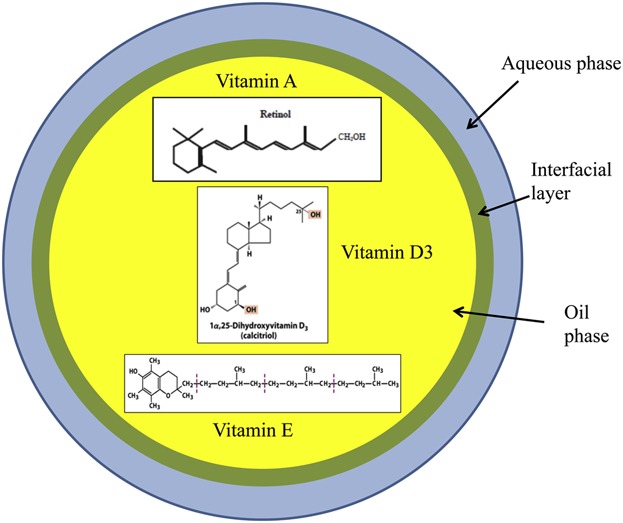
Oil-in-water nanoemulsions are consisted of a lipophilic core (oil phase) where lipophilic bioactive compound is entrapped and hydrophilic shell (aqueous phase), and an amphiphilic interfacial layer composed of the emulsifier/surfactant. Nanoemulsions produced by both low- and high-energy methods are promising delivery systems to encapsulate and stabilize the lipophilic vitamins during food fortification and enhance their bioavailability. The challenges in production methods, factors affecting the stability, and the most recent studies on bioavailability evaluation of vitamins A, D, E encapsulated in oil-in-water nanoemulsions are covered in this review.
Research Articles
Structural analysis of phosphatidylcholine using a thin layer chromatography-based method
- First Published: 24 December 2016
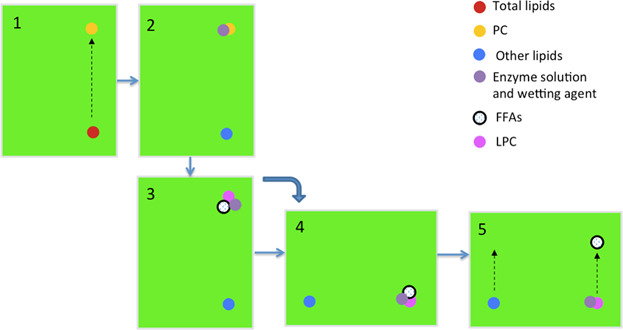
Step 1: Total lipids were applied to a thin layer chromatography (TLC) plate, and then phosphatidylcholine (PC) is separated from other lipids. Step 2: Enzyme solution and wetting agent are applied to the PC band. Step 3: After in situ enzymatic reaction, PC is partly hydrolyzed into lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) and free fatty acids (FFAs), and the hydrolysis rate are 87.7% (with 0.12 mL PLA1 enzyme) and 84.8% (with 0.30 mL PLA2 enzyme), respectively. Step 4: The TLC plate is rotated by 90°. Step 5: The FFAs released from PC are isolated from products mixtures by a second-dimensional chromatography.
The use of ATR-FTIR spectroscopy to measure changes in the oxirane content and iodine value of vegetable oils during epoxidation
- First Published: 02 January 2017
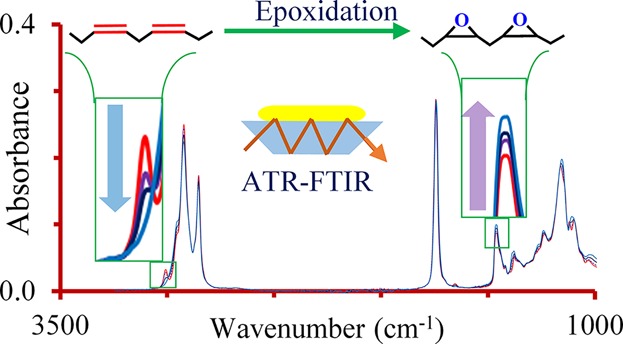
The ATR-FTIR methods described in this paper provide a simple and rapid means of monitoring OOC and IV changes during the epoxidation of vegetable oils. These methods are calibrated against standard titrimetric procedures and have been shown to produce similar results. It is especially useful that OOC and ΔIV, the two measures that are most relevant for monitoring the progress of a triacylglycerol oil epoxidation reaction, can be obtained from a single analysis. This facilitates monitoring and optimizing epoxidation processes. If the initial IV of oil is known, the method can also be used to calculate the yield, conversion, and selectivity of the reaction, as well as a study the reaction kinetics.
Effects of quercetin or rutin on the oxidative stability of stripped or non-stripped soybean oils containing α-tocopherol
- First Published: 27 November 2016
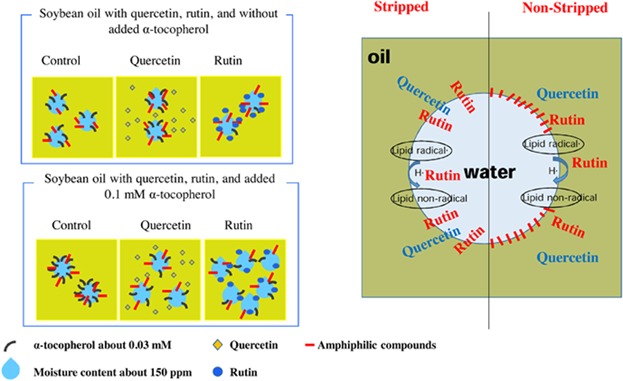
Added quercetin or rutin acted as an antioxidant in stripped soybean oils and as a prooxidant in non-stripped soybean oils. Quercetin and rutin increased the moisture content in stripped oils, but not in non-stripped oils. Quercetin and rutin accelerated the decomposition of α-tocopherol in both stripped and non-stripped oils. The oxidative stability of oils containing tocopherols and phenolic compounds depended on the stripping process.
Linolelaidic acid induces apoptosis, cell cycle arrest and inflammation stronger than elaidic acid in human umbilical vein endothelial cells through lipid rafts
- First Published: 06 December 2016
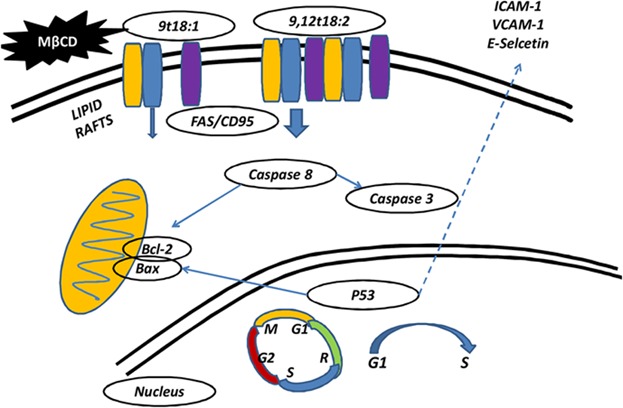
Both linoelaidic acid and elaidic acid induced HUVECs apoptosis and increased expression of pro-apoptotic proteins. However, supplementation of TFAs to MβCD-treated cells increased the cell viability and significantly decreased the number of apoptotic cells. Moreover, linolelaidic acid induces a stronger lesion effect on HUVECs by lipid rafts mediation compared to elaidic acid.
Rapeseed hull oil as a source for phytosterols and their separation by organic solvent nanofiltration
- First Published: 15 December 2016
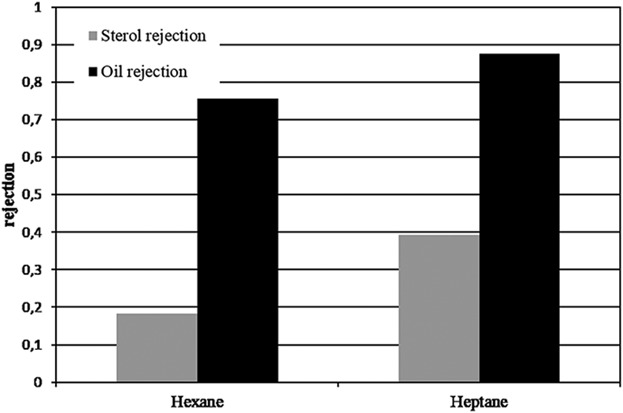
Rapeseed hull oil has a remarkably high content of alpha-tocopherol and sterols. It was shown that organic solvent nanofiltration is a process, which can be used for a partial separation of sterols and triglycerides. An enrichment by a factor of five is possible, leading to oils with such a high sterol concentration that crystallization occurred.
Preparation and characterization of glycyrrhetinic-acid loaded PEG-modified liposome based on PEG-7 glyceryl cocoate
- First Published: 05 January 2017
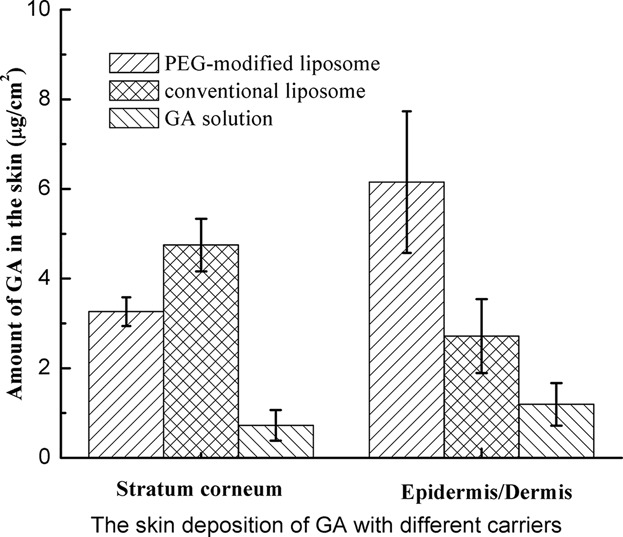
The forming mechanism of the GA modified liposome in this chart was as follows: the water insoluble GA dissolved in the PEG-7 glyceryl cocoate and the organic phase of phospholipids was put into the water phase at the same time, the phospholipid molecules wrapped the GA in the bilayers and the PEG-7 glyceryl cocoate was bonded to the hydrophilic group of liposome vesicles. This structure made the liposome more smaller and higher encapsulation efficiency, and it also brought a prolonged release rate and better drug deposition in epidermis compare with the non-modified ones.
Rump and shoulder muscles from grass and linseed fed cattle as important sources of n-3 fatty acids for beef consumers
- First Published: 20 December 2016
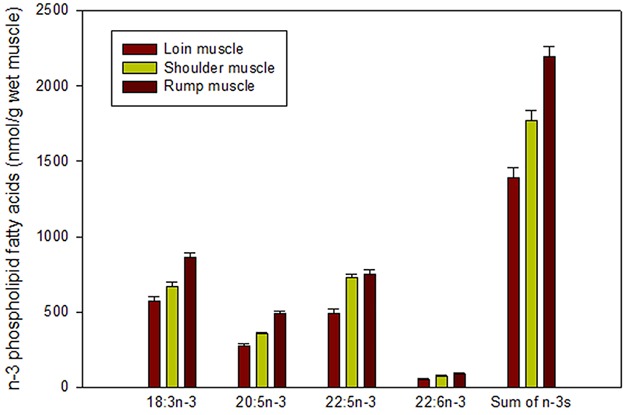
Compared to bovine loin muscle, bovine shoulder and rump muscles tend to have higher concentrations of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA; 18:3n-3) and the long-chain omega-3 fatty acids eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA; 20:5n-3), docosapentaenoic acid (DPA; 22:5n-3), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA; 22:6n-3). This is healthful for many people in that shoulder and rump muscles are less expensive beef which is eaten by millions of people as ground/minced beef in foods such as hamburgers, tacos, and empanadas; thus, providing a practical source of omega-3 fatty acids for people who seldom eat expensive sources such as salmon and tuna.
Dulce de leche-like product enriched with emulsified pecan oil: Assessment of physicochemical characteristics, quality attributes, and shelf-life
- First Published: 02 January 2017
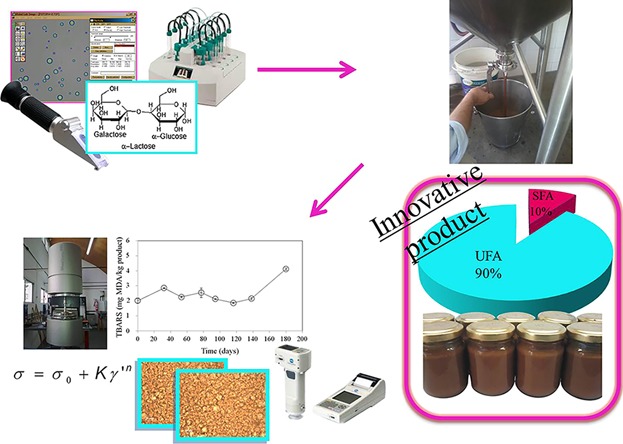
A DL-like product with pre-emulsified pecan oil as fat source was developed. Pecan oil-DL showed physicochemical and rheological characteristics similar to those of commercial DL containing ∼6% milk fat. DL fatty acid (FA) profile showed high content of unsaturated FA (UFA, 89–90% w/w), mainly oleic and linoleic acids, effectively protected by both tocopherols and antioxidant compounds. Pecan oil-DL presented good sensorial characteristics, with 82.6% less saturated FA and 200% more UFA than a traditional milk fat-product, being an alternative product with lipid profile enriched in unsaturated fatty acids.
Extraction and preconcentration of triazine pesticides using rapid, simple, and disperser solventless microextraction technique followed by gas chromatography–nitrogen phosphorous detection
- First Published: 16 January 2017
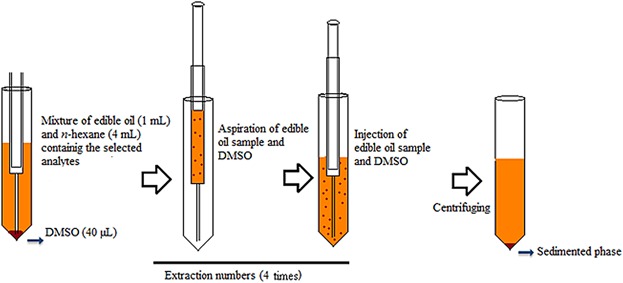
Triazine pesticides often contaminate the seeds and hence will be transferred into the oils during the extraction process. For trace determination of triazines in edible oil, 1 mL edible oil was diluted with 4 mL n-hexane in conical tube and 40 µL DMSO was added. The mixture was rapidly aspirated into a 10-mL glass syringe and then injected into the tube (4 times) to form a cloudy solution. The method showed low limits of detection and quantification between 0.02 to 0.09 and 0.07 to 0.30 µg/L, respectively. Extraction recoveries were in the range of 74–96%.
Microwave radiation and conventional roasting in conjunction with hulling on the oxidative state and physicochemical properties of rapeseed oil
- First Published: 12 January 2017
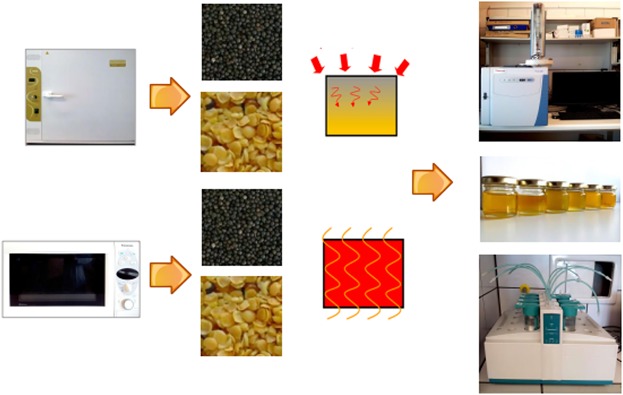
Thermal pre-treatment is currently being used in oilseeds pre-processing, but very little researches studied its effect on color change and oxidative state of oil. Although rapeseed thermal pre-treatment can cause a number of positive quality changes, such as an increase of bioactive compounds, the results should be interpreted with caution since application of too harsh heating conditions may result in unsaturated fatty acids degradation, lipid oxidation, or undesirable color change.
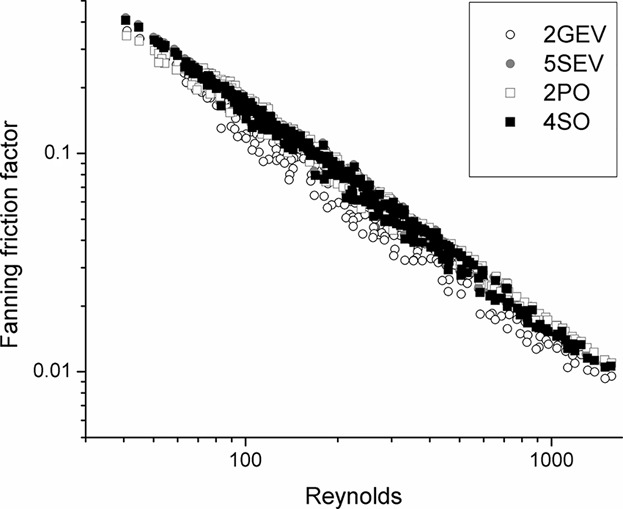
Thermophysical properties of different olive oils: Evaluating density and rheology through a fluid dynamic approach
- First Published: 28 February 2017
Antioxidant activity of deodorizer distillate fractions in rapeseed oil
- First Published: 17 October 2016
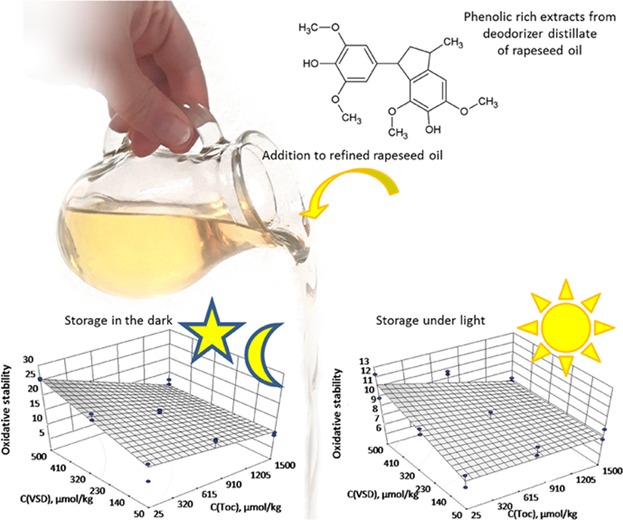
Fractions of rapeseed oil deodorizer distillate rich in phenolic compounds were investigated for their potential use as antioxidants in rapeseed oil. The isolated compounds effectively inhibited lipid oxidation in the dark and under light. In the presence of tocopherol, the addition of the dimer increased the oxidative stability considerably at low tocopherol and high vinly syringol dimer concentrations. The addition of polyphenolic rich fractions of the deodorizer distillate to commercial rapeseed oil resulted in slightly accelerated lipid oxidation in the dark at 40°C but did not influence the formation of hydroperoxides under light at 25°C.
Effect of alkylglycerol-rich oil and rosemary extract on oxidative stability and antioxidant properties of a cooked meat product
- First Published: 12 January 2017
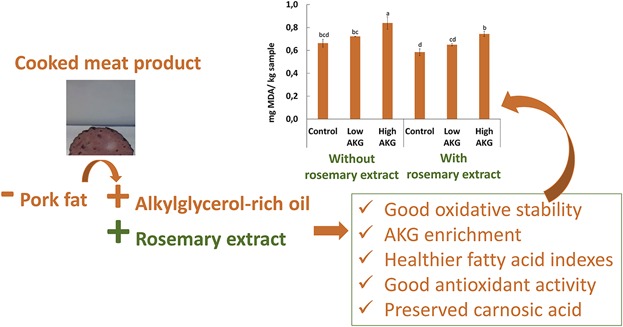
Taking into account the bioactive and healthy properties of alkylglycerols (AKG) and the antioxidant rosemary extract (RE), the production of a cooked meat product with partial replacement of animal fat by AKG-rich oil and inclusion of RE was performed. Meat products combining both bioactive ingredients might be produced, without compromising the oxidative stability and with potential healthier and functional interest.
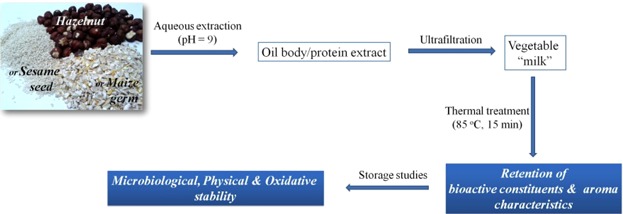
Influence of thermal treatment on the stability of vegetable “milk” obtained by ultrafiltration of aqueous oil body extracts from various sources
- First Published: 23 January 2017
Effect of dietary bioactive compounds and biopolymer encapsulated lipids on metabolism of lipids in high fat diet-fed mice
- First Published: 02 November 2016
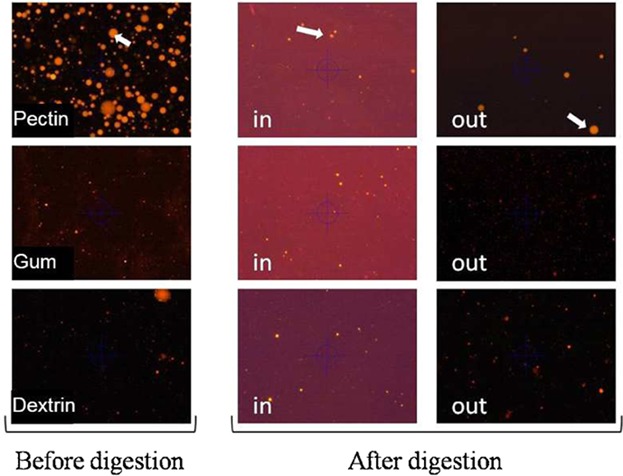
We investigated effects of dietary bioactive components and biopolymer encapsulation on lipids’ metabolism in obese mice. Bio-active components could enhance the effect of body and adipose tissue weight reduction in obese mice models. Dietary bio-active compounds together with biopolymer encapsulated lipids showed a great reduction in serum triglycerides and cholesterol.
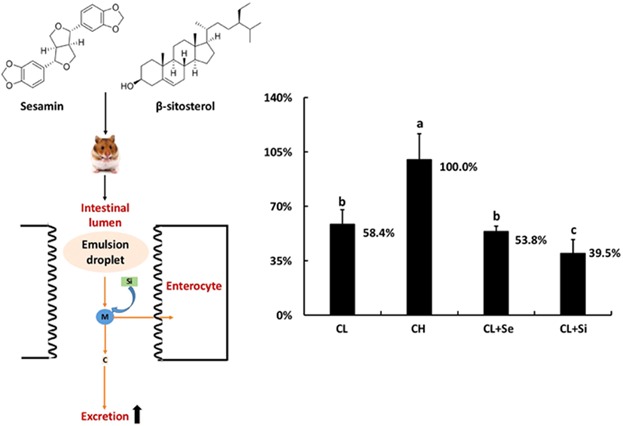
Dietary β-sitosterol is more potent in reducing plasma cholesterol than sesamin in hypercholesterolemia hamsters
- First Published: 14 December 2016
Short Communication
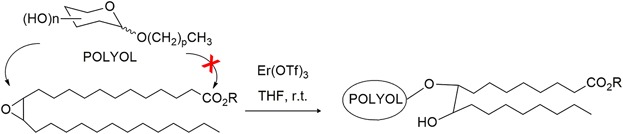
Ring opening of epoxidized methyl or ethyl oleate by alkyl glycosides
- First Published: 20 December 2016