Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
MINI-REVIEW
Application of metabolomics to the study of irritable bowel syndrome
- First Published: 19 May 2020
POSITION PAPER
Anorectal manometry in children with defecation disorders BSPGHAN Motility Working Group consensus statement
- First Published: 27 January 2020
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
D-methionine improves cisplatin-induced anorexia and dyspepsia syndrome by attenuating intestinal tryptophan hydroxylase 1 activity and increasing plasma leptin concentration
- First Published: 27 January 2020
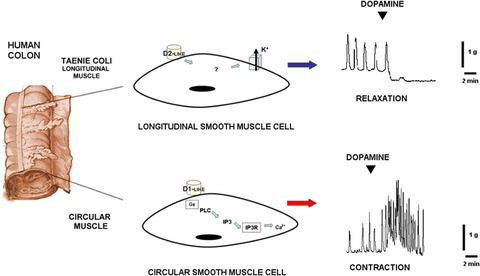
Opposite effects of dopamine on the mechanical activity of circular and longitudinal muscle of human colon
- First Published: 03 February 2020
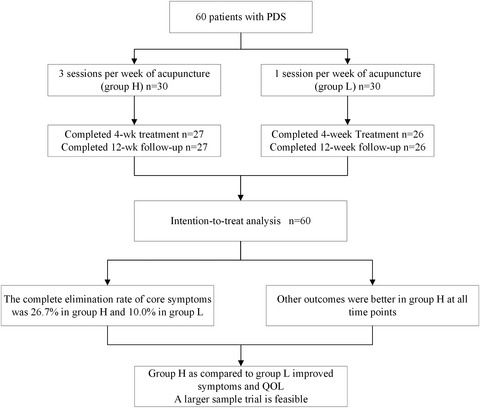
Acupuncture of different treatment frequency in postprandial distress syndrome: A pilot randomized clinical trial
- First Published: 12 February 2020
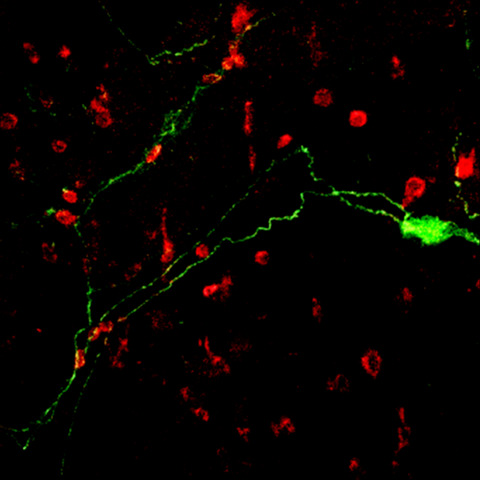
Mast cell-nerve interactions correlate with bloating and abdominal pain severity in patients with non-celiac gluten / wheat sensitivity
- First Published: 05 February 2020
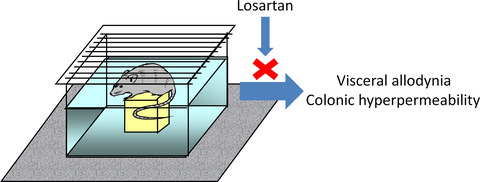
Losartan improves visceral sensation and gut barrier in a rat model of irritable bowel syndrome
- First Published: 14 February 2020
A randomized clinical trial on the acute therapeutic effect of TRPA1 and TRPM8 agonists in patients with oropharyngeal dysphagia
- First Published: 16 February 2020
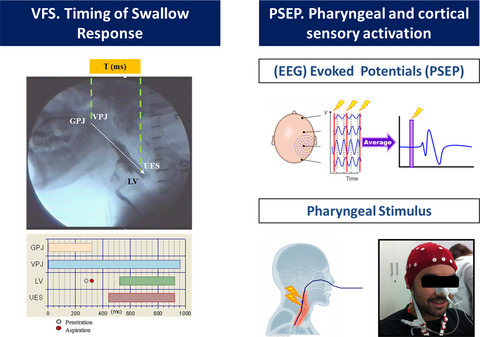
Methodology used in the manuscript includes the videofluoroscopy (VFS) to evaluate VFS signs of safety and efficacy of swallow, and the timing of the oropharyngeal swallow response; and pharyngeal sensory evoked potentials (PSEP) to electrical stimulation to measure the latency and amplitude of PSEP peaks.
A novel method of sacral nerve stimulation for colonic inflammation
- First Published: 01 March 2020
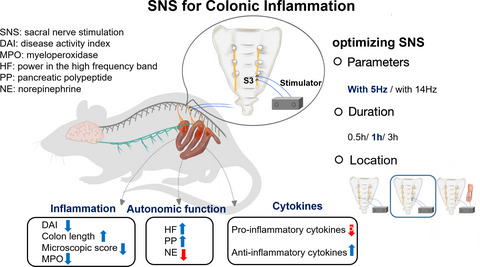
Three major efforts were made in optimizing SNS: (1) to determine the best stimulation duration; (2) to determine the best stimulation position; (3) to determine the best stimulation parameters. Bipolar stimulation for 1 hour daily using intermittent 5 Hz parameters is most effective in improving colonic inflammation.
Endoscope presence during endoluminal functional lumen imaging probe (FLIP) influences FLIP metrics in the evaluation of esophageal dysmotility
- First Published: 25 February 2020
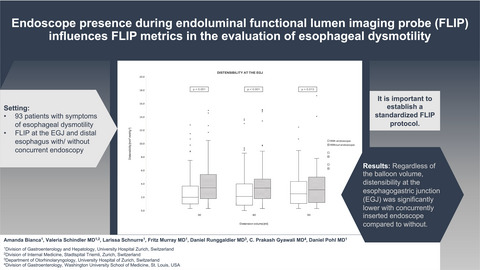
A significant difference in functional lumen imaging probe (FLIP) measurements with and without endoscope presence was found at the esophagogastric junction. Our study underlines the importance of establishing a standardized FLIP protocol for overall comparability and for guidance of future FLIP diagnostic studies.
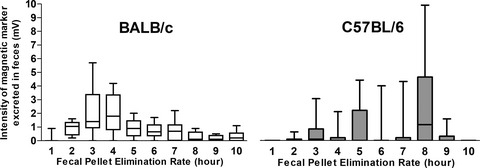
Gastrointestinal motility and morphology in mice: Strain-dependent differences
- First Published: 24 February 2020
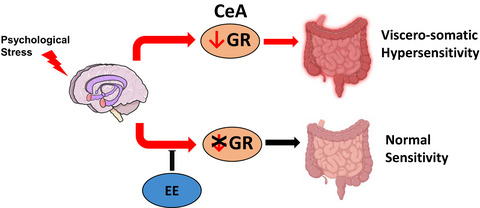
Environmental enrichment prevents chronic stress-induced brain-gut axis dysfunction through a GR-mediated mechanism in the central nucleus of the amygdala
- First Published: 21 February 2020
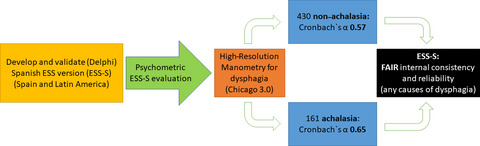
Fair reliability of eckardt scores in achalasia and non-achalasia patients: Psychometric properties of the eckardt spanish version in a multicentric study
- First Published: 25 February 2020
Normative values for gastric motility assessed with the 3D-transit electromagnetic tracking system
- First Published: 10 March 2020
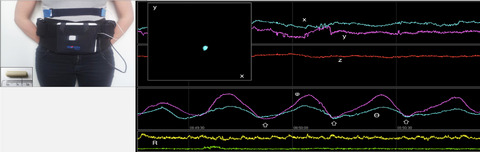
The Motilis 3D-Transit system allows ambulatory description of transit patterns throughout the gastrointestinal tract. Using the 3D-transit system, we have established normative values for gastric motility patterns. Gastric emptying time was not associated with age, gender, BMI, or the minor differences in the composition of the meal given with the capsule. In contrast, the contraction frequency was affected by gender and age while position and rotation amplitudes were associated with gender, BMI, and calorific content of the meal. This has to be considered when future studies with the 3D-Transit system are designed.
Characteristics of fecal metabolic profiles in patients with irritable bowel syndrome with predominant diarrhea investigated using 1H-NMR coupled with multivariate statistical analysis
- First Published: 03 March 2020
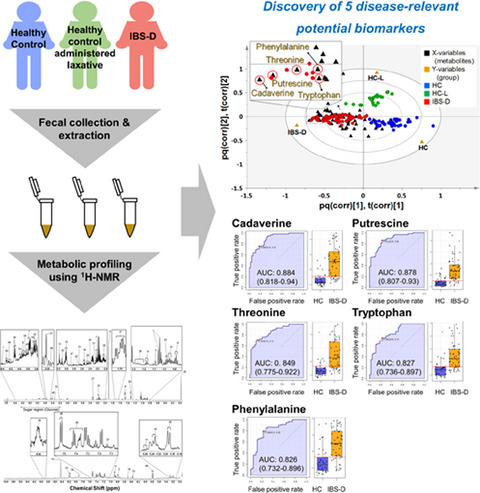
Fecal metabolic profiling of patients with IBS-D was clearly differentiated from that of healthy controls administered laxatives or not. Five disease-relevant potential biomarkers (cadaverine, putrescine, threonine, tryptophan, and phenylalanine) were found in patients with IBS-D, excluding the effects of fast colon transit. It provides fundamental information for developing novel therapies for IBS-D.
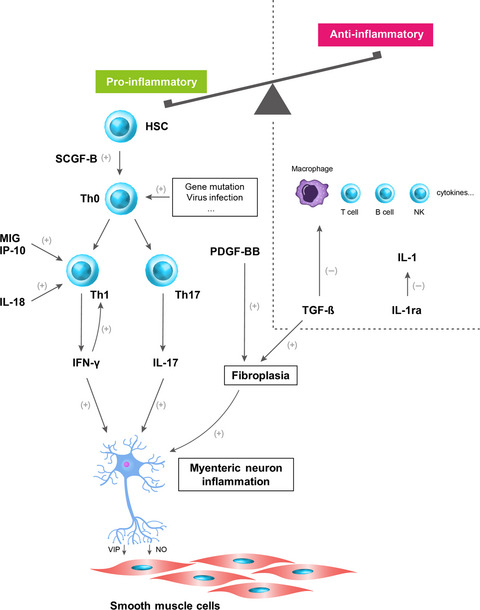
Multiplex immunoassays reveal increased serum cytokines and chemokines associated with the subtypes of achalasia
- First Published: 05 March 2020
LETTERS TO THE EDITOR
Response letter to the editor: Clinical impact of proton pump inhibitor response and dependence
- First Published: 19 May 2020