Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
EDITOR'S CHOICE
EDITORIAL
The challenges of clinical trials in rare diseases
- Pages: 453-454
- First Published: 03 October 2022
COMMENTARIES
Advances in acne clinical research: a new class of topical treatment for moderate-to-severe facial acne
- Pages: 455-456
- First Published: 11 July 2022
Linked Article: Picardo et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:507–514.
Can technology change the status quo for pressure injury prevention?
- Page: 456
- First Published: 26 July 2022
Linked Article: Jiang et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:571–579.
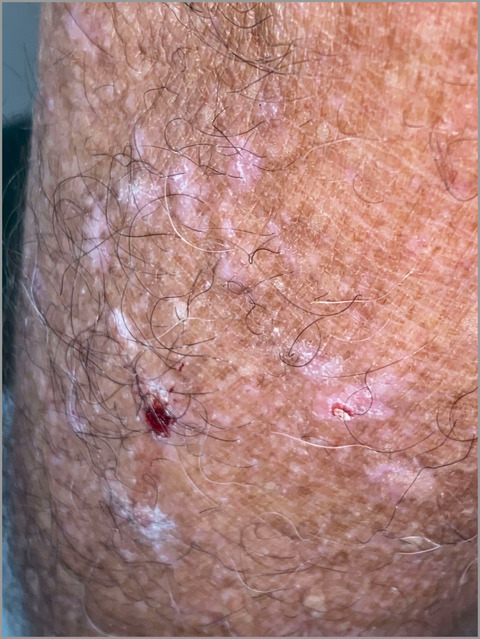
Delusional infestation – do not be scared!
- Page: 457
- First Published: 29 July 2022
Linked Article: Ahmed et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:472–480.
Impaired epidermal barriers in congenital ichthyoses house a changing microbial landscape
- Pages: 457-458
- First Published: 29 July 2022
Linked Article: Tham et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:557–570.
Predicting the outcome of psoriasis treatment
- Pages: 458-459
- First Published: 22 July 2022
Linked Article: Corbett et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:494–506.
Melanoma overdiagnosis: why it matters and what can be done about it
- Pages: 459-460
- First Published: 05 August 2022
Linked Article: Whiteman et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:515–522.
Noticeability of vitiligo is in the eye of the beholder
- Pages: 461-462
- First Published: 29 July 2022
Linked Article: Batchelor et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:548–556.
Implementing evidence-based strategies to optimize the journey of patients with hidradenitis suppurativa
- Pages: 462-463
- First Published: 16 August 2022
Linked Article: Ring et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:523–530.
Reviews
REVIEW ARTICLE
Chronic prurigo
- Pages: 464-471
- First Published: 03 June 2022
Chronic prurigo is defined by the presence of chronic pruritus and multiple localized or generalized pruritic skin lesions (whitish or pinkish papules, nodules and/or plaques). Chronic prurigo occurs due to neural sensitization to pruritus and the development of a vicious pruritus-scratching cycle. Recent research results on the pathophysiology of pruritus evidenced neuroimmune interactions and allow new therapeutic perspectives.
Evidence-Based Dermatology
GUIDELINES
British Association of Dermatologists guidelines for the management of adults with delusional infestation 2022
- Pages: 472-480
- First Published: 18 May 2022
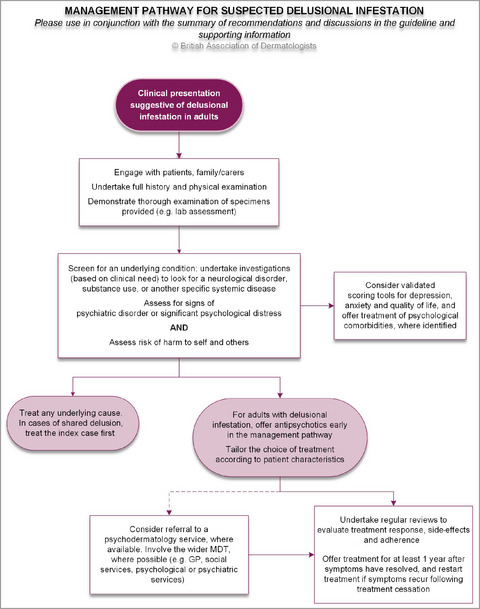
The overall objective of the guideline is to provide up-to-date, evidence-based recommendations for the management of delusional infestation (DI) in adults.
Linked Comment: I. Coulson. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:457.
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
Biomarkers of disease progression in people with psoriasis: a scoping review
- Pages: 481-493
- First Published: 28 April 2022
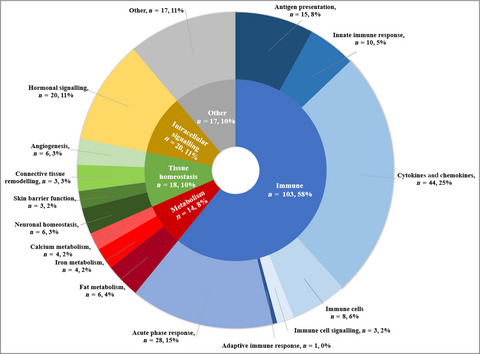
This review is the first to scope, collate, and catalogue research investigating biomarkers of disease progression in psoriasis. The review identifies potentially promising candidate biomarkers for further investigation and highlights common important limitations that should be considered when designing and conducting future studies in this area.
Plain language summary available online
Biomarkers of systemic treatment response in people with psoriasis: a scoping review
- Pages: 494-506
- First Published: 23 May 2022
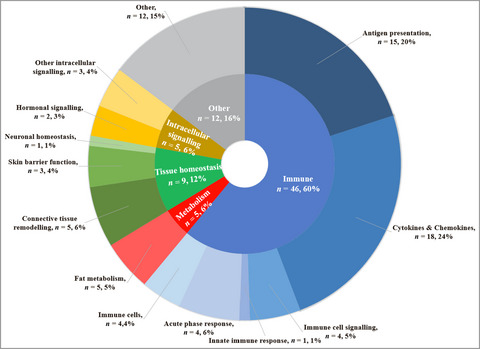
Responses to the systemic treatments commonly used to treat psoriasis vary. Biomarkers that accurately predict effectiveness and safety would enable targeted treatment selection, improved patient outcomes and more cost-effective healthcare. This review provides a comprehensive catalogue of investigated biomarkers of systemic treatment response in psoriasis.
Linked Comment: A.D. Ormerod. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:458–459.
Original articles
CLINICAL TRIAL
Efficacy and safety of N-acetyl-GED-0507-34-LEVO gel in patients with moderate-to severe facial acne vulgaris: a phase IIb randomized double-blind, vehicle-controlled trial
- Pages: 507-514
- First Published: 12 May 2022
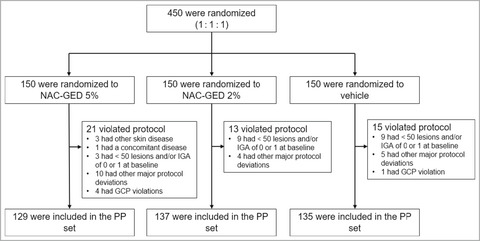
The topical application of NAC-GED 5% reduced TLC, increased the IGA success rate and was safe for patients with acne vulgaris #10;- NAC-GED, a new PPAR gamma; modulator, showed an effective clinical response.
Linked Comment: C. Dessinioti. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:455–456.
Plain language summary available online
EPIDEMIOLOGY
The effect of screening on melanoma incidence and biopsy rates
- Pages: 515-522
- First Published: 09 May 2022
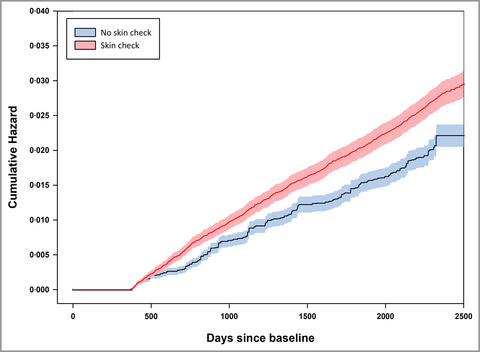
Melanoma is a common cancer, for which skin examinations are promoted as an early detection tool. In a large, prospective cohort, we documented the incidence of melanoma among people who had and had not been screened. Melanoma incidence was about 29% higher in the screened group over more than 5 years of follow-up, suggesting possible overdiagnosis among people undergoing skin examinations.
Linked Comment: K.J.L. Bell and T. Nijsten. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:459–460.
Plain language summary available online
The road to biologics in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa: a nationwide drug utilization study
- Pages: 523-530
- First Published: 23 May 2022
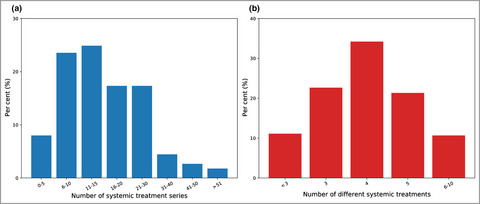
In this study we found that 225 HS patients on average were treated with systemic therapies for eight years before starting biologic therapy. The high number of systemic treatment series used prior to initiation of biologics may reflect referral delays or difficulties in obtaining disease control in patients with moderate-to-severe HS.
Linked Comment: T. Tzellos. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:462–463.
Plain language summary available online
OUTCOMES AND QUALITATIVE RESEARCH
The Validated Investigator Global Assessment for Atopic Dermatitis (vIGA-AD™): a clinical outcome measure for the severity of atopic dermatitis
- Pages: 531-538
- First Published: 20 April 2022
Analysis of alopecia areata surveys suggests a threshold for improved patient-reported outcomes
- Pages: 539-547
- First Published: 03 June 2022

Although alopecia areata is common and greatly impacts patients’ wellbeing, there is no adequate validation of disease-specific surveys in clinical trials, hindering sufficient representation of patient-reported outcomes. This study found that in a clinical trial setting, the Alopecia Areata Symptom Impact Scale (AASIS) questionnaire is strongly correlated with alopecia areata severity and clinical response. Patients with ≤ 20% of scalp hair loss after treatment reported improvement in multiple quality-of-life items, suggesting a meaningful therapeutic outcome that may guide clinicians and improve the development of future clinical trials.
Using the Vitiligo Noticeability Scale in clinical trials: construct validity, interpretability, reliability and acceptability
- Pages: 548-556
- First Published: 21 May 2022
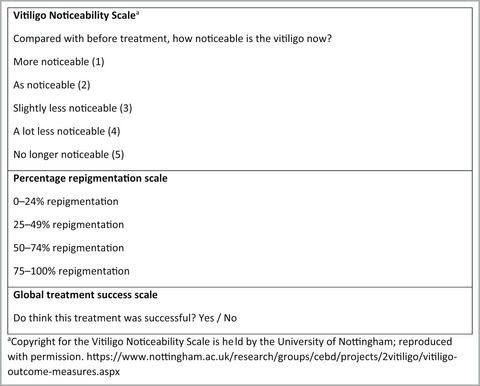
• A Vitiligo Core Outcome Set is being developed, to enable the results of vitiligo trials to be compared and combined more easily • The VNS shows good construct validity, reliability and acceptability. It can be used in all ages and skin phototypes • The VNS can be used as a PROM to assess cosmetic acceptability of repigmentation at individual patches of vitiligo
Linked Comment: A.G. Pandya and K. Ezzedine. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:461–462.
TRANSLATIONAL RESEARCH
Distinct skin microbiome community structures in congenital ichthyosis
- Pages: 557-570
- First Published: 28 May 2022
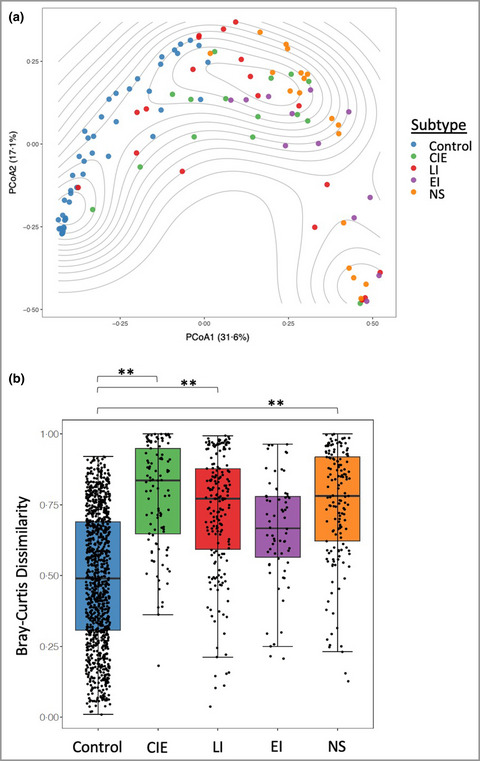
• A common skin microbiome signature was observed across congenital ichthyoses • Distinct microbiome features were associated with ichthyosis subtypes • Changes in microbiome may contribute to Th17 immune polarization
Linked Comment: A.M. Schneider and A.M. Nelson. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:457–458.
GENERAL DERMATOLOGY
Application of an infrared thermography-based model to detect pressure injuries: a prospective cohort study
- Pages: 571-579
- First Published: 13 May 2022
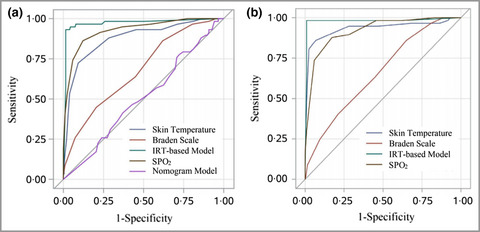
IRT-based model is a useful and reliable method for early identification of pressure induced tissue damage by clinical nurses. This model can objectively and accurately detect PIs one day before visual cues and help guide prevention.
Linked Comment: L.J. Gould and E. White-Chu. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:456.
Plain language summary available online
Correspondence
PERSPECTIVES
Caring for transgender and gender-diverse patients in phototherapy settings: better practices
- Pages: 580-581
- First Published: 09 May 2022
Giving a voice: dermatologists’ legislative advocacy for patients with hair loss
- Pages: 582-583
- First Published: 17 May 2022
Human papillomavirus vaccination: a missed opportunity
- Pages: 584-585
- First Published: 03 June 2022
RESEARCH LETTERS
Prevalence of Hidradenitis Suppurativa in Berekum, Ghana
- Pages: 586-587
- First Published: 08 March 2022
Measuring patient-relevant benefits in the treatment of psoriasis with the Patient Benefit Index: development and preliminary validation of a 10-item short form
- Pages: 588-589
- First Published: 05 April 2022
Delay in diagnosis and treatment of patients with psoriasis: a population-based cross-sectional study
- Pages: 590-591
- First Published: 05 April 2022
Maintenance of response in moderate-to-severe psoriasis after withdrawal of the interleukin (IL)-17A and IL-17F nanobody sonelokimab: is there a role for IL-17F in disease reoccurrence?
- Pages: 591-593
- First Published: 20 April 2022
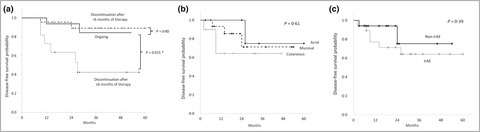
Prognoses of patients with melanoma who continue/discontinue anti-programmed death-1 therapy after achieving a complete response in a real-world setting: a multicentre retrospective study
- Pages: 594-596
- First Published: 29 March 2022
The utility of negative histopathological analysis of debulk specimens during Mohs micrographic surgery for basal cell carcinoma
- Pages: 596-597
- First Published: 20 April 2022
Characterizing basal cell carcinoma in Hispanic individuals undergoing Mohs micrographic surgery: a 7-year retrospective review at an academic institution in the Bronx
- Pages: 597-599
- First Published: 20 April 2022
Interleukin-33 antibody failed to demonstrate benefit in a phase II, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study in adult patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis
- Pages: 599-602
- First Published: 28 April 2022
Longer dupilumab dosing intervals in adult patients with atopic dermatitis: experience from a French multicentre retrospective cohort study
- Pages: 602-603
- First Published: 28 April 2022
Impact of nonsegmental vitiligo on patients’ health-related quality of life in the United States
- Pages: 603-606
- First Published: 21 May 2022
The effect of skin colour and Fitzpatrick skin type on Bullous Pemphigoid Disease Area Index (BPDAI) scores
- Pages: 606-607
- First Published: 09 May 2022
Association between prurigo nodularis and substance use disorders
- Pages: 608-609
- First Published: 23 May 2022
Colonization with Staphylococcus aureus in healthcare workers: consequences of hand eczema
- Pages: 609-611
- First Published: 23 May 2022
Patients’ attitudes towards active surveillance for basal cell carcinoma
- Pages: 611-613
- First Published: 15 February 2022
US academic dermatologists’ attitudes towards active surveillance for basal cell carcinoma
- Pages: 613-615
- First Published: 23 May 2022
Sweet-like syndrome and multiple COVID arm syndrome following COVID-19 vaccines: ‘specific’ patterns in a series of 192 patients
- Pages: 615-617
- First Published: 02 June 2022
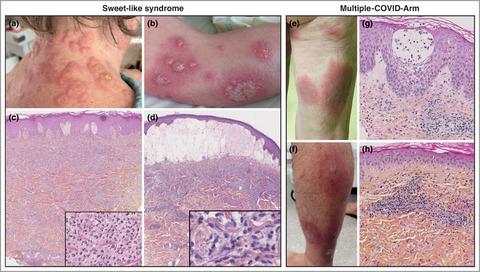
The two clinico-pathological patterns are ‘Sweet-like syndrome’ and ‘Multiple COVID-Arm’. ‘Sweet-like syndrome’ presents clinically as erythematous and oedematous papules or plaques, sometimes developing vesiculation or bullae. Histology shows classical Sweet syndrome with a diffuse dermal neutrophilic infiltrate, or an infiltrate of histiocyte-like immature myeloid cells consistent with a histiocytoid Sweet syndrome. ‘Multiple COVID-arm’ is characterized by multiple large inflammatory plaques with histological analyses showing a perivascular and interstitial inflammatory infiltrate with eosinophils.
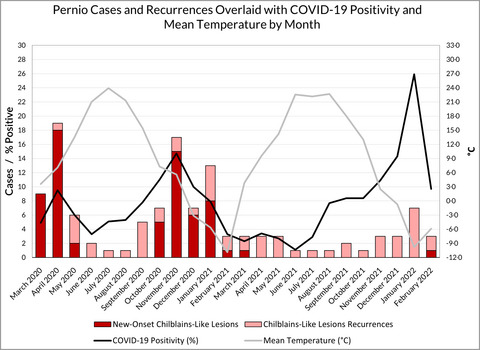
Pernio and early SARS-CoV-2 variants: natural history of a prospective cohort and the role of interferon
- Pages: 617-619
- First Published: 02 June 2022
Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms in patients hospitalized with COVID-19: a case series from a large US healthcare system
- Pages: 619-622
- First Published: 14 June 2022
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
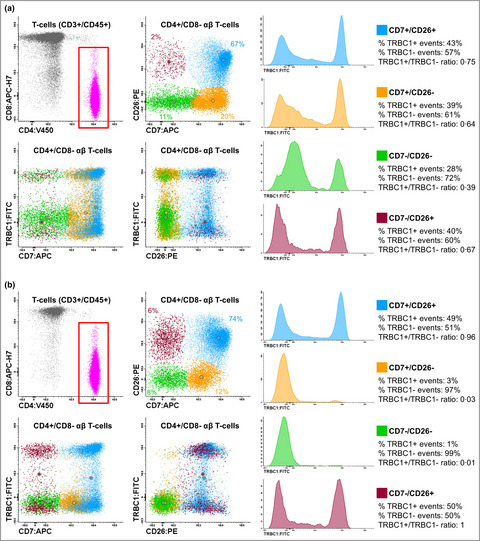
TRBC1 expression assessed by flow cytometry as a novel marker of clonality in cutaneous αβ T-cell lymphomas with peripheral blood involvement
- Pages: 623-625
- First Published: 23 May 2022
Erratum
ANNOUNCEMENT
Seeking a new chair for the UK Dermatology Clinical Trials Network (UK DCTN)
- Page: 626
- First Published: 03 October 2022
CORRESPONDENCE: IMAGE GALLERY
Successful treatment of severe subcorneal pustular dermatosis with the 308-nm ultraviolet B excimer laser
- Page: e157
- First Published: 28 May 2022
PLAIN LANGUAGE SUMMARIES
The search for measurable predictors linked with negative health complications in psoriasis
- Page: e158
- First Published: 03 October 2022
Linked Article: Ramessur et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:481–493.
Results from a clinical trial about a new topical medication for facial acne
- Page: e159
- First Published: 03 October 2022
Linked Article: Picardo et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:507–514.
Infrared thermography to detect pressure injuries
- Page: e160
- First Published: 03 October 2022
Linked Article: Jiang et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:571–579.
A better understanding about the road to biologic therapy in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa
- Page: e161
- First Published: 03 October 2022
Linked Article: Ring et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:523–530.
The impact of screening on melanoma incidence and biopsy rates
- Page: e162
- First Published: 03 October 2022
Linked Article: Whiteman et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:515–522.
寻找与银屑病负面健康并发症相关的可测量预测指标
- Page: e163
- First Published: 03 October 2022
Linked Article: Ramessur et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:481–493.
关于一种新的面部痤疮外用药的临床试验的结果
- Page: e164
- First Published: 03 October 2022
Linked Article: Picardo et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:507–514.
红外热成像检测压力性损伤
- Page: e165
- First Published: 03 October 2022
Linked Article: Jiang et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:571–579.
更好地了解化脓性汗腺炎患者的生物疗法之路
- Page: e166
- First Published: 03 October 2022
Linked Article: Ring et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:523–530.
筛查对黑色素瘤发病率和活检率的影响
- Page: e167
- First Published: 03 October 2022
Linked Article: Whiteman et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:515–522.










2690-442X.cover.png)