Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
EDITOR'S CHOICE
EDITORIAL
Stepping up efforts to support Ukrainian refugees: the role of the dermatological community
- Pages: 1-2
- First Published: 03 July 2022
COMMENTARIES
Systemic treatments for psoriasis: not another network meta-analysis!
- Pages: 3-4
- First Published: 03 May 2022
Linked Article: Guelimi et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:29–41.
Evidence should inform more than prescribing decisions
- Page: 4
- First Published: 01 May 2022
Linked Article: Hewitt et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:82–88.
Body dysmorphic disorder, skin diseases and psychological morbidity: common and complex
- Page: 5
- First Published: 03 May 2022
Linked Article: Schut et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:115–125.
Survival from cutaneous malignant melanoma is improving, but is it because of a trend in decreasing melanoma thickness or the advent of new ‘revolutionary’ therapeutics?
- Pages: 6-7
- First Published: 12 April 2022
Linked Article: Zamagni et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:52–63.
Experience from an outright ban of commercial sunbeds in the Australian context
- Page: 7
- First Published: 04 May 2022
Linked Article: Eden et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:105–114.
A new avenue for treatment of chronic hand eczema
- Pages: 7-8
- First Published: 01 May 2022
Linked Article: Worm et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:42–51.
Isotretinoin does not contribute to increased neuropsychiatric risk in the overall acne population, but risk management during treatment remains essential
- Pages: 8-9
- First Published: 21 April 2022
Linked Article: Paljarvi et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:64–72.
Identity and psychological distress in alopecia areata
- Pages: 9-10
- First Published: 13 May 2022
Linked Article: Macbeth et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:73–81.
Weighing in on weight-based secukinumab dosing for psoriasis
- Pages: 10-11
- First Published: 16 May 2022
Linked Article: Augustin et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:942–954.
Reviews
REVIEW ARTICLES
Bacterial antimicrobial resistance and dermatological ramifications
- Pages: 12-20
- First Published: 26 January 2022

Antimicrobial resistance is exceeding stewardship efforts and the rates of new drug development and approval in the market. Dermatologist are among the most common prescribers of oral and topical antibiotics, making antimicrobial resistance a prime concern in daily practice. Through this review of dermatologically relevant pathogens and innovative therapeutics, we hope to further contribute to efforts of bringing the crisis of resistance to the forefront of dermatological practice.
Plain language summary available online
Flow cytometry for the assessment of blood tumour burden in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma: towards a standardized approach
- Pages: 21-28
- First Published: 14 February 2022
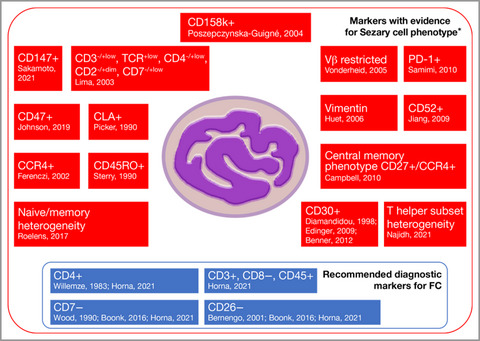
We summarize the role of blood involvement in mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome along with the changes in guideline recommendations for blood involvement assessment. The preferred assessment method is now flow cytometry (FC), and we look at the need for a standardized FC panel and how this might be achieved.
Evidence-Based Dermatology
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
Overlapping network meta-analyses on psoriasis systemic treatments, an overview: quantity does not make quality
- Pages: 29-41
- First Published: 02 December 2021
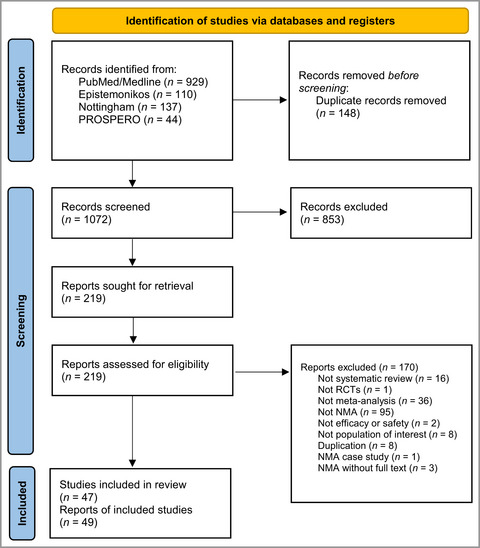
What is already known about this topic?
- Network meta-analyses (NMAs) have become successful in addressing gaps in the comparative effectiveness of the systemic treatments in moderate-to-severe psoriasis.
- Their increasing number carries both a risk of overlap and reproducibility issues that can hamper clinical decision-making.
- Different methodological choices could have an important impact on the results of both classical and network meta-analysis.
What does this study add?
- This overview provides an assessment of the redundancy of the NMAs on the systemic treatments in psoriasis, as well as an evaluation of their methodological quality and discrepancies.
- Of the 47 included studies, only two evaluated all the available treatments, 26 received industry funding and 39 provided results of critically low confidence.
- Awareness is needed among authors and reviewers of the thoroughness of the methods of systematic reviews and meta-analyses.
Linked Comment: J. Leonardi-Bee and A.M. Drucker. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:3–4.
Original articles
CLINICAL TRIALS
The pan-JAK inhibitor delgocitinib in a cream formulation demonstrates dose response in chronic hand eczema in a 16-week randomized phase IIb trial
- Pages: 42-51
- First Published: 27 January 2022
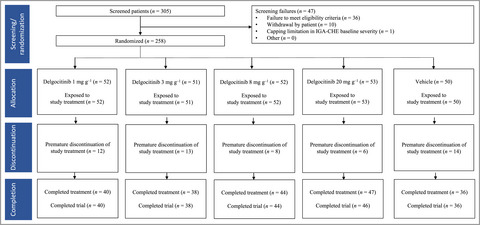
This article reports the efficacy and safety results from the first chronic hand eczema trial with the topical pan-JAK inhibitor delgocitinib in a cream formulation.
Linked Comment: M.L.A. Schuttelaar. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:7–8.
Plain language summary available online
EPIDEMIOLOGY
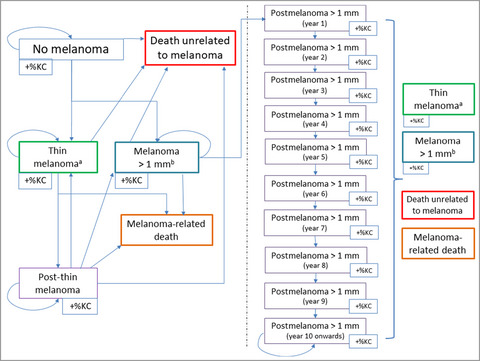
The relative contribution of the decreasing trend in tumour thickness to the 2010s increase in net survival from cutaneous malignant melanoma in Italy: a population-based investigation
- Pages: 52-63
- First Published: 06 March 2022
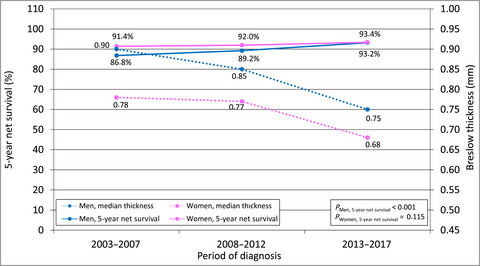
What is already known about this topic?
- Long-term increase in survival from cutaneous malignant melanoma (CMM) is generally attributed to the decreasing trend in tumour thickness, the single most important prognostic factor.
- Targeted therapies and immune checkpoint inhibitors, introduced during the past decade, were shown in phase III trials to improve the prognosis of patients with unresectable and metastatic CMM, but their contribution to the persistent upward trend in overall survival at the population level in Europe is ill-defined.
What does this study add?
- In Italy, the 5-year net survival from CMM in 2013–2017 improved vs. 2003–2007, especially among male patients and in the two highest tumour thickness categories.
- Male patients, for the first time, exhibited the same survival as female patients despite having still thicker lesions. The decrease in median tumour thickness accounted for a small part of the improvement.
- Novel therapies, approved in 2013, are the factor most likely to account for the remaining improvement.
In Italy, the 5-year net survival from melanoma in 2013–2017 improved vs. 2003–2007, especially among male patients and in the two highest tumour thickness categories. Male patients, for the first time, exhibited the same survival as female patients despite having still thicker lesions. The decrease in median tumour thickness accounted for a small part of the improvement. Novel therapies, approved in 2013, are the factor most likely to account for the remaining improvement.
Linked Comment: I.T. Harvima and R.J. Harvima. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:6–7.
Plain language summary available online
Isotretinoin and adverse neuropsychiatric outcomes: retrospective cohort study using routine data
- Pages: 64-72
- First Published: 10 February 2022
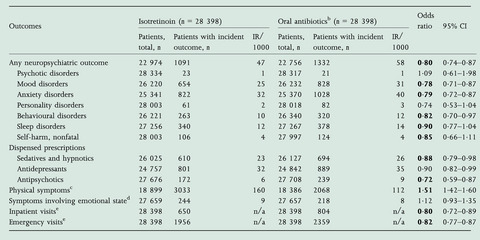
What is already known about this topic?
- Severe neuropsychiatric outcomes have been reported in individuals exposed to isotretinoin, but the evidence is inconclusive and complicated by several methodological limitations.
- The neuropsychiatric risks potentially associated with isotretinoin treatment are an ongoing concern to clinicians and individuals with treatment-resistant acne.
- Current isotretinoin prescribing guidelines recommend close monitoring for adverse mental health outcomes during isotretinoin treatment.
What does this study add?
- After controlling for various potential sources of bias, isotretinoin was associated with a reduced incidence of adverse psychiatric outcomes (odds ratio 0·80, 95% confidence interval 0·74–0·87) compared with oral antibiotics.
- Isotretinoin appeared to reduce the excess psychiatric risk associated with treatment-resistant moderate-to-severe acne.
- In monitoring potential adverse outcomes during isotretinoin treatment, clinicians should also consider the high mental health burden associated with treatment-resistant acne and the potential contribution of physical side-effects of the prescribed medication on mental health.
In this propensity score matched cohort study of electronic medical records, we found that after controlling for various potential sources of bias, isotretinoin was associated with a reduced incidence of adverse psychiatric outcomes (odds ratio 0.80, 95% confidence interval 0.74–0.87) when compared to oral antibiotics. Isotretinoin thus appeared to reduce the excess psychiatric risk associated with treatment-resistant moderate-to-severe acne.
Linked Comment: J. Ravencroft and L. Eichenfield. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:8–9.
Plain language summary available online
The associated burden of mental health conditions in alopecia areata: a population-based study in UK primary care
- Pages: 73-81
- First Published: 14 February 2022
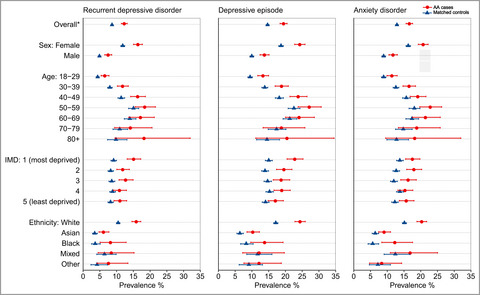
What is already known about this topic?
- Alopecia areata is a common cause of nonscarring hair loss.
- Psychological comorbidity is common in people with alopecia areata, but limited information is available on the co-occurrence and impact of depression and anxiety in this group.
What does this study add?
- Adults newly diagnosed with alopecia areata (5435 in UK primary care) have a higher background prevalence of depression and anxiety than population controls, and are also at 30–38% higher risk of being subsequently diagnosed with new-onset depression and anxiety.
- After alopecia areata diagnosis, people with the condition are more likely to be issued time off work certificates (56% higher) and to be recorded as unemployed (82% higher risk) than population controls.
Adults newly diagnosed with alopecia areata (n=5435 in UK primary care) have a higher background prevalence of depression and anxiety than population controls. After diagnosis they are additionally had a 30–38% higher risk of being diagnosed with new onset depression and anxiety after diagnosis and are more likely to be issued time-off work certificates (56% higher) and be recorded as unemployed (82% higher risk), than population controls.
Linked Comment: N. Hunt. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:9–10.
Plain language summary available online
QUALITATIVE AND OUTCOMES RESEARCH
How do dermatologists’ personal models inform a patient-centred approach to management: a qualitative study using the example of prescribing a new treatment (Apremilast)
- Pages: 82-88
- First Published: 22 January 2022
What is already known about this topic?
- ‘Personal models’ is the term used to describe the thoughts, feelings and experiences that determine behaviour.
- Research has shown that clinicians’ personal models can influence their approach to psoriasis management, although the evidence base is limited.
What does this study add?
- Some, but not all, clinicians endorse a patient-centred approach. Clinicians’ beliefs and attitudes about patients, psoriasis and evidence for psoriasis treatments all potentially influence the degree to which clinicians champion whole-person management.
- Clinicians’ personal models impact how clinicians communicate with and behave towards patients during consultations and more specifically, the extent to which they demonstrate techniques to engage patients in joint decisions related to their condition and treatment.
What are the clinical implications of this work?
- Additional specialized training and education could help clinicians to recognize how their beliefs, feelings and experiences influence their clinical practice, extend their skills in shared decision making, and facilitate whole-person management.
Linked Comment: F. Cowdell. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:4.
Plain language summary available online
TRANSLATIONAL RESEARCH
Patients with psoriasis have a dysbiotic taxonomic and functional gut microbiota
- Pages: 89-98
- First Published: 15 March 2022
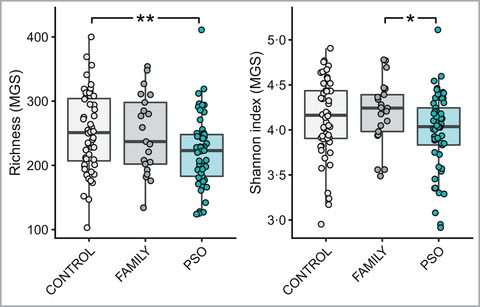
Shotgun metagenomic sequencing analysis demonstrated a dysbiotic taxonomic and functional gut microbiota in psoriasis cases when compared with age, sex and BMI matched healthy controls. In addition, the gut microbiota discriminates patients with psoriasis from their healthy partners
Plain language summary available online
GLOBAL HEALTH AND EQUITY
The Eumelanin Human Skin Colour Scale: a proof-of-concept study
- Pages: 99-104
- First Published: 29 March 2022
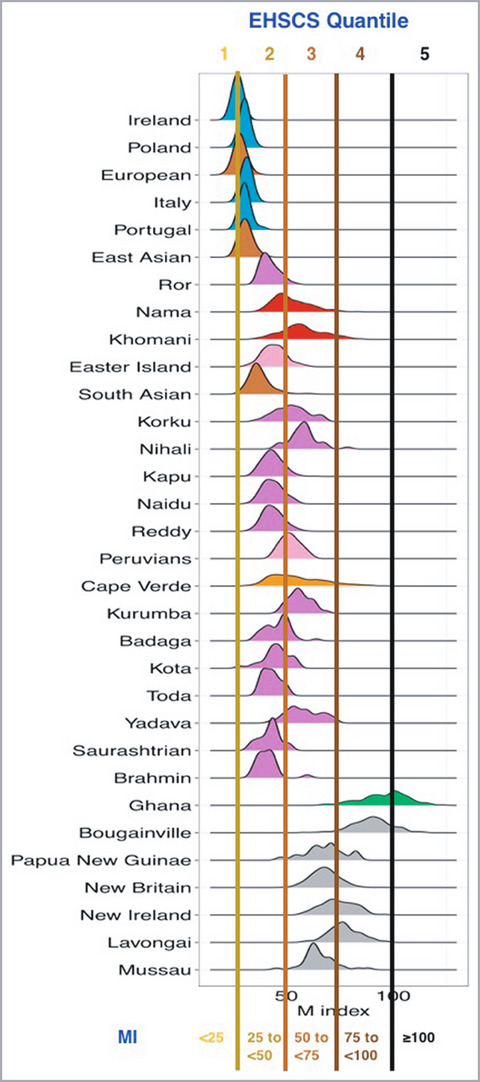
What is already known about this topic?
- At present, there is no standard nomenclature for describing the spectrum of constitutive skin colour across human populations.
- The Fitzpatrick scale of skin phototypes was developed as a simple method for describing the sun reactivity of human skin.
- The widespread and incorrect use of the Fitzpatrick scale to describe skin colour has led to a systematic lack of recognition of the diversity of darker skin colours.
What does this study add?
- The Eumelanin Human Skin Colour Scale is a five-point scale that describes the full spectrum of human constitutive skin colour.
- Eumelanin, the dominant chromophore of human skin, is a central descriptive word in the nomenclature of the scale.
- The scale is referenced on published skin reflectance data.
The Eumelanin Human Skin Colour Scale and how it correlates to the diversity of human skin pigmentation across human populations.#10.
GENERAL DERMATOLOGY
Cost-effectiveness of a policy-based intervention to reduce melanoma and other skin cancers associated with indoor tanning
- Pages: 105-114
- First Published: 10 February 2022
What is already known about this topic?
- Melanoma and keratinocyte skin cancers have a significant impact on population health and healthcare budgets, and a proportion are attributable to indoor tanning.
- Policy-based interventions that restrict or ban the commercial provision of indoor tanning are in place around the world to reduce the burden of skin cancer, but economic evidence to support decision making is lacking.
What does this study add?
- Banning indoor tanning, supported by a public health campaign, would be an efficient use of healthcare resources to reduce melanoma and keratinocyte cancers in England.
- This policy-intervention would save lives (4.6% melanoma deaths avoided) and reduce skin cancer treatment costs with a high degree of confidence.
- The structured and transparent analysis means that decision makers in other jurisdictions can assess the relevance of these findings to their context.
The use of indoor tanning devices causes harm to individuals and increases healthcare costs. A model-based cost-effectiveness anlaysis was used to estimate the economic impact of a policy-based intervention to reduce skin cancers associated with indoor tanning. Implementation of the intervention across England would realise health gains and reduce healthcare costs.
Linked Comment: M. Janda and C. Sinclair. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:7.
Plain language summary available online
Body dysmorphia in common skin diseases: results of an observational, cross-sectional multicentre study among dermatological outpatients in 17 European countries
- Pages: 115-125
- First Published: 18 January 2022
What is already known about this topic?
- Body dysmorphic disorder (BDD) is a common psychiatric disorder with a prevalence of about 2% in the general population.
- Skin diseases pose a high psychological burden on patients. People with these problems often experience increased self-consciousness, skin-related shame and stigmatization.
- Single-centre studies including small samples of patients with skin conditions showed that these patients show symptoms of a similar nature to BDD more often than the general population.
What does this study add?
- In this large multicentre study, BDD symptoms were fivefold more prevalent in dermatological patients than in healthy skin controls, and were related to young age, female sex, psychological stress and stigmatization experience.
- Certain patient groups (e.g. hyperhidrosis) had a greater than 11-fold increased chance of BDD symptoms compared with controls.
- Doctors should consider appearance-related concern and BDD more often and refer patients when needed to an appropriate service for assessment and treatment.
Body dysmorphic disorder (BDD) is a psychiatric condition affecting about 2.5 % of the general population. Patients with this condition are preoccupied with negative thoughts about their own appearance which highly impair their daily functioning. Skin diseases can pose a high psychological burden on patients partly due to visible skin lesions. BDD has been shown to affect dermatological patients quite often, but there are no large studies that include both patients with different dermatological conditions and healthy skin controls. This study included 8295 participants: 5487 patients with different skin diseases (56% female) recruited among dermatological out-patients at 22 clinics in 17 European countries and 2808 people with healthy skin (66% female). Symptoms of BDD were measured using a self-report questionnaire. In addition, each patient was given a dermatological diagnosis by a dermatologist. It was shown that BDD symptoms were five times more prevalent in patients with dermatological conditions than in people with healthy skin (10.5% vs. 2.1%). Certain dermatological patients (e.g. with excessive sweating, circular hairloss and white spot disease) had a more than eleven-fold increased chance of BDD symptoms compared to people with healthy skin. It was also shown that BDD symptoms more often occurred in younger and in female persons, and those experiencing higher psychological stress and feeling stigmatized. As BDD symptoms are so common in dermatological patients, general practitioners and dermatologists should consider both BDD and appearance related distress and refer patients when identified to an appropriate service for further assessment and management.
Linked Comment: P. Magin and K. Fisher. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:5.
Plain language summary available online
Correspondence
RESEARCH LETTERS
Clinical and direct immunofluorescence characteristics of cutaneous toxicity associated with enfortumab vedotin
- Pages: 126-127
- First Published: 19 January 2022
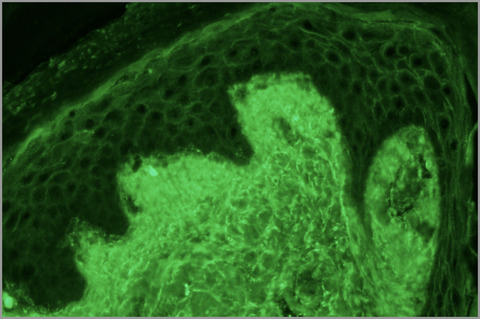
Enfortumab vedotin (EV), a novel antibody-drug conjugate approved for metastatic urothelial carcinoma, causes a variety of cutaneous adverse reactions. We present two cases of bullous eruptions following treatment with EV, both demonstrating IgG deposition on direct immunofluorescence (DIF) correlating to the location of nectin-4 in the epidermis. This suggests that the IgG component of EV binding to nectin-4 in keratinocytes is likely a primary contributor to the high rates of cutaneous toxicity.
Characterization of discontinuation and nonpublication of phase III randomized clinical trials of psoriasis
- Pages: 127-129
- First Published: 21 January 2022
Head and neck granulomatous rash associated with mogamulizumab mimicking mycosis fungoides
- Pages: 129-131
- First Published: 26 January 2022
Corrigenda
CORRESPONDENCE: IMAGE GALLERY
Abstracts
British Society for Investigative Dermatology Virtual Annual Meeting, 29–31 March 2021
- Pages: e1-e45
- First Published: 03 July 2022
PLAIN LANGUAGE SUMMARIES
A health campaign and sunbed ban to reduce skin cancer: a good use of the healthcare budget
- Page: e46
- First Published: 03 July 2022
Linked Article: Eden et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:105–114.
Antibiotic-resistant bacteria and the skin
- Page: e47
- First Published: 03 July 2022
Linked Article: Muhaj et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:12–20.
How do dermatologists’ beliefs, emotions and experiences influence the care of people with psoriasis? An interview study using the example of prescribing a new treatment called apremilast
- Page: e48
- First Published: 03 July 2022
Linked Article: Hewitt et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:82–88.
People who develop alopecia areata have an increased risk for depression, anxiety, time off work and unemployment
- Page: e49
- First Published: 03 July 2022
Linked Article: Macbeth et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:73–81.
Testing different doses of delgocitinib cream for the treatment of chronic hand eczema
- Page: e50
- First Published: 03 July 2022
Linked Article: Worm et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:42–51.
Body dysmorphic disorder in patients with skin conditions
- Page: e51
- First Published: 03 July 2022
Linked Article: Schut et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:115–125.
Investigation of the reasons for improvement in the survival of patients with melanoma in Italy
- Page: e52
- First Published: 03 July 2022
Linked Article: Zamagni et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:52–63.
In patients with psoriasis, the types of microbes in the gut are different from those in healthy people
- Page: e53
- First Published: 03 July 2022
Linked Article: Todberg et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:89–98.
Is the acne medication isotretinoin associated with poor mental health?
- Page: e54
- First Published: 03 July 2022
Linked Article: Paljarvi et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:64–72.
开展健康宣传活动,禁售日光浴床,以减少皮肤癌: 合理利用医疗预算
- Page: e55
- First Published: 03 July 2022
Linked Article: Eden et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:105–114.
抗药性细菌和皮肤
- Page: e56
- First Published: 03 July 2022
Linked Article: Muhaj et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:12–20.
皮肤科医生的信心、情绪和经验对银屑病患者护理有哪些影响?一项以使用新疗法阿普米司特为例的访谈研究
- Page: e57
- First Published: 03 July 2022
Linked Article: Hewitt et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:82–88.
斑秃患者面临抑郁、焦虑、休假和失业高风险
- Page: e58
- First Published: 03 July 2022
Linked Article: Macbeth et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:73–81.
测试迪高替尼乳膏治疗慢性手部湿疹的不同剂量
- Page: e59
- First Published: 03 July 2022
Linked Article: Worm et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:42–51.
皮肤病患者的身体畸形恐惧症
- Page: e60
- First Published: 03 July 2022
Linked Article: Schut et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:115–125.
关于意大利黑色素瘤患者生存率提高原因的研究
- Page: e61
- First Published: 03 July 2022
Linked Article: Zamagni et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:52–63.
银屑病患者肠道中的微生物类型与健康人不同
- Page: e62
- First Published: 03 July 2022
Linked Article: Todberg et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:89–98.
痤疮药异维 A 酸是否与不良心理健康相关?
- Page: e63
- First Published: 03 July 2022
Linked Article: Paljarvi et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 187:64–72.











2690-442X.cover.png)