Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER IMAGE
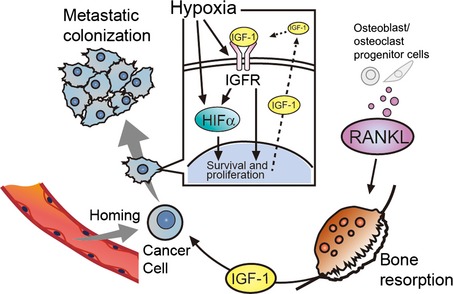
Bone resorption facilitates osteoblastic bone metastasis by insulin-like growth factor and hypoxia. Von Kossa staining showing aberrant bone formation due to bone metastasis of murine osteosarcoma LM8 cells.
- Page: May cover
- First Published: 07 May 2014
ISSUE INFORMATION
IN THIS ISSUE
REVIEW ARTICLE
Not just gRASping at flaws: Finding vulnerabilities to develop novel therapies for treating KRAS mutant cancers
- Pages: 499-505
- First Published: 24 February 2014
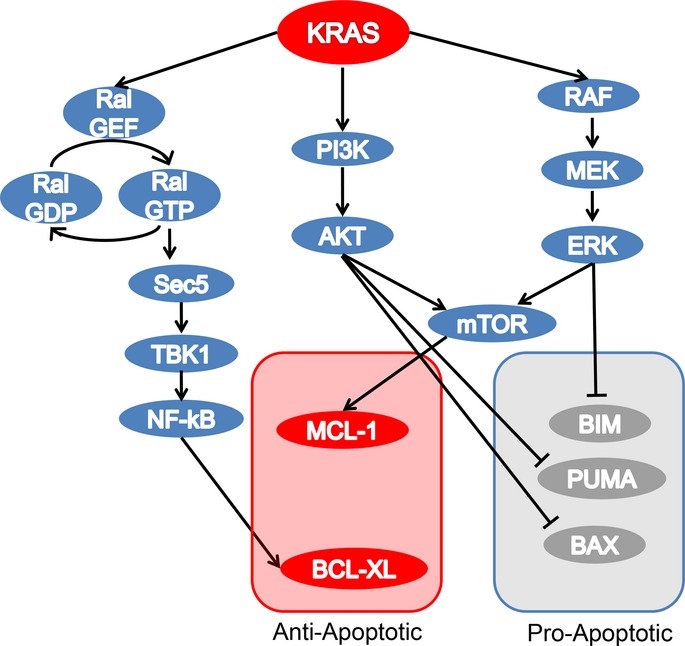
Mutations in Kirsten rat-sarcoma (KRAS) are well appreciated to be major contributors of human cancers through dysregulation of multiple growth and survival pathways. The main effector pathways of KRAS and current approaches to develop combination therapies targeting these KRAS-effector pathways are discussed. Also, other approaches targeting KRAS, including synthetic lethal screening are summarized.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
CARCINOGENESIS
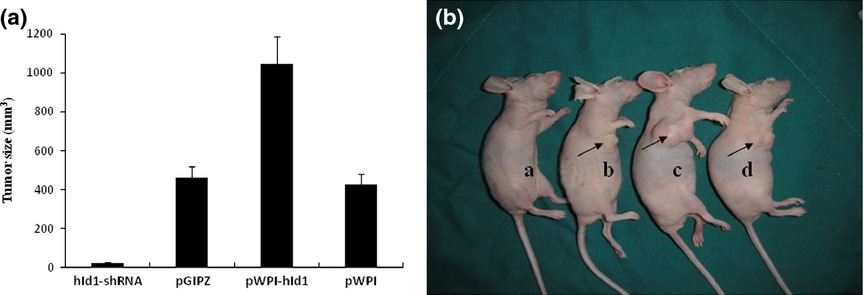
Inhibitors of differentiation-1 promotes nitrosopyrrolidine-induced transformation of HPV 16-immortalized cervical epithelial cell
- Pages: 506-511
- First Published: 15 March 2014
Inhibition of histone methyltransferase EZH2 depletes leukemia stem cell of mixed lineage leukemia fusion leukemia through upregulation of p16
- Pages: 512-519
- First Published: 25 February 2014
Leukemia stem cells (LSCs) are main cause of relapse or refractoriness to conventional chemotherapy. Although eradicating LSCs are ideal goal for anti-leukemia therapy, drugs targeting LSCs have scarcely been identified. Polycomb group proteins are associated with controlling stemness including activity of cancer stem cells, and can be pharmacologically targeted by a selective inhibitor of H3K27, DZNep. To our surprise, EZH2 inhibition by DZNep or shRNA not only suppressed MLL fusion leukemia proliferation but also reduced LSCs frequency. Dysregulation of p16 is supposed to be responsible for the effect. We also show that EZH2 are highly enriched around the transcription-start-site of p16, together with H3K27 methylation marks in MLL/ENL cells. Although high expression of Hoxa9 in MLL fusion leukemia is supposed to be responsible for the recruitment of EZH2, our data also suggests that there may be some other mechanisms independent of Hoxa9 activation to suppress p16 expression. We believe that these findings would help us to develop LICs targeted therapy for MLL fusion leukemia.
Quercetin enhances apoptotic effect of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) in ovarian cancer cells through reactive oxygen species (ROS) mediated CCAAT enhancer-binding protein homologous protein (CHOP)-death receptor 5 pathway
- Pages: 520-527
- First Published: 10 March 2014
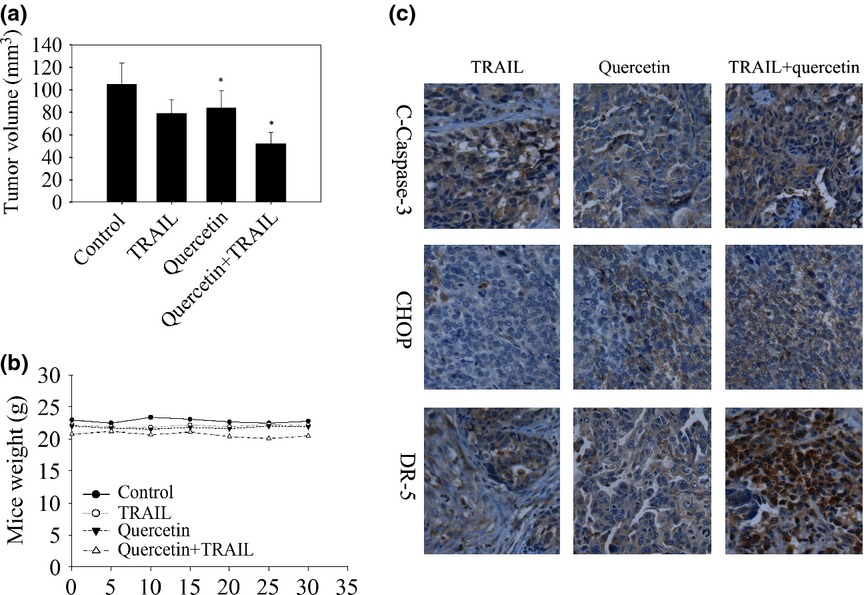
Mitochondrial proteins (ROS) are mediating the apoptotic process, downstream or in parallel, CHOP might be a crucial player for DR5 upregulation and cancer cell killing by quercetin. IRE1a-JNK signaling could also be considered to be the major ER-stress pathway for quercetin induced CHOP expression, thus contributing to the enhanced apoptotic death of ovarian cancer cells to TRAIL. Quercetin could be an attractive candidate for combined chemotherapy against cancer.
CELL, MOLECULAR, AND STEM CELL BIOLOGY
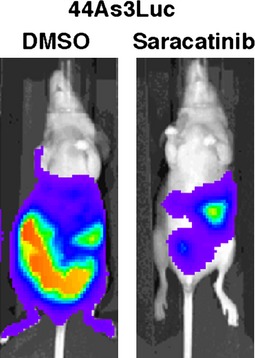
Saracatinib impairs the peritoneal dissemination of diffuse-type gastric carcinoma cells resistant to Met and fibroblast growth factor receptor inhibitors
- Pages: 528-536
- First Published: 25 February 2014
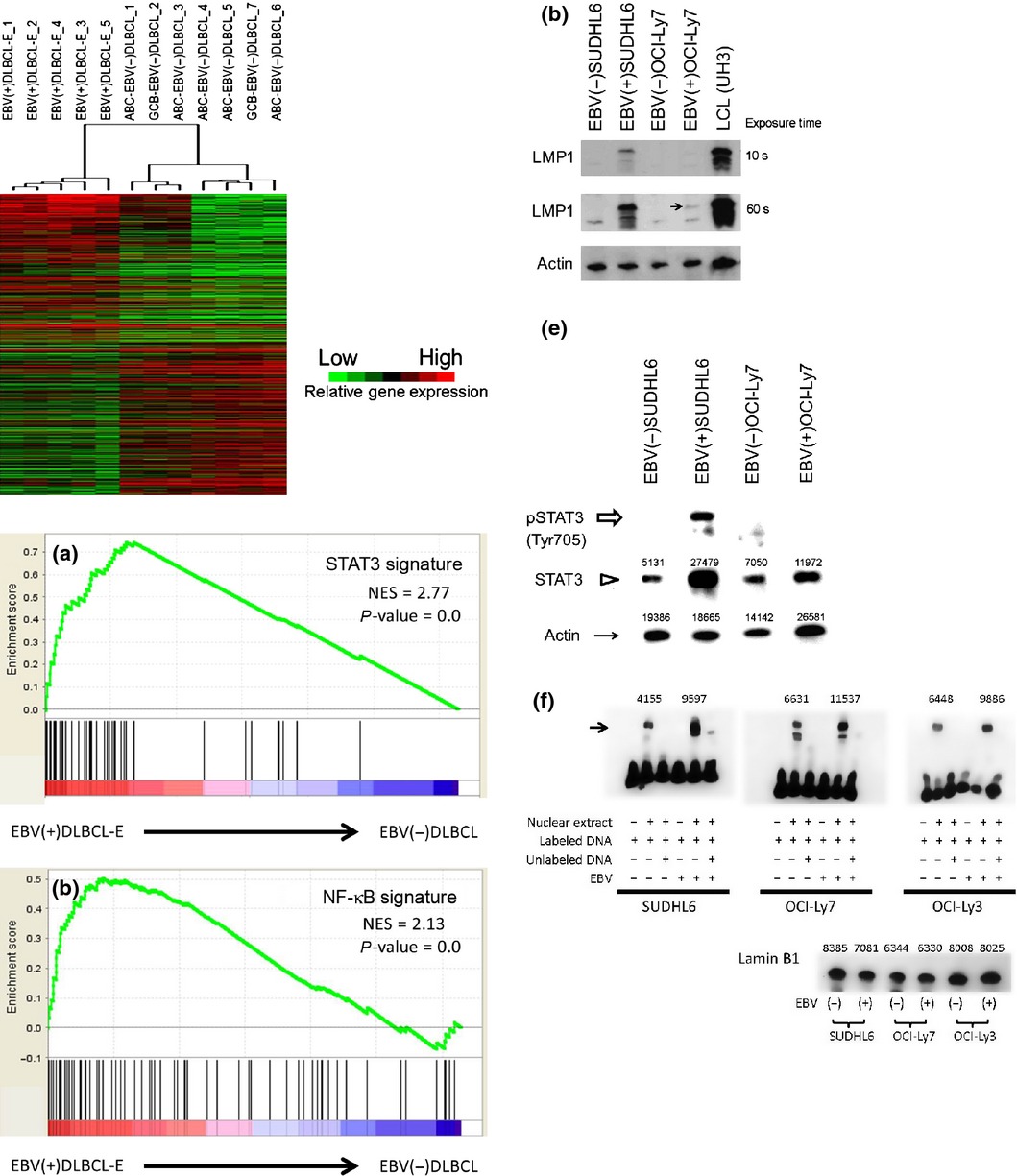
Gene expression profiling of Epstein–Barr virus-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the elderly reveals alterations of characteristic oncogenetic pathways
- Pages: 537-544
- First Published: 01 March 2014
Suppression of REV7 enhances cisplatin sensitivity in ovarian clear cell carcinoma cells
- Pages: 545-552
- First Published: 05 March 2014
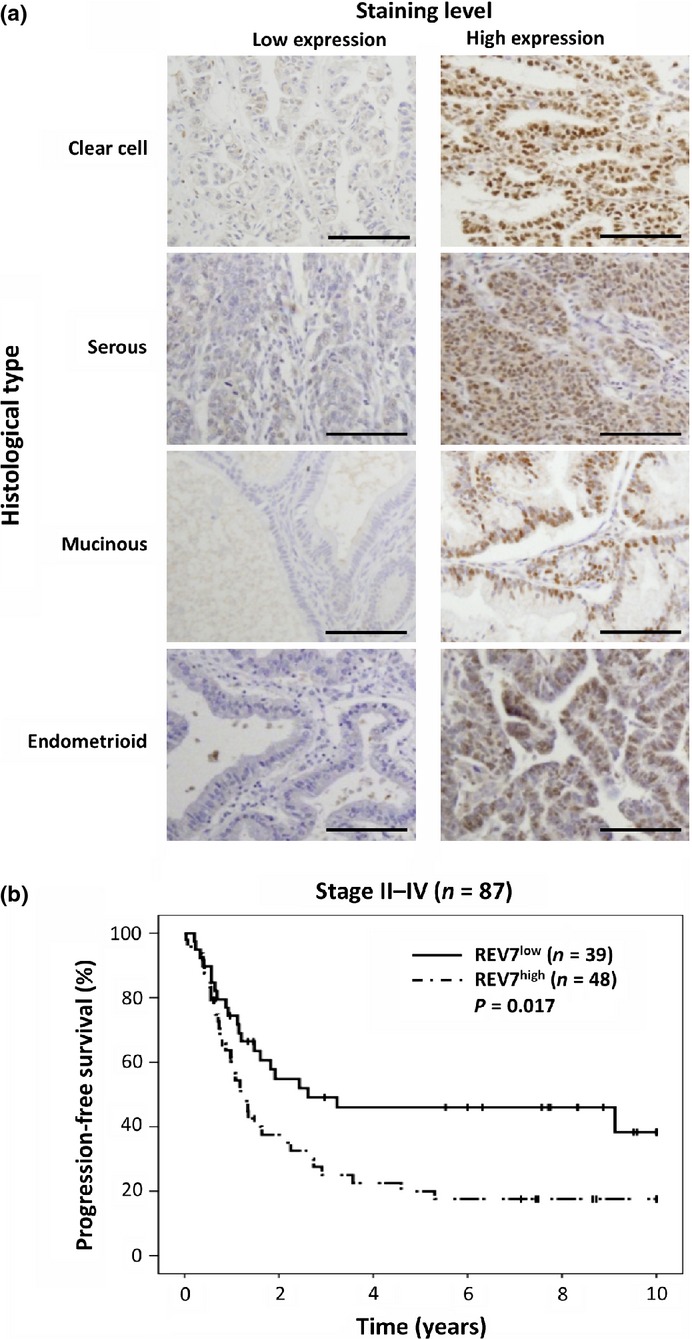
Immunohistochemical analysis of 137 epithelial ovarian cancer specimens revealed that high levels of REV7 expression were detected in clear cell carcinomas (CCC), and were associated with poor prognosis of advanced epithelial ovarian cancer. REV7 depletion in CCC cells enhanced sensitivity to cisplatin in vitro and in vivo, suggesting that REV7 could be a molecular target for CCC therapy.
Bone resorption facilitates osteoblastic bone metastatic colonization by cooperation of insulin-like growth factor and hypoxia
- Pages: 553-559
- First Published: 05 March 2014
Identification of novel targets for antiangiogenic therapy by comparing the gene expressions of tumor and normal endothelial cells
- Pages: 560-567
- First Published: 06 March 2014

We identified 131 genes that were differentially upregulated in mTECs. Functional analysis using siRNA-mediated gene silencing revealed five novel TEC markers that were involved in the proliferation or migration of mTECs. The expression of DEF6 and TMEM176B was upregulated in tumor vessels of human renal cell carcinoma (RCC) specimens, suggesting that they are potential targets for antiangiogenic intervention for RCC.
An inhibition of p62/SQSTM1 caused autophagic cell death of several human carcinoma cells
- Pages: 568-575
- First Published: 11 March 2014
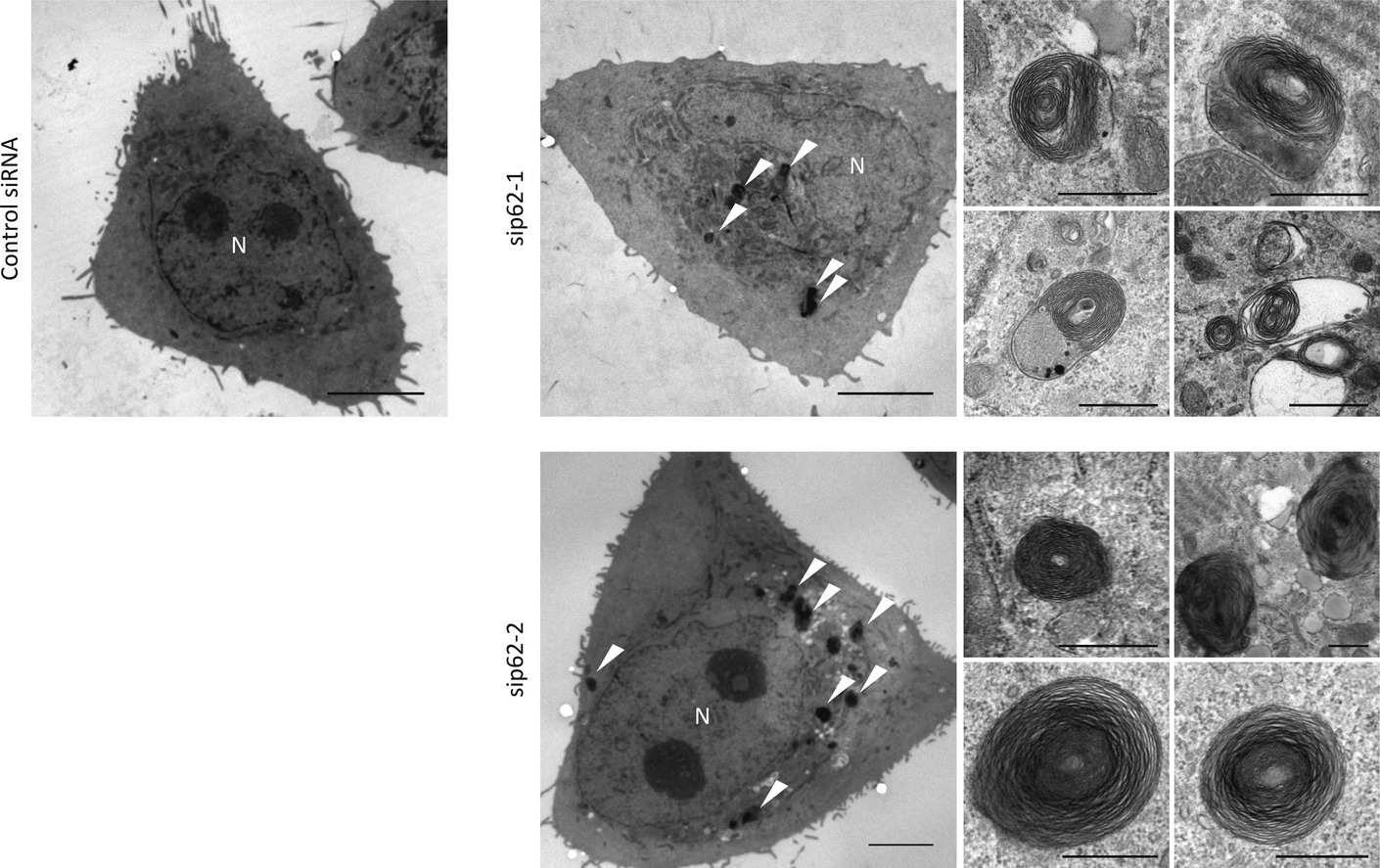
p62/SQSTM1 (p62) is a multifunctional protein implicated in several signal transduction pathways and selectively degraded by autophagy, a process for lysosomal degradation of protein and organelle. Results of our present study revealed that p62-silencing resulted in the formation of mis-regulated multilayer autophagosomes and an autophagic cell death, and p62 can therefore be an attractive target for the development of anti-neoplastic agents.
CLINICAL RESEARCH
Incidence and prediction of invasive disease and nodal metastasis in preoperatively diagnosed ductal carcinoma in situ
- Pages: 576-582
- First Published: 17 February 2014
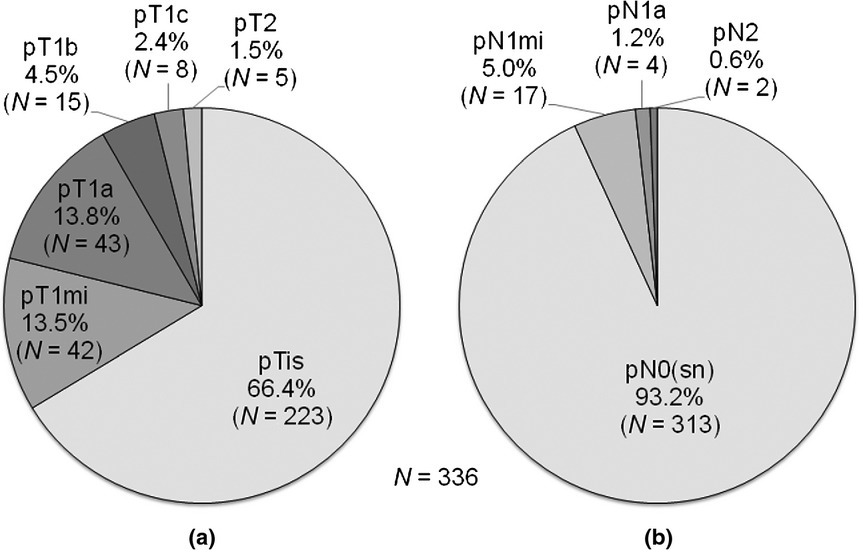
Most patients with a preoperative diagnosis of ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast had no metastasis or only micrometastasis in axillary nodes, even though invasive disease was found on final pathology. Predictors of the invasive disease were not completely consistent with those of nodal metastasis. Therefore, the selective application of sentinel node biopsy in patients with a higher risk of invasive disease may not accurately identify the patients with a higher likelihood of sentinel node metastasis.
DRUG DISCOVERY AND DELIVERY
Antitumor effect of fibrin glue containing temozolomide against malignant glioma
- Pages: 583-591
- First Published: 27 March 2014
Fibrin glue containing temozolomide has the anti-tumor effect against malignant glioma with the sustained release.
GENETICS, GENOMICS AND PROTEOMICS
High-resolution genomic copy number profiling of primary intraocular lymphoma by single nucleotide polymorphism microarrays
- Pages: 592-599
- First Published: 26 February 2014
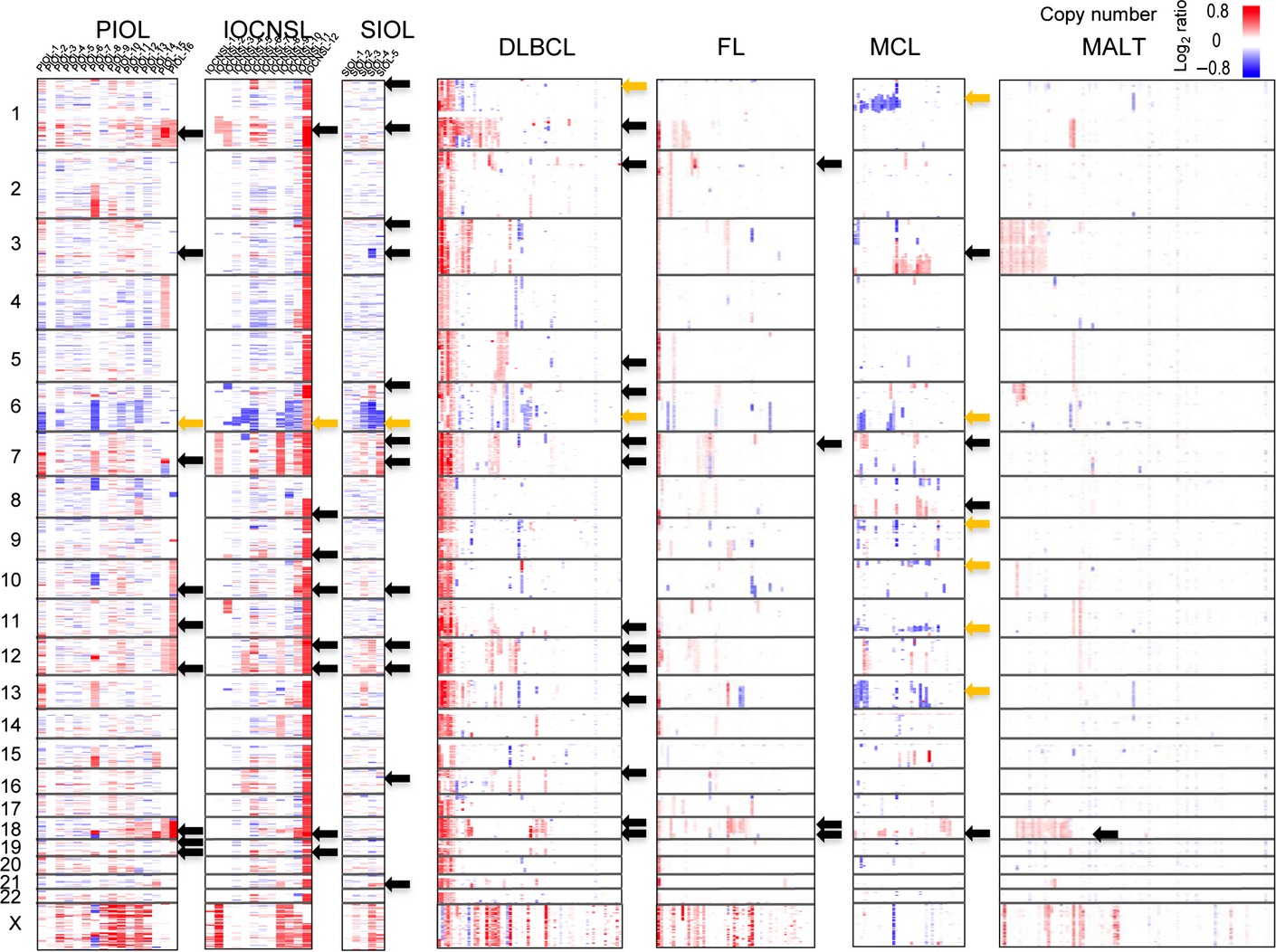
The genetic features of primary intraocular lymphoma (PIOL) have not yet been elucidated. We carried out single nucleotide polymorphism array karyotyping of IOL using genomic DNA extracted from vitreous fluid. Recurrent copy number gain regions in PIOLs were detected most frequently on chromosome 1q followed by 18q and 19q. There was a correlation between gain of the IL-10 gene located on 1q and intravitreal interleukin-10 concentration, which was higher in IOL than in benign uveitis.
PATHOLOGY
GATA4 immunolocalization in breast carcinoma as a potent prognostic predictor
- Pages: 600-607
- First Published: 20 February 2014
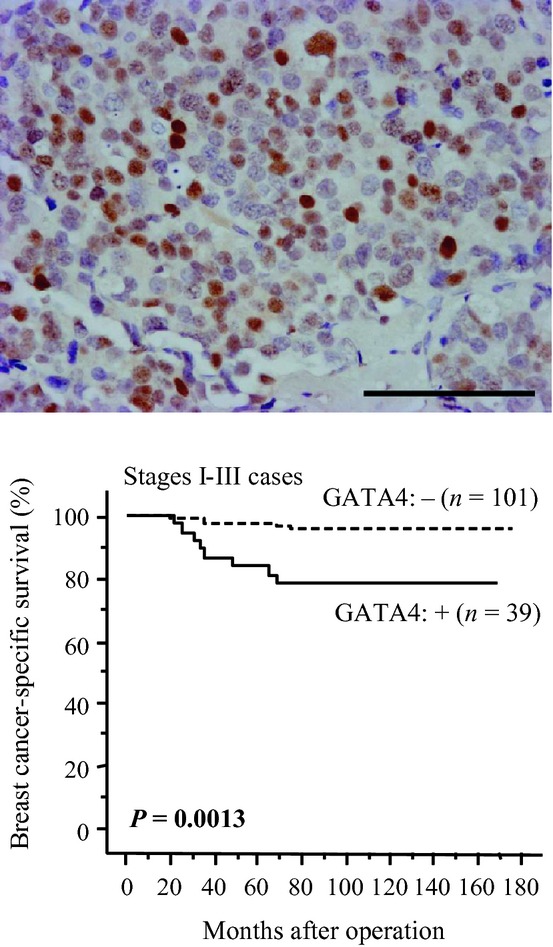
In this study, we explored the possible roles of GATA4 in human breast cancer. GATA4 immunoreactivity was positively associated with distant metastasis, and outcome analyses revealed that GATA4 immunoreactivity was associated with shorter disease-free and breast cancer-specific survival of the patients. These data may suggest important roles of GATA4 in the process of breast cancer progression.
Duodenal follicular lymphoma: Comprehensive gene expression analysis with insights into pathogenesis
- Pages: 608-615
- First Published: 06 March 2014
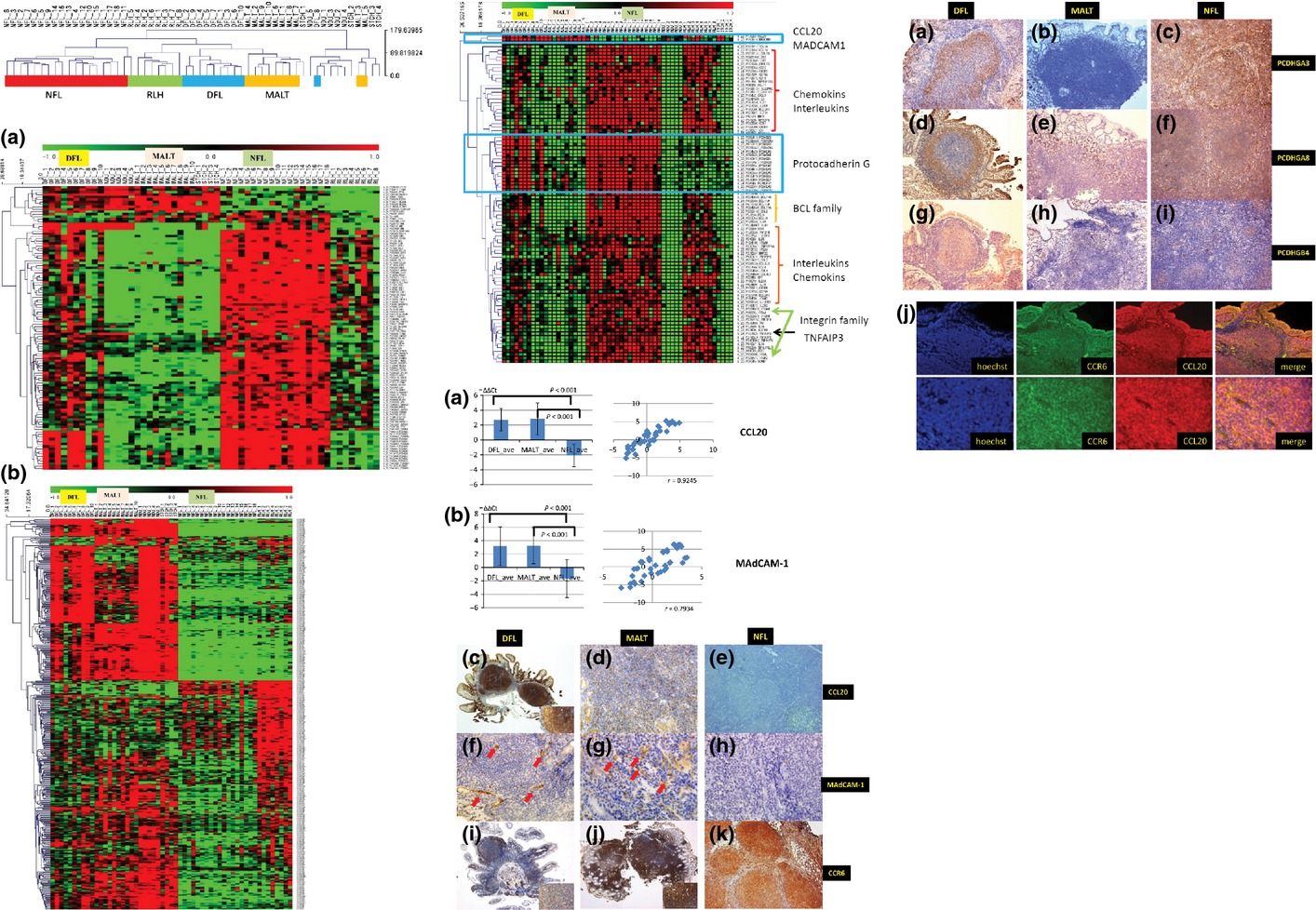
In the present study, we examined 10 DFL, 18 NFL, 10 gastric MALT lymphoma samples by gene expression analysis. Gene expression profiles of the 3 lymphoma types were compared using 2918 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) and results suggested that DFL shares characteristics of MALT lymphoma. Increased expression of CCL20 and MAdCAM-1 and co-expression of CCL20 and CCR6 may play an important role in tumorigenesis in DFL.
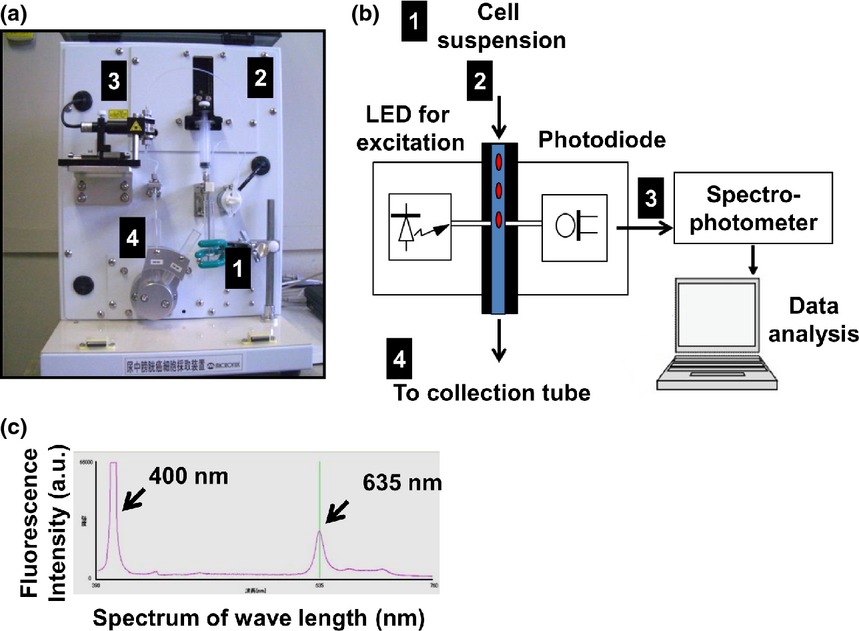
Diagnostic approach for cancer cells in urine sediments by 5-aminolevulinic acid-based photodynamic detection in bladder cancer
- Pages: 616-622
- First Published: 06 March 2014