Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover
Masthead
Communications
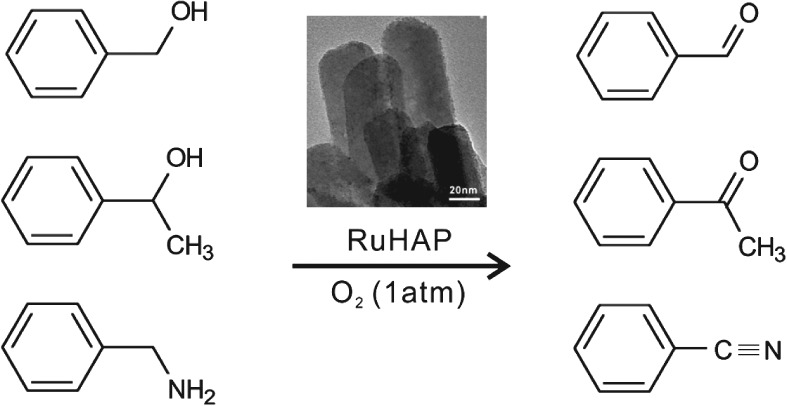
Ruthenium-Incorporated Hydroxyapatites for the Oxidation of Alcohols and Amines Using Molecular Oxygen as an Oxidant
- Pages: 1-2
- First Published: 19 December 2014
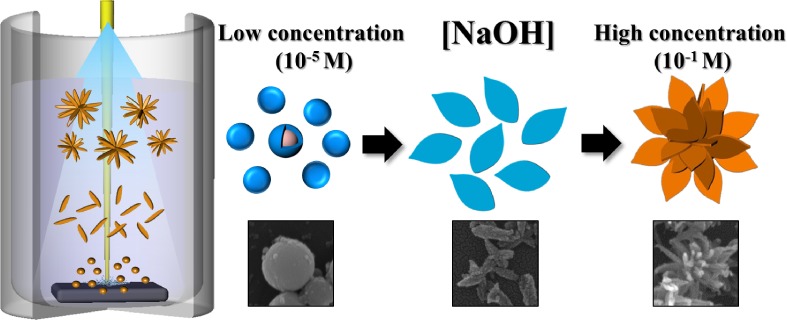
Facile Preparation of Cu2O and CuO Nanoparticles by Pulsed Laser Ablation in NaOH Solutions of Different Concentration
- Pages: 3-4
- First Published: 05 January 2015
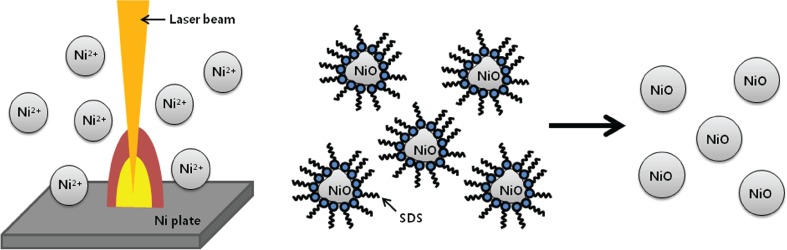
Effects of Laser Energy Density on Size and Morphology of NiO Nanoparticles Prepared by Pulsed Laser Ablation in Liquid
- Pages: 5-6
- First Published: 05 January 2015
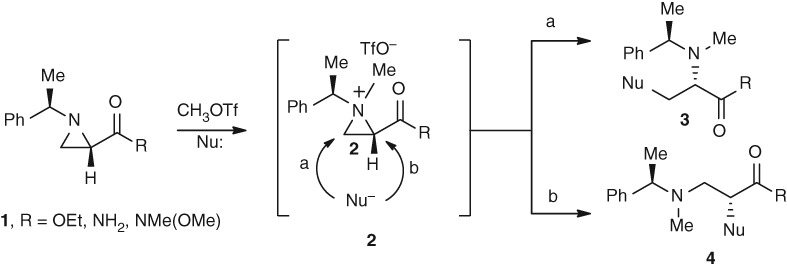
Facile Synthesis of N-Methylated Amino Acids from Chiral Aziridine-2-carboxylate
- Pages: 7-8
- First Published: 05 January 2015
Enhanced Adhesion of Marine Diatoms on a Solid Substrate by Tannic Acid Coating
- Pages: 9-10
- First Published: 05 January 2015
Articles
CO2 Adsorption on H2O-Saturated BaO(1 0 0) and Induced Barium Surface Dissociation
- Pages: 11-16
- First Published: 05 January 2015
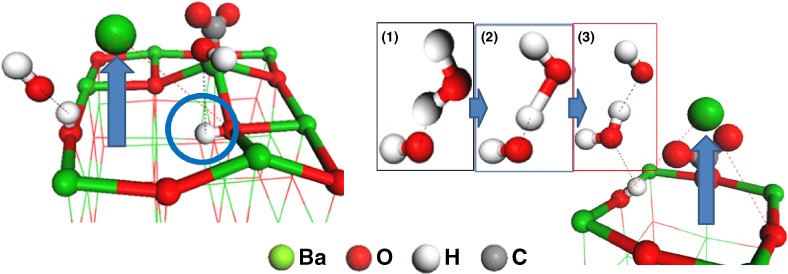
The aggregated H2O molecules tend to produce a hydrogen-terminated surface, and then generate barium dissociation of the barium oxide (BaO) surface. The dissociated barium of the surface, driven by the high affinity of H2O to the surface, contributes to a reduction in basicity, which may gradually cause the reduction of CO2 adsorption performance.
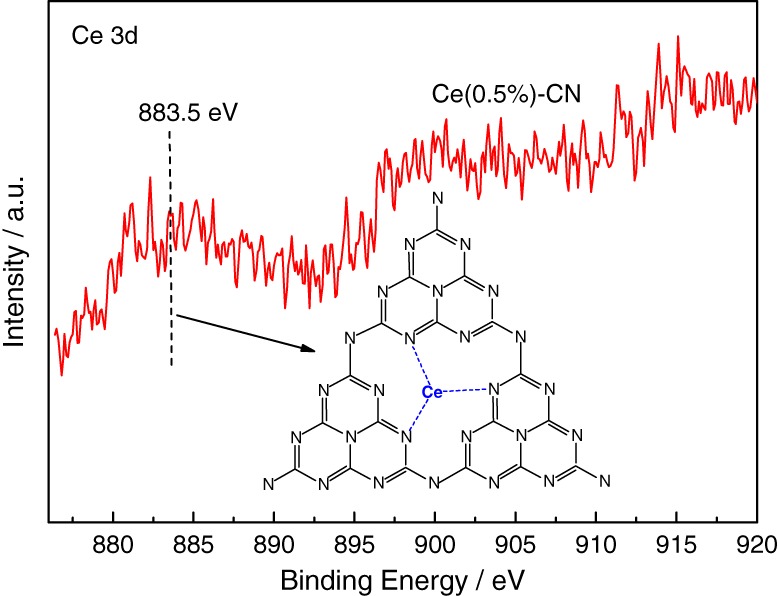
A Convenient Method to Prepare Novel Rare Earth Metal Ce-Doped Carbon Nitride with Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity Under Visible Light
- Pages: 17-23
- First Published: 05 January 2015
mPW1PW91-Calculated Structures, IR Spectra, and Frontier Orbitals of Benzoylmethoxythiacalix[4]arene Complexed with Alkali Metal Ions
- Pages: 24-31
- First Published: 18 December 2014
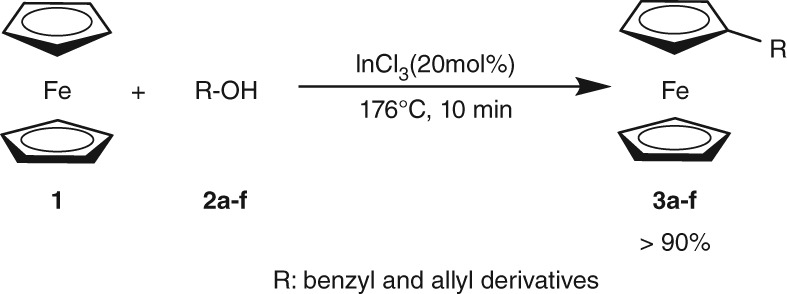
An Efficient Synthesis of Mono-Substituted Benzyl Ferrocene Derivatives
- Pages: 32-35
- First Published: 18 December 2014
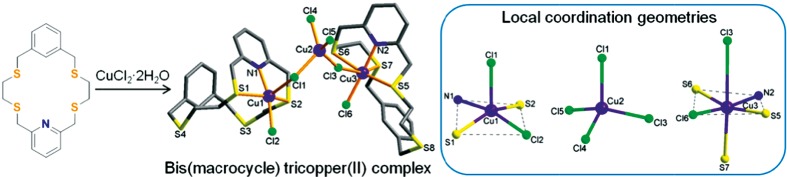
Syntheses and Crystal Structures of Mercury(II) and Copper(II) Complexes of an 18-Membered NS4 -Macrocycle
- Pages: 36-42
- First Published: 18 December 2014
Antitubercular Activities of the Novel Synthesized 1,2,4-Triazole Derivatives
- Pages: 43-51
- First Published: 05 January 2015
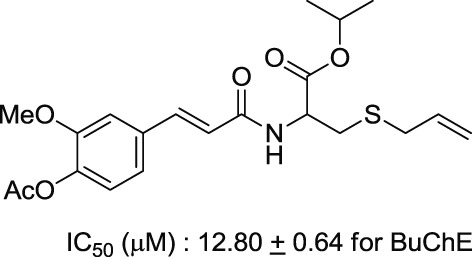
(S)-Allyl Cysteine Derivatives as a New-type Cholinesterase Inhibitor
- Pages: 52-58
- First Published: 05 January 2015
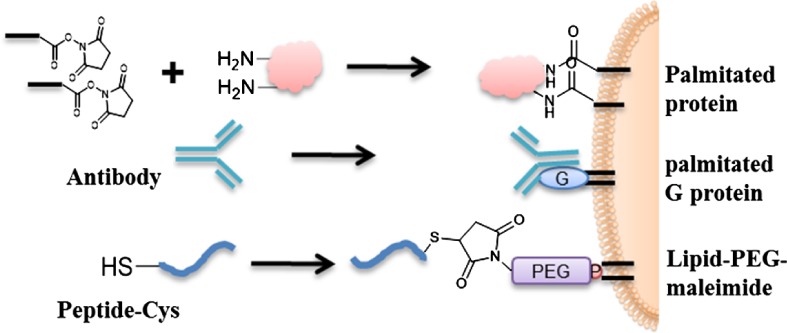
Recent Advances in Cell surface Engineering Focused on Cell Therapy
- Pages: 59-65
- First Published: 05 January 2015
Searching for Growth Conditions for Optimized Expression of Recombinant Proteins in Escherichia coli by Using Two-Dimensional NMR Spectroscopy
- Pages: 66-73
- First Published: 05 January 2015
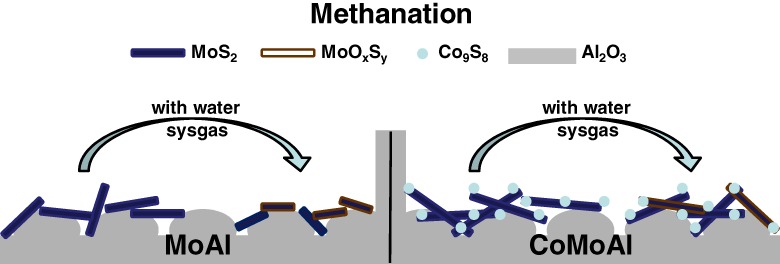
Influence of Water on the Methanation Performance of Mo-Based Sulfur-Resistant Catalysts with and without Cobalt Additive
- Pages: 74-82
- First Published: 05 January 2015
Enhanced Stability of Hydroxyapatite-coated Liposomes for Ultrasound-triggered Drug Release
- Pages: 83-87
- First Published: 05 January 2015
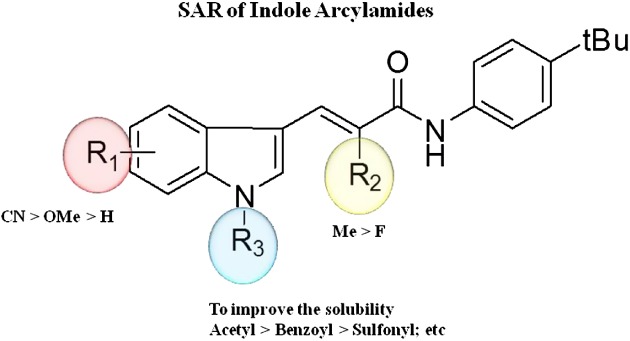
Synthesis and Structure–Activity Relationship of Novel Indole Acrylamide Derivatives as HCV Replication Inhibitors
- Pages: 88-98
- First Published: 05 January 2015
Influence of Adiponitrile Additive on Ethylene Carbonate-based Electrolyte for Capacitors
- Pages: 99-103
- First Published: 05 January 2015
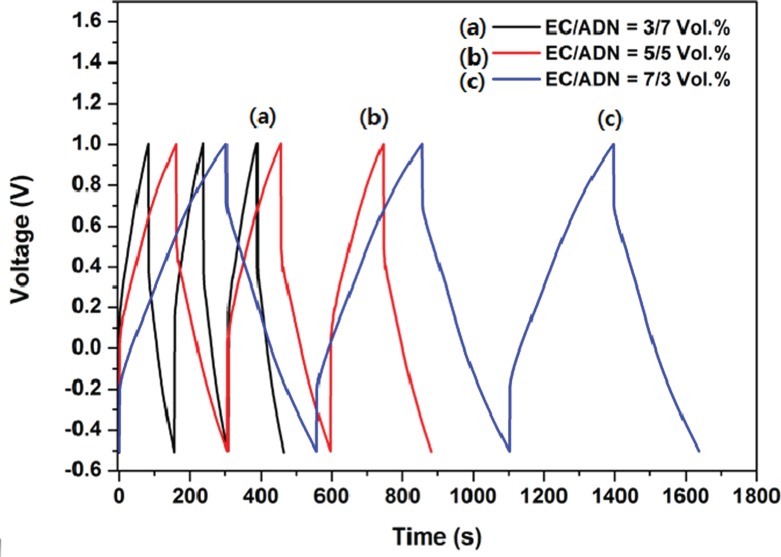
The effect of ADN additive on EC electrolyte of EDLC was confirmed by various chemical and electrochemical performances. When adding ADN (30%), the capacitance of the capacitor had a value similar to that when using the commercial ACN electrolyte of EDLCs (about 40 F/g). Among the studied electrolytes, 70% EC/30% ADN electrolyte solution gave the best electrochemical properties, such as specific capacitance (44.6 F/g at a scan rate of 5 mV/s) and cycle ability (98% retention of initial value after 2000 cycles).
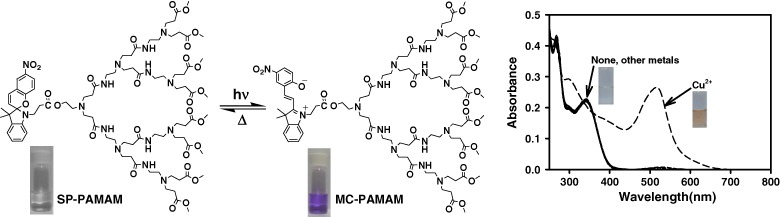
Solvatochromic and Photochromic Behavior of Spiropyran-cored PAMAM Dendron and Cu2+-Selective Sensing
- Pages: 104-110
- First Published: 05 January 2015
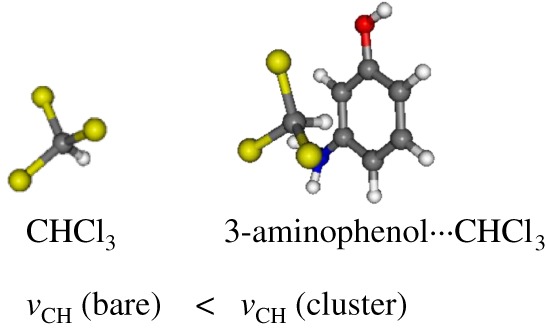
Quantum Mechanical Study on the Blue-Shifting Hydrogen-Bond between 3-Aminophenol and CHX3 (X ═ F, Cl)
- Pages: 111-116
- First Published: 05 January 2015
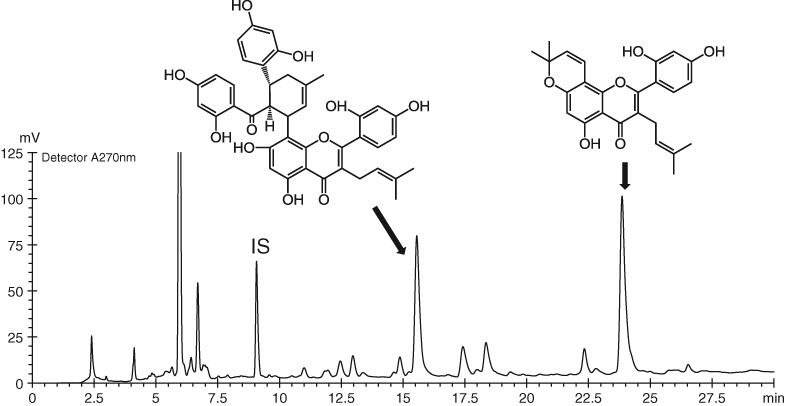
Specification and Analysis of Multiple Marker Compounds for Quality Control of Mori Cortex Radicis by HPLC
- Pages: 117-122
- First Published: 05 January 2015
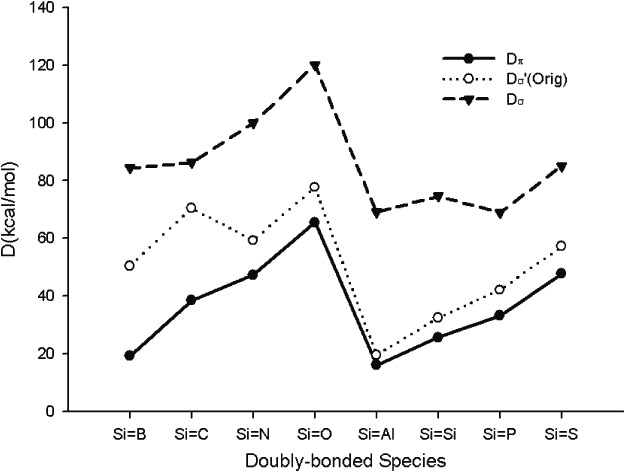
A Theoretical Reexamination of the π-Bond Strengths within the SiH2═XHn System
- Pages: 123-129
- First Published: 05 January 2015
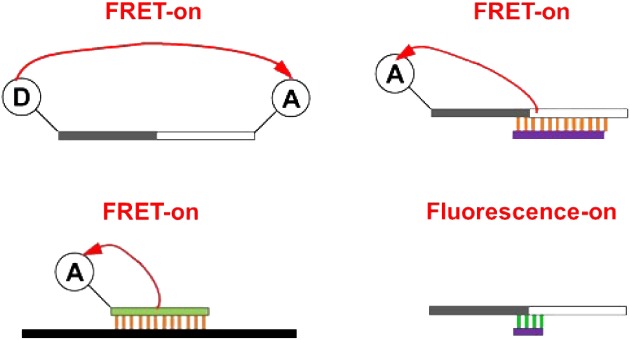
Allele-specific, Hybridization-based, Washing-free Fluorescence Signal Production Platforms for Quantitation of Single-Base Change (C → U) in RNA
- Pages: 130-138
- First Published: 05 January 2015
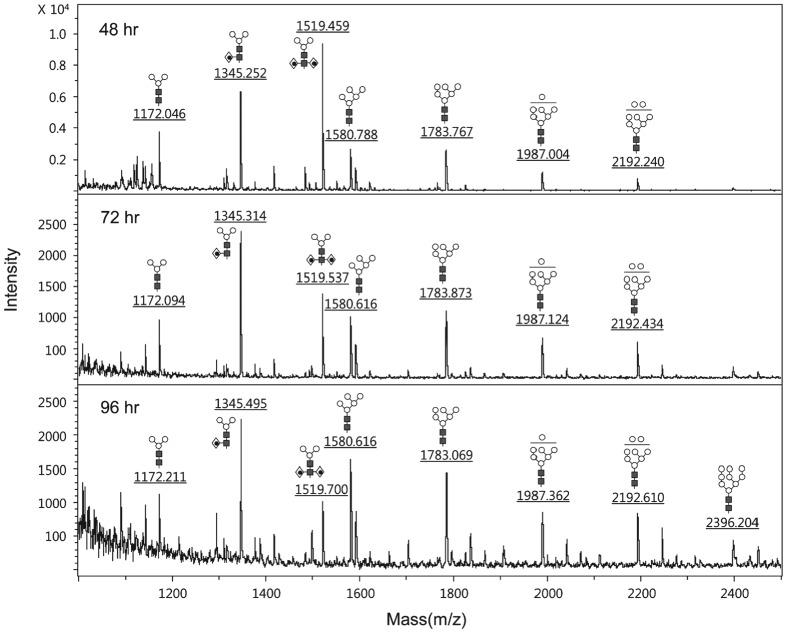
Characterization of the Glycan Structures of Glycoprotein GA733-Fc Expressed in a Baculovirus-Insect Cell System
- Pages: 139-149
- First Published: 05 January 2015
Hard Carbon-coated Natural Graphite Electrodes for High-Energy and Power Lithium-Ion Capacitors
- Pages: 150-155
- First Published: 05 January 2015
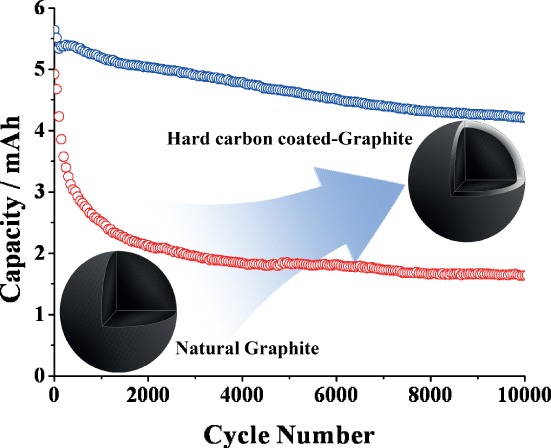
A hard carbon-coated natural graphite is proposed for use in high-power lithium-ion capacitors. By using polyacrylonitrile precursor, hard carbon is uniformly coated on the surface of natural graphite with the thickness of 20–30 nm. The coating layer on natural graphite is mainly responsible for the improved cycle life and excellent rate capability of LIC full cell.
Upconversion Photoluminescence Properties of KGd(WO4 )2:Ho3+/Yb3+ Phosphors Synthesized by Microwave-assisted Sol-Gel Method
- Pages: 156-161
- First Published: 05 January 2015
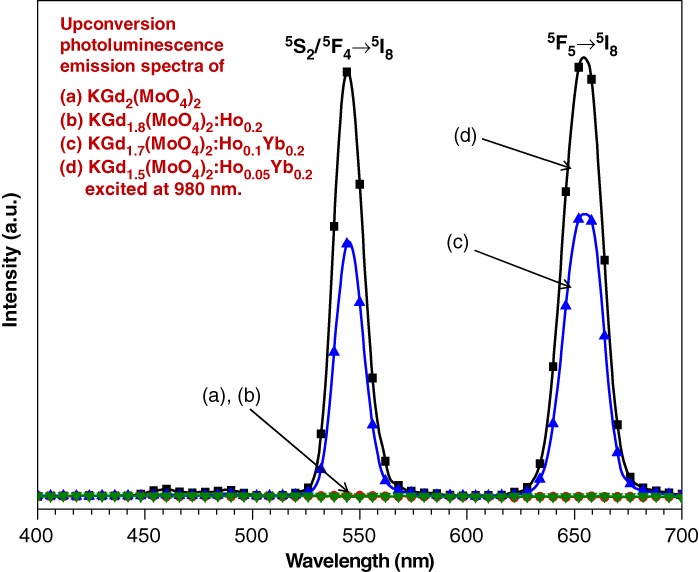
Under excitation at 980 nm, the UC intensities of KGd0.7(WO4)2:Ho0.1Yb0.2 and KGd0.5(WO4)2Ho0.05Yb0.45 particles exhibited yellow emissions based on strong 550- and 655-nm emission bands in the green and red regions, respectively, which in turn were assigned to the 4S2/5F4→5I8 and 5F5→5I8 transitions, respectively.
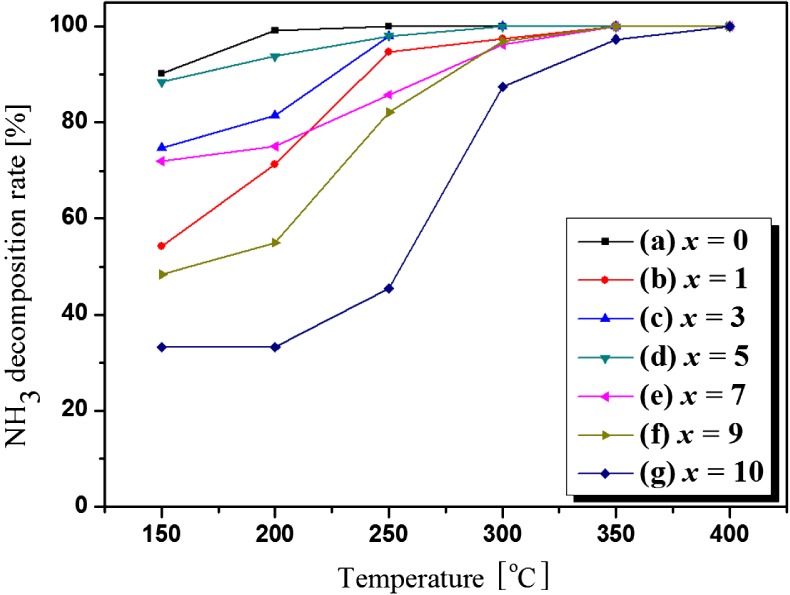
Preparation of Ag–Cu/Al2O3 Composite Catalyst for Ammonia Decomposition
- Pages: 162-167
- First Published: 05 January 2015
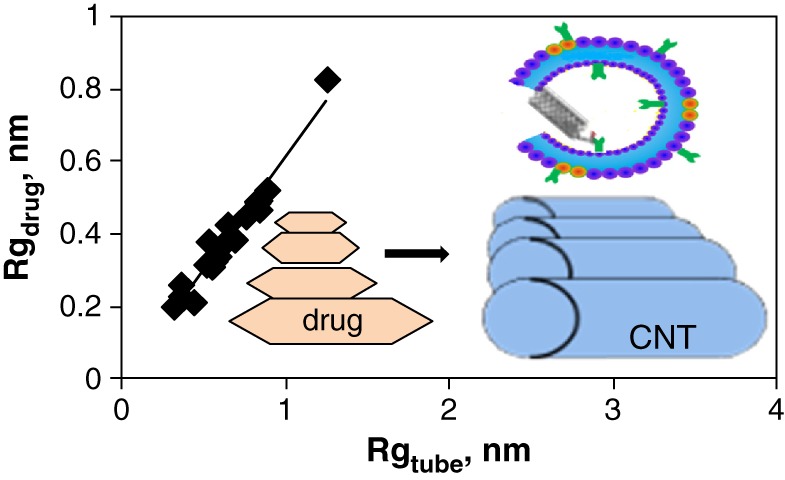
Correlation of Drug and Carbon Nanotube Size in Encapsulation and Free Energy Calculation: A Molecular Insight
- Pages: 168-179
- First Published: 05 January 2015
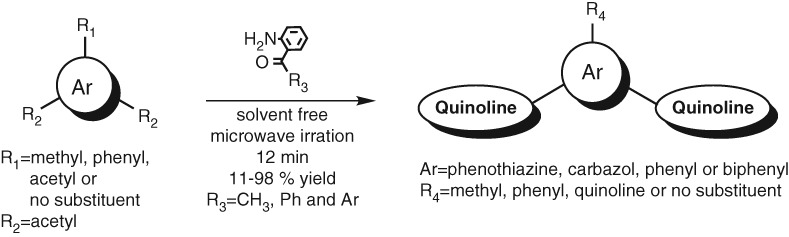
Environmentally Benign Synthesis of Symmetrically Substituted Oligoquinolines under Solvent-free Microwave Irradiation
- Pages: 180-182
- First Published: 05 January 2015
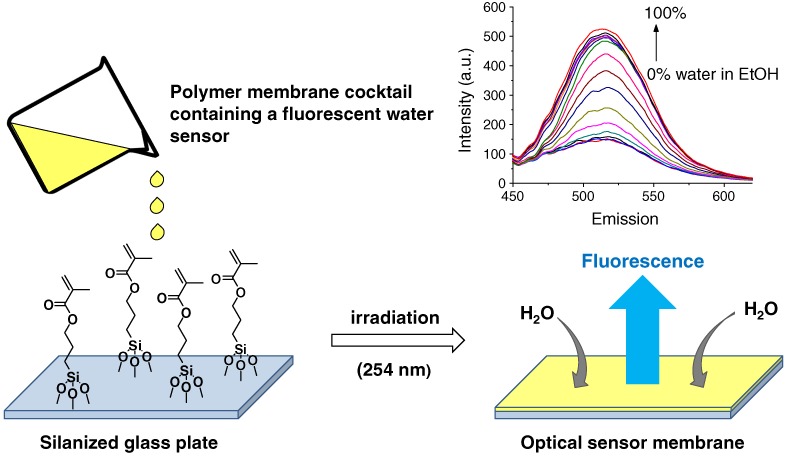
Optode Membrane for Detecting a Wide Range of Water Content in Organic Solvents
- Pages: 183-188
- First Published: 05 January 2015
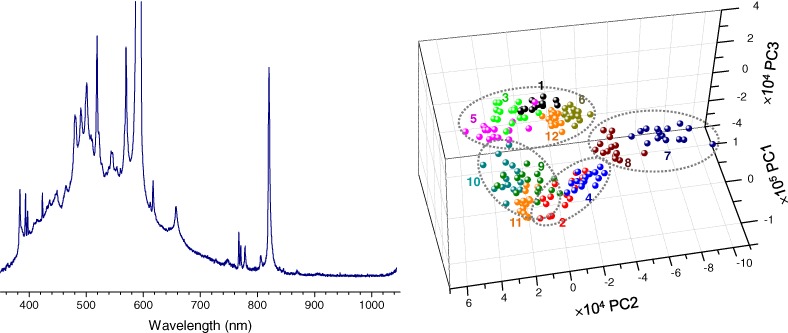
Feasibility of Rapid Classification of Edible Salts by a Compact Low-Cost Laser-induced Breakdown Spectroscopy Device
- Pages: 189-197
- First Published: 05 January 2015
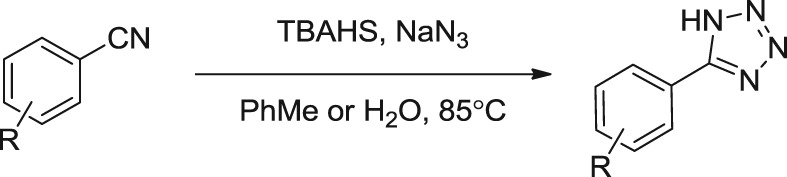
Facile Synthesis of 5-Substituted 1H-Tetrazoles Catalyzed by Tetrabutylammonium Hydrogen Sulfate in Water
- Pages: 198-202
- First Published: 05 January 2015
Synthesis of Pyrazolo[4,3-c]quinolines from Morita–Baylis–Hillman Adducts of 2-Bromobenzaldehydes
- Pages: 203-210
- First Published: 05 January 2015
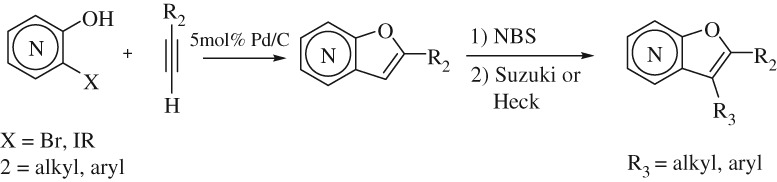
Copper- and Ligand-free Heteroannulation of o-Halohydroxypyridine with Terminal Alkynes Using Pd/C Catalyst: One-Pot Synthesis of 2-Substituted Furopyridines and their Functionalization
- Pages: 211-218
- First Published: 05 January 2015
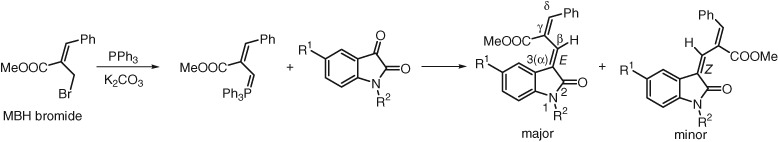
Synthesis of 3-(γ,δ-Disubstituted)allylidene-2-Oxindoles from Isatins by Wittig Reaction with Morita–Baylis–Hillman Bromides
- Pages: 219-225
- First Published: 05 January 2015
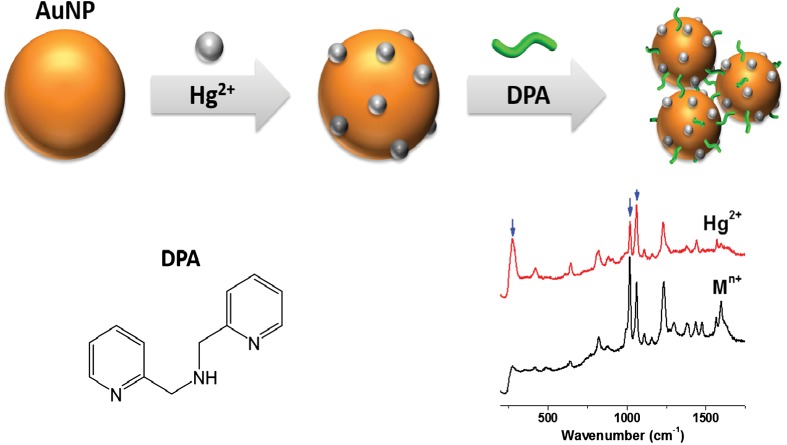
Raman Spectroscopy of Di-(2-picolyl)amine on Gold Nanoparticles for Hg(II) Detection
- Pages: 226-229
- First Published: 05 January 2015
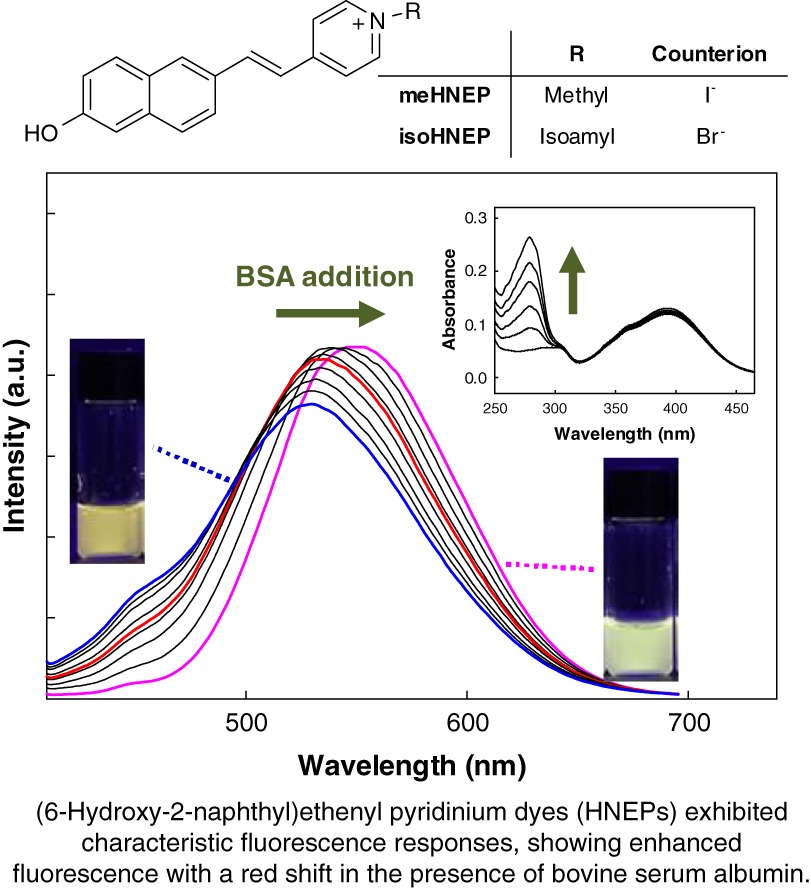
Characteristic Fluorescence Response of (6-Hydroxy-2-naphthyl)ethenyl Pyridinium Dyes with Bovine Serum Albumin
- Pages: 230-236
- First Published: 05 January 2015
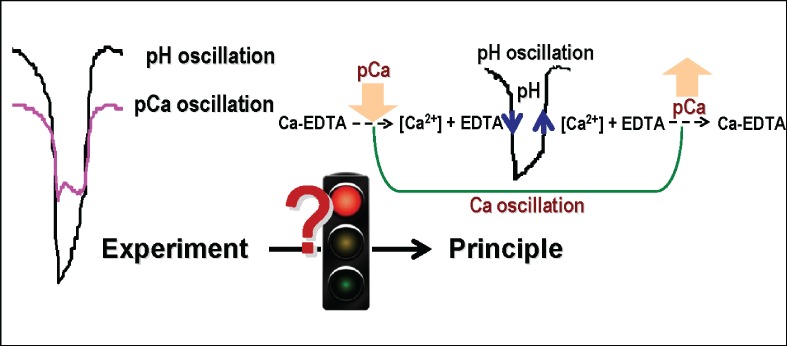
On pH and Ca2+ Oscillations Monitored by pH Electrode and Ca-ISE in Bromate–Sulfite–Ferrocyanide System Introduced Ca-EDTA
- Pages: 237-243
- First Published: 05 January 2015
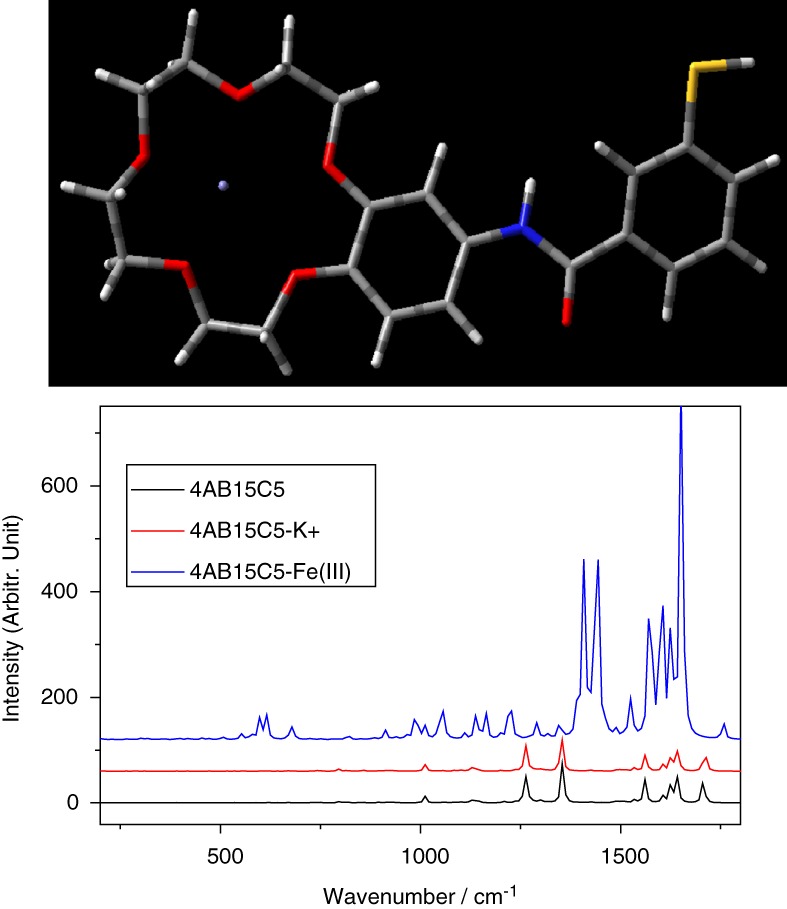
Gold Nanoparticle-based Surface-enhanced Raman Scattering Fe(III) Ion Sensor
- Pages: 244-249
- First Published: 05 January 2015
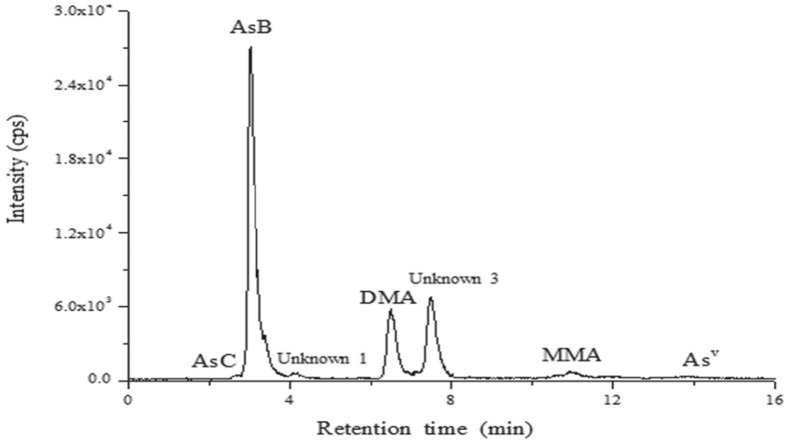
A Study on Arsenic Speciation in Korean Oyster Samples using Ion Chromatography Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry
- Pages: 250-257
- First Published: 05 January 2015
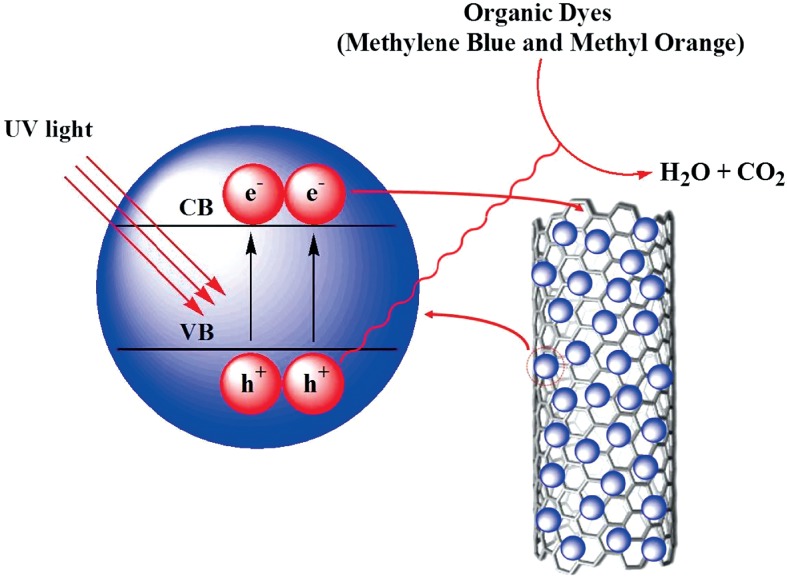
Preparation of Carbon-Nanotube-supported TiO2 for Enhanced Dye-degrading Photocatalytic Activity
- Pages: 258-264
- First Published: 05 January 2015
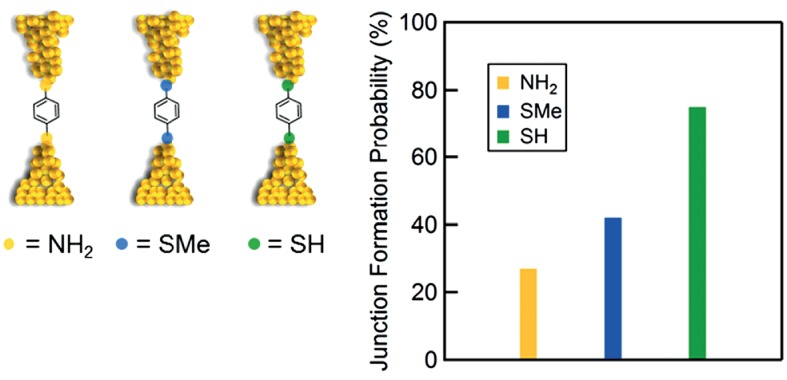
Linker-dependent Junction Formation Probability in Single-Molecule Junctions
- Pages: 265-268
- First Published: 05 January 2015
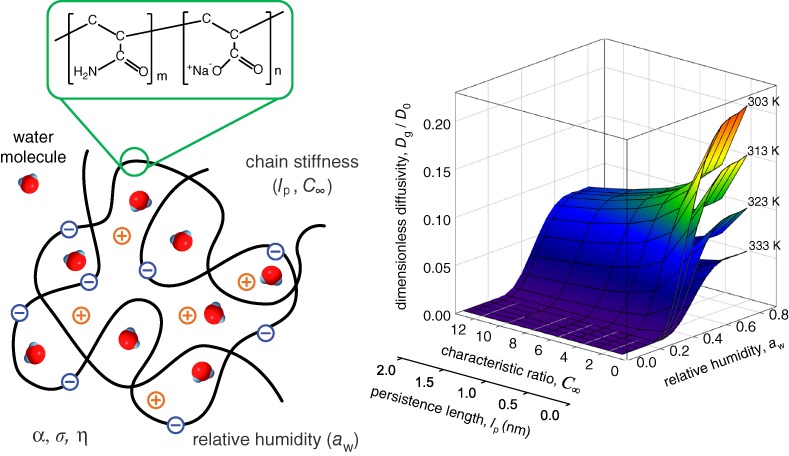
Water Sorption and Hindered Diffusion with Different Chain Stiffness of Superabsorbent Polymer
- Pages: 269-275
- First Published: 05 January 2015
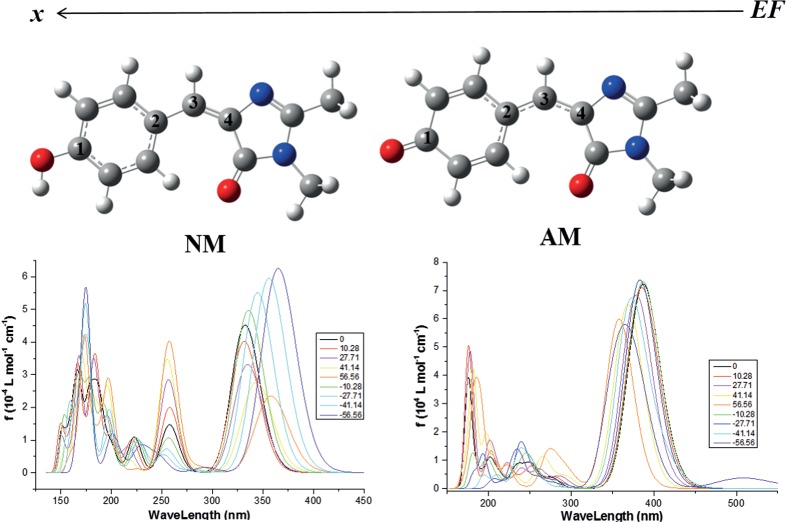
Electric Field Effect on trans-p-Hydroxybenzylideneimidazolidinone: A DFT Study and Implication to Green Fluorescent Protein
- Pages: 276-281
- First Published: 05 January 2015
Fine-Tuning the Emission Color of a Transparent Suspension of SrMoO4:Eu3+,Tb3+ Nanophosphors
- Pages: 282-286
- First Published: 05 January 2015
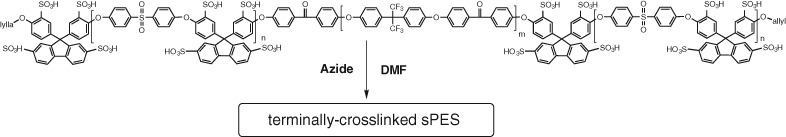
Terminal Crosslinking of Highly Sulfonated Poly(arylene ether sulfone) Block Copolymers: Synthesis and Properties as Polymer Electrolyte Membranes
- Pages: 287-294
- First Published: 05 January 2015
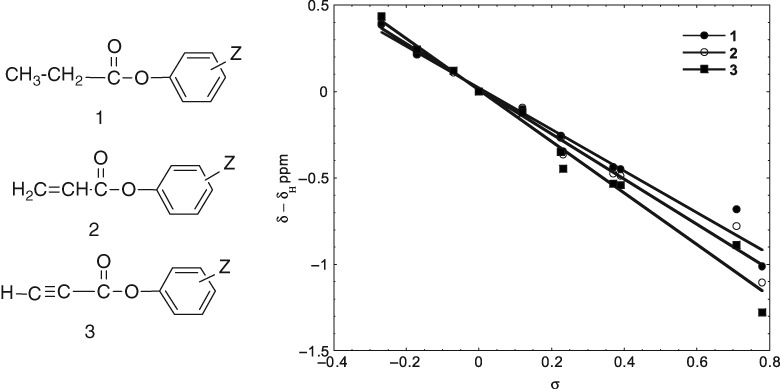
How Much Does the Hybridization of a Carbon Atom Affect the Transmission of the Substituent Effect on the Chemical Shift?
- Pages: 295-299
- First Published: 05 January 2015
Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitory Constituents from Selaginella tamariscina
- Pages: 300-304
- First Published: 05 January 2015
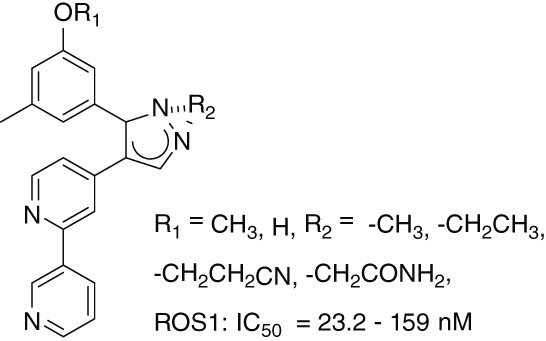
Optimization of Bipyridinyl Pyrazole Scaffolds via Design, Synthesis and Screening of a New Series of ROS1 Kinase-modulating Compounds
- Pages: 305-311
- First Published: 05 January 2015
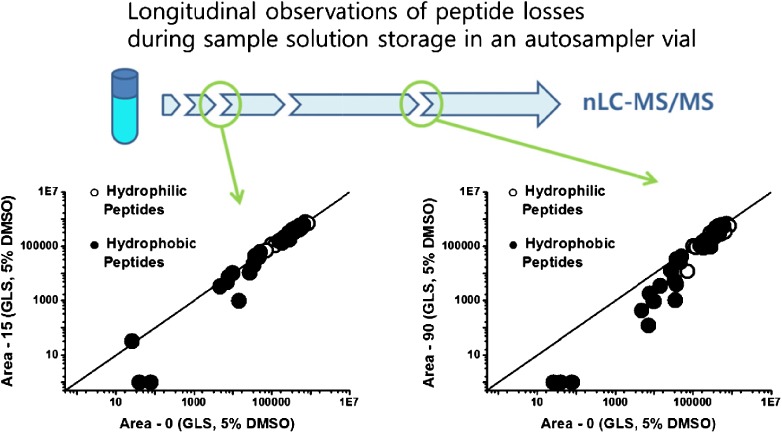
Longitudinal Assessment of Peptide Recoveries from a Sample Solution in an Autosampler Vial for Proteomics
- Pages: 312-321
- First Published: 05 January 2015
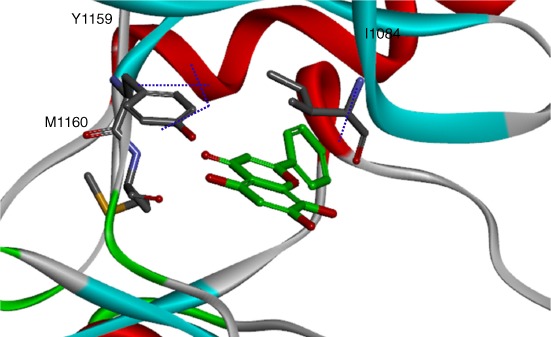
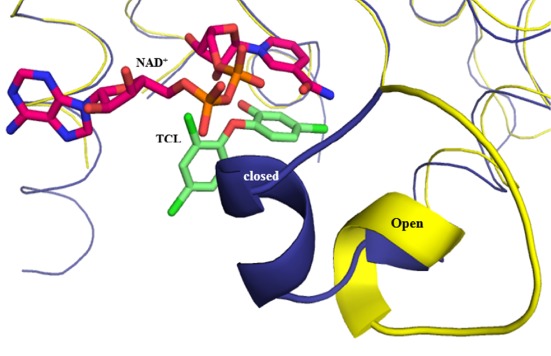
Crystal Structures of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Enoyl-ACP Reductase (FabI) in the Presence and Absence of NAD+ and Triclosan
- Pages: 322-326
- First Published: 05 January 2015
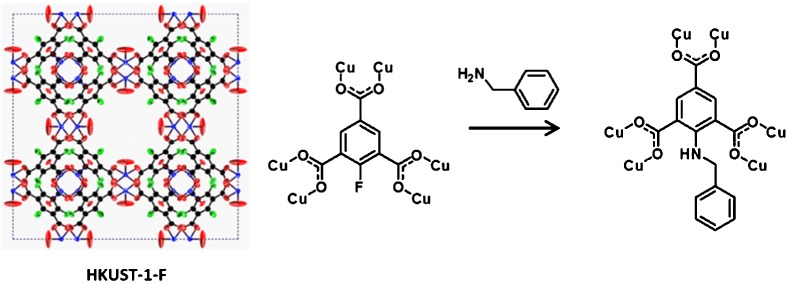
Chemical Property Change in a Metal-Organic Framework by Fluoro Functionality
- Pages: 327-332
- First Published: 05 January 2015
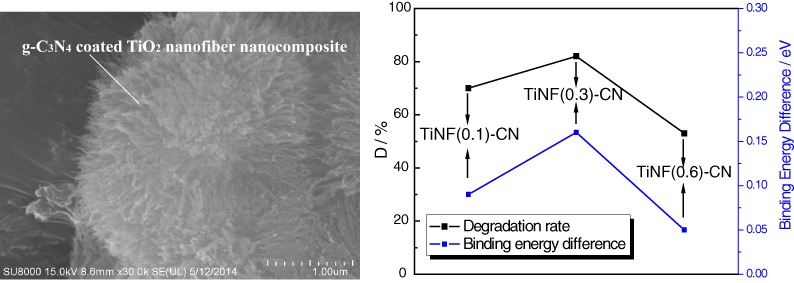
Simulated Solar Light Responsive Carbon Nitride/TiO2 Nanofiber Heterojunction Photocatalyst: Synthesis, Characterization, and Photocatalytic Performance
- Pages: 333-339
- First Published: 05 January 2015
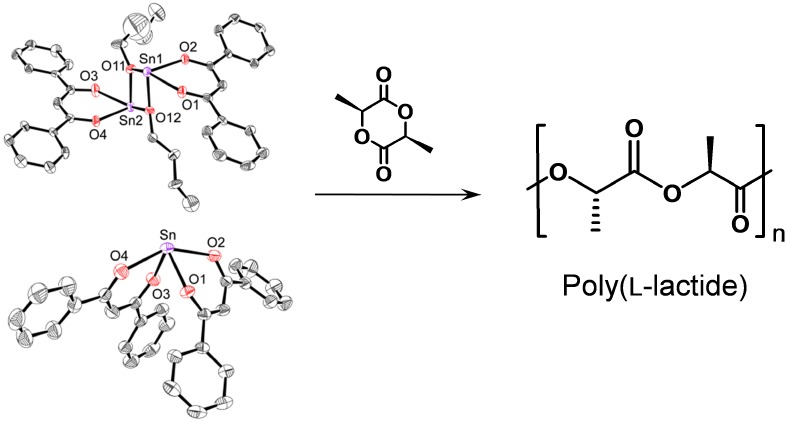
Bulk Polymerization of l-Lactide with Dibenzoylmethane Sn(II) Compounds
- Pages: 340-345
- First Published: 05 January 2015
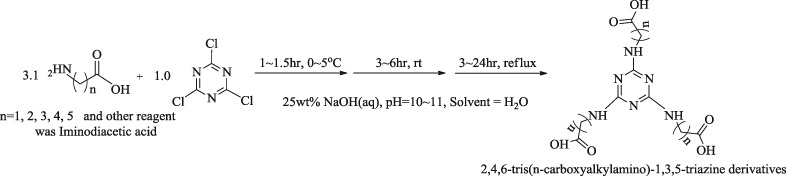
Effects of the Chain Length of Tris(carboxyalkylamino)triazine on Corrosion Inhibition Properties
- Pages: 346-355
- First Published: 05 January 2015
Notes
A New Triterpene Glycoside from the Stems of Akebia quinata
- Pages: 356-359
- First Published: 05 January 2015
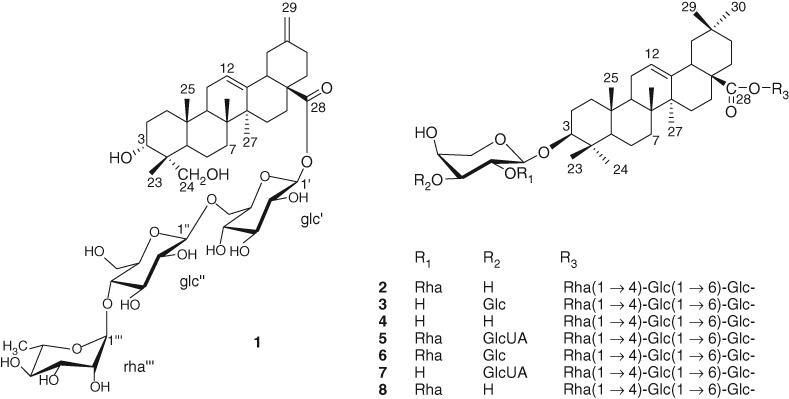
A new triterpene glycoside, named akeqintoside E, 3 αα,23αα-dihydroxy-30-norolean-12,20(29)-dien-28-oic acid 28-O-αα-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→4)-O-ββ-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→6)-O-ββ-D-glucopyranosyl ester (1), along with seven known compounds, akeboside Sth (2), begoniifolide A (3), akebia saponin PJ2 (4), 3ββ-[(O-GlcUA-(1–3)-O-[Rha-(1–2)]-Ara)oxy]olean-12-en-28-oic acid O-Rha-(1–4)-Glc-(1–6)-Glc ester (5), kalopanax saponin D (6), 3ββ-[(O-GlcUA-(1–3)-Ara)oxy]olean-12-en-28-oic acid O-Rha-(1–4)-Glc-(1–6)-Glc ester (7), and akebia saponin PJ3 (8), was isolated from Akebia quinata. The structures of the compounds were identified on the basis of 1D and 2D NMR, including 1H– 1H COSY, HSQC, HMBC, and NOESY spectroscopic analyses.
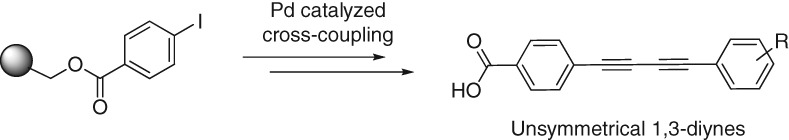
Efficient Synthesis of Unsymmetrical 1,3-Diynes Utilizing a Palladium-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling Reaction Without Homo-Coupling
- Pages: 360-362
- First Published: 19 December 2014
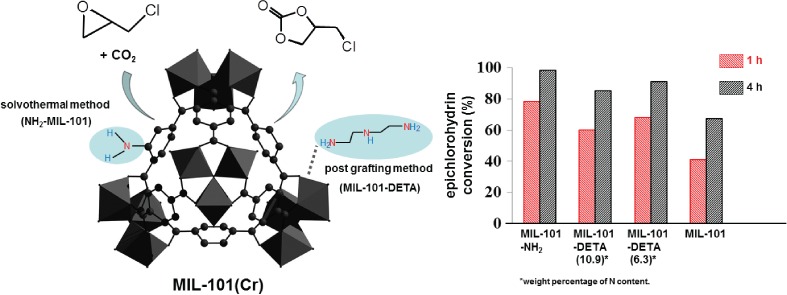
CO2 Cycloaddition of Epichlorohydrin over NH2-Functionalized MIL-101
- Pages: 363-366
- First Published: 05 January 2015
Tiliabisflavan A, a New Flavan-3-ol Dimer from Tilia amurensis with Cytotoxic and Anti-Inflammatory Effects
- Pages: 367-369
- First Published: 05 January 2015
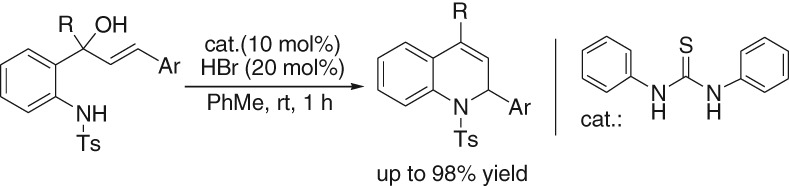
Thiourea-catalyzed Intramolecular Allylic Amination: Synthesis of Dihydroquinoline Derivatives
- Pages: 370-373
- First Published: 05 January 2015
Structural and Luminescent Properties of [N-benzyl-N-(2-pyridyl)methylamine]dichlorozinc(II): Dual Fluorescence of N-benzyl-N-(2-pyridyl)methylamine
- Pages: 374-377
- First Published: 05 January 2015
Direct Asymmetric Aldol Reactions Promoted by (1R, 3S, 4S)-2-Aza-bicyclo[2.2.1]heptane-3-carboxylic Acid as an Organocatalyst
- Pages: 378-380
- First Published: 05 January 2015
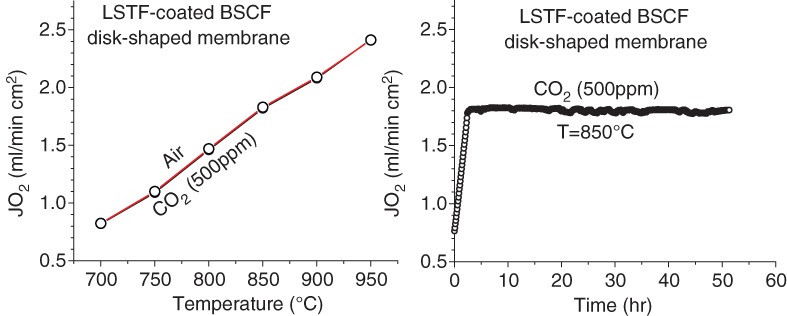
Oxygen Permeation Properties of La0.6Sr0.4Ti0.3Fe0.7O3–d-Coated Ba0.5Sr0.5Co0.8Fe0.2O3–d Disk-Shaped Membrane
- Pages: 381-383
- First Published: 05 January 2015
Chemical Constituents with Anti-allergic Activity from the Barks of Cinnamomum cambodianum Collected in Cambodia
- Pages: 384-387
- First Published: 05 January 2015
Diastereoselective Alkyl Radical Addition to the C═N Bond in Aqueous Media for the Synthesis of Enantio-enriched Chiral Alkylamines
- Pages: 388-390
- First Published: 05 January 2015
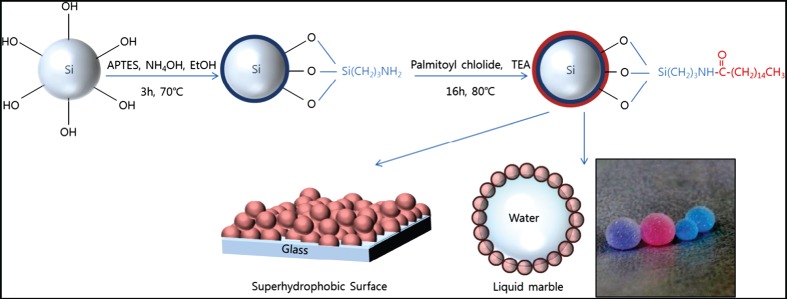
Fabrication of Superhydrophobic Silica Nanoparticles and Nanocomposite Coating on Glass Surfaces
- Pages: 391-394
- First Published: 05 January 2015
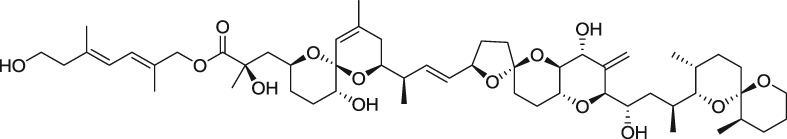
A New Diol Ester Derivative of Dinophysistoxin-1 from Cultures of Prorocentrum lima Collected in South Korea
- Pages: 395-398
- First Published: 05 January 2015
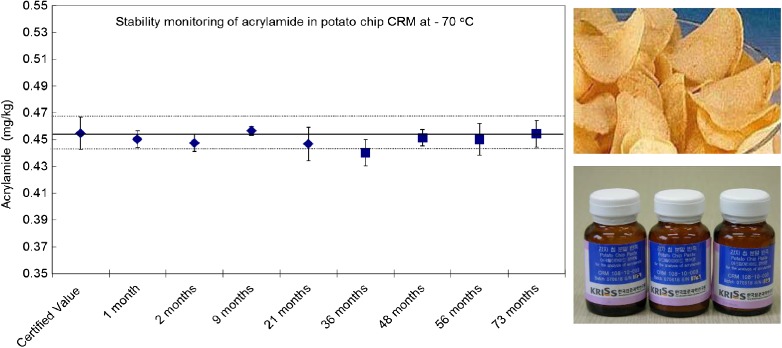
Stability Monitoring of Acrylamide in Potato Chip Certified Reference Material
- Pages: 399-401
- First Published: 05 January 2015
c-Met and ALK Inhibitory Constituents from Scutellaria baicalensis
- Pages: 402-405
- First Published: 05 January 2015
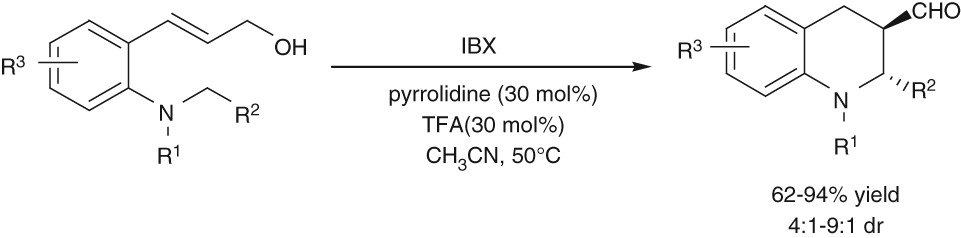
Synthesis of Tetrahydroquinoline Derivatives via Oxidation and 1,5-Hydride Transfer/Cyclization Cascade
- Pages: 406-409
- First Published: 05 January 2015
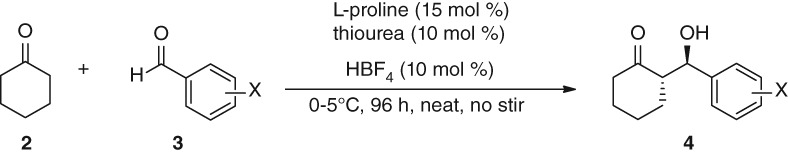
Asymmetric Aldol Reaction Catalyzed by l-Proline and Achiral Thiourea Fluoroboric Acid Salt
- Pages: 410-412
- First Published: 05 January 2015
Bis-styrylnaphthalene and Bis-styrylnaphthyridine Derivatives with High Binding Affinity to β-Amyloid Fibrils
- Pages: 413-416
- First Published: 05 January 2015
One-Pot Synthesis of Functionalized 2,3-Disubstituted Indolines via K2CO3-Promoted Cascade Michael/Aza-Cyclization Reactions
- Pages: 417-420
- First Published: 05 January 2015
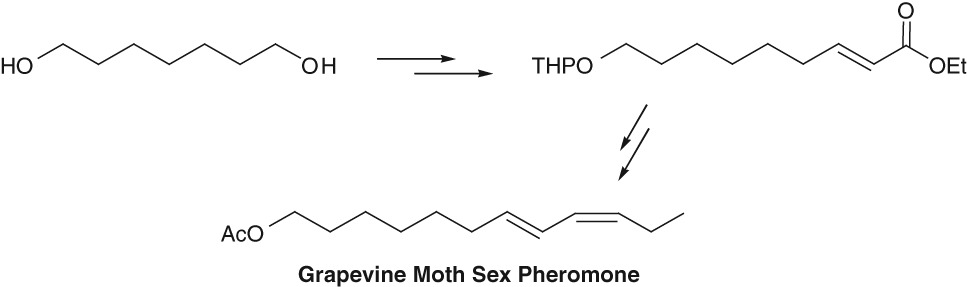
Economical Synthesis of Grapevine Moth Sex Pheromone
- Pages: 421-423
- First Published: 05 January 2015
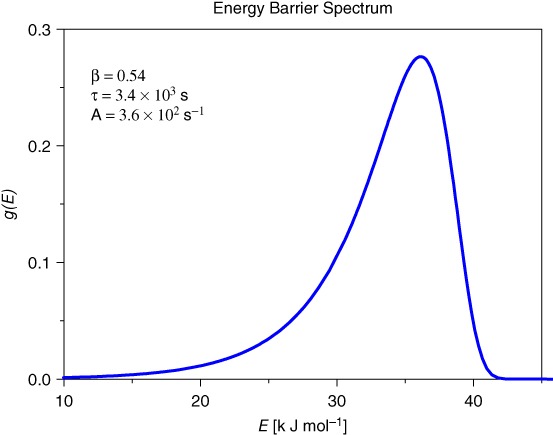
Stretched Exponential Change of Magnetic Weight of Magnetite Ferrofluid: Distribution of Energy Barrier for Agglomeration of Nanoparticles
- Pages: 424-426
- First Published: 05 January 2015
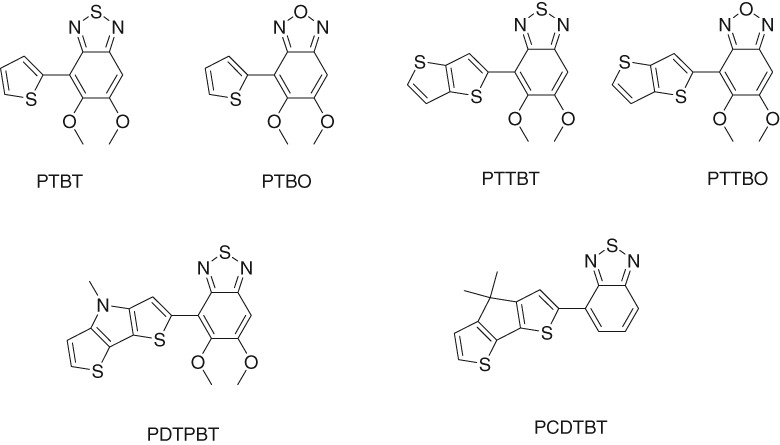
Density Functional Theoretical and Time-dependent Density Functional Theoretical Study on Thiophene–Benzothiadiazole-based Polymers
- Pages: 427-430
- First Published: 05 January 2015
Caspase-mediated Apoptotic Effects of Diol-type Ginseng Sapogenins on Human Hepatoma Cell Lines
- Pages: 431-434
- First Published: 05 January 2015
Solid-phase Synthesis of Combinatorial 2,4-Disubstituted-1,3,5-Triazine via Amine Nucleophilic Reaction
- Pages: 435-438
- First Published: 05 January 2015
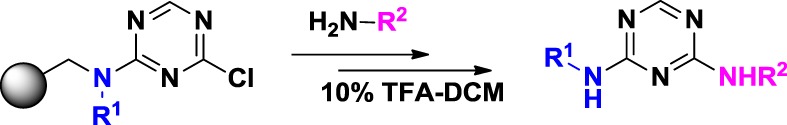
We report a solid-phase synthesis of 2,4-diamino-1,3,5-triazines, starting from 2,4-dichloro-1,3,5-triazine captured by resin-bound amines followed by amination and acidic mild cleavage. The derivatives of 22 diamino-1,3,5-triazine compounds were prepared in high purity without extensive reaction conditions.






![mPW1PW91-Calculated Structures, IR Spectra, and Frontier Orbitals of Benzoylmethoxythiacalix[4]arene Complexed with Alkali Metal Ions](/cms/asset/7e193d57-4c22-4cfe-9051-71464c8b1aa9/bkcs10003-toc-0001-m.jpg)
![Synthesis of Pyrazolo[4,3-c]quinolines from Morita–Baylis–Hillman Adducts of 2-Bromobenzaldehydes](/cms/asset/b7a7b9e9-8238-4123-9054-66911c42d1ad/bkcs10050-toc-0001-m.jpg)

![Structural and Luminescent Properties of [N-benzyl-N-(2-pyridyl)methylamine]dichlorozinc(II): Dual Fluorescence of N-benzyl-N-(2-pyridyl)methylamine](/cms/asset/20907f2e-5320-4820-beee-d0488ccae47e/bkcs10015-toc-0001-m.jpg)
![Direct Asymmetric Aldol Reactions Promoted by (1R, 3S, 4S)-2-Aza-bicyclo[2.2.1]heptane-3-carboxylic Acid as an Organocatalyst](/cms/asset/daa12a56-a9fd-4bb5-8b9e-282320c4c675/bkcs10018-toc-0001-m.jpg)