Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Accelerated Publication
High rate (~7 nm/s), atmospheric pressure deposition of ZnO front electrode for Cu(In,Ga)Se2 thin-film solar cells with efficiency beyond 15%
- Pages: 1559-1566
- First Published: 07 October 2013
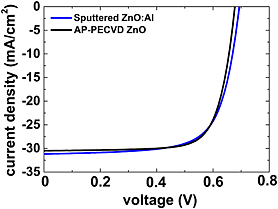
Undoped zinc oxide (ZnO) has been grown by plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition at atmospheric pressure. After post-deposition exposure to near-ultraviolet light, a low value of resistance (15 Ω/sq) is achieved in films that are highly transparent (90 %) in the visible range. ZnO is used as front electrode in Cu(InGa)Se2 solar cells achieving an efficiency of 15.4%, similar to reference cells with a sputtered Al:ZnO electrode.
Research Articles
Geometrical optimization and contact configuration in radial pn junction silicon nanorod and microrod solar cells
- Pages: 1567-1579
- First Published: 13 June 2012
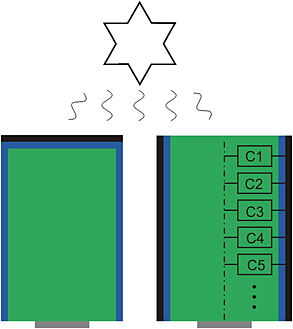
Computer-based simulations were performed on radial pn junction silicon nanorod and microrod solar cells to find optimized geometric dimensions and explore the effects of different types of contact configurations. A top contact configuration rendered superior to a wrapped contact configuration within the chosen set of material parameters. Maximization of cell efficiency assuming Lambert–Beerian absorption led to optimized rod radii in the 1-μm range and to optimized rod lengths in the 100-μm range for top contact configuration.
CdTe/CdS thin film solar cells grown in substrate configuration
- Pages: 1580-1586
- First Published: 13 June 2012
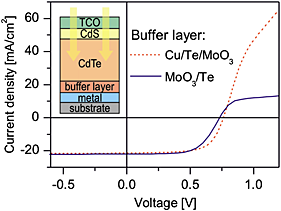
In this work, CdTe/CdS solar cells in substrate configuration were developed, and the results on different combinations of back contact materials are presented. A Cu-containing back contact buffer layer of MoO3, Te, and Cu leads to remarkably high VOC and fill factor of 768 mV and 68.6%, respectively, yielding 11.3% conversion efficiency. With a Cu-free MoO3/Te buffer material, a VOC of 733 mV, a fill factor of 62.3%, and an efficiency of 10.0% efficiency could be achieved.
The effect of Zn1−xSnxOy buffer layer thickness in 18.0% efficient Cd-free Cu(In,Ga)Se2 solar cells
- Pages: 1588-1597
- First Published: 10 July 2012

The influence of the thickness of atomic layer deposited Zn1-xSnxOy buffer layers and the presence of an intrinsic ZnO layer on the performance of Cu(In,Ga)Se2 solar cells are investigated. Both the open circuit voltage and the fill factor values are found to be thickness dependent, where a highest conversion efficiency of 18.0 % is obtained for a cell with a Zn1-xSnxOy layer thickness of approximately 13 nm.
Validation of energy prediction method for a concentrator photovoltaic module in Toyohashi Japan
- Pages: 1598-1610
- First Published: 20 June 2012
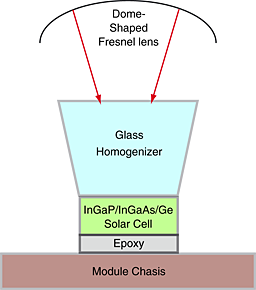
The behaviour of a 20-cell InGaP/In0.01GaAs/Ge multi-junction concentrator system was simulated in 5-min intervals over an entire year with agreement within 2% between measured and modelled annual energy yields. Air mass, aerosol optical depth and precipitable water have been identified as the atmospheric parameters with the largest impact on system efficiency.
The wind chill temperature effect on a large-scale PV plant—an exergy approach
- Pages: 1611-1624
- First Published: 18 June 2013
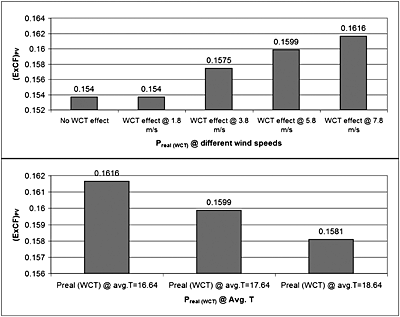
In this paper, a detailed exergetic analysis based on the variation of meteorological parameters was performed for a solar power generation system. The air psychrometric analysis, under this case study, showed that air density varies from site to site and monthly as well (1.152–1.228 kg/m3), affecting the energy productivity. It was found that for the proposed PV park, production is 3.2% higher compared with what would happen if this parameter was neglected.
Fabrication of grid type dye sensitized solar modules with 7% conversion efficiency by utilizing commercially available materials
- Pages: 1625-1633
- First Published: 22 June 2012
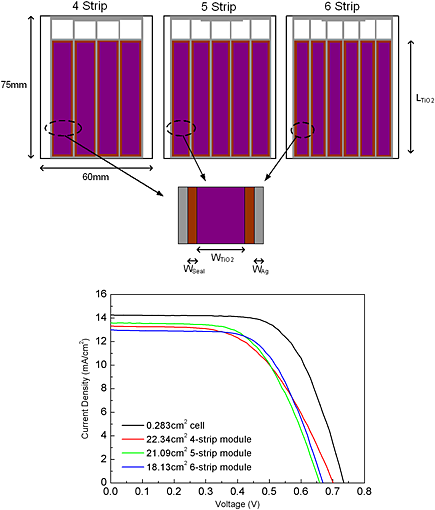
A process to fabricate a parallel connection dye-sensitized solar cell (DSSC) module has been developed using commercially available materials and screen printed silver grid. The process is not only simple but also easy to manipulate and therefore facilitates researchers in evaluating new materials in a module platform. By changing the design of the silver grid pattern, it was found that the performance of DSSC modules can be controlled, and a 7% conversion efficiency can be reached.
Short Communications
Comparing lifetime and photoluminescence imaging pattern recognition methodologies for predicting solar cell results based on as-cut wafer properties
- Pages: 1634-1639
- First Published: 05 July 2012
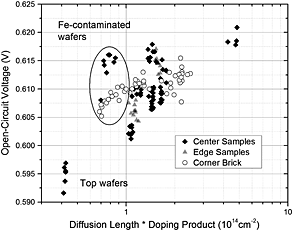
Wafer quality is extremely important in determining yield and efficiency of solar cells. Ideally, this wafer quality should be determined for incoming wafers before solar cell fabrication based on the electronic quality of the wafers. This paper compares results from quasi-steady-state photoconductance lifetime measurements with photoluminescence (PL) imaging pattern recognition. A detailed physical picture is presented here that reconciles contradictions between previous results. The trends in voltage prediction based on measured lifetime, doping, and PL-determined dislocation densities are shown.
Impact of laterally non-uniform carrier lifetime on photoconductance-based lifetime measurements with self-consistent calibration
- Pages: 1640-1644
- First Published: 21 June 2012
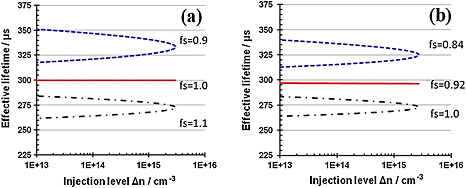
The impact of lateral nonuniform carrier lifetime on the determination of the lifetime from photoconductance-based measurements, based on the self-consistent method, is investigated. It is shown that the method can result in an overestimation of the mean lifetime, with the magnitude of the error mainly dependent on the distribution of the effective lifetime across the area sensed by the photoconductance coil. The error can be eliminated through independent measurement of the sample optical properties. Experimental measurements confirm the model predictions.
InGaP/GaAs/Ge triple-junction solar cells with ZnO nanowires
- Pages: 1645-1652
- First Published: 04 December 2012
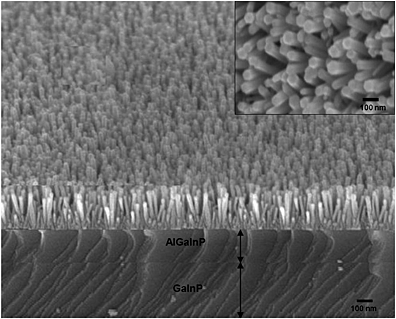
In this research, it was found that ZnO nanowire (NW) enhances the conversion efficiency by 6.92%, as compared with the conventional triple-junction (TJ) solar cell. In contrast, SiNx and TiO2/Al2O3 antireflection coatings only enhance the conversion efficiency by 3.72% and 6.46% increase, respectively. Compared with the unencapsulated ZnO NW TJ cell, it was found that Jsc of the encapsulated TJ cell with ZnO NW increased by 0.41 mA/cm2. The encapsulated results suggested that cell with ZnO NW could provide the best electrical performances.
Applications
Realization of high performance large area Z-series-interconnected opaque dye solar cell modules
- Pages: 1653-1658
- First Published: 20 June 2012
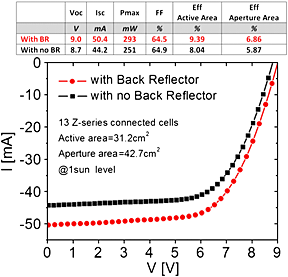
We have designed and fabricated dye solar cell (DSC) Z-type modules with optimized geometries and materials. Through optimization of the layout of the modules using PSPICE simulations, the multilayer combination and treatments of the TiO2 active layers, and the fabrication processes, a conversion efficiency of 6.9% on the 43-cm2 aperture area and 9.4% on the active area was achieved. This result confirms that an effective scale-up of opaque high-performance Z-series-connected DSC modules, all realized with commercially available materials, can be accomplished.
Initial field performance of a hybrid CPV-T microconcentrator system
- Pages: 1659-1671
- First Published: 25 May 2012

The first prototype of the hybrid CPV-T ANU-Chromasun micro-concentrator (MCT) has been installed at The Australian National University (ANU, Canberra, Australia). The results of electrical and thermal performance of the MCT system, including instantaneous and full-day monitoring, show that combined efficiency of the system can exceed 70%. Over the span of a day, the average electrical efficiency was 8% and the average thermal efficiency was 50%.
Analysis of short circuit current gains by an anti-reflective textured cover on silicon thin film solar cells
- Pages: 1672-1681
- First Published: 28 July 2012
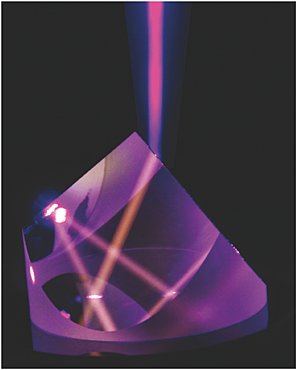
A texture foil attached to the substrate glass of solar cells surpasses the maximum efficiency gains achievable by anti-reflective coatings. The photograph shows the substructure of the scattering foil on top of a reflecting silicon wafer. Besides the anti-reflex effect, the texture enhances the internal light-trapping.
Literature Survey
Photovoltaics literature survey (No. 106)
- Pages: 1682-1684
- First Published: 25 November 2013




