Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLES
A biophysical and computational study unraveling the molecular interaction mechanism of a new Janus kinase inhibitor Tofacitinib with bovine serum albumin
- First Published: 09 December 2016
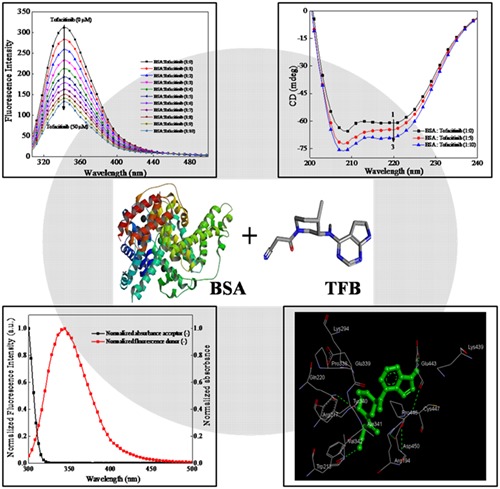
Tofacitinib caused fluorescence quenching of BSA with binding constant of approximately 104·M−1. Tofacitinib-BSA interaction was spontaneous and exothermic. Increase in helical content of BSA was observed in the presence of Tofacitinib. Tofacitinib altered tertiary structure and decreased hydrodynamic radii of BSA. The BSA-Tofacitinib interaction was by hydrophobic and hydrogen bonding at site II.
Discovery of novel potent nuclear factor kappa-B inhibitors (IKK-β) via extensive ligand-based modeling and virtual screening
- First Published: 23 December 2016
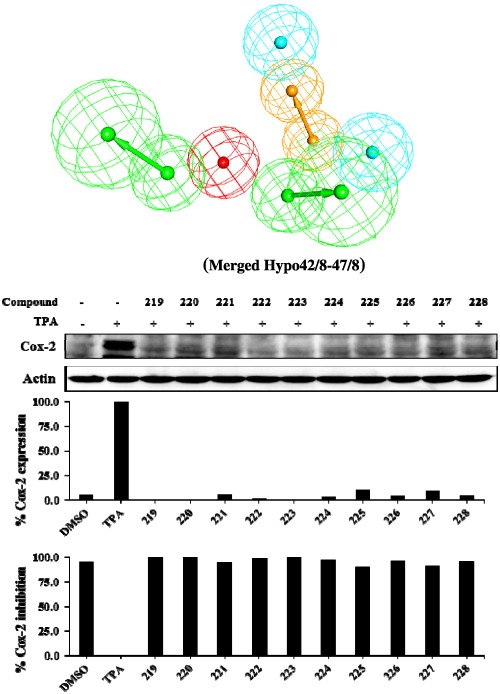
Inhibitor kappa-B kinase-beta (IKK-β) controls the activation of nuclear transcription factor kappa-B and has been linked to inflammation and cancer. The merged pharmacophore and the associated quantitative structure-activity relationship equations were applied to screen the National Cancer Institute list of compounds. Ten hits were found to exhibit potent anti–IKK-β bioactivity, of which one illustrates IC50 of 11.0nM.
Comparative study of the binding of 3 flavonoids to the fat mass and obesity-associated protein by spectroscopy and molecular modeling
- First Published: 06 January 2017
SPECIAL ISSUE ARTICLES
Direct mapping of melanoma cell - endothelial cell interactions
- First Published: 23 December 2016
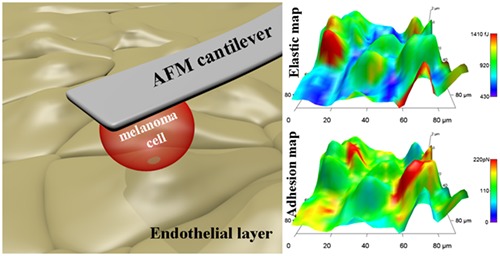
The key step in the process of brain metastasis formation is the establishment of firm adhesion between the cancer cell and the cerebral endothelial layer. Direct mapping of a confluent layer of cerebral endothelial cells is reported with a melanoma cell as a probe. The reconstructed topography-based maps reveal elastic, plastic, and adhesive heterogeneity of the endothelial layer but not directly linking these parameters.
Characterizing the effect of polymyxin B antibiotics to lipopolysaccharide on Escherichia coli surface using atomic force microscopy
- First Published: 05 January 2017
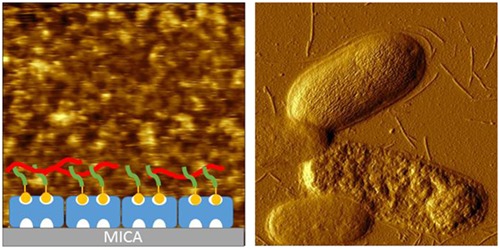
The effects of antibiotic polymyxin B (PMB) to lipopolysaccharides on gram-negative bacterial outer membranes were investigated using atomic force microscopy and single molecular force spectroscopy. Specific binding forces between lipopolysaccharides and PMB deduced energetic and kinetic parameters of the interaction. Experiments on bacterial cells revealed that PMB exposure enhances the roughness of the outer bacterial membrane, finally leading to membrane damage.
SPECIAL ISSUE REVIEW
Phenotypic assays for analyses of pluripotent stem cell–derived cardiomyocytes
- First Published: 20 December 2016
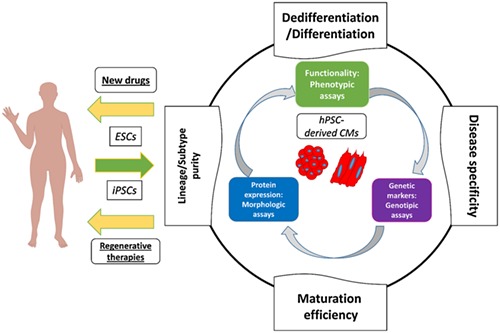
Human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes allow the characterization of realistic cellular models, cellular mass production for cardiac regenerative therapies, and novel and faster drug development. Once extracted from human blastocyst or dedifferentiated from somatic cells, stem cell clones can be differentiated into genetically stable, ultrastructured, and functional cardiomyocytes. The investigative methods (genotypic, morphologic, and phenotypic) are equally important, although phenotypic assays provide the definitive characterization of the obtained cells, variable in differentiation efficiency, disease specificity, maturation level, and lineage purity.