Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Throughput performance of a non-linear energy-harvesting cognitive radio-enabled device-to-device network
- First Published: 21 February 2022
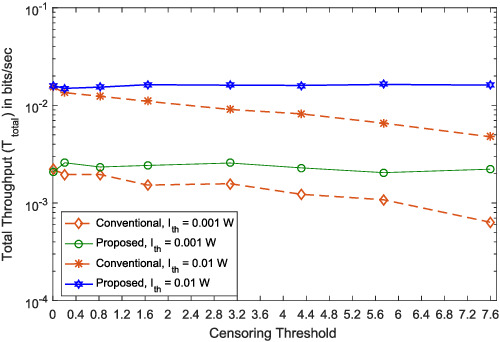
The performance of a non-linear energy-harvesting D2D communication underlaying a cellular network is studied under a channel quality constraint. The D2D devices are enabled with CR technology and equipped with an energy-harvesting circuit that harvests from power transfer units and cellular users (CUs). A cellular user channel is shared in hybrid mode by a D2D user. An algorithm is proposed based on threshold-based censoring to maximize the throughput.
A dual-band circular patch antenna using hexagon-shaped slots
- First Published: 16 February 2022
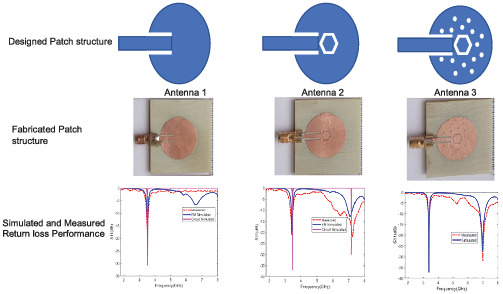
A novel hexagon-shaped slot was preferred to achieve dual-band performance in the circular patch antenna. The simulation level performance of the antenna is verified using the Advanced Design System 2019 tool. An FR4 material with a height of 1.6 mm is selected as a substrate for the patch antennas. The return loss and radiation pattern behaviour of the patch antennas are measured using a network analyser and an anechoic chamber. The fabricated prototype achieves dual-band performance at 3.47 and 6.96 GHz. Simulated and measured results show that the proposed hexagonal-shaped slot in the circular patch provides a dual-band behaviour.
Fully cooperative and distributed focal underdetermined system solver compressive sensing recovery algorithm for wireless sensor networks
- First Published: 16 February 2022
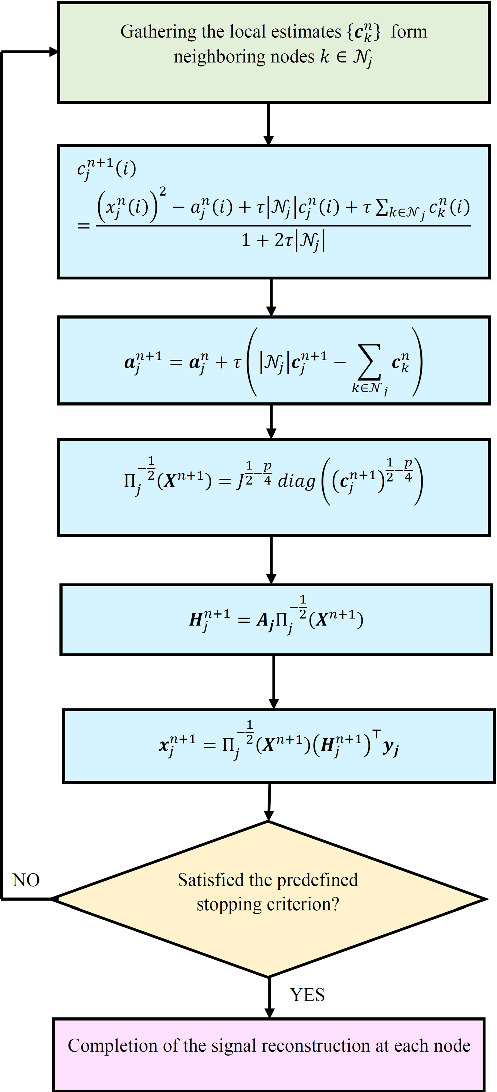
In this study, we proposed a distributed and cooperative algorithm based on the focal underdetermined system solver (FOCUSS) for compressive sensing signal reconstruction in wireless sensor networks (WSNs). In the proposed approach, the structure of cooperation between neighboring nodes is achieved by minimizing a Lagrange function. The proposed algorithm is quite distributed and implemented by one-hop communication between the neighboring node without collaborating any fusion center (FC). Furthermore, in the proposed method, the nodes exchange only an intermediate estimated vector in each iteration, so their estimated signals and measurements are private. The overall operation of the proposed algorithm can be described as follows. The aim of each node j is to recover the s-sparse vector xj using yj and Aj, where . At each iteration, the node j receives the local estimates form its neighbors and updates . Then this node updates using and (i). Subsequently, is used to obtain the new estimate of which is used in updating of . Finally, the current estimate of the sparse vector is calculated. This iteration is concluded after node j broadcasts to its neighbors.
Generic MGF-based tight approximation for the error rate analysis
- First Published: 20 February 2022
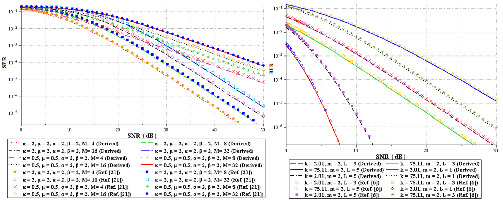
Moment generating function-based approach for error rate analysis fails in the case of several modulation schemes with constellation size (M) due to the computational complexity of the involved integration. This manuscript overcomes the problem by providing generic MGF-based tight approximation for the error rate analysis with any constellation size. Various results from different literatures have been reproduced to prove the validity and usefulness of the proposed approach.
Low power hardware design and its mathematical modeling for fast-exact geolocalization system in wireless networks
- First Published: 22 February 2022
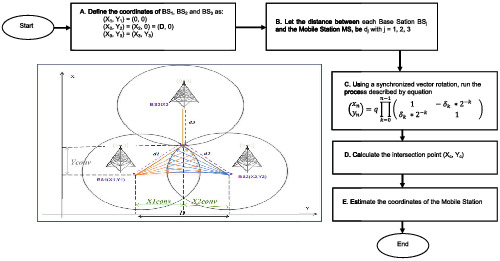
Hardware circuit for exact geolocalization in wireless network is designed. Proposed localization algorithm is based on Coordinate Rotation Digital Computer-Time of Arrival (CORDIC-ToA) combination. Current proposal is governed by the hardware implementation in order to alleviate its cost, which most of the localization systems suffer from.
A hybrid Harrison Hawk optimization based on differential evolution for the node localization problem in IoT networks
- First Published: 24 February 2022
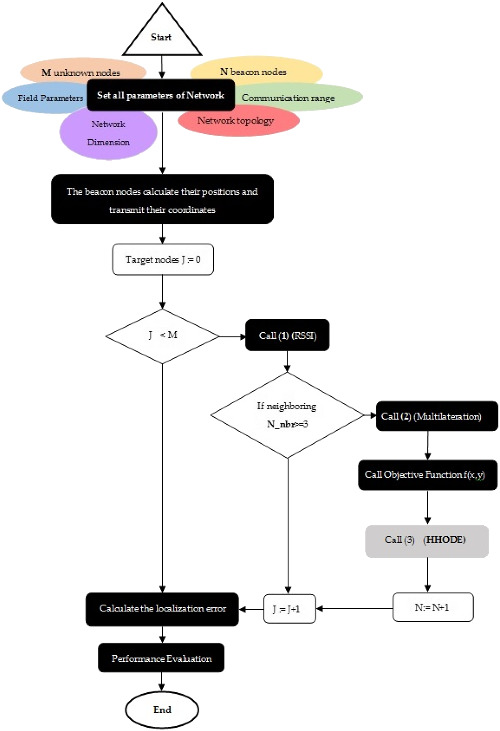
The paper presents a node localization optimization scheme using a hybrid bio-inspired algorithm called Harris Hawks Optimization Algorithm based on differential evolution (HHODE). It is shown that the proposed paradigm is capable of increasing the localization rate, as well as minimizing the computing cost. Developing this algorithm on a huge IoT network with millions of nodes reveals a particularly high performance. To assess this, several experiments in different scenarios are carried out in a decentralized environment of IoT network. Finally, a comparative study is carried out also to some recent bio-inspired algorithms.
An asymmetric CPW-fed modified bow tie-shaped antenna with parasitic elements for ultra-wideband applications
- First Published: 18 February 2022
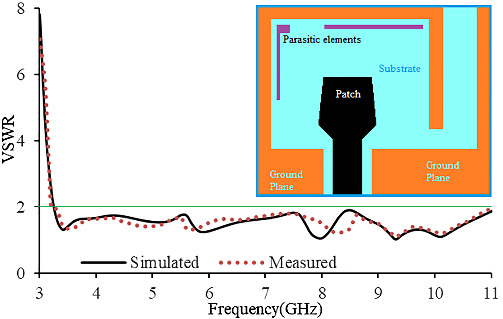
This paper presents a modified bow tie-shaped UWB antenna that comprises an asymmetric CPW-fed patch and two ground planes with a pair of parasitic elements. Mathematical analysis of the antenna demonstrates that the patch, ground plane, and parasitic elements are coupled strongly, and the designed antenna exhibits multiple resonance modes. With an overall size of 0.21λ×0.26λ, the fabricated antenna achieved an operating band of 3.2 – 11.0 GHz, realized a peak gain of 4.32 dBi, and maximum radiation efficiency of 87.3%.
A tri-band triangular lamp post shaped quad port MIMO antenna
- First Published: 21 February 2022
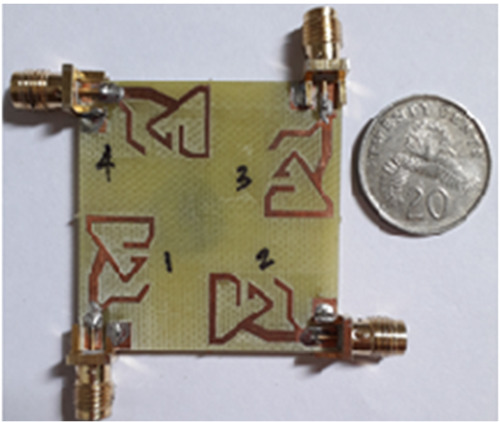
In this article, a novel and compact multiband quad port asymmetric coplanar strip-fed triangular lamp post shaped printed multiple-input and multiple-output (MIMO) antenna has been presented. The proposed MIMO antenna is designed and developed on a FR-4 (εr = 4.4) dielectric (40 × 40 × 1.6) mm3. The proposed MIMO antenna utilizes the pattern diversity technique to obtain the desired isolation among closely spaced radiators. Simulated and measured results indicate that |S11| of proposed lamp post shaped MIMO antenna array < −10 dB, that assures the operation in three frequency bands, namely, (2.27–2.42), (3.38–3.62), and (4.5–6.23) GHz, which are the operating bands of WiBro, Bluetooth, WiMAX, and WLAN/WiMAX, respectively. A peak radiation gain of 5.1 dBi is observed alongside with a maximal radiation efficiency close to 92% in operating band for the proposed MIMO antenna. A minimal isolation of −18 dB between the antenna elements has been observed in all three operating bands, which is necessary for improved performance to achieve high data transfer rates. Performance critical diversity characteristics such as DG, ECC, TARC, MEG, and CC of the compact proposed lamp post shaped MIMO antenna have been calculated and found that the correlation coefficient was <0.001 with higher diversity gain > 9.95 dB and achieved better CCL < 0.4 bits/s/Hz in the respective operating bands. With these results, the proposed triangular lamp post shaped MIMO array is suitable for high data rate applications, which is one of the main concerns of 5G and beyond networks.
Vanet-TSMA: A traffic safety management approach for smart road transportation in vehicular ad hoc networks
- First Published: 02 March 2022
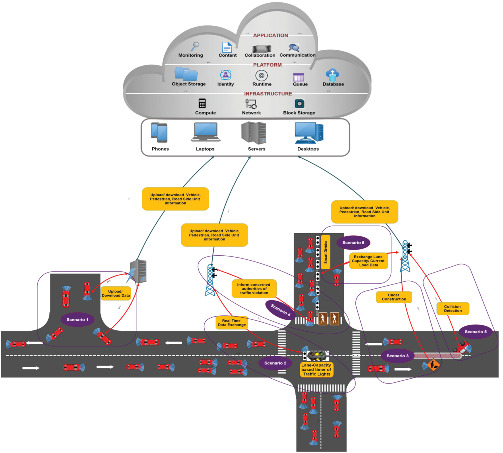
A VANET-based traffic safety management approach (VANET-TSMA) is proposed to reduce road accidents in India. This approach uses message distribution, traffic management, and congestion control efficiently for reducing the overall rate of road accidents. This method is based on multiple information and communication technology (ICT)-based safety mechanisms which include collision avoidance, collision detection, and traffic congestion avoidance for the protection of future connected automobiles on roads.
FIRST: Fuzzy based intelligent relay selection and transition technique for delay tolerant networks
- First Published: 22 February 2022

In this paper, a fuzzy logic-based relay node selection technique is proposed, which includes four input parameters and a single output parameter (“Grade”). Fuzzy logic system calculates the value of “Grade” for each node, which comes in the communication range. At the source node, the node which has the highest value of “Grade” will be selected as relay node. Further, at intermediate node, the message will transfer only if the difference between “Grade” value is greater than or equal to 50%.
Fault monitoring in passive optical network through the integration of machine learning and fiber sensors
- First Published: 24 February 2022
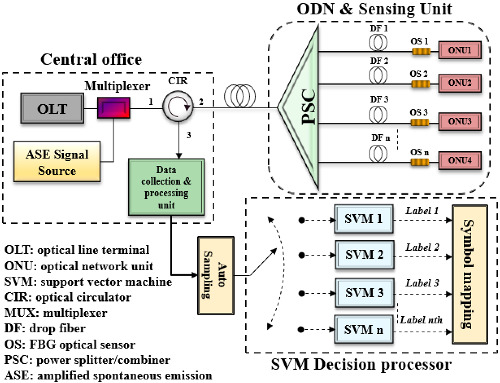
A technique for detecting optical link deterioration in PON was developed using the kernel SVM. The monitoring system was developed using monitoring signals received from the FBG and a machine learning network. The reflecting signal from the FBG is used by the monitoring system to assess the state of the fiber link in the branch network. The findings of the proposed SVM approach were consistent with the findings of Optisystem simulation and experiment, which show a precision of up to 99%.
Energy-efficient resource allocation in heterogeneous networks under different backhaul capacity constraints
- First Published: 28 February 2022
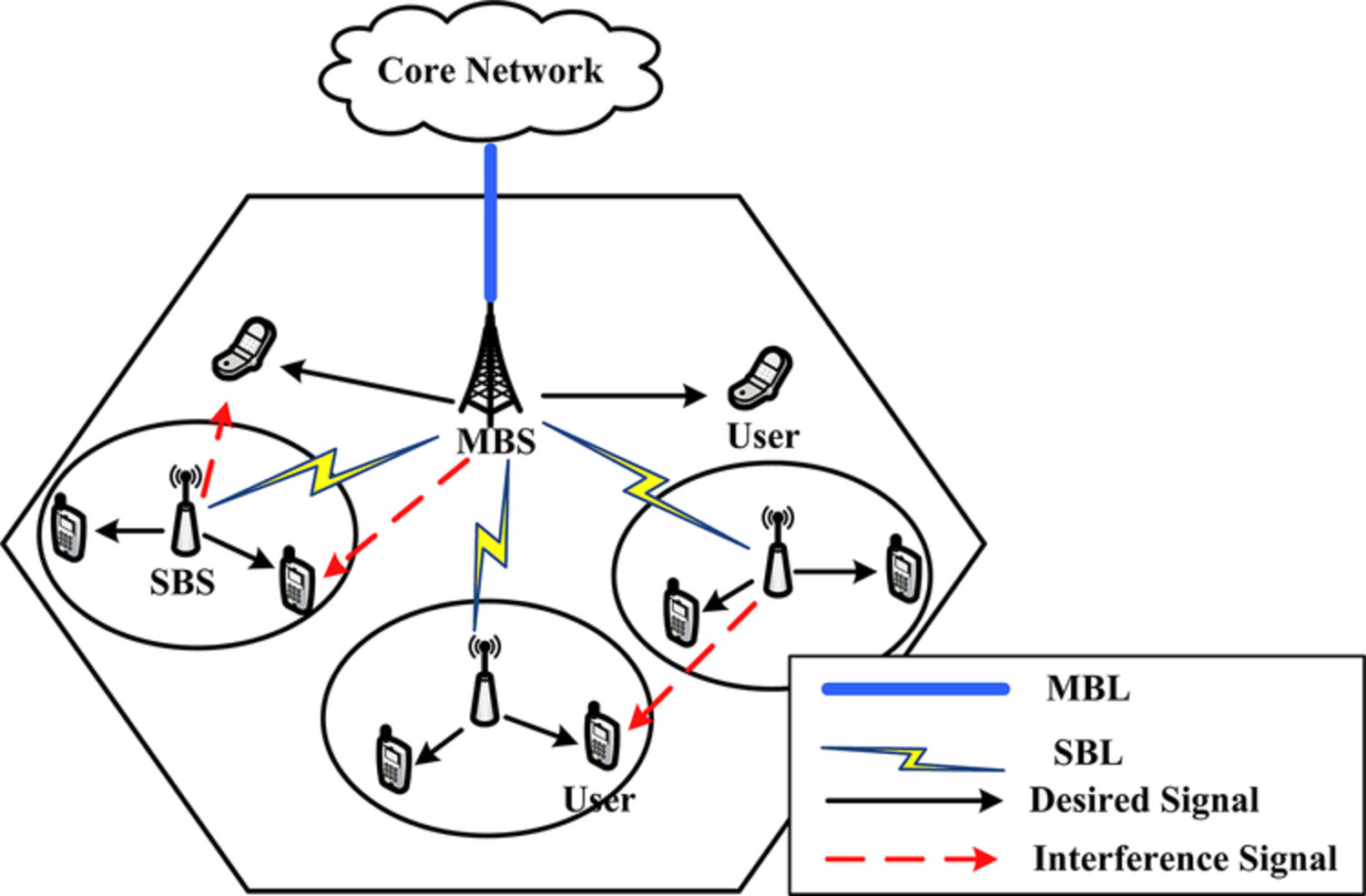
Aiming at improving the network energy efficiency and relieving data volume traffic pressure on backhaul links, we investigate energy efficient resource allocation which restricts small cell data traffic by imposing different kinds of backhaul capacity constraints. Based on the Dinkelbach and dual decomposition methods, we propose iterative resource allocation algorithms under different backhaul capacity constraints, where resource block and power are jointly allocated among users in each cell. Numerical results reveal that the proposed algorithms have good convergence performance, and also evaluates the impact of different backhaul capacity constraints on network performance.
ND-ADR: Nondestructive adaptive data rate for LoRaWAN Internet of Things
- First Published: 14 March 2022
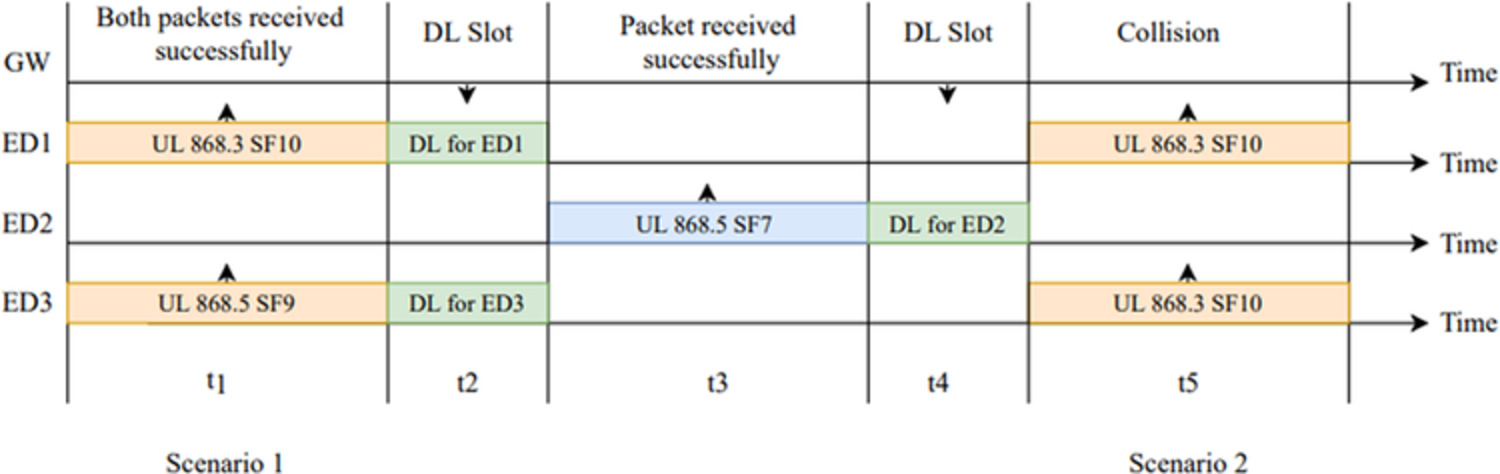
We proposes a novel “nondestructive adaptive data rate (ND-ADR)” to address the packet collision problem.
The proposed ND-ADR aims to monitor the destructive concurrent transmissions proactively and mitigate them by allocating non-destructive transmission time to Eds.
The proposed ND-ADR ensures high robustness and reliability by reducing the chances of destructive transmissions and retransmissions.
Results show that the proposed ND-ADR outperforms the existing state-of-the-art ADRs in packet success ratio and energy consumption.
A novel approach on energy-efficient clustering protocol for wireless sensor networks
- First Published: 04 March 2022
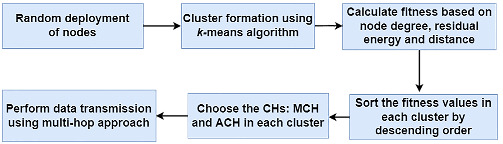
This proposed method provides a hybrid approach by combining k-means clustering and dual cluster head selection. For routing, an energy-efficient mechanism using multi-hop approach is adopted. The proposed algorithm shows a far better performance in terms of network lifetime, PDR, throughput, total energy consumption, and end to end delay.
k-means clustering based energy and trust management routing algorithm for mobile ad-hoc networks
- First Published: 08 March 2022
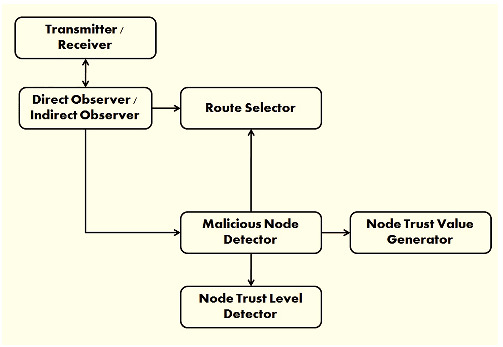
The main focus of this research is identifying the unstable cluster heads and replacing them with other nodes that implement the self-configurable cluster method. For defining the cluster heads successfully, we presented a k-means protocol approach. A node is designated as a cluster head (CH) in MANET after the cluster value remains lesser than the existing routing threshold value. Information gathering, computing trust levels, and trust-based configuration are the three key elements of the proposed trust management system, which communicates with each node to establish secure network connections.
Energy efficient and effective node deployment for wireless sensor network
- First Published: 07 March 2022
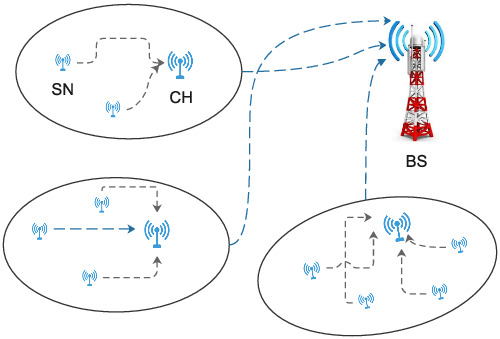
An active–passive node topology on deployed Sensor nodes is proposed to enhance the network lifetime. The proposed scheme performed significant improvement in both homogeneous and heterogeneous environments. The simulations show that the proposed protocol increases the network lifetime and stability of the network.
Modeling and reliability verification of industrial control network protocol based on time state transition matrix
- First Published: 11 March 2022
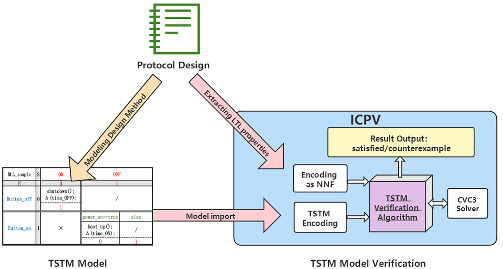
This paper reconstructs the time semantics of TSTM to make it more suitable for modeling and verification of industrial control network protocols. On this basis, the corresponding modeling design method, model verification method, and verification tool called ICPV are proposed. Finally, the effectiveness of the method is illustrated by a complete case study of an actual industrial control network protocol.
Low profile multiband microstrip patch antenna with frequency reconfigurable feature using PIN diode for S, C, X, and Ku band applications
- First Published: 07 March 2022

This paper provides the solution to achieve the frequency responsibility using two PIN diodes. Simulation is carried by a high-frequency structure simulator tool and compared with the fabricated structure for the authentication. Antenna fabrication is performed by low-profile material FR-4. Three modes analyzed and compared in terms of resonating frequency, reflectance response, gain, bandwidth, and electric field based upon switching of PIN diodes. The proposed antenna structure provides a multiband response with the four frequency tunable bands along with maximum frequency tunability of 700 MHz and a minimum reflectance response of −28.22 dB. The proposed structure opens a new door of applications for the S, C, X, and Ku bands. The presented design also compared with the previously published papers to identify the improvement.
Colored scheduling scheme for fast and reliable beacon safety messages broadcast in vehicular ad-hoc networks
- First Published: 09 March 2022
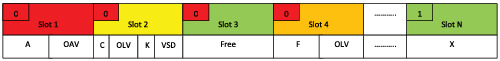
We propose colored velocity-based TDMA (CVTDMA), an original colored scheduling scheme for the broadcast of safety beacons on the control channel. Based on vehicles speed and colors that it assigns to time slots according to their occupation statuses, it mitigates the mobility effect and maximizes the reuse of slots while avoiding collisions. The simulation results show that our protocol uses the wireless channel much more effectively than the default one defined in IEEE 802.11p.
Faulty node detection and recovery scheme for large-scale wireless sensor network using hosted cuckoo optimization algorithm
- First Published: 14 March 2022
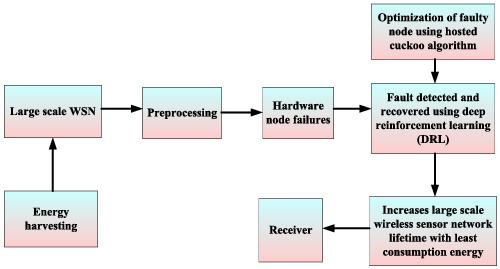
This manuscript proposes an effective deep reinforcement learning (DRL)-adopted faulty node detection and recovery scheme (FND-RS) integrated with the hosted cuckoo-based optimal routing scheme for large-scale wireless sensor networks. Here, the DRL process is utilized for noticing and recovering the hardware node fault on sensor.





