Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Exploring the Molecular Interaction Between NR2E3 and NR1D1 in Retinitis Pigmentosa: A Docking and Molecular Dynamics Study
- First Published: 18 November 2024
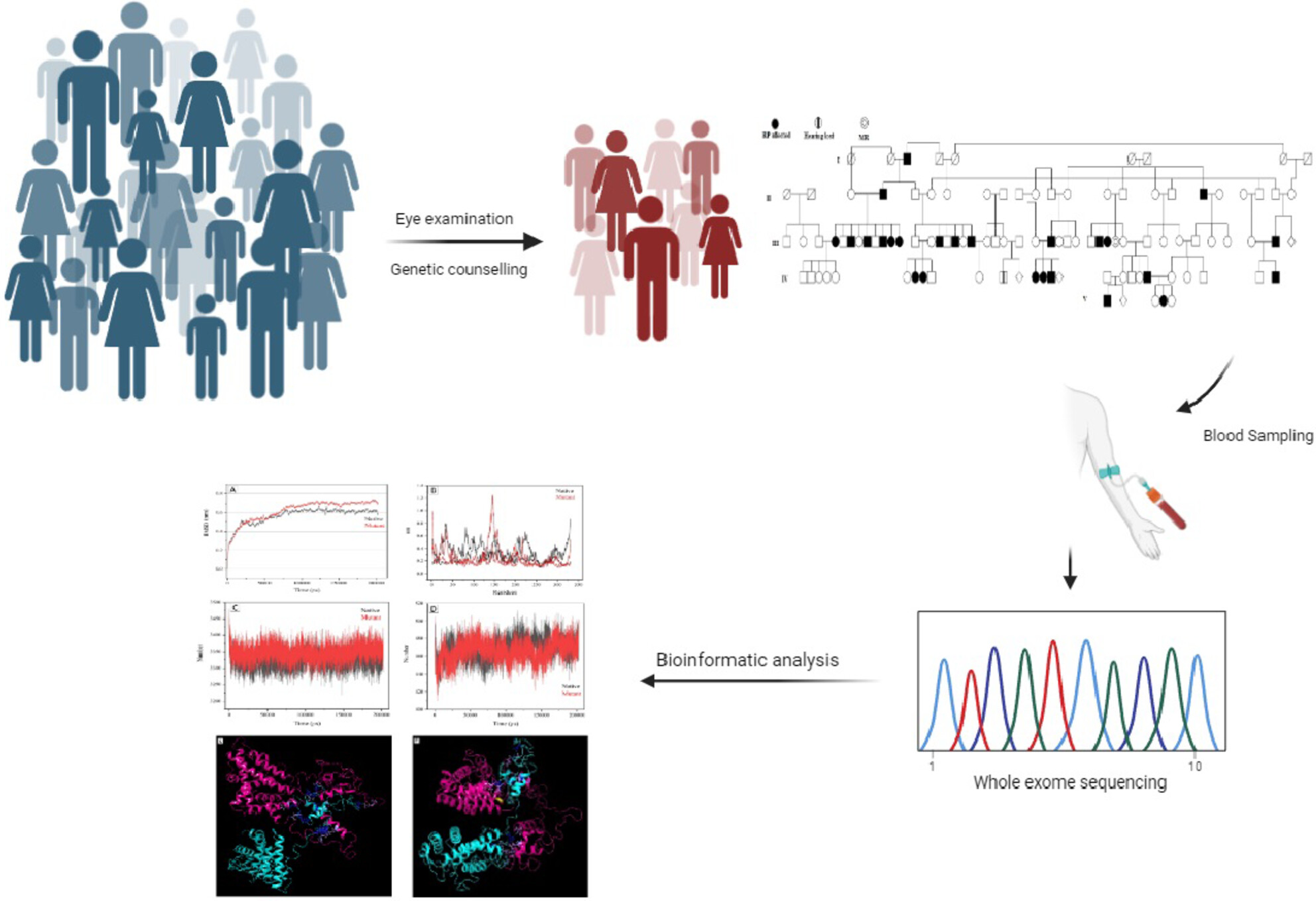
This study delves into the clinical and genetic aspects of retinitis pigmentosa (RP) within a large Iranian family, focusing on mutations in the NR2E3 gene. Through whole-exome sequencing and in silico analysis, a homozygous missense variant (c.934G>A/p.R311Q) in NR2E3 was identified as a potential culprit behind RP in affected family members. Molecular modeling and dynamics simulations shed light on the pathogenic effects of this mutation, emphasizing the disruption in protein–protein interactions and providing valuable insights into the disease mechanism.
Interpretable Machine Learning Algorithms Identify Inetetamab-Mediated Metabolic Signatures and Biomarkers in Treating Breast Cancer
- First Published: 21 November 2024
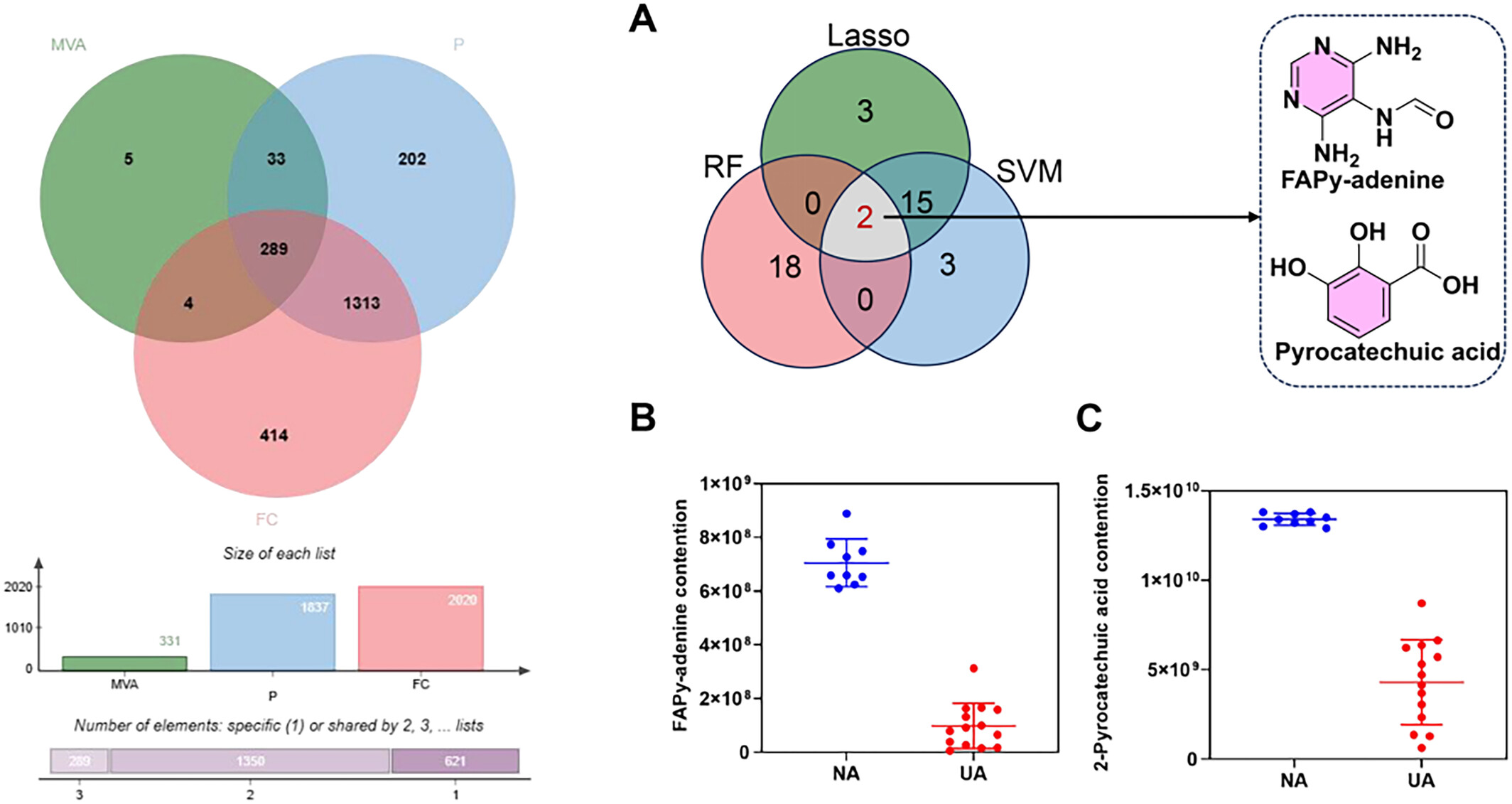
This study harnesses the power of metabolomics and machine learning to reveal two key metabolites of inetetamab in breast cancer therapy. The identification of these two significant differential metabolites holds promise as potential biomarkers for evaluating and predicting inetetamab treatment outcomes in breast cancer, ultimately contributing to the diagnosis of the disease and the discovery of prognostic markers.
REVIEW ARTICLE
Mycobacterium tuberculosis: The Mechanism of Pathogenicity, Immune Responses, and Diagnostic Challenges
- First Published: 26 November 2024
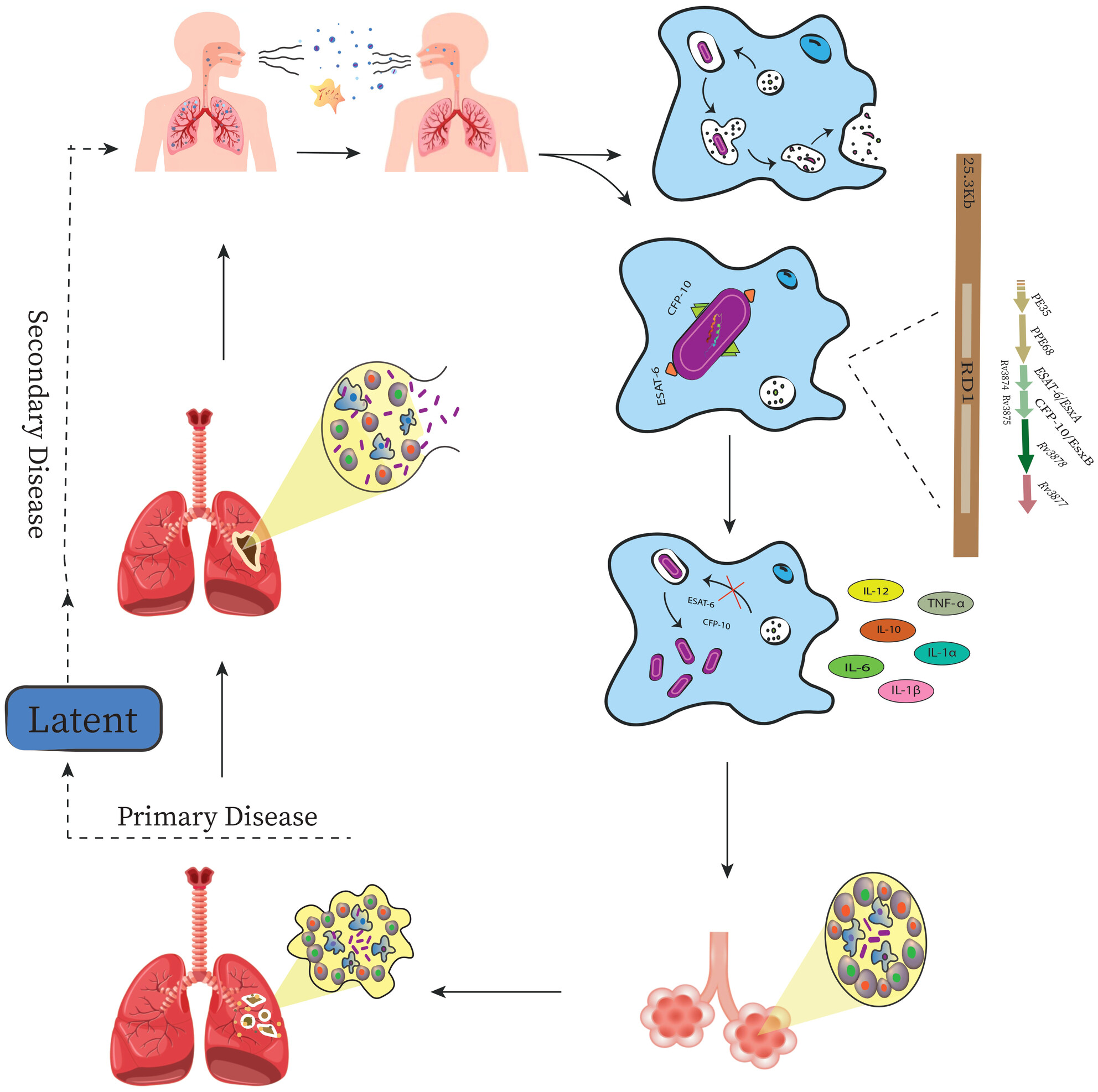
Mycobacterium tuberculosis acts as the causative agent of human tuberculosis and is regarded as one of the most adaptable human pathogens. M. tuberculosis possesses several virulence factors that help the bacterium evade mucous barriers. The infection caused by M. tuberculosis arises from a complex interplay between the host immune system and the bacteria. Early and effective treatment of this disease is of great importance in order to prevent the emergence of drug-resistant strains. This necessitates the availability of fast and reliable diagnostic methods for managing affected cases. One reason why this study is significant is the lack of a comprehensive review in this field that thoroughly examines the importance, pathogenesis, and diagnosis of M. tuberculosis.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Impact of Overweight on Renal Prognosis in Malignant Hypertension Patients With Thrombotic Microangiopathy
- First Published: 05 November 2024
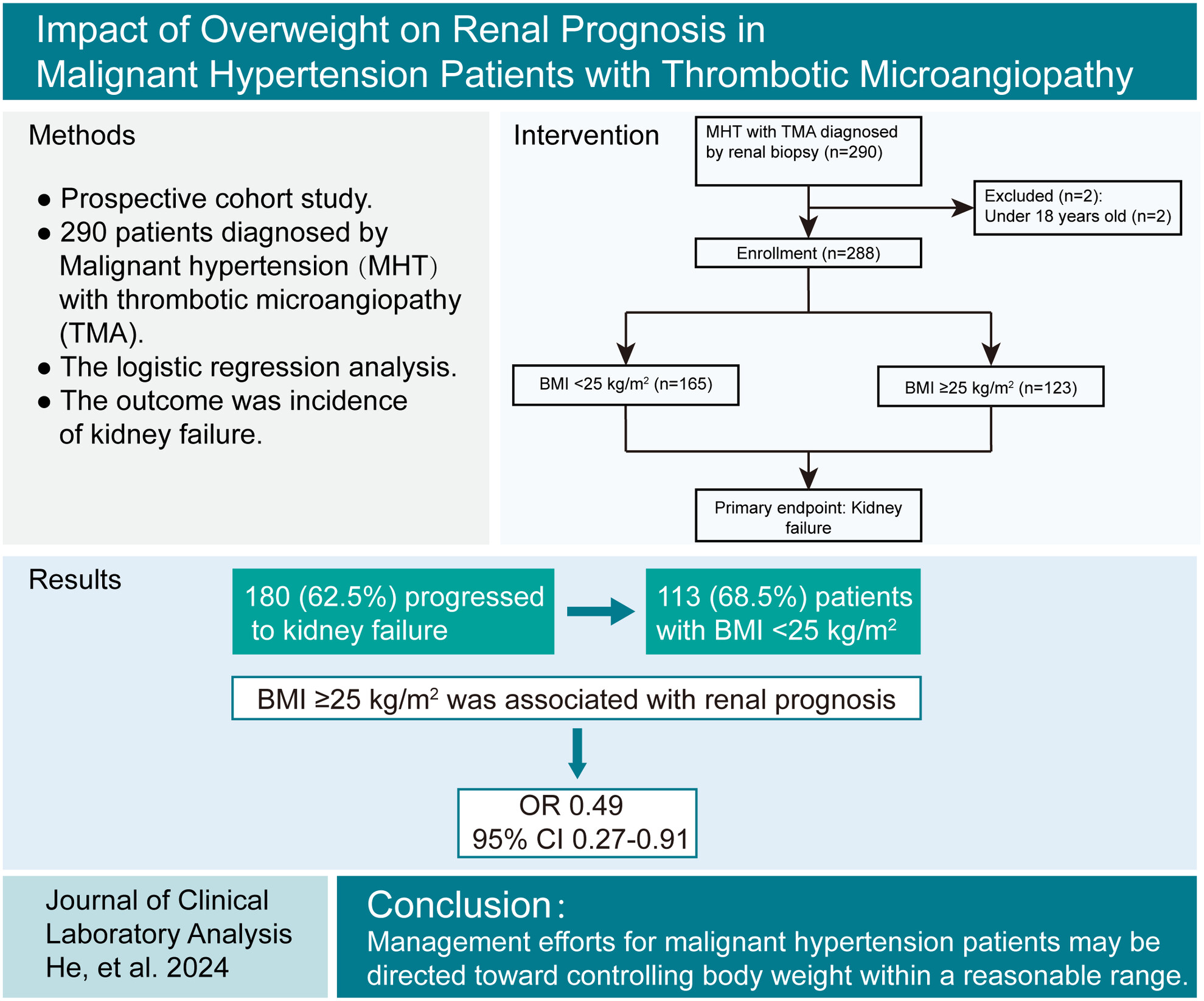
The present study first reveals the association of overweight and obesity and renal outcome for kidney failure in MHT patients with renal TMA. We have identified that normal weight, rather than overweight or obesity, contributes to a worse renal outcome of kidney failure in MHT patients with renal TMA. The study proposes that management efforts for MHT may be directed toward controlling body weight within a reasonable range for patients.
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Letter to the Editor Based on Article “Analysis of Genotype–Phenotype Correlation in Patients With α-Thalassemia From Fujian Province, Southeastern China”
- First Published: 22 November 2024






