Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER
Cover Image, Volume 86, Issue 8, August 2019
- Page: i
- First Published: 12 August 2019

Cover Caption: The cover image is based on the Research Article Thymoquinone reduces intracytoplasmic oxidative stress and improves epigenetic modification in polycystic ovary syndrome mice oocytes, during in-vitro maturation by Fatemeh Eini et al., https://doi.org/10.1002/mrd.23222.
Credit: Cover image © Dr. Fatemeh Eini Images.
ISSUE INFORMATION
Table of Contents, Volume 86, Issue 8, August 2019
- Pages: 923-924
- First Published: 12 August 2019
VISIONS: THE ART OF SCIENCE
Microtubule depletion domain 1 localizes at the boundary between female gametes in Arabidopsis thaliana
- Page: 925
- First Published: 10 July 2019
CORRESPONDENCE
Sydney Brenner: The birth of a model organism and the worm's connection to reproductive biology
- Pages: 926-927
- First Published: 05 June 2019
Birth of a marmoset following injection of elongated spermatid from a prepubertal male
- Pages: 928-930
- First Published: 19 June 2019
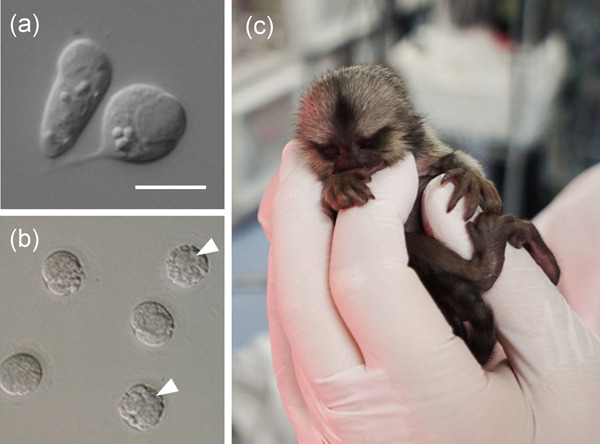
We examined the feasibility of injection of elongates spermatids from prepubertal male marmosets for early production of the offspring. One female infant was born after transfer of two embryos derived from elongated spermatid injection. She is growing normally without any morphological and physiological abnormalities.
Single cell RNA-seq in the sea urchin embryo show marked cell-type specificity in the Delta/Notch pathway
- Pages: 931-934
- First Published: 14 June 2019
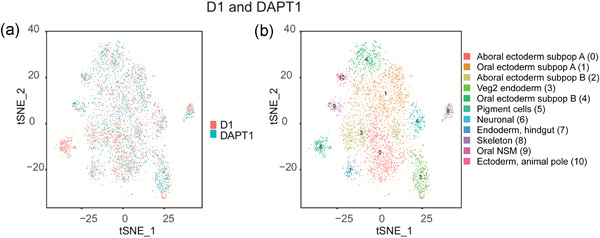
Through single cell, mRNA-seq (drop-seq) approaches we find specificity and distinct effects of the Wnt and Delta/Notch pathways in differential cell lineages. The results illuminate how these conserved pathways selectively regulate cell fates at a single cell level. Overall, we conclude that single cell RNA-seq analysis in this embryo is revealing of the cell types present during development, of the changes in the gene regulatory network resulting from inhibition of various signaling pathways and of the selectivity of these pathways, in influencing developmental trajectories.
REVIEW ARTICLE
An update of the regulatory factors of sperm migration from the uterus into the oviduct by genetically manipulated mice
- Pages: 935-955
- First Published: 27 May 2019
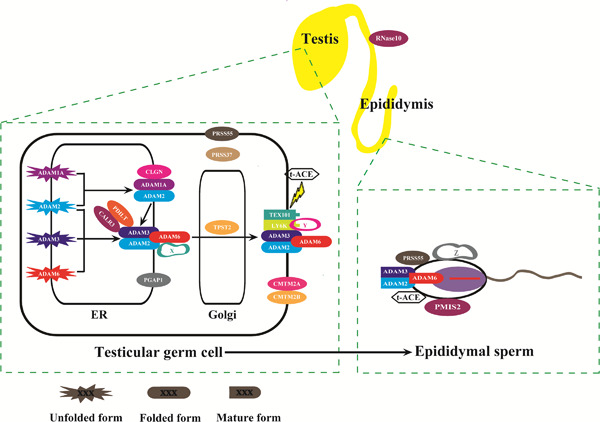
Recent gene disruption approaches in mice have revealed that many of the factors previously described as important for fertilization are largely dispensable in gene-knockout (KO) animals, and some previously unknown factors are emerging. As a result, the molecular mechanisms of fertilization, especially sperm migration from the uterus into the oviduct, have recently been revised by the emergence of genetically modified animals. In this review, we only focus on and update the essential genes for sperm migration through the uterotubal junction and describe recent advances in our knowledge of the basis of mammalian sperm migration.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Transcriptome-wide changes in testes reveal molecular differences in photoperiod-induced seasonal reproductive life-history states in migratory songbirds
- Pages: 956-963
- First Published: 25 April 2019
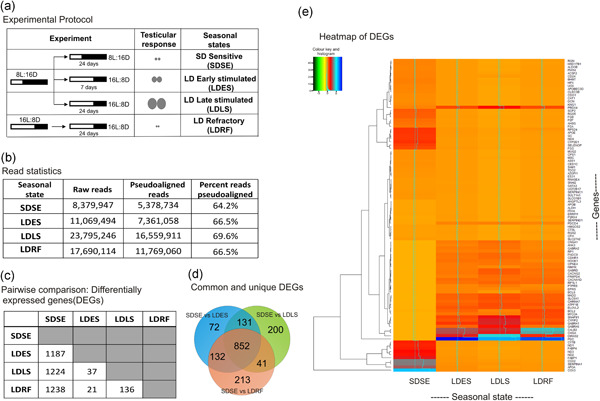
We identified genetic pathways putatively involved in the seasonal testicular cycle. Differentially expressed genes that enriched the calcium ion binding and cell junction pathways were highly expressed in testicular maturation states. More specifically, quantitative polymerase chain reaction showed significant seasonal differences in testicular expression of genes (HOOK1, RGS2, PRDX4, BCL6, CYFIP2, PDCD4, P2RX4, and GABRA1) involved in the gametogenesis and associated pathways. Overall, these results show significant transcriptional differences between the testicular phenotypes and provide insights into molecular mechanisms involved in the annual reproductive life-history of a photoperiodic seasonal species.
The implication of single-nucleotide polymorphisms in ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
- Pages: 964-971
- First Published: 22 May 2019
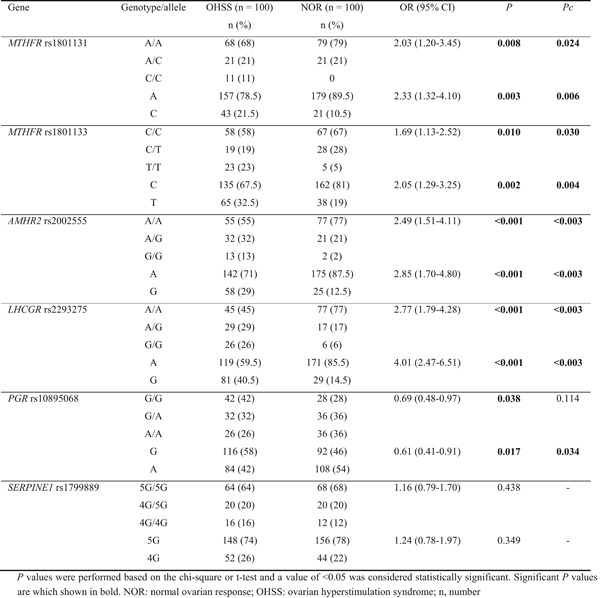
The polymorphisms of MTHFR, AMHR2, and LCGHR genes could promote the risk in susceptibility to ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS), which highlight the impact of these genes and their polymorphisms on OHSS and could potentially provide a genetic profile, which may help to adjust an optimized protocol for ovarian stimulation before the in vitro fertilization (IVF) procedure in different individuals, especially in patients who are genetically predisposed to high responses to controlled ovarian stimulation (COS) or developed OHSS.
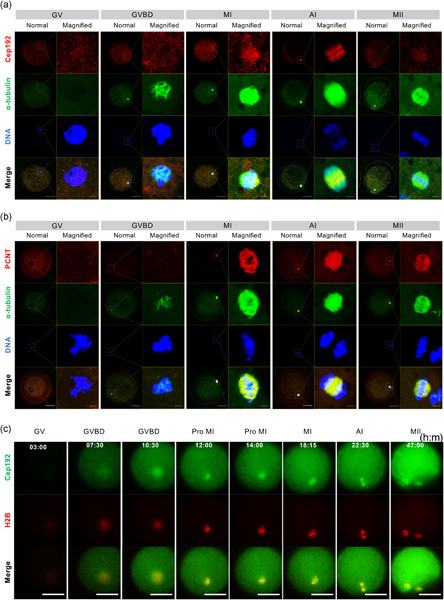
Acentriolar microtubule organization centers and Ran-mediated microtubule formation pathways are both required in porcine oocytes
- Pages: 972-983
- First Published: 28 May 2019
Functional importance of palmitoyl protein thioesterase 1 (PPT1) expression by Sertoli cells in mediating cholesterol metabolism and maintenance of sperm quality
- Pages: 984-998
- First Published: 27 May 2019
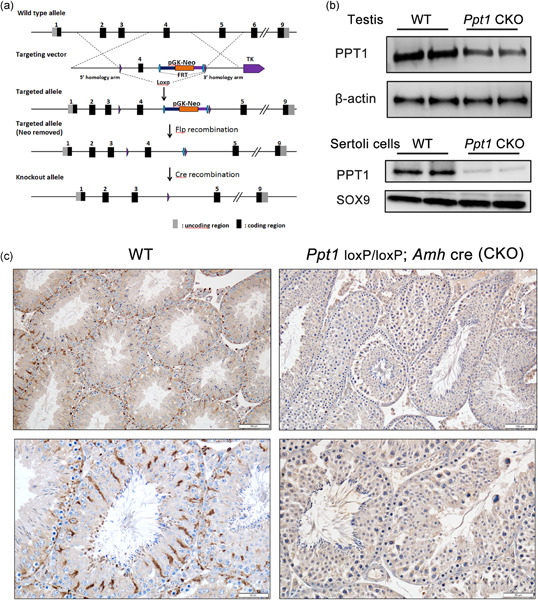
Palmitoyl protein thioesterase 1 (PPT1) expression in Sertoli cells is essential for cell viability, lysosome function, and cholesterol metabolism. Its involvement in these processes is critical for Sertoli cells ability to sustain spermatogenesis and that specific knockout of Ppt1 in Sertoli cells causes male subfertility associated with poor sperm quality and a high ratio of sperm deformity.
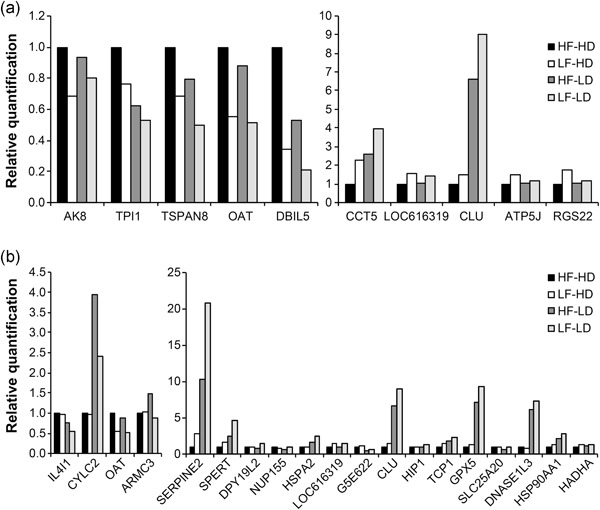
Proteomic markers of low and high fertility bovine spermatozoa separated by Percoll gradient
- Pages: 999-1012
- First Published: 27 May 2019
Enhancement of epigenetic reprogramming status of porcine cloned embryos with zebularine, a DNA methyltransferase inhibitor
- Pages: 1013-1022
- First Published: 05 June 2019
Treatment with the optimal condition of zebularine (5 nM; 24 hr) during IVC could promote porcine subsequent embryo development. 2. Zebularine treatment could positively regulate the methylation levels on various stages of porcine SCNT preimplantation embryos. 3. The expression of development-, reprogramming-related genes of blastocyst could be positively regulated by the zebularine treatment.
LncRNA Gm2044 promotes 17β-estradiol synthesis in mpGCs by acting as miR-138-5p sponge
- Pages: 1023-1032
- First Published: 09 June 2019
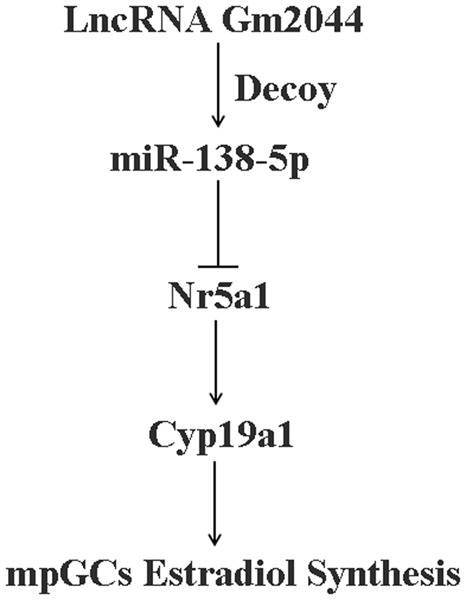
Our results provide an insight into the mechanistic roles of lncRNA Gm2044 for 17β-estradiol synthesis by acting as competing-endogenous RNAs to modulate the function of mpGCs. Studying the potential lncRNAs, which regulate estradiol release, will be beneficial for the diagnosis and treatment of steroid hormone-related disease.
Longitudinal analysis of somatic and germ-cell telomere dynamics in outbred mice
- Pages: 1033-1043
- First Published: 17 June 2019

This longitudinal study examines telomere length (TL) dynamics in somatic tissue and gametes during an entire lifespan in an outbred mouse population. While with aging, a clear reduction in TL was produced in somatic cells and oocytes, telomeres in sperm cells significantly lengthened. Finally, we found evidence indicating that telomere elongation in sperm during aging may be dependent on different mechanisms, such as the survival of spermatogonia with longer telomeres and the alternative lengthening of telomeres mechanism in meiotic and postmeiotic spermatogenic cells.
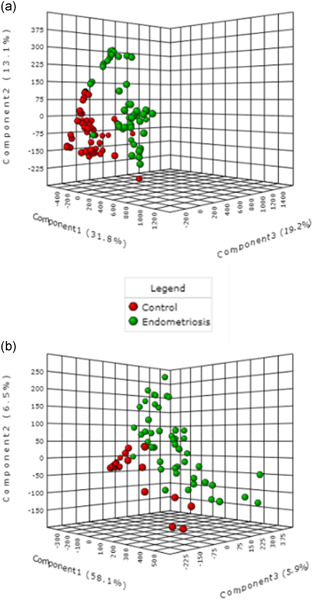
Metabolomic profile as a noninvasive adjunct tool for the diagnosis of Grades III and IV endometriosis-related infertility
- Pages: 1044-1052
- First Published: 18 June 2019
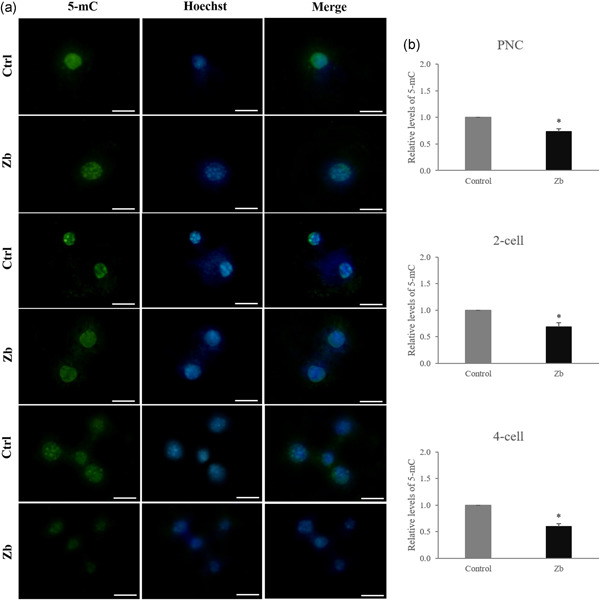
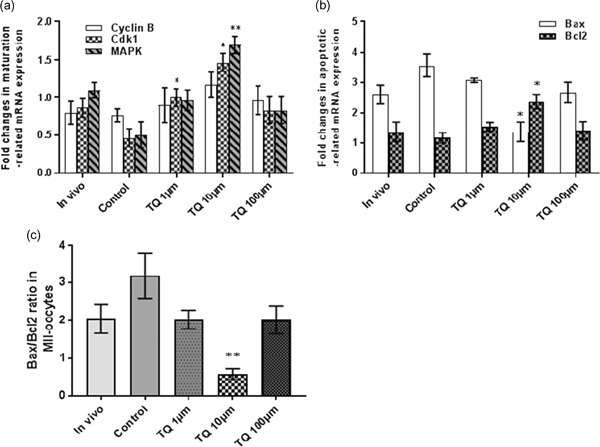
Thymoquinone reduces intracytoplasmic oxidative stress and improves epigenetic modification in polycystic ovary syndrome mice oocytes, during in-vitro maturation
- Pages: 1053-1066
- First Published: 17 June 2019
Graphical Abstract
Although in-vitro maturation (IVM) of oocytes has been presented as an alternative treatment to traditional stimulated in-vitro fertilization, the culture condition could be improved by natural antioxidants. Thus, we investigated the protective effect of thymoquinone (TQ) during IVM in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) mice model. Our results suggested that TQ may enhance the developmental competence of PCOS oocytes via modulation of oxidative stress and epigenetic alterations.
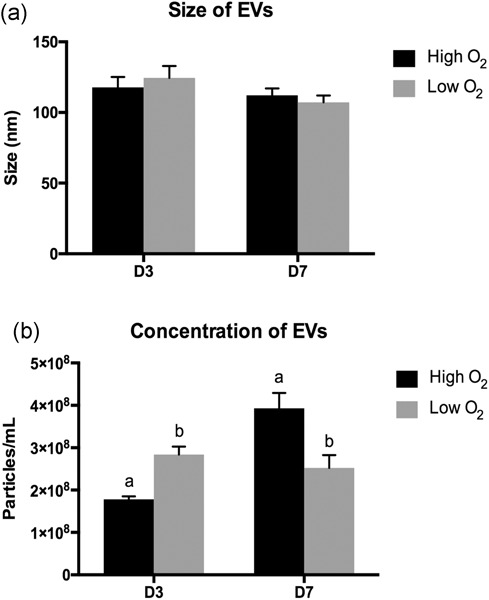
Oxygen tension modulates extracellular vesicles and its miRNA contents in bovine embryo culture medium
- Pages: 1067-1080
- First Published: 13 June 2019