Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER IMAGE
Cover Image, Volume 142, Issue 32
- First Published: 14 July 2025

The cover image is based on the article Recent Advances in Antimicrobial Food Packaging From Bio-Based Polymers: A Comprehensive Review by Purba Purnama et al., https://doi.org/10.1002/app.57275.
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW
Recent Advances in Antimicrobial Food Packaging From Bio-Based Polymers: A Comprehensive Review
- First Published: 05 May 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
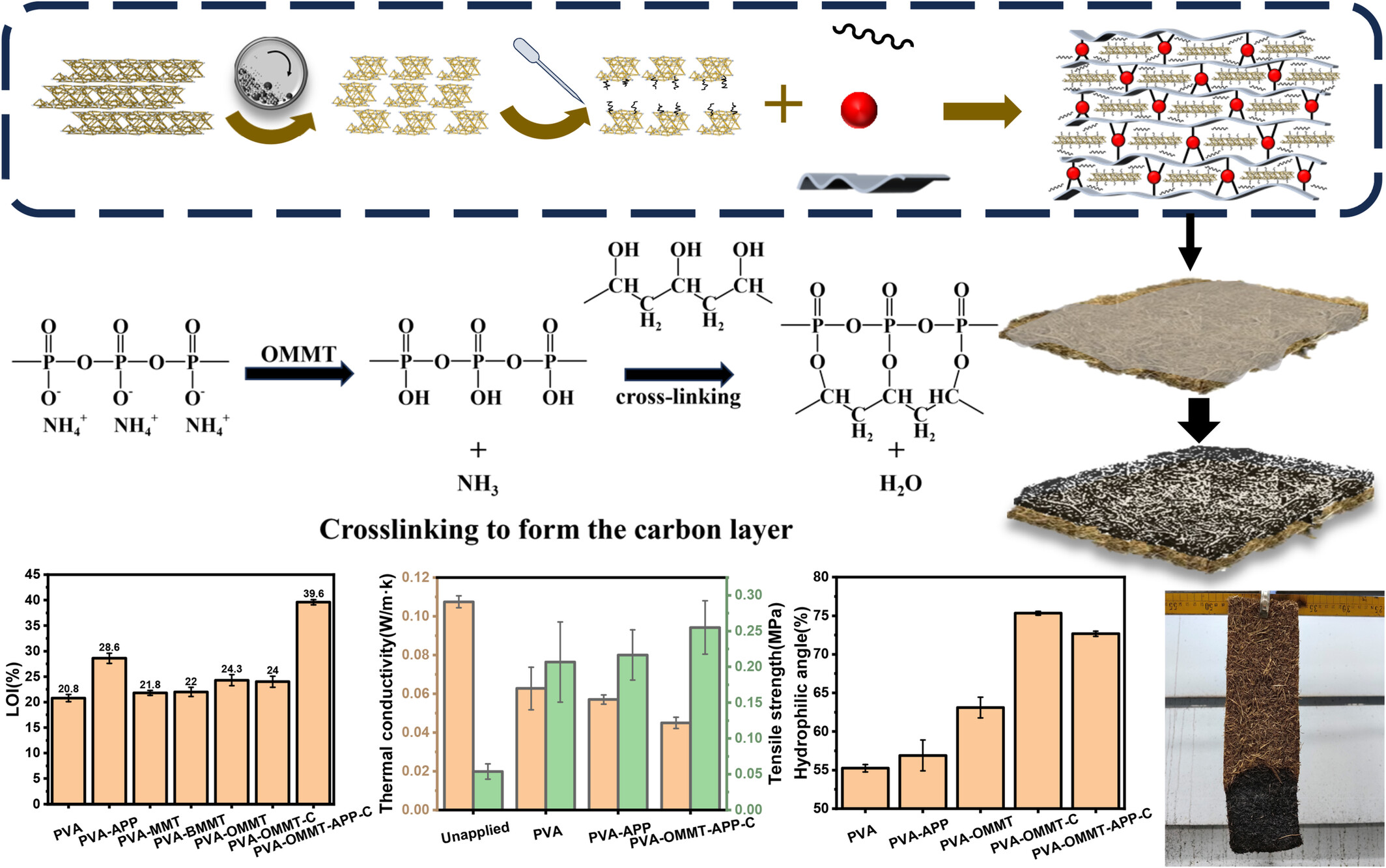
Biomimetic Nanocomposite Coatings With Flame Retardancy, Mechanical Strength, and Water Resistance via Physicochemical Dual Cross-Linking
- First Published: 02 May 2025
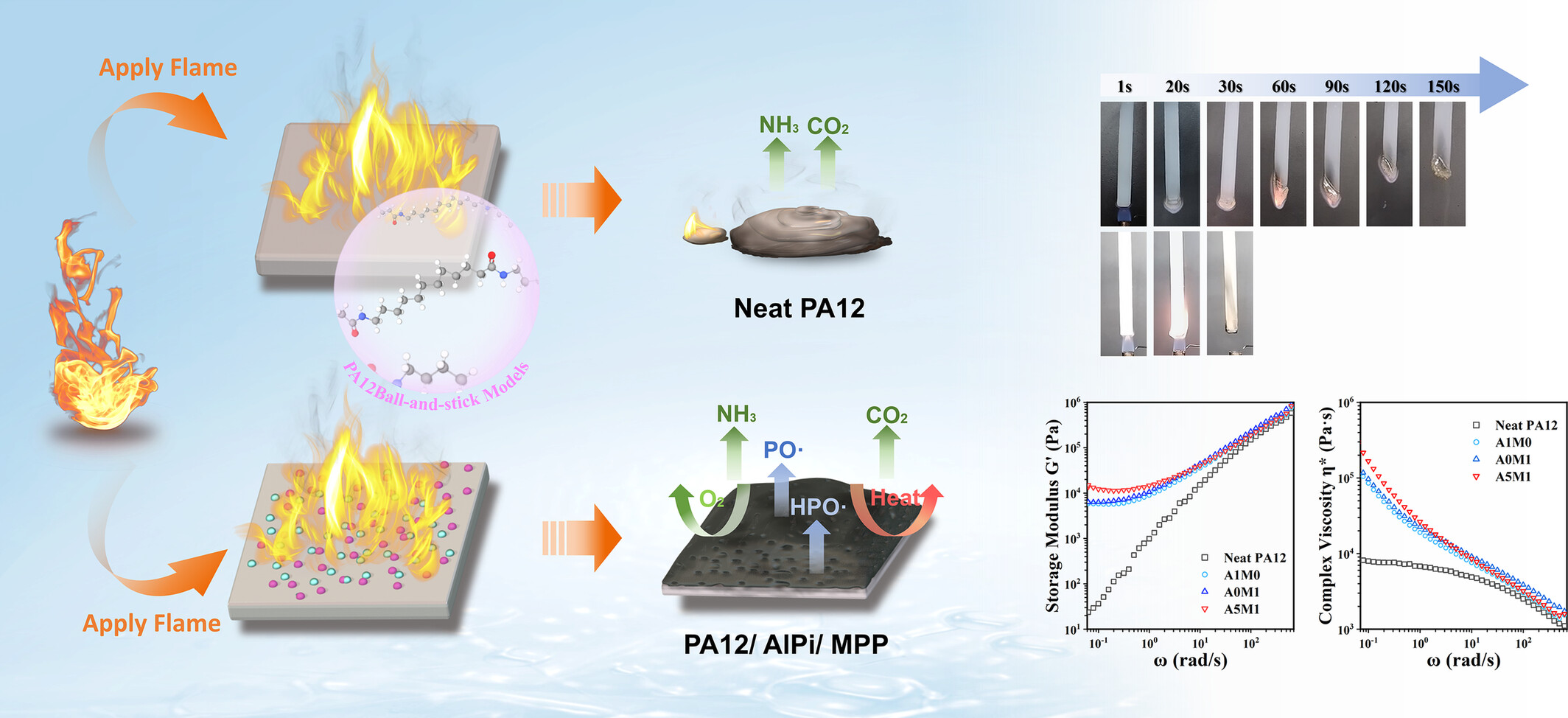
Enhanced Flame Retardancy in PA12 Composites via the Synergy of Aluminum Diethylphosphonate and Melamine Polyphosphate
- First Published: 03 May 2025
Porous Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene Membrane Prepared by One- and Two-Step Biaxially Stretching Method
- First Published: 30 April 2025
All-In-One 2D Intumescent Flame Retardants [Fe(OH)2]+ Anchored Melamine Trimetaphosphate (Fe@MAP) Enable Enhanced Flame Retardancy and Smoke Suppression of Epoxy Resins
- First Published: 30 April 2025
Flame Retardant Performance of Phosphatized Starch in Epoxy Resins: A Sustainable Approach to Enhancing Fire Safety
- First Published: 07 May 2025
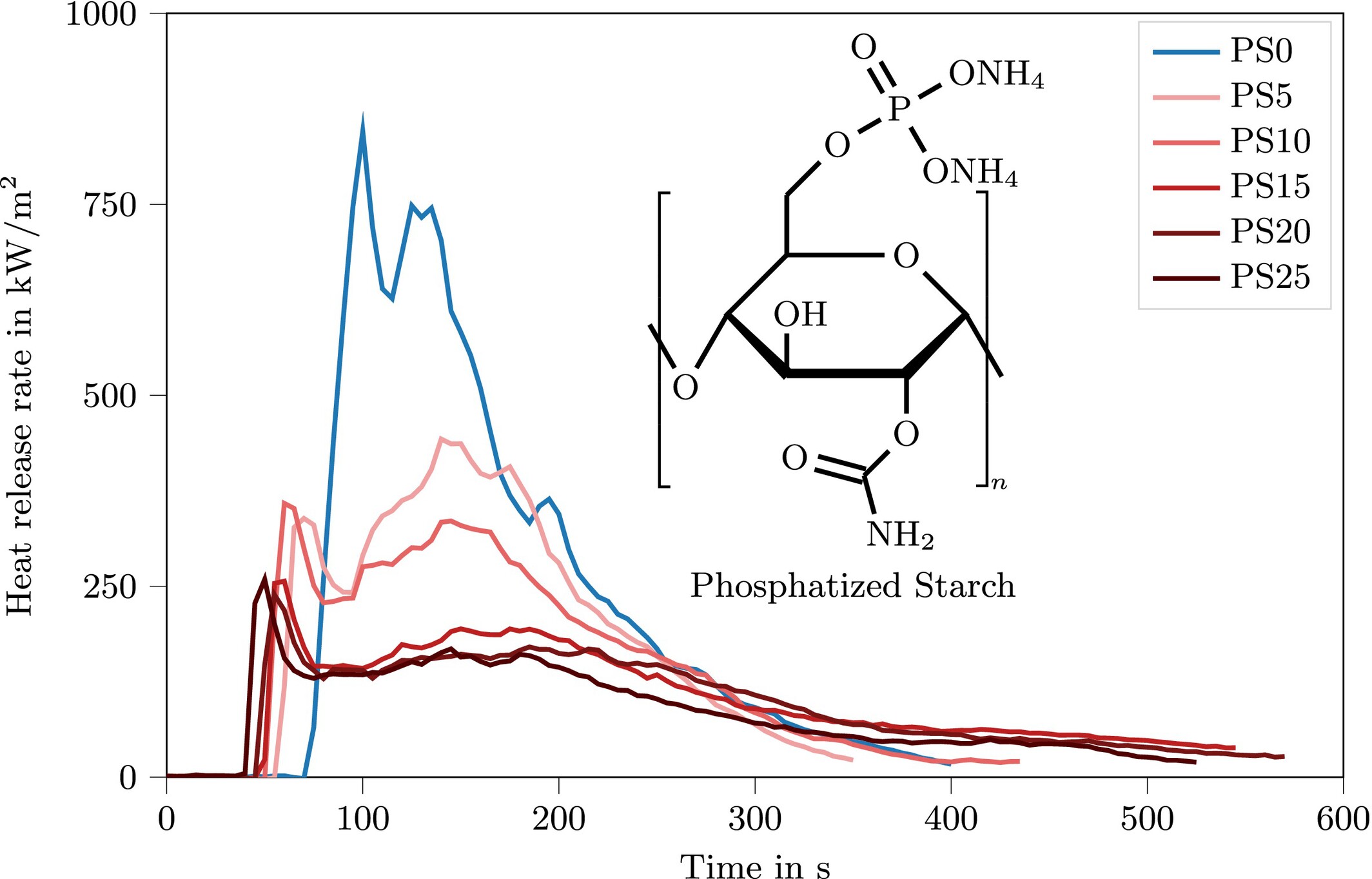
This study explores phosphatized starch (PS) as a bio-based flame retardant in epoxy thermosets. PS promotes char and intumescent layer formation, reducing peak heat release rate by 70%, total heat release by 52%, and smoke release by 53%. Thermal and combustion analyses confirm PS's effectiveness, highlighting its potential for sustainable fire-safe materials.
The Role of Isocyanate Index and Flame Retardant in Reducing CO(g) and Smoke Emissions of Soy-Based Rigid Polyisocyanurate Foams
- First Published: 30 April 2025
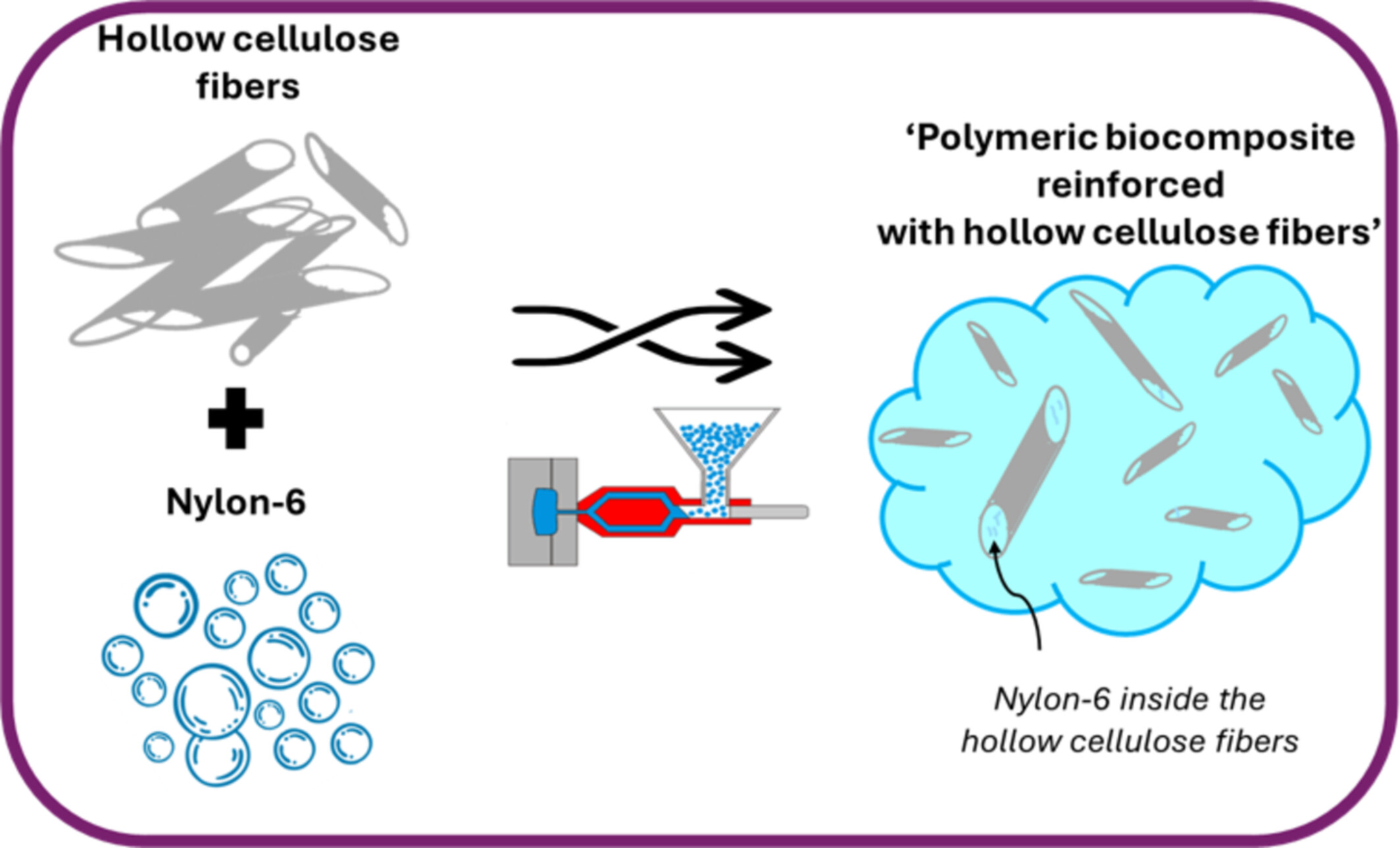
Effect of Hollow Cellulose Fibers From Agro-Industrial Waste on the Mechanical, Morphological, and Thermal Properties of Nylon-6 Biocomposites
- First Published: 05 May 2025
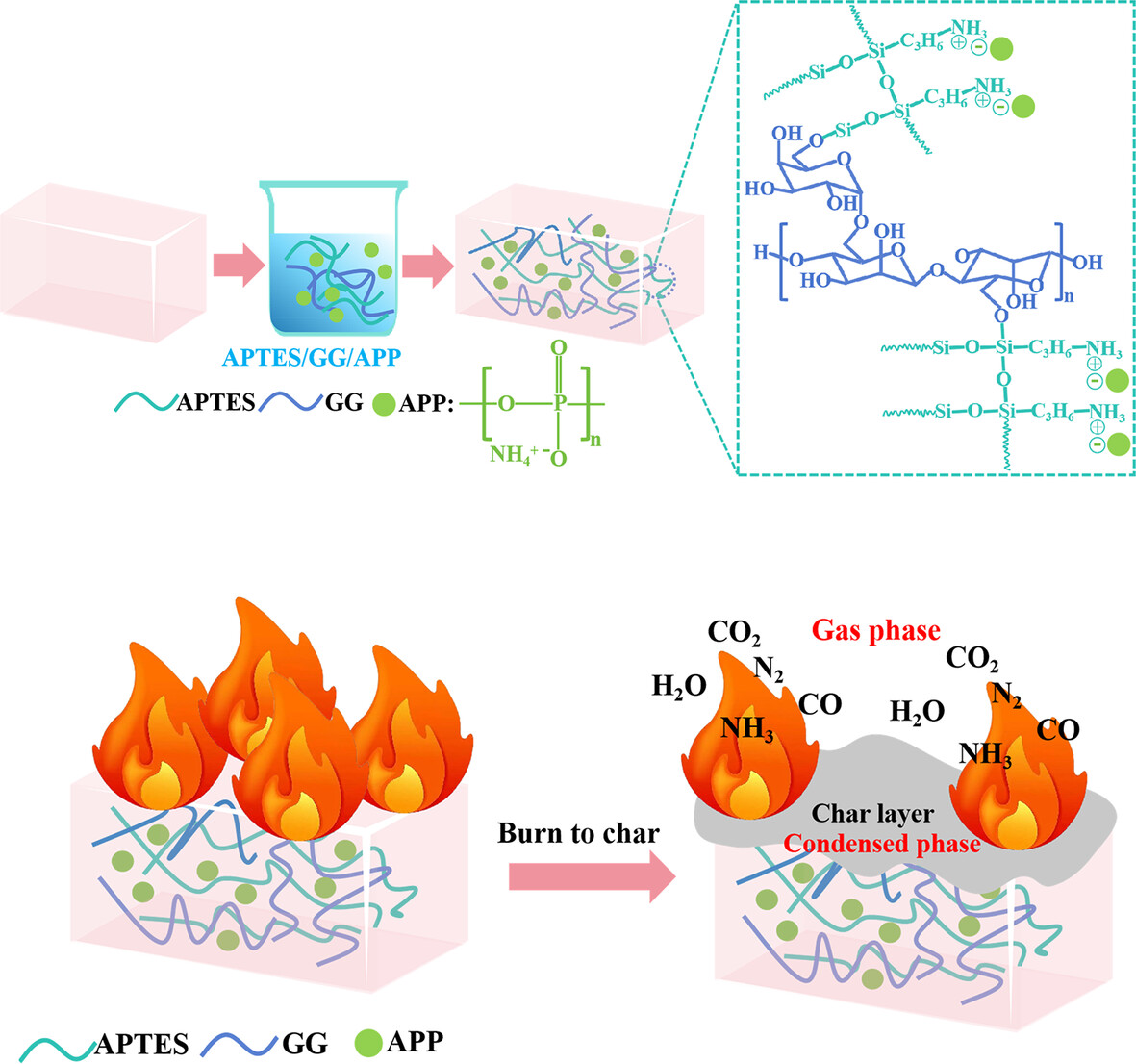
Excellent Flame Retardant of Flexible Polyurethane Foams With Green Coatings by Sol–Gel Method
- First Published: 05 May 2025
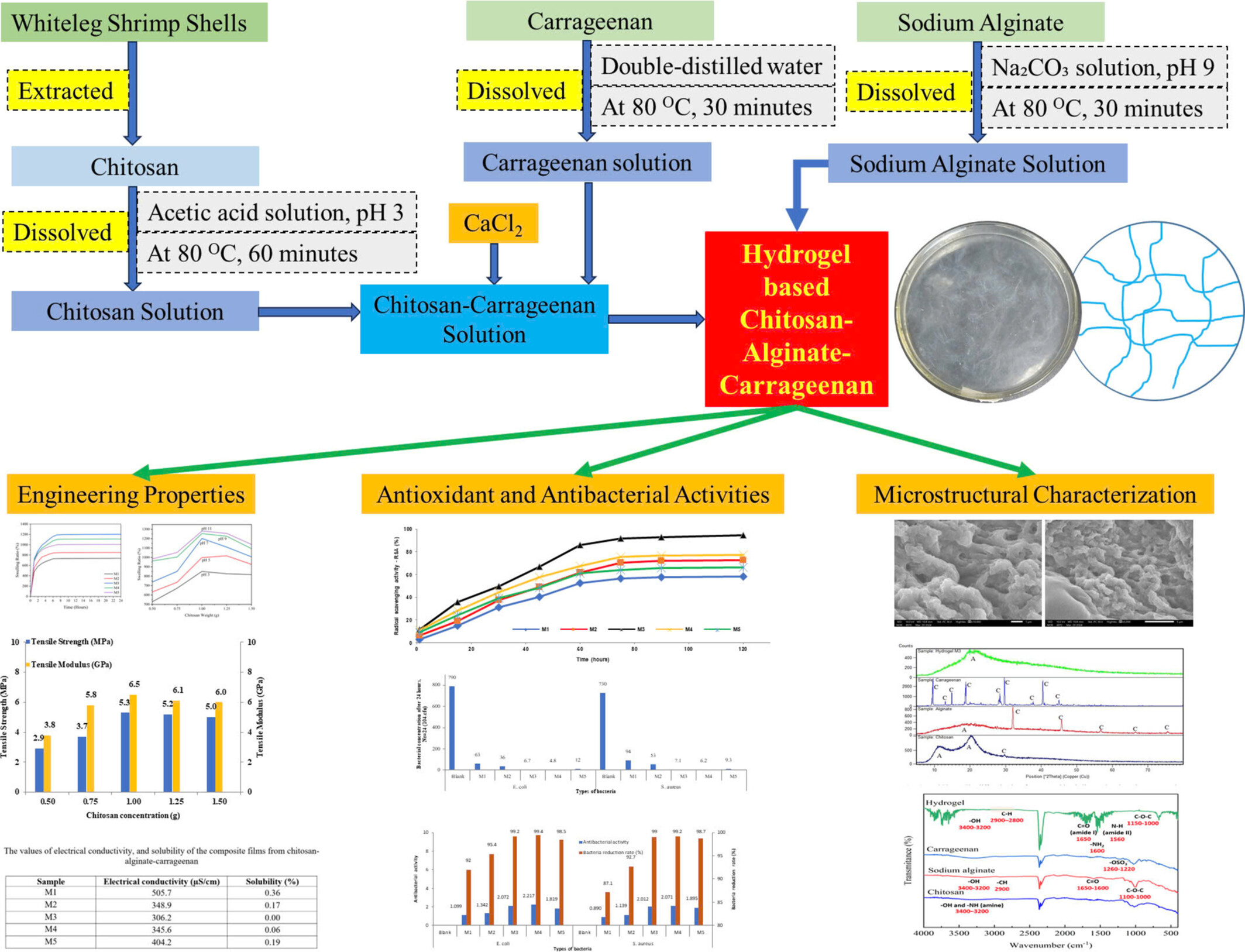
Evaluation on Effects of Chitosan Derived From Shrimp Shells on Engineering Properties, Antioxidant, Antibacterial, and Microstructural Characteristics of Chitosan–Alginate–Carrageenan-Based Hydrogels
- First Published: 06 May 2025
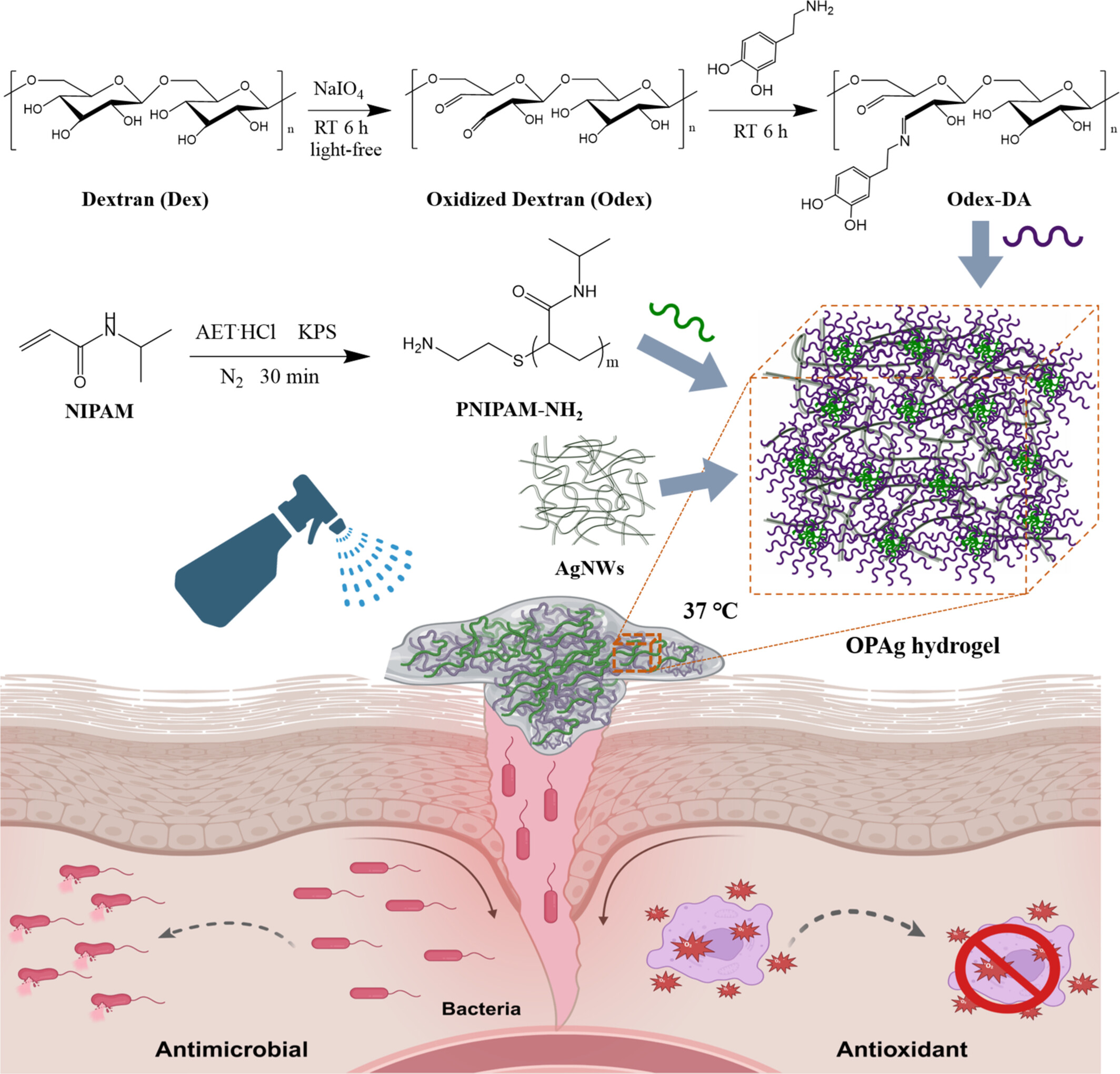
Potential Multi-Functional Sprayable Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide)/Dextran Hydrogel Dressings With Incorporation of Silver Nanowires
- First Published: 29 May 2025
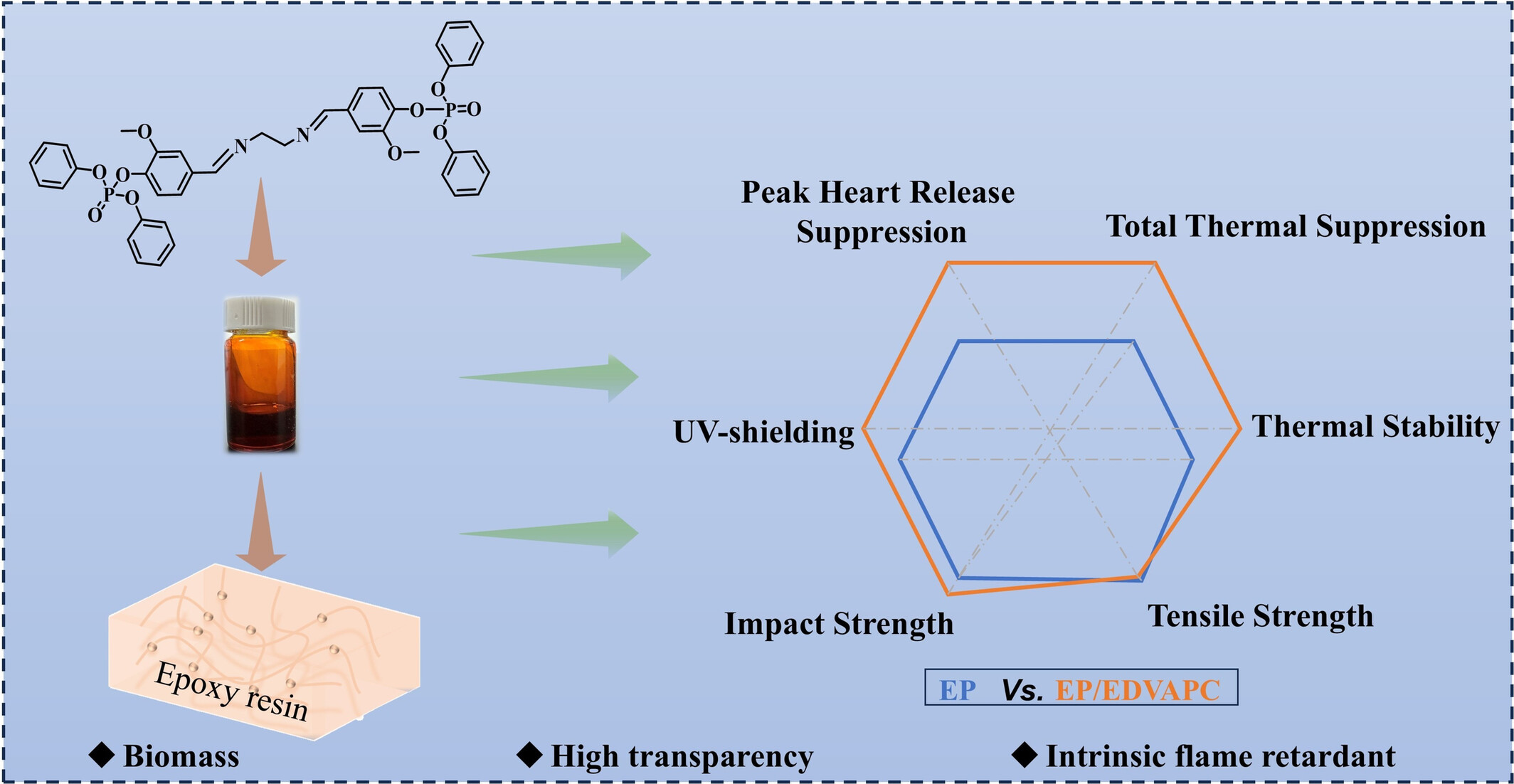
Synthesis of Novel Bio-Based Schiff Base Flame Retardant to Improve the Fire Safety of Epoxy Resin
- First Published: 05 May 2025
Mechanically Robust and Highly Transparent Polyurethane Elastomer With Excellent Adhesion Enabled by Hierarchical Hydrogen Bonds
- First Published: 02 May 2025
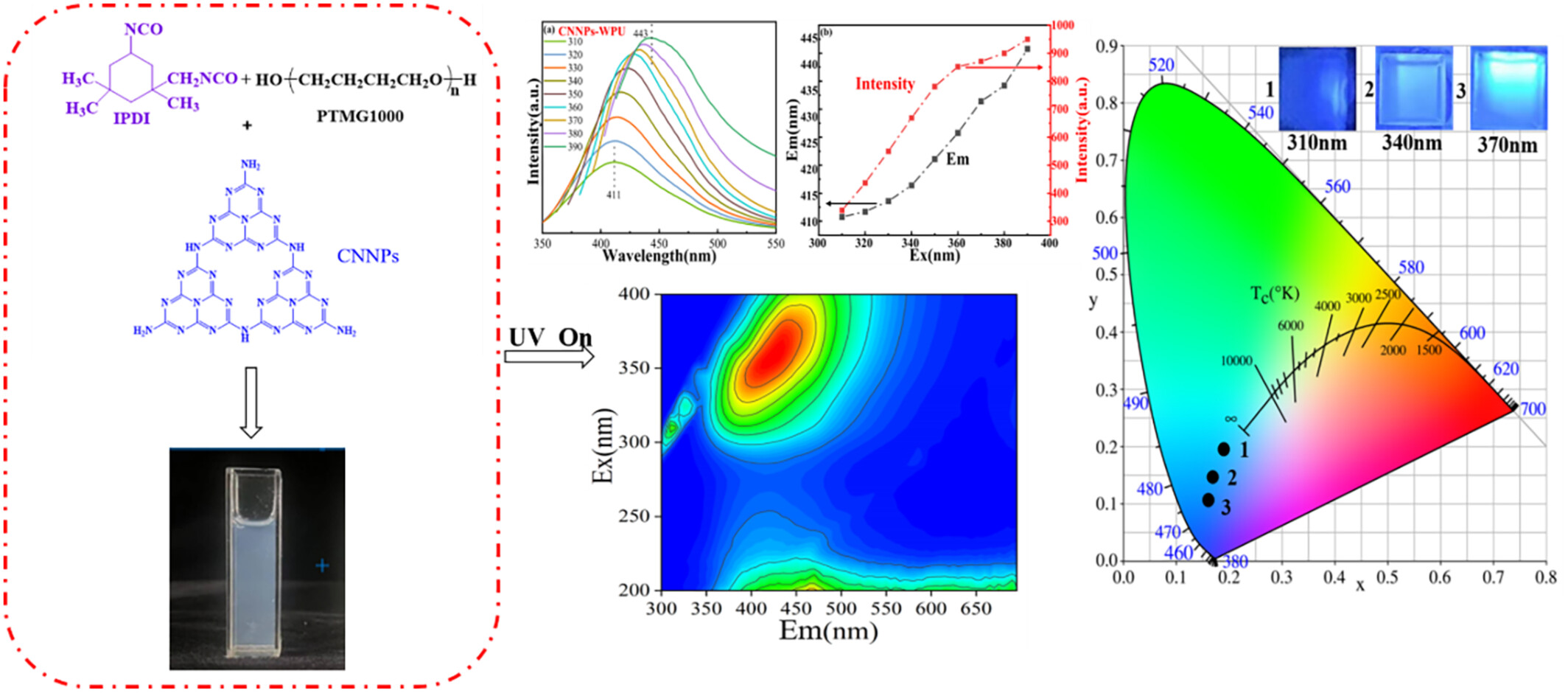
A Blue Tunable Waterborne Polyurethane-Based Carbon Nitride With Wide Excitation-Wavelength-Dependent Fluorescence
- First Published: 30 April 2025
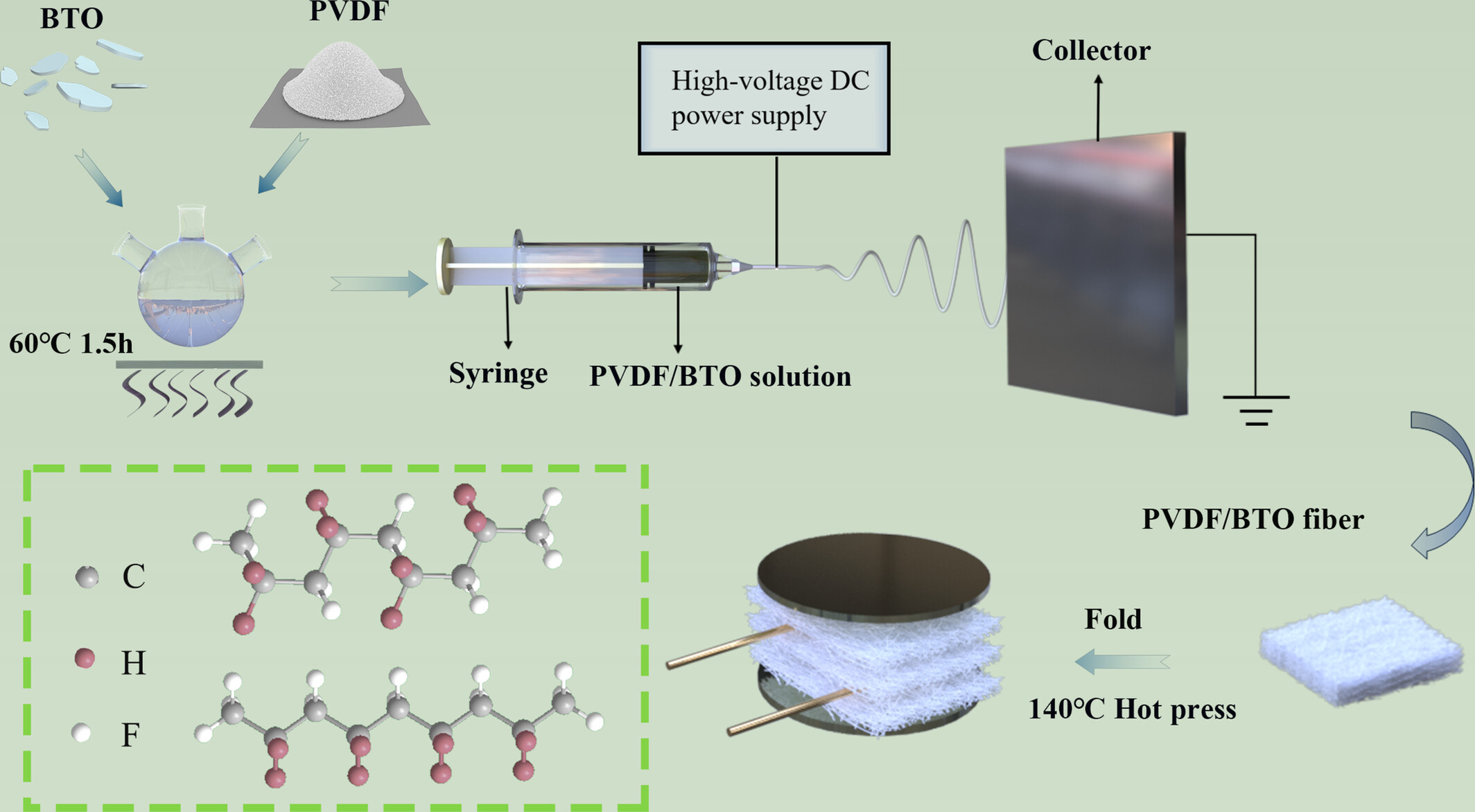
Preparation of High-Performance BTO/PVDF Piezoelectric Pressure Sensors Based on Soybean Rhizobacteria Mimicry Using Electrostatic Spinning-Thermal Pressing Method
- First Published: 30 April 2025
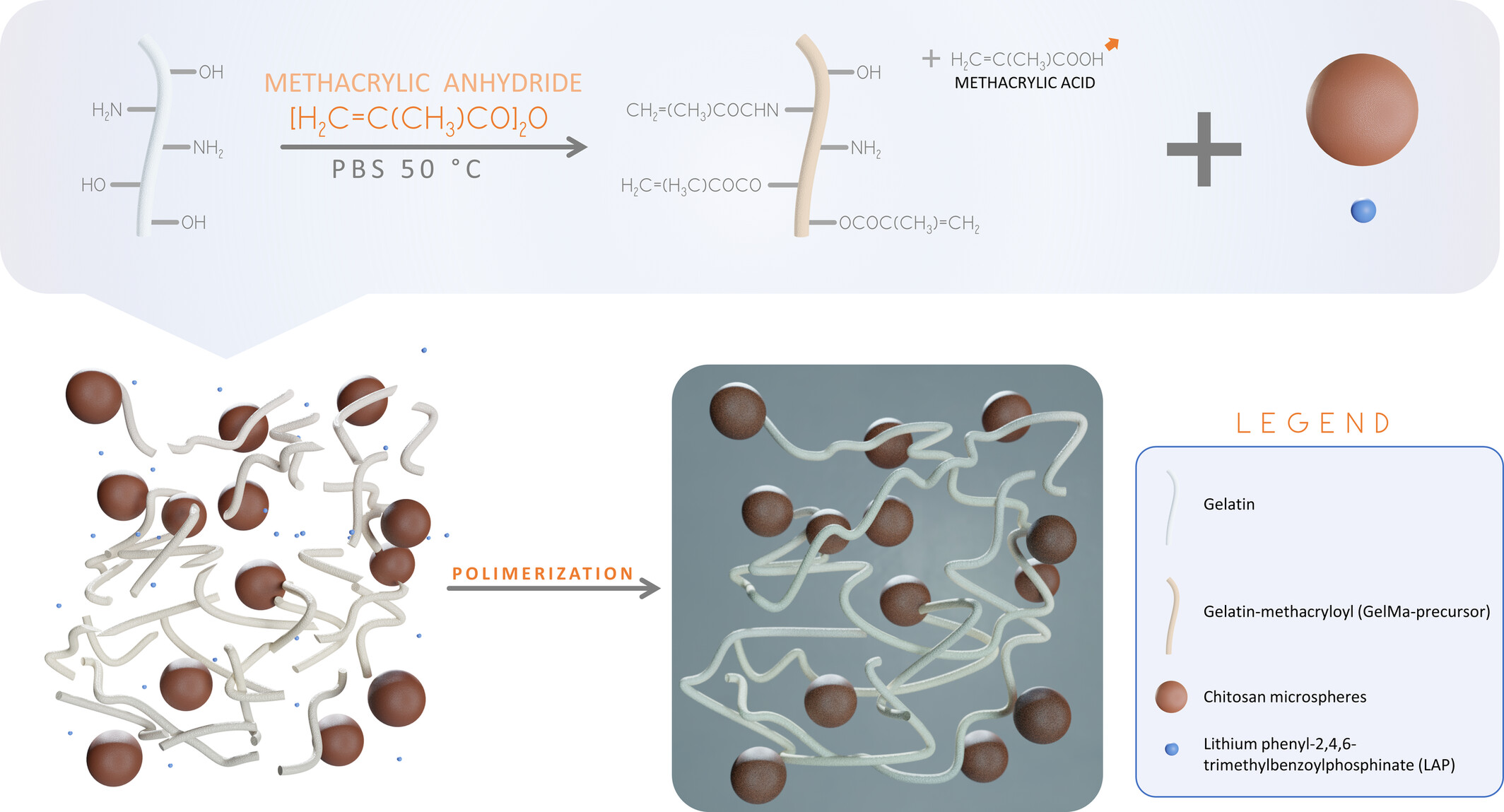
Simvastatin-Release Photocurable Hydrogel With Microsphere Delivery System for Improved Dental Applications
- First Published: 05 May 2025
Alkaline Stability Study of Poly(Norbornene)-Based Stereocyclic and Cross-Linked Anion Exchange Membranes
- First Published: 03 May 2025
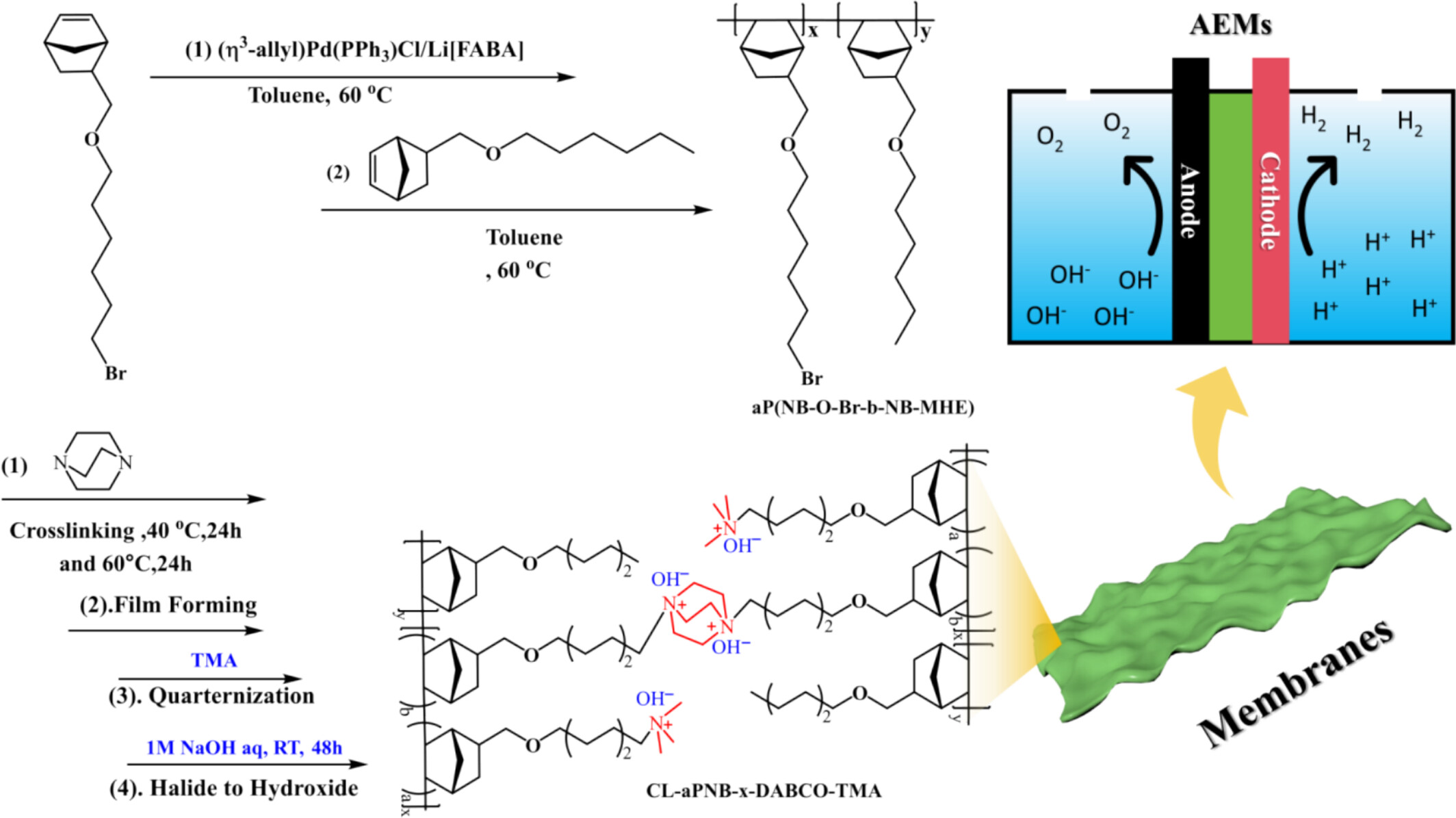
Our current work was to use allyl palladium chloride complex ((η3-allyl)Pd(Cl)PPh3) as a catalyst to catalyze the polymerization of 5-norbornene-2-methylenehexyl ether (NB-MHE) and 5-norbornene-2-methylene-(6-bromohexyl) ether (NB-O-Br), and under the action of the crosslinking agent 1,4-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane (DABCO), a series of CL-aPNB-x-DABCO-TMA with different crosslinking degrees were prepared. The designed decomposition temperature of the crosslinked AEMs was about 200°C. The OH− conductivity of CL-aPNB-5%-DABCO-TMA was 135.41 mS cm−1 at 80°C. The AEMs with the 20% crosslinking degree exhibited the best alkali-resistant stability, retaining 89.29% after 35 days, And the AEMs with the 5% crosslinking degree lost less than 20% after 35 days.
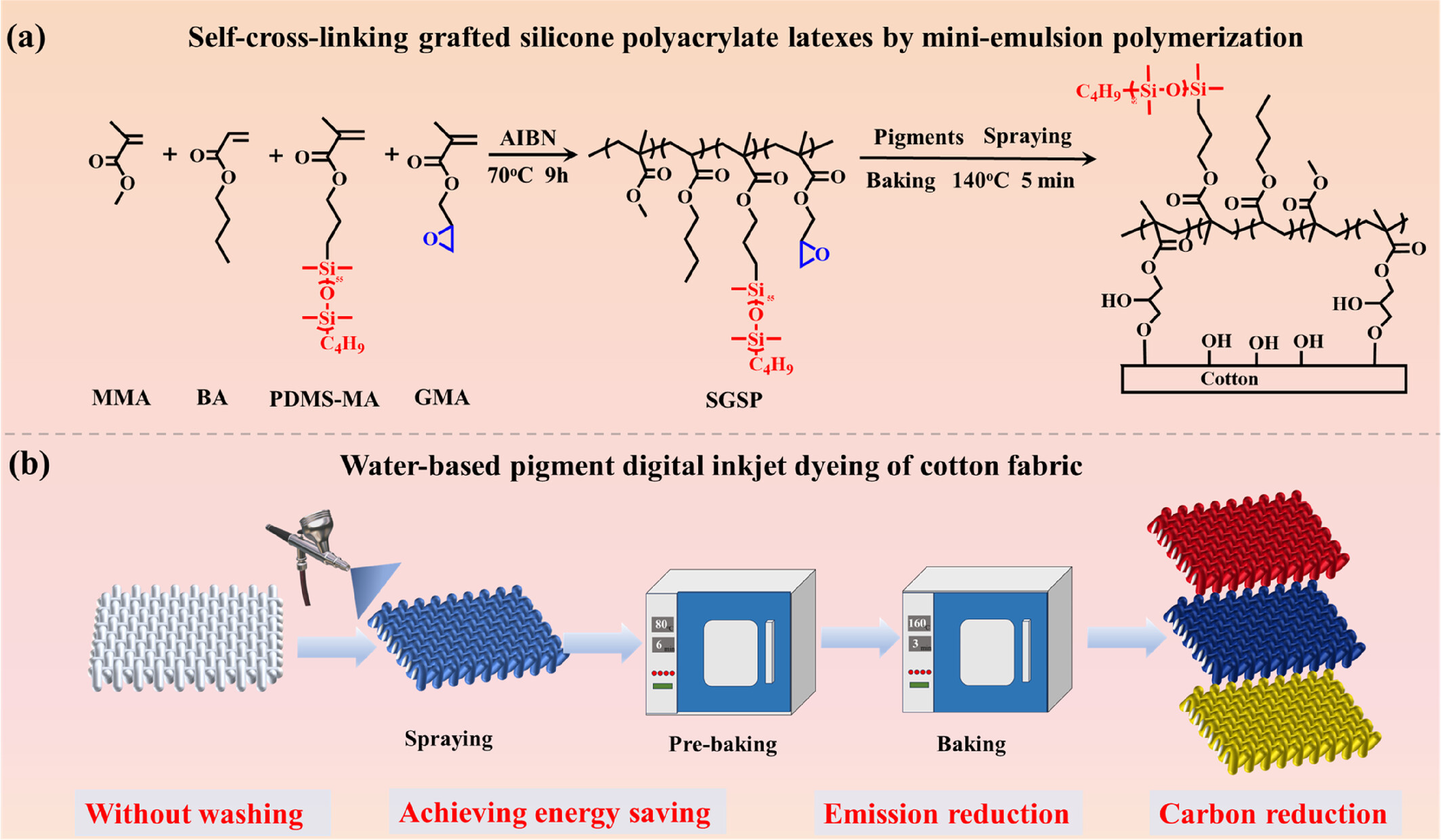
Water-Based Pigment Digital Inkjet Dyeing of Cotton Fabric Using of Self-Cross-Linking Grafted Silicone Polyacrylate Emulsions
- First Published: 05 May 2025
A Bilayered Electrospun Vascular Graft Enabling Differentiation of Adipose Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Toward Smooth Muscle Lineage
- First Published: 08 May 2025

A bilayered scaffold with an inner layer of electrospun polyvinyl alcohol co-ethylene and an outer layer of electrospun gelatin vinyl acetate copolymer and polycaprolactone blend is fabricated and characterized. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells are cultured on the scaffold, and differentiation to smooth muscle lineage using all-trans retinoic acid is performed and characterized. The bilayered scaffold provides an ideal matrix for vascular regeneration.
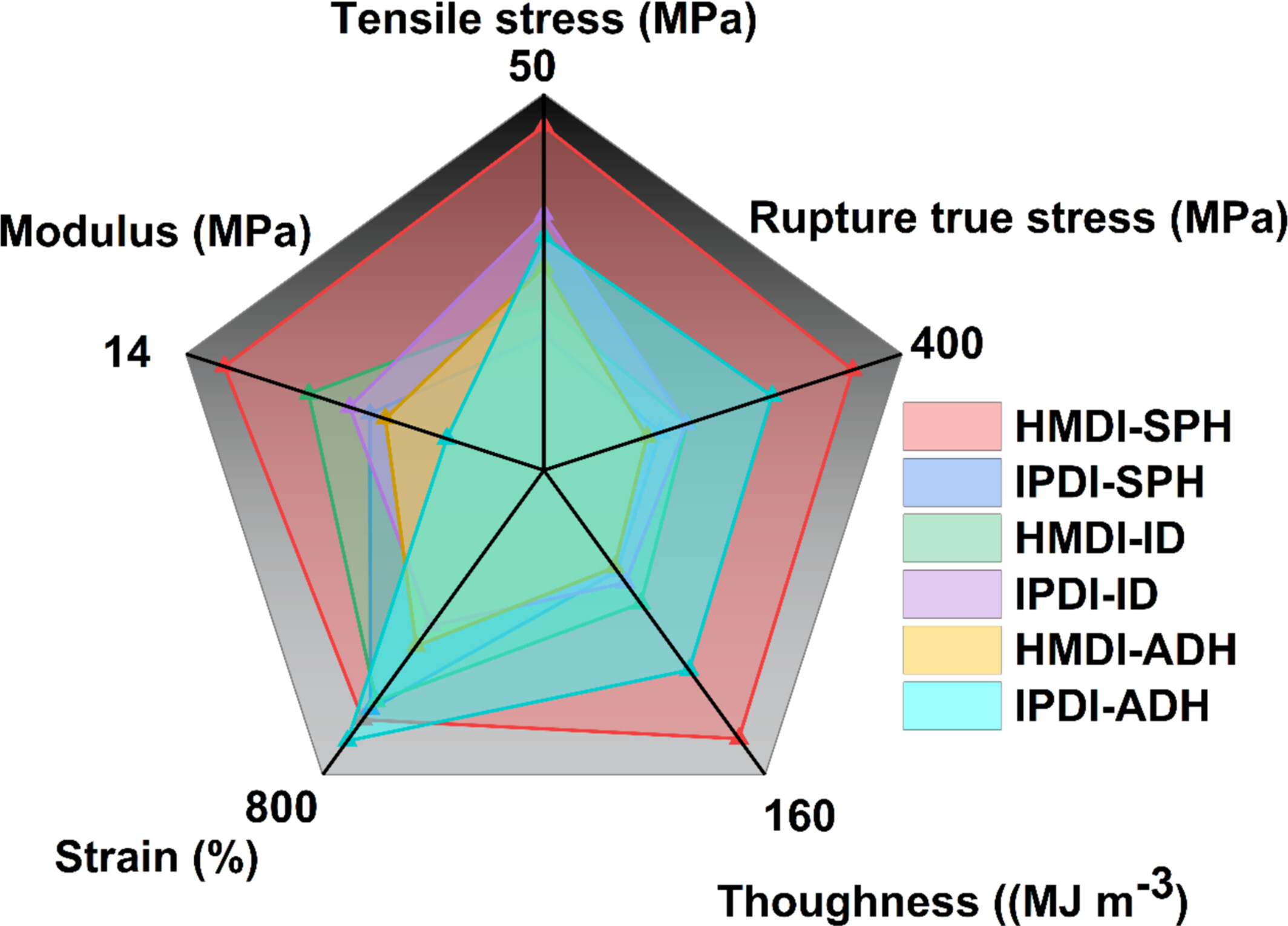
Polymerization Kinetics Optimization for Synthesizing Biobased Long Carbon-Chain Polyamide Elastomers With Tunable Hardness and Mechanical Properties
- First Published: 11 May 2025
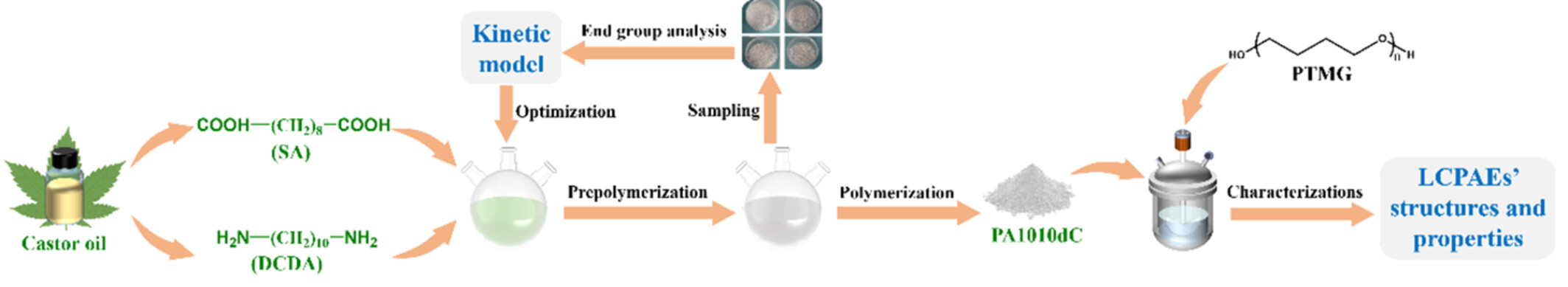
First, a stable and efficient polymerization process for synthesizing dicarboxylic-terminated polyamide 1010 prepolymer (PA1010dC) is obtained based on polymerization kinetics optimization. Subsequently, a series of biobased long carbon-chain polyamide elastomers (LCPAEs) with tunable hardness and mechanical properties is successfully prepared via changing the relative content of wholly biobased hard segments (PA1010dC) and soft segments (polytetramethylene ether glycol (PTMG)).
The Effect of Crosslinking Density and Carbon Black Content on the Performance of EPDM for CO2 Transport Applications
- First Published: 11 May 2025
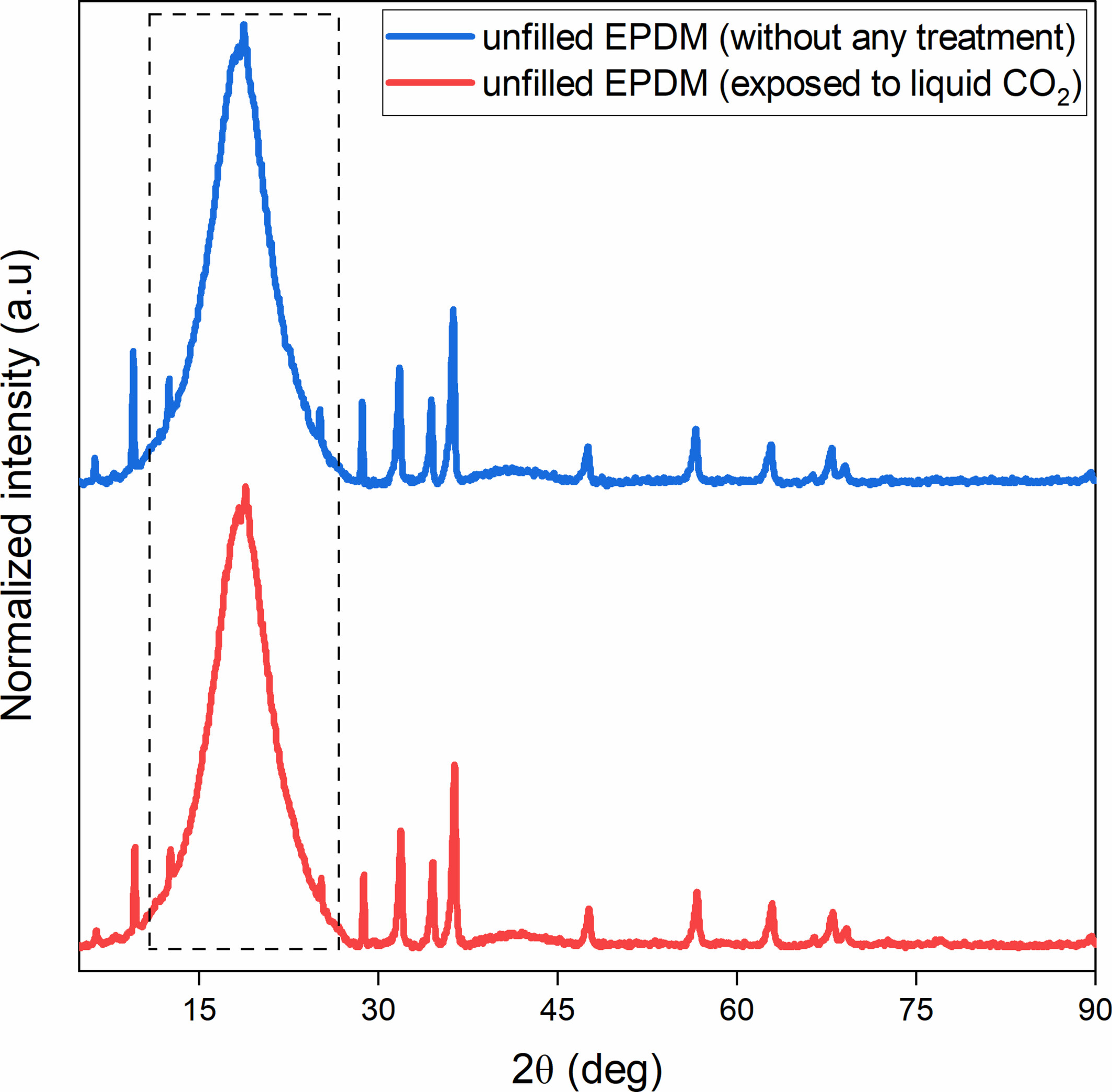
This study investigates EPDM compounds for CO2 transport systems. Carbon black significantly improves barrier properties, while crosslinking density has minimal impact. Liquid CO2 causes negligible extraction compared to organic solvents. Solvent extraction increases stiffness, enhancing barrier performance. WAXS analysis confirms the structural stability of the polymer after LCO2 exposure, suggesting its suitability for CO2 transport applications under relevant test conditions.
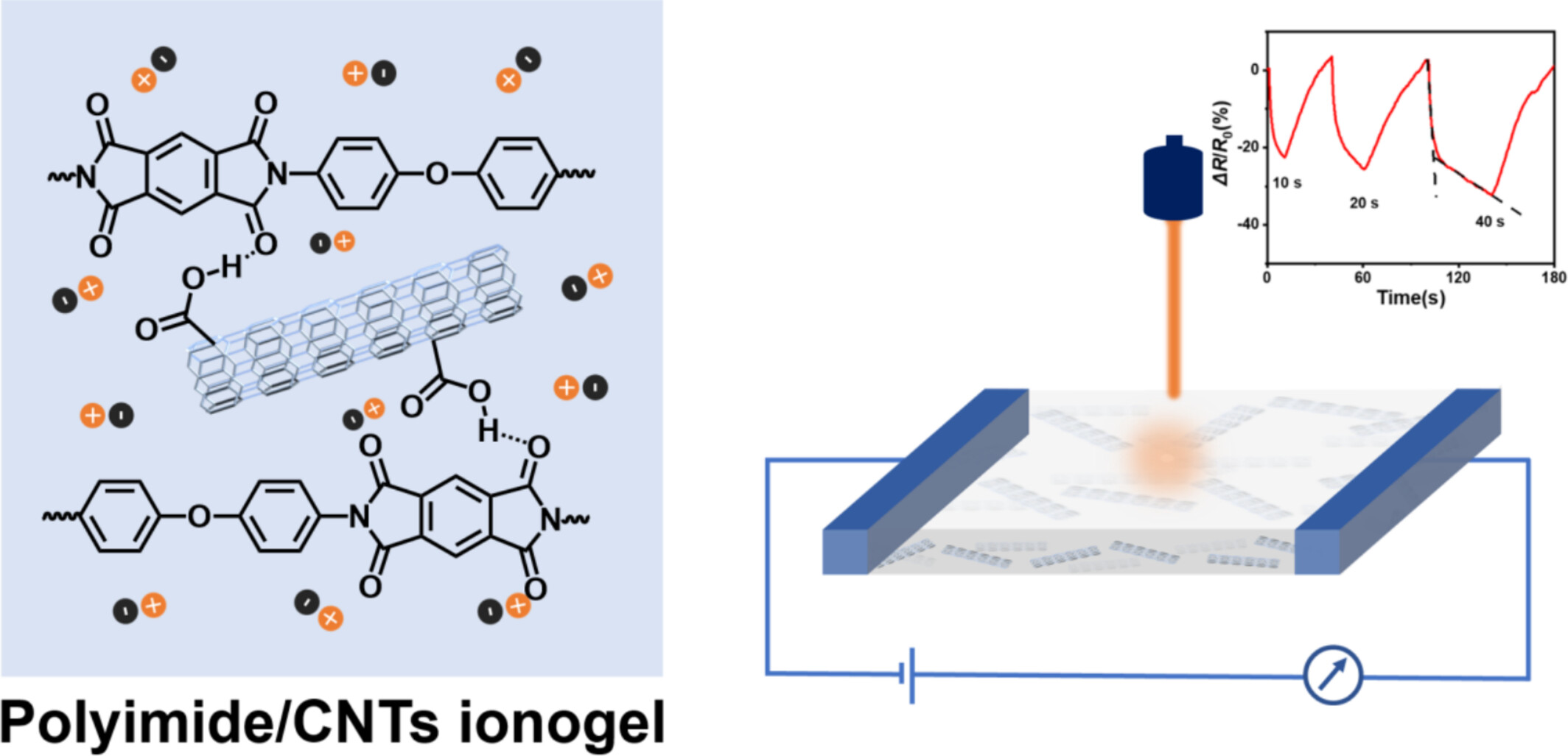
Polyimide/CNTs Ionogel for Application in Photo-Thermal-Resistance Response Materials
- First Published: 11 May 2025
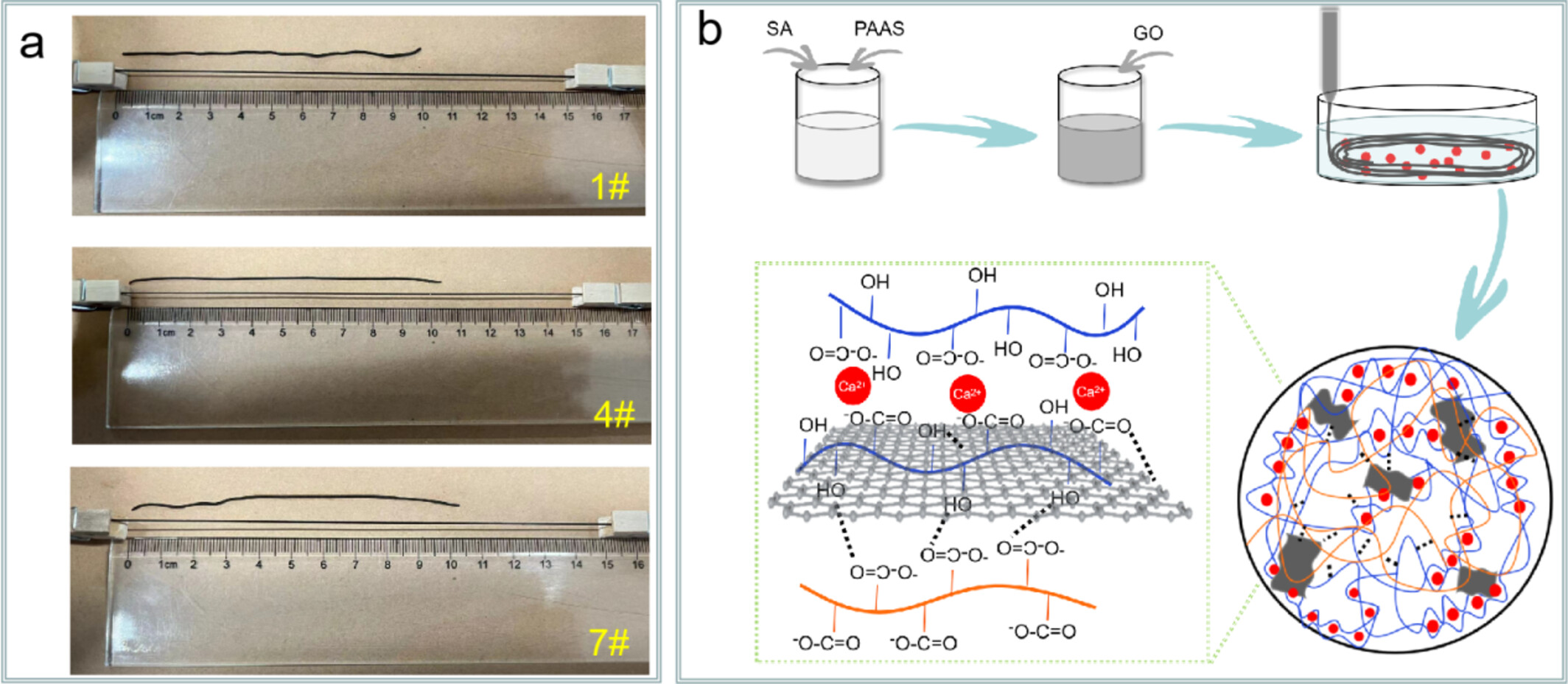
Preparation and Characterization of Sodium Polyacrylate/Sodium Alginate/Graphene Oxide Conductive Hydrogel Fiber
- First Published: 07 May 2025
A Process Optimization and Release Modeling of Coaxial Electrospun Aligned Core-Shell Poly (Ethylene Oxide-Poly(l-Lactide-Co-Glycolide)) (PEO-PLGA) Nanofibers Encapsulating Nerve Growth Factor
- First Published: 08 May 2025
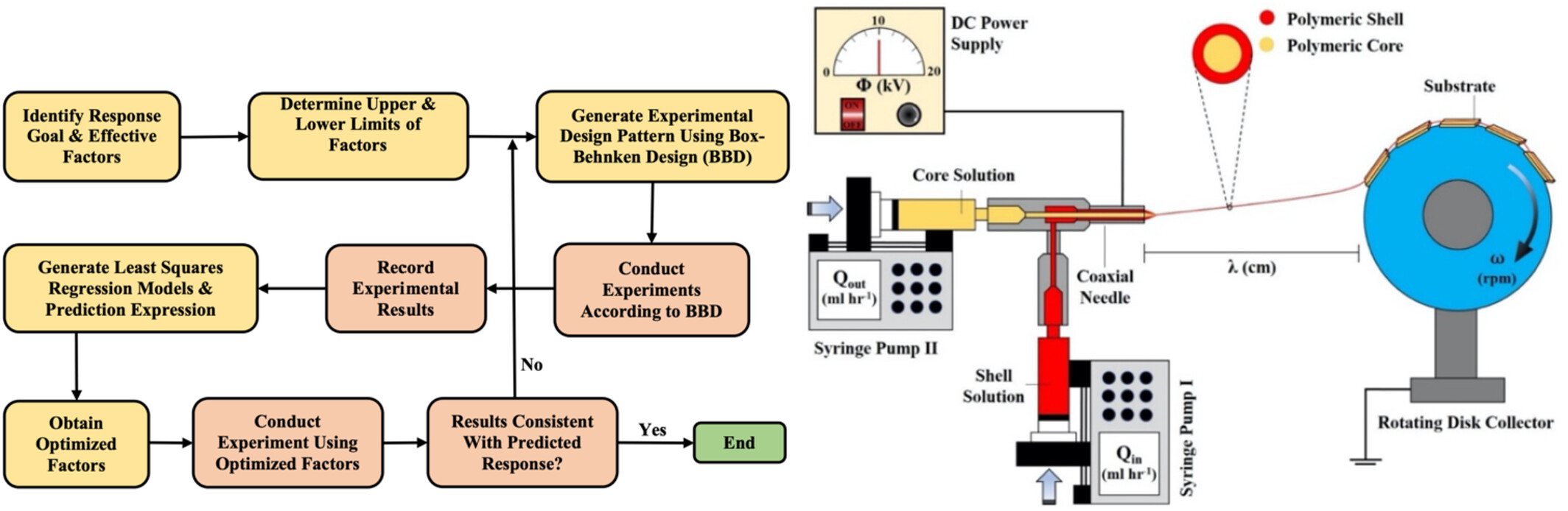
This work presents a more efficient and sustainable method for fabricating NGF-loaded, highly aligned core-shell nanofibers with minimal diameter and narrow size distribution. In this study, we employed a design-of-experiment approach to systematically investigate how controllable parameters in coaxial electrospinning influence the diameter and size distribution of aligned poly(ethylene oxide/poly(l-lactide-co-glycolide)) nanofibers loaded with nerve growth factor.
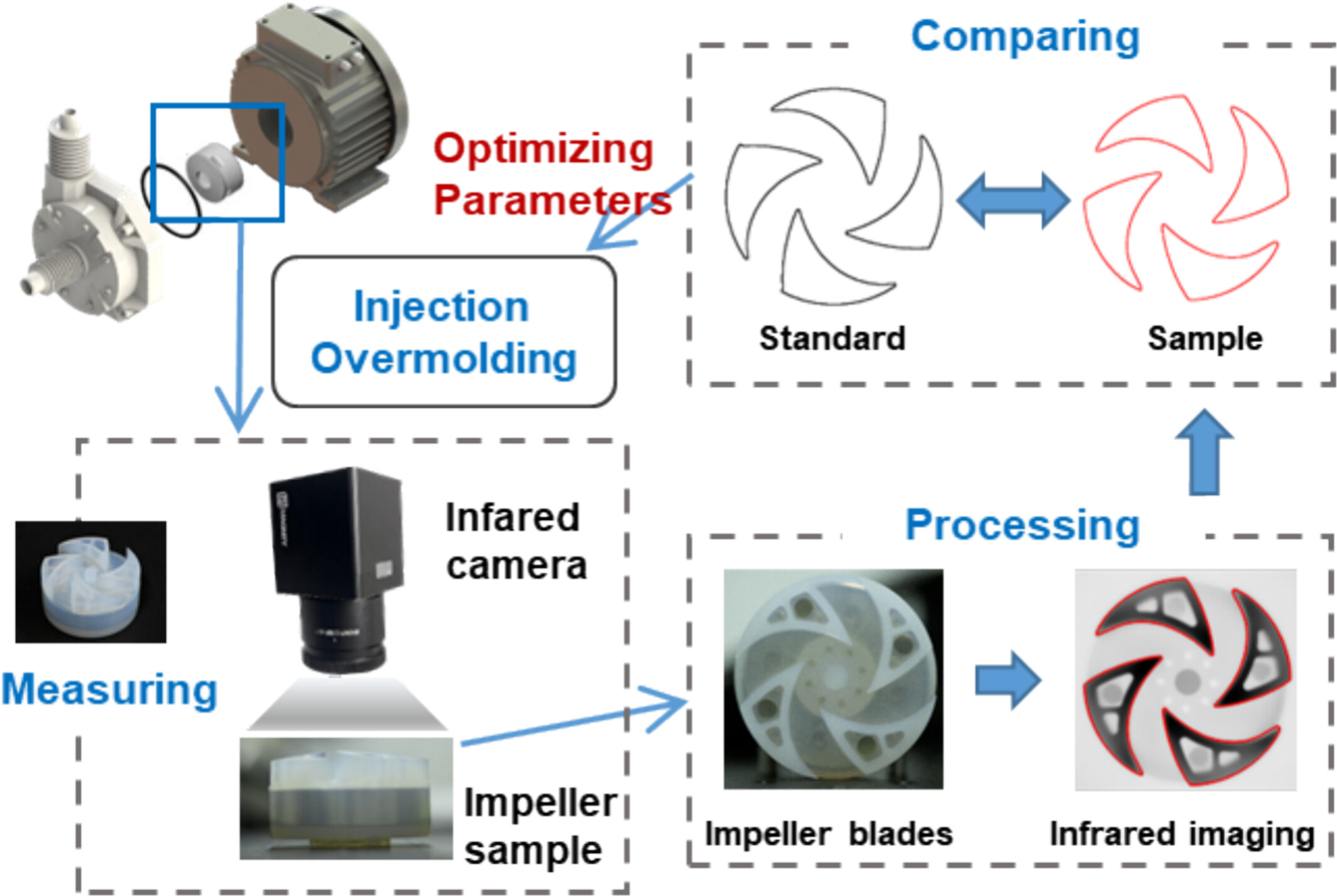
Optimization of Processing Parameters for Improved Complex Shape Accuracy in PFA Injection Overmolding
- First Published: 07 May 2025
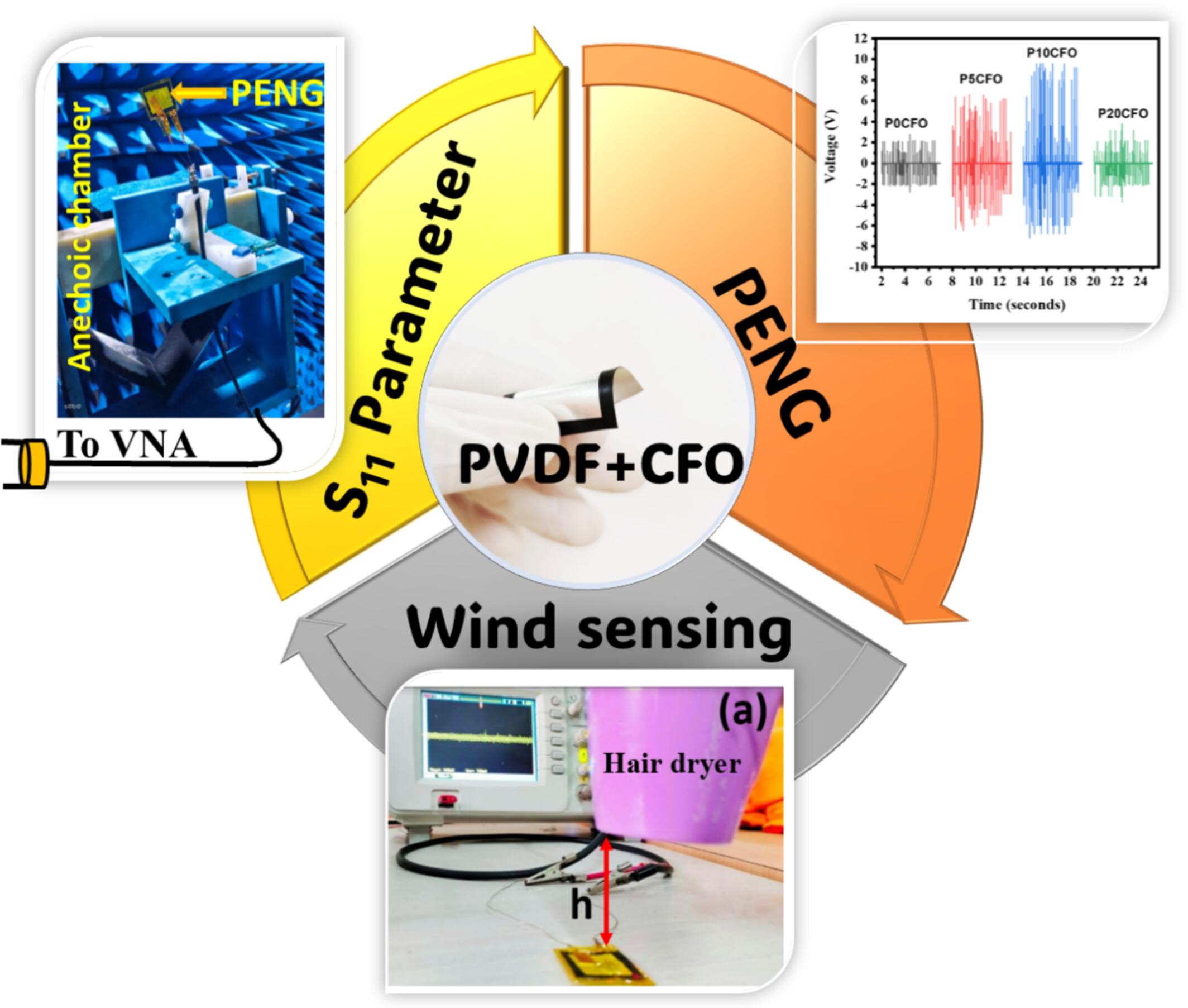
Microwave Absorption and Energy Harvesting Performance of Electroactive PVDF- CoFe2O4 Nanocomposites
- First Published: 11 May 2025
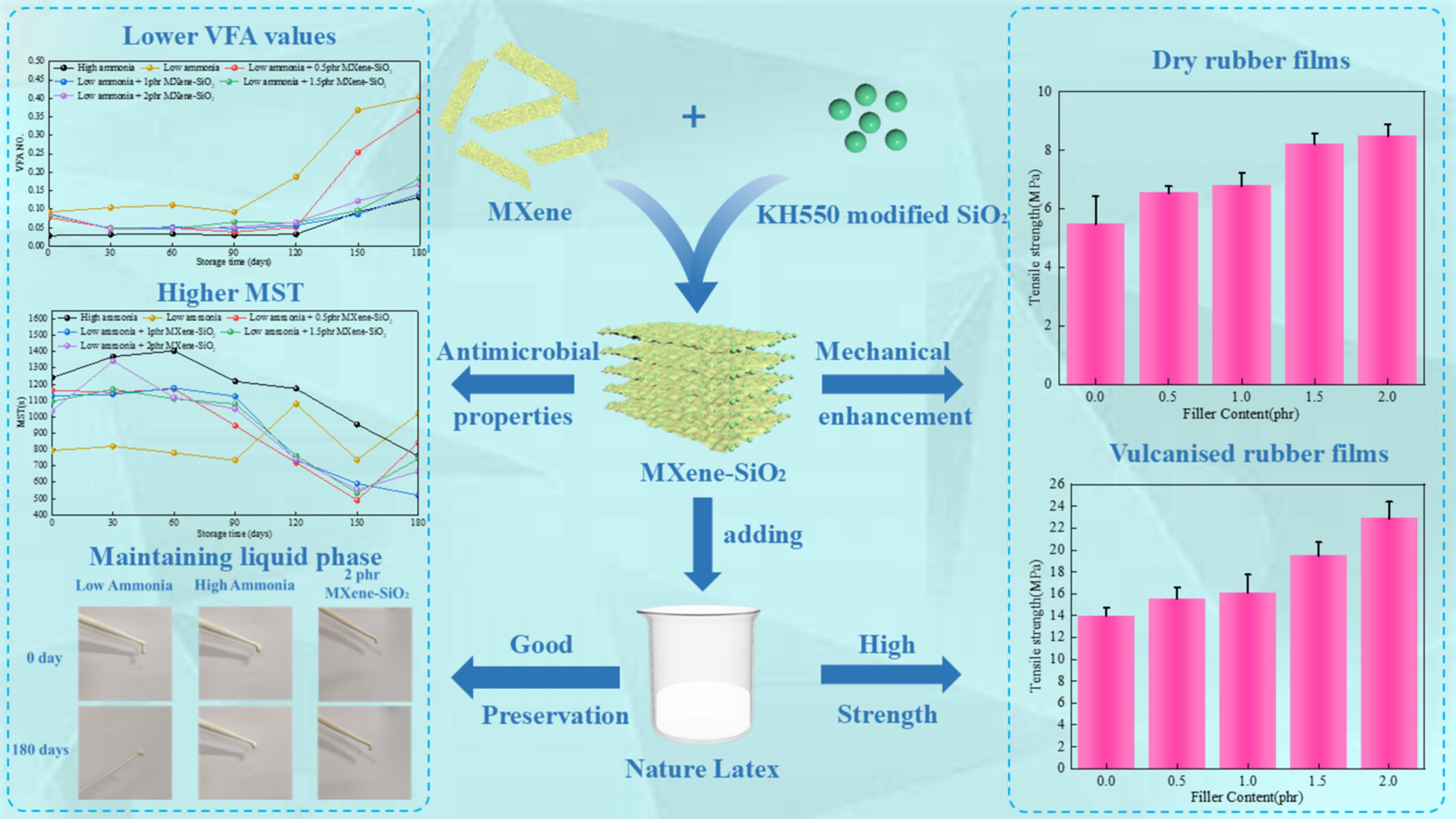
Low-Ammonia Preservation and Functional Reinforcement of Natural Rubber Latex Enabled by MXene-SiO2 Nanocomposites
- First Published: 08 May 2025
Statistics Specificity of the Adhesion Strength Origination Between Non-Crystalline Solids With Acutely Different Chain Mobility
- First Published: 13 May 2025
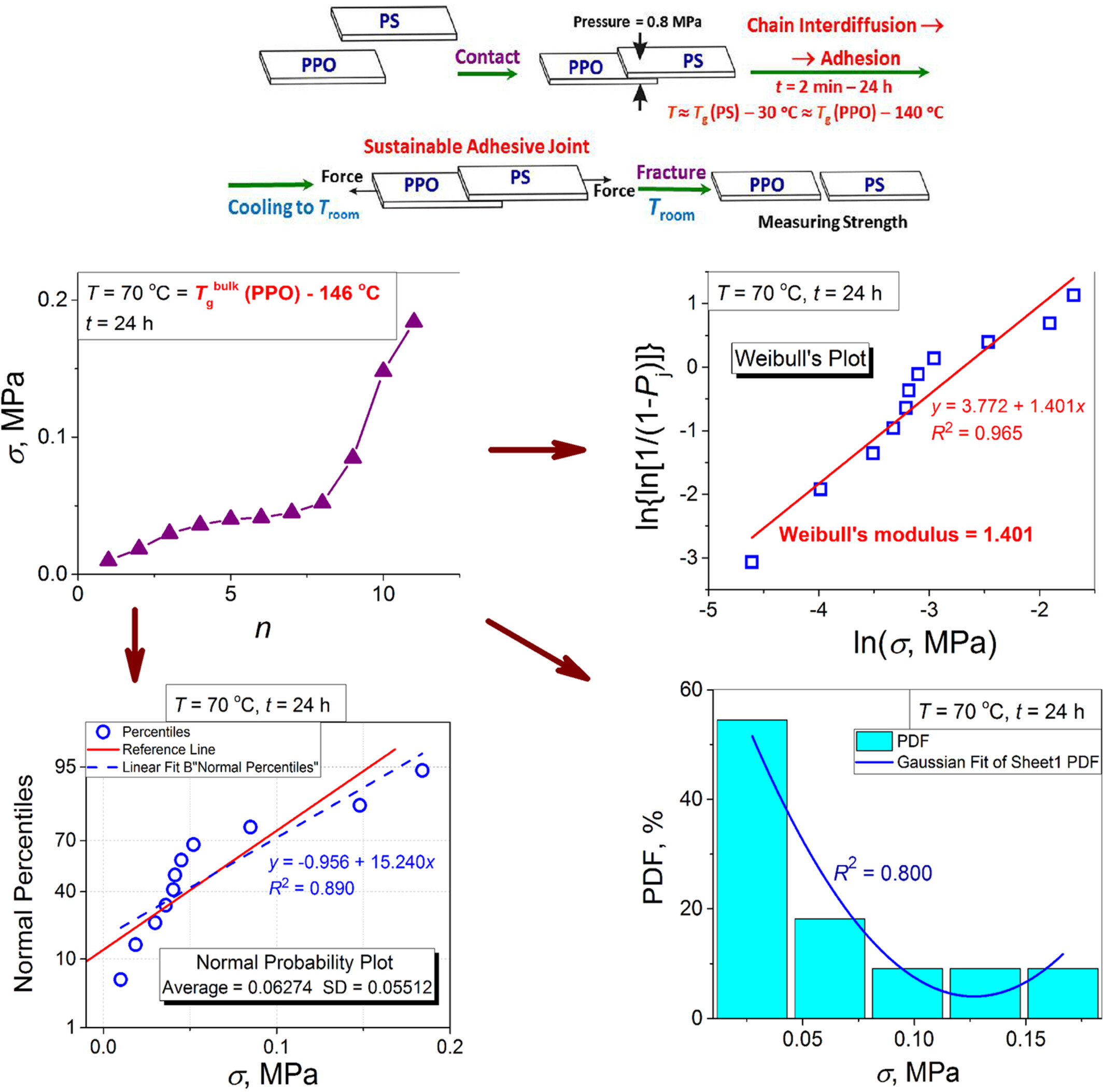
The distribution of the adhesion strength developed upon the adhesion origination at the interface between the specimens of polystyrene and poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene oxide), the polymers with acutely different intensities of chain mobility, is analyzed for its conformity to the Weibull and normal distributions using the Weibull and normal probability plots and by performing a series of standard tests for normality.
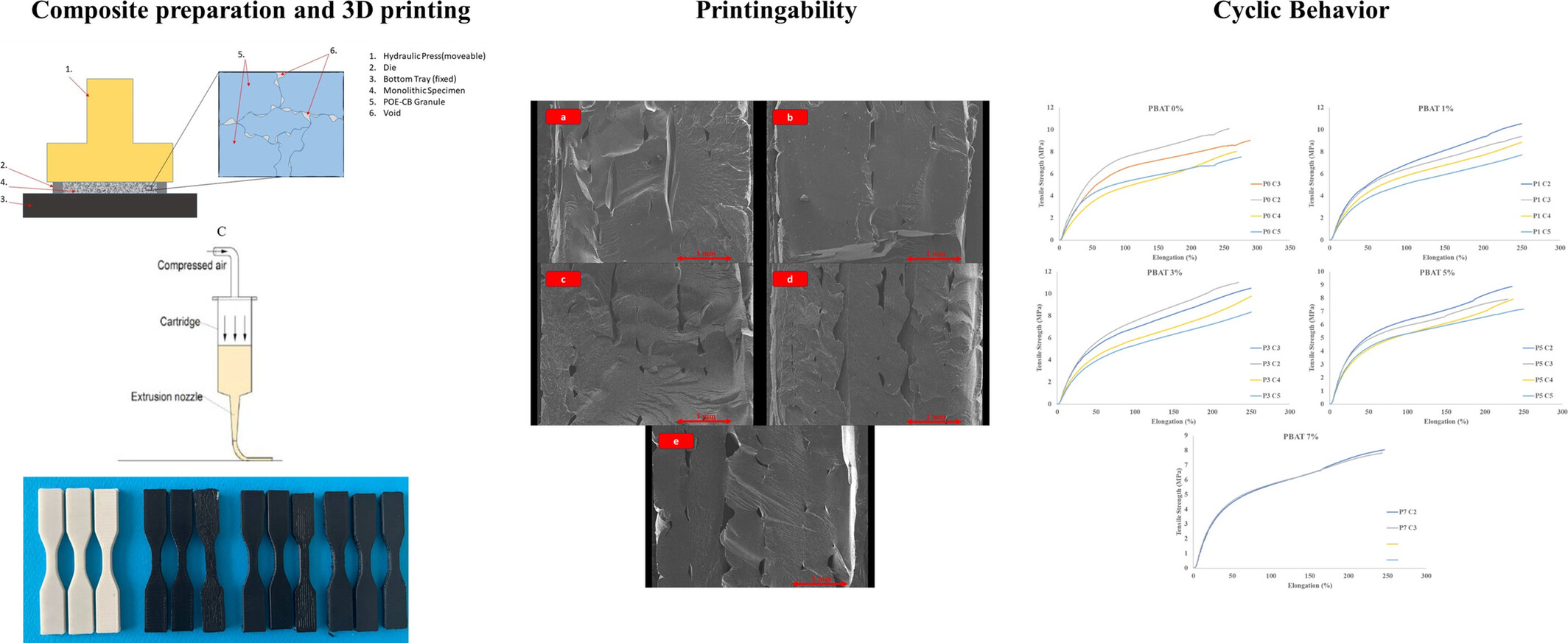
Comprehensive Investigation of 3D/4D-Printed Biodegradable PBAT-CB Composites: Thermal, Morphology, Cyclic Shape Memory, and Mechanical Properties
- First Published: 12 May 2025
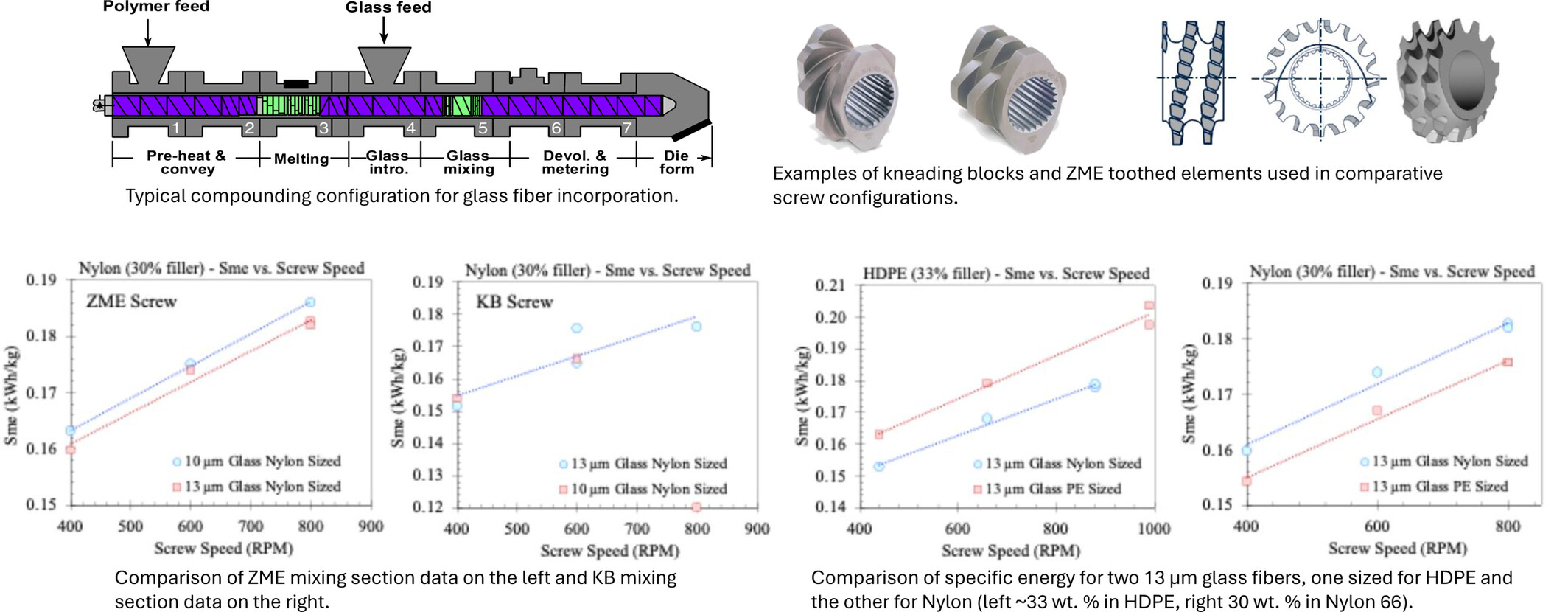
Compounding Fiber Reinforced Polymers: Process Development, Implementation, and Observations While Investigating the Impact of Surface Treatment and Screw Design on Fiber Unbundling, Breakage, and Distribution
- First Published: 15 May 2025
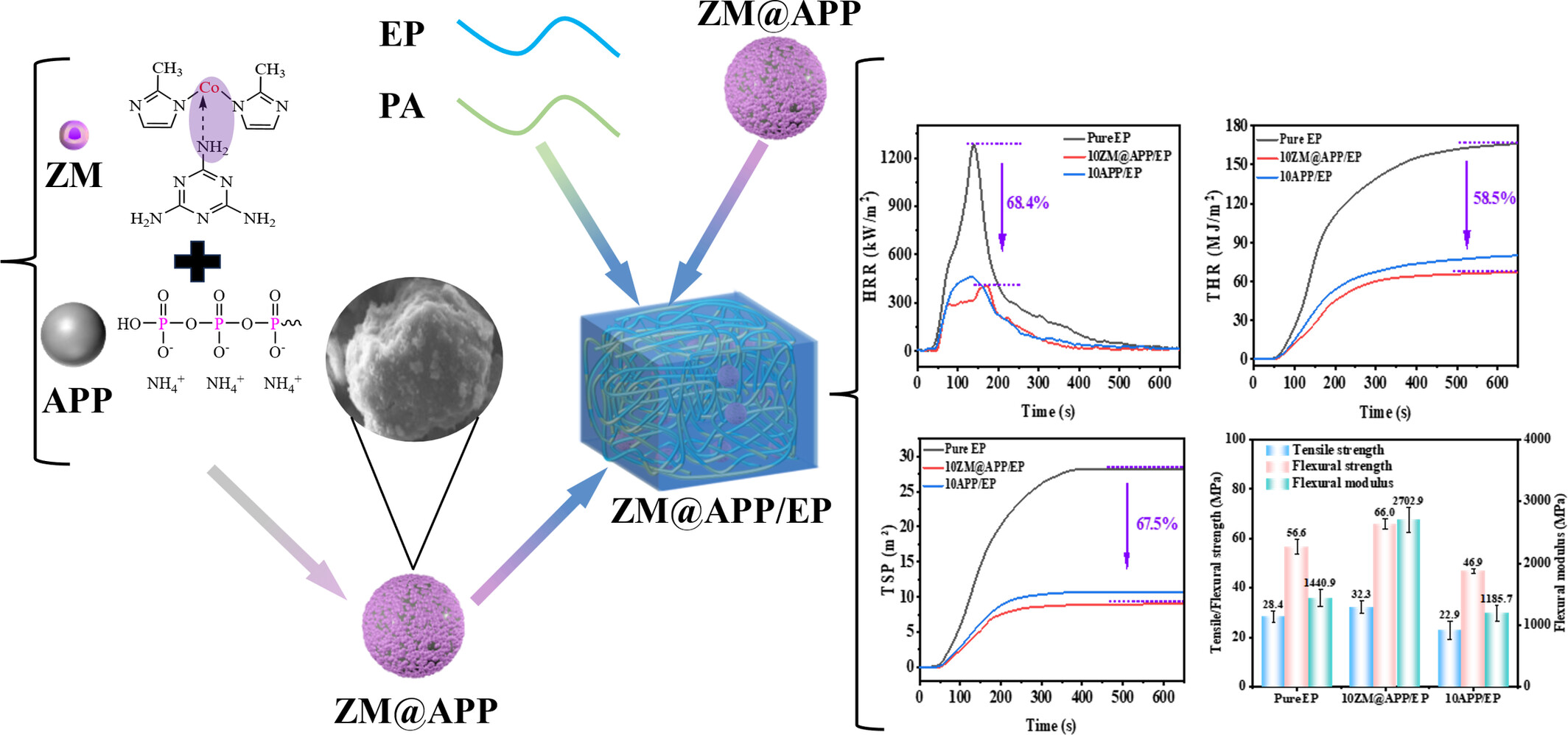
A Strategy for Designing Hierarchical Structure Flame Retardant ZM@APP for Improving Flame Retardancy, Mechanical Performance, and Smoke Suppression of Epoxy Resin
- First Published: 07 May 2025
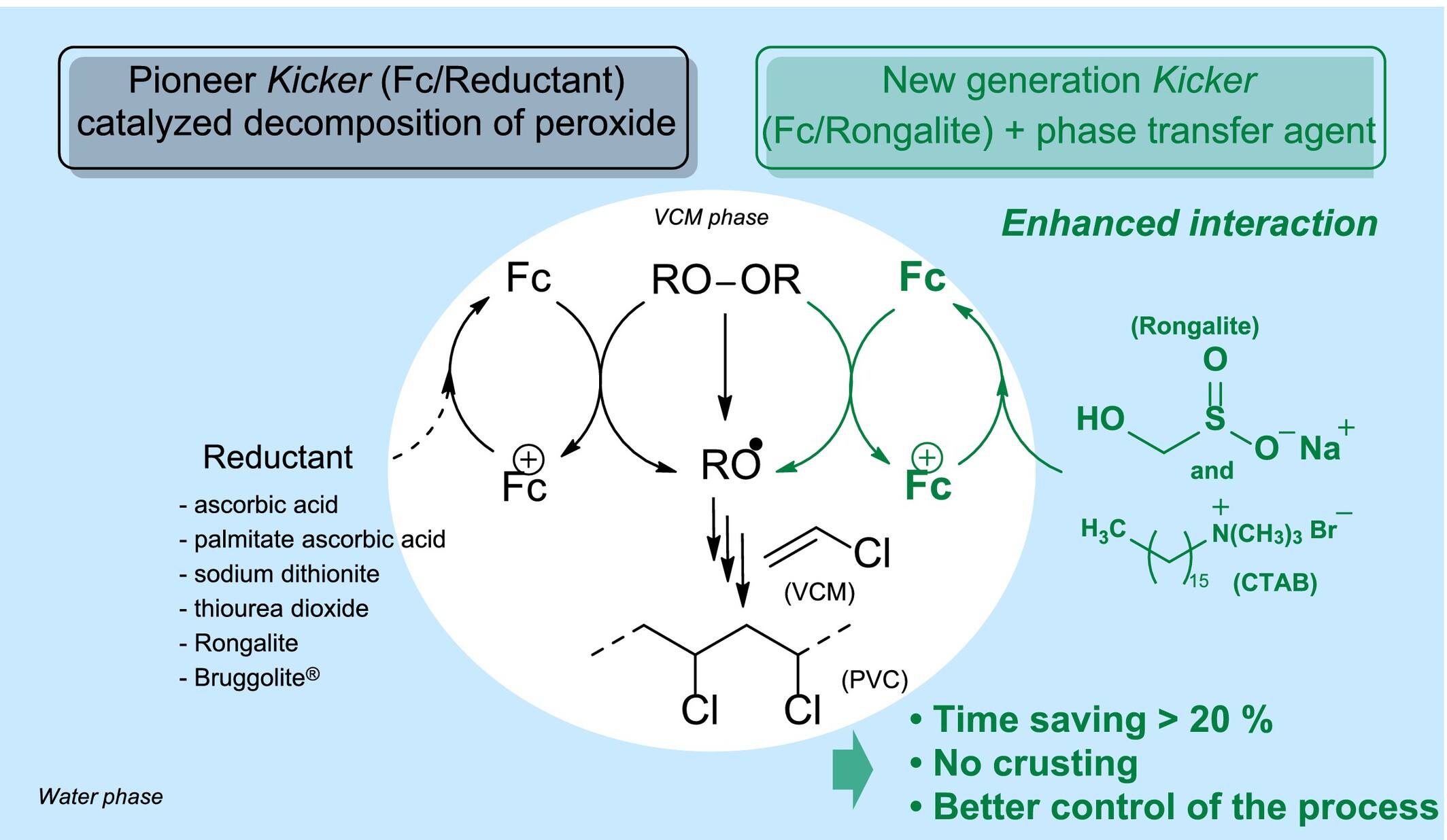
Ferrocene-Based Kickers for the Radical Polymerization of Vinyl Chloride Under Suspension Conditions: Improvement of the Process
- First Published: 10 May 2025
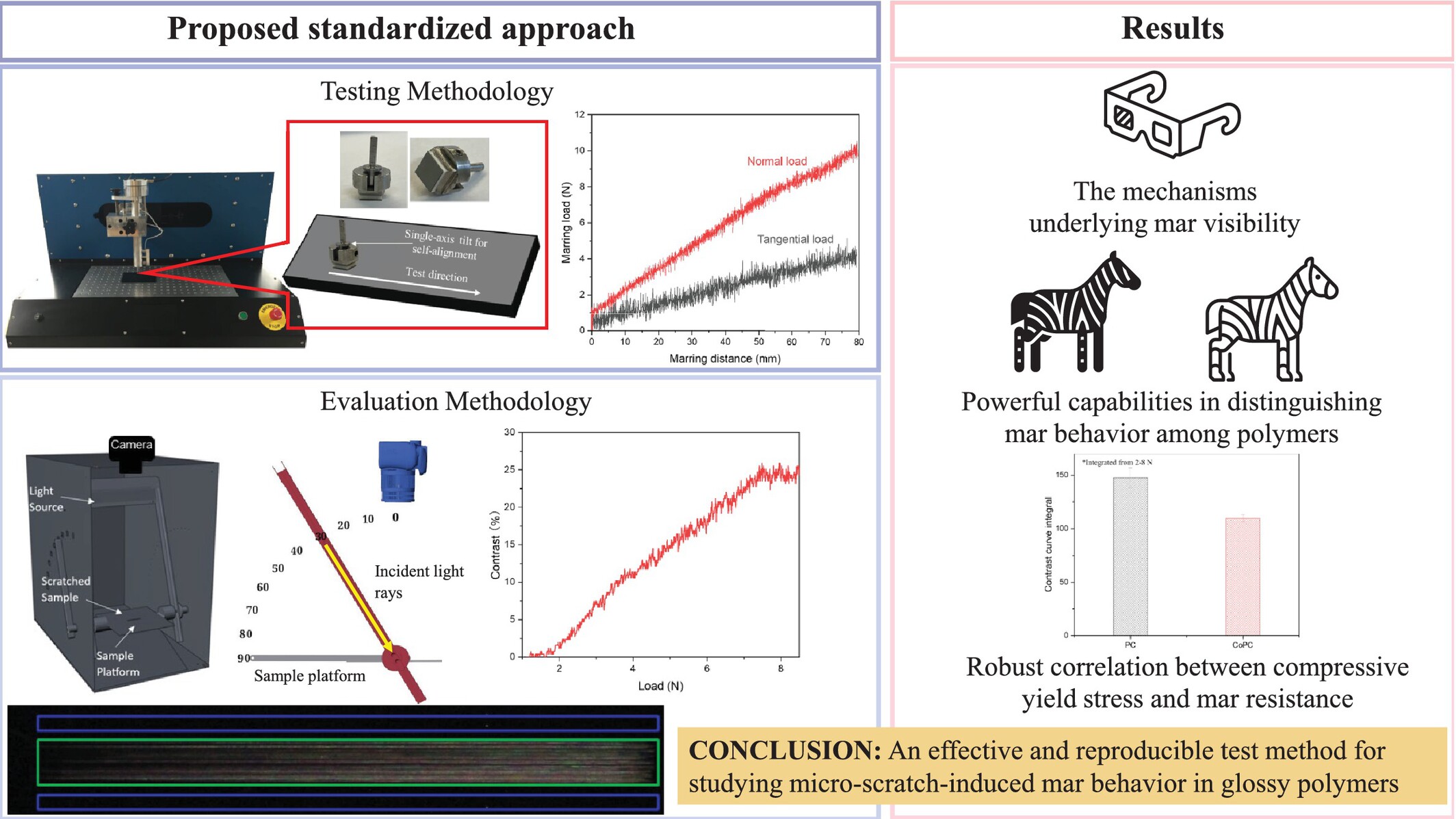
Evaluation of Roughening Mar Resistance of Glossy Ductile Thermoplastics
- First Published: 11 May 2025






![All-In-One 2D Intumescent Flame Retardants [Fe(OH)2]+ Anchored Melamine Trimetaphosphate (Fe@MAP) Enable Enhanced Flame Retardancy and Smoke Suppression of Epoxy Resins](/cms/asset/3a52b389-a10e-4e15-9e5f-3e62ea4917cd/app57272-toc-0001-m.jpg)