Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Research Articles
Fractional-order electronically controlled generalized filters
- Pages: 595-612
- First Published: 21 September 2016
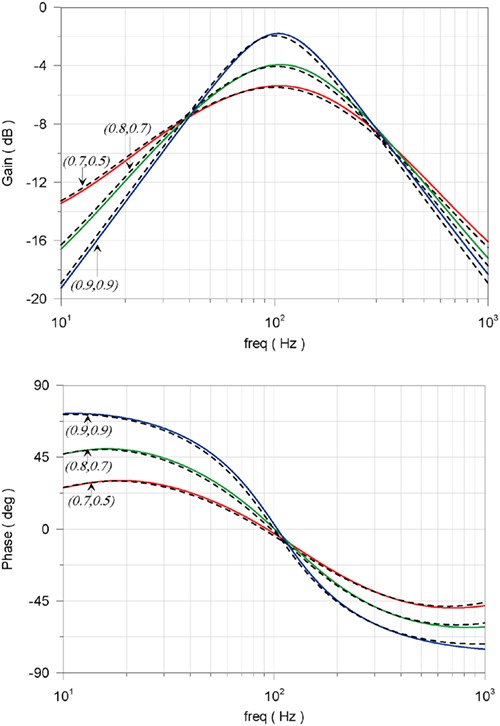
Novel topologies of fractional-order generalized filters are introduced in this paper. These offer the following benefits: (1) realization of lowpass, highpass, bandpass, allpass, or bandstop filter functions by the same topology; (2) resistorless realizations; (3) electronic adjustment of their frequency characteristics as well as their order; and (4) employment of only grounded capacitors. All the above have been achieved using Operational Transconductance Amplifiers as active elements and appropriate multi-feedback topologies. The behavior of the proposed designs is verified through simulation results using the Cadence IC design suite and the Design Kit provided by the Austrian Micro Systems 0.35-µm complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor process
A series-coupled LC quadrature oscillator using phase/amplitude calibration
- Pages: 613-624
- First Published: 19 December 2016
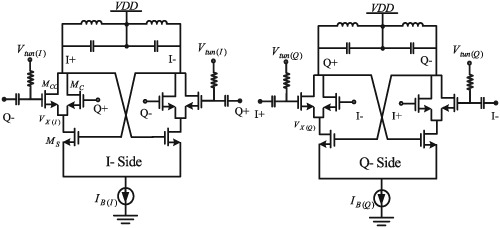
This work presents a phase and amplitude-tunable series coupled quadrature oscillator (PAT-SC-QO). Using added nMOS in parallel with coupling transistor and tuning its bias voltage can control output phase and amplitude. Also, the proposed SC-QO generates the phase shift in output current, which reduces resonator phase shift (RPS) in LC tank and causes phase noise improvement.
Numerical analysis of stochastic resonance in a bistable circuit
- Pages: 625-635
- First Published: 01 August 2016
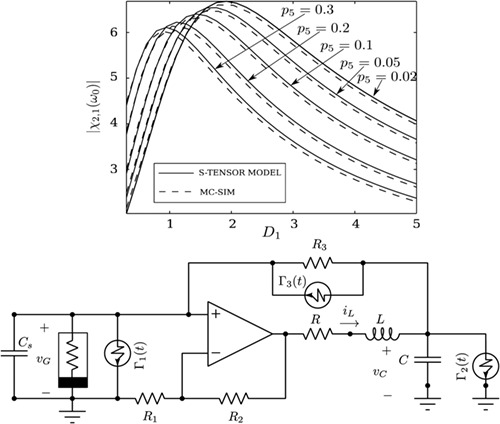
The paper details the development of a novel model representing a nonlinear circuit driven by noise. Simulations are performed in order to characterize the performance of the circuit demonstrating stochastic resonance. It is shown that reduced-order modelling of a higher-dimensional system will lead to incorrect results. The numerical analysis tools introduced herein have application for the design of nonlinear energy harvesters.
Amplitude and phase dynamics of noisy oscillators
- Pages: 636-659
- First Published: 20 September 2016
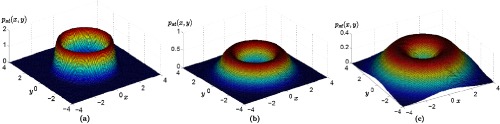
We derive amplitude and phase equations for nonlinear oscillators subject to white Gaussian noise. The equations derived are rigorous, and their validity is not limited to weak noise. It is shown that the phase variable coincides with the asymptotic phase in a neighborhood of a limit cycle. Two techniques for the solution of the phase and amplitude equations are discussed, i.e. asymptotic expansion and phase reduction. Formulas for the expected angular frequency, expected oscillation amplitude and amplitude variance are given.
Efficient and reliable fault analysis methodology for nanomagnetic circuits
- Pages: 660-680
- First Published: 08 September 2016
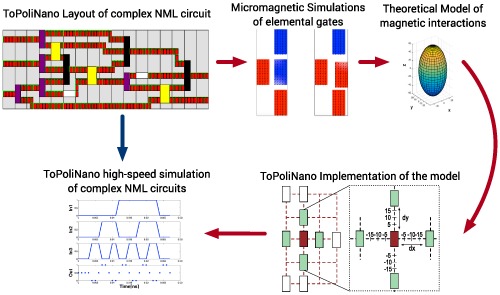
In this paper, a new methodology for taking into account defect due to process variations on emerging technologies has been elaborated. As a case study we have chosen NanoMagnetic logic technology. We developed a model (fanomag) for each basic magnetic blocks suitable for simulations in presence of defects. Starting from physical design of complex circuits, obtained with our CAD tool ToPoliNano, we simulated using fanomag the circuit behavior in presence of process variations using a MonteCarlo approach.
DC analysis and design of a PWM buck converter operated as a dynamic power supply
- Pages: 681-706
- First Published: 10 October 2016
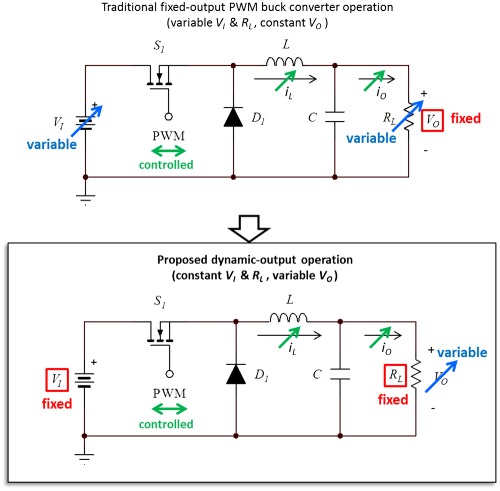
This paper examines the dc operation of an asynchronous PWM buck converter as a stand-alone dynamic power supply with variable output voltage. Complete dc analysis and a design procedure are derived and verified experimentally. This unique variation on the standard PWM dc-dc converter topology offers efficient, direct control of the output voltage when converter input voltage and load resistance are fixed.
A new bridgeless buck PFC rectifier
- Pages: 707-719
- First Published: 17 August 2016
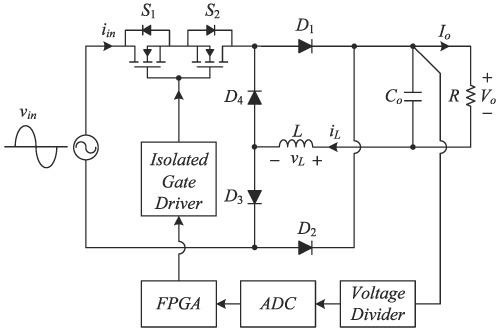
In this study, a new bridgeless buck power factor correction (PFC) rectifier is presented. The proposed buck PFC rectifier is designed to operate in the discontinuous conduction mode. Because of the discontinuous conduction mode operation, the control scheme of the proposed buck PFC rectifier is simple and easy, and the reverse recovery problem of the diodes can be alleviated. Because the input current follows the input voltage naturally, the current loop circuit is not required. Thus, only the traditional voltage-mode control is employed to sense the output voltage, and a suitable control effort for the proposed buck PFC rectifier is generated to drive the power switches. Consequently, the output voltage of the proposed buck PFC rectifier can be kept at a desired value. Finally, the mathematical deductions and experimental results are provided to verify the effectiveness of the proposed bridgeless buck PFC rectifier.
Letter
An offset cancellation technique of complementary input pair buffers for continuous time applications
- Pages: 720-726
- First Published: 24 August 2016
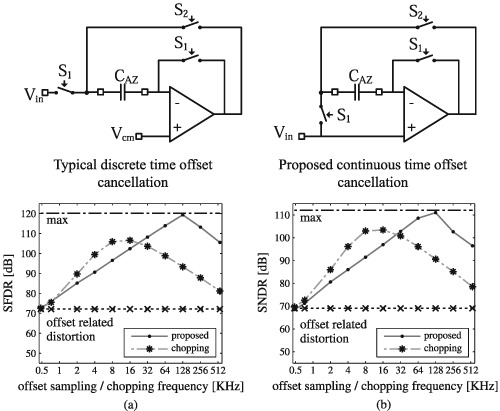
An offset cancellation technique for complementary input amplifiers in unity gain buffer configuration that overcomes the variable offset and minimizes distortion is presented. The proposed technique is geared toward continuous time applications. Simulation results show up to 40 dB increase in spurious-free dynamic range and up to 30 dB increase in signal-to-noise and distortion ratio. Buffering a continuous time modulator, the proposed technique matches the performance of chopping amplifier. Measurement results verify the technique, illustrating effective offset cancellation regardless of the input signal level.




