Diabetic Medicine focuses on disseminating research on all aspects of diabetes to improve the management of people with the disease. This hybrid open access journal is the official title of Diabetes UK, which over the last decade has invested £67+ million in diabetes research. Diabetic Medicine provides a forum for the exchange of ideas and knowledge between clinicians and researchers worldwide.
Journal Metrics
- 6.9CiteScore
- 3.4Journal Impact Factor
- 20%Acceptance rate
- 7 days Submission to first decision
Diabetic Medicine is inviting applications for Handling Editor roles
This is an exciting opportunity to become involved in the development and management of an academic journal with a global profile. We welcome applications from researchers at all career stages who are passionate about shaping the research agenda and building broad networks and communities in their field.
For more information about the role, click here.
Deadline for applications: 31st August 2025
Featured
Articles
The predictive value of cumulative plantar tissue stress on future plantar foot ulceration in people with diabetes—A 12‐month prospective observational study
- 31 July 2025
Illustrating stories of stigma from the perspective of people living with diabetes while experiencing homelessness: An arts‐based community participatory research project
- 29 July 2025
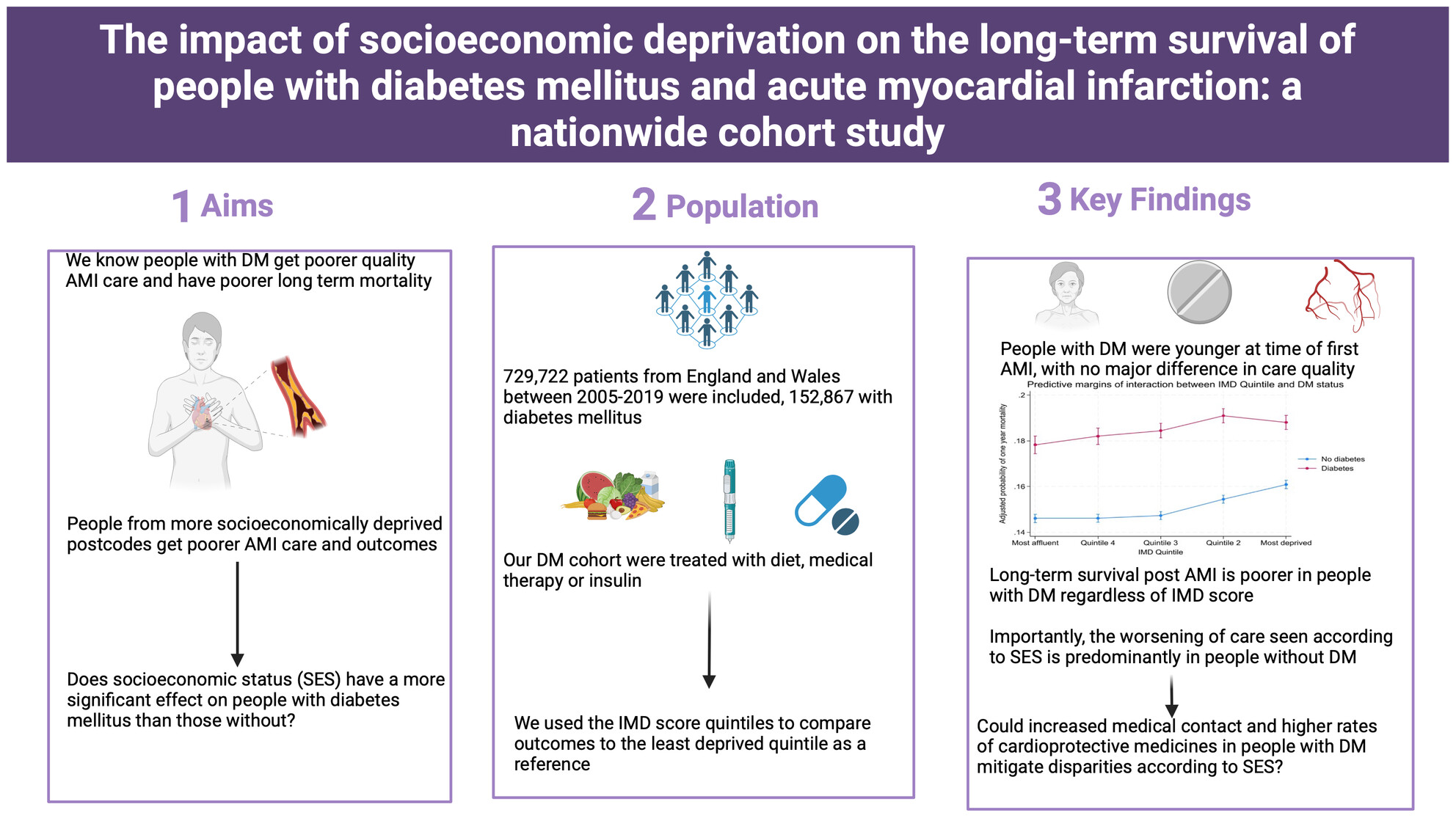
The impact of socio‐economic deprivation on the long‐term survival of people with diabetes and acute myocardial infarction: A nationwide cohort study
- 28 July 2025
Satisfaction with continuous glucose monitoring and diabetes care among hospitalised patients with type 2 diabetes managed by inpatient diabetes teams
- 28 July 2025
The following is a list of the most cited articles based on citations published in the last three years, according to CrossRef.
Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Provisional report of a WHO Consultation
- 539-553
- 19 July 2004
Metabolic syndrome—a new world‐wide definition. A Consensus Statement from the International Diabetes Federation
- 469-480
- 20 April 2006
Twenty‐five years of diabetes distress research
- 393-400
- 22 October 2019
What's new?
- Diabetes distress is common among people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes, and is associated with lower levels of self-care, general emotional well-being and possibly metabolic outcomes of diabetes care.
- Whilst there has been a wealth of research on diabetes distress, we have limited data to show that distress is associated with the development of long-term complications of diabetes, and we have little insight into how diabetes distress develops.
- There is emerging evidence that the way healthcare professionals communicate with people with diabetes may be exacerbating the distress experienced by people with diabetes, or possibly contributing to its development.
- Healthcare professionals need to ensure that the way they communicate with people who have diabetes does not add to the distress that diabetes engenders.
- We need to embed the assessment and management of diabetes distress into the routine diabetes care services we offer people with diabetes.
The cost of diabetic foot ulcers and amputations to the National Health Service in England
- 995-1002
- 19 April 2019
What's new?
- At least 2% of people with diabetes experience new foot ulcers annually, and one in 400 undergoes amputation.
- The cost of diabetic foot disease in England is almost 1% of the health service budget.
- More than 90% of these costs are for ulcer care.
- It is hoped that knowledge of human and financial costs will increase research effort, clinical attention and compliance with national guidance, to improve ulcer healing rates and reduce amputations.
Recent issues
- Volume 42, Issue 8August 2025
- Volume 42, Issue 7July 2025
- Volume 42, Issue 6June 2025
- Volume 42, Issue 5May 2025