Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Articles
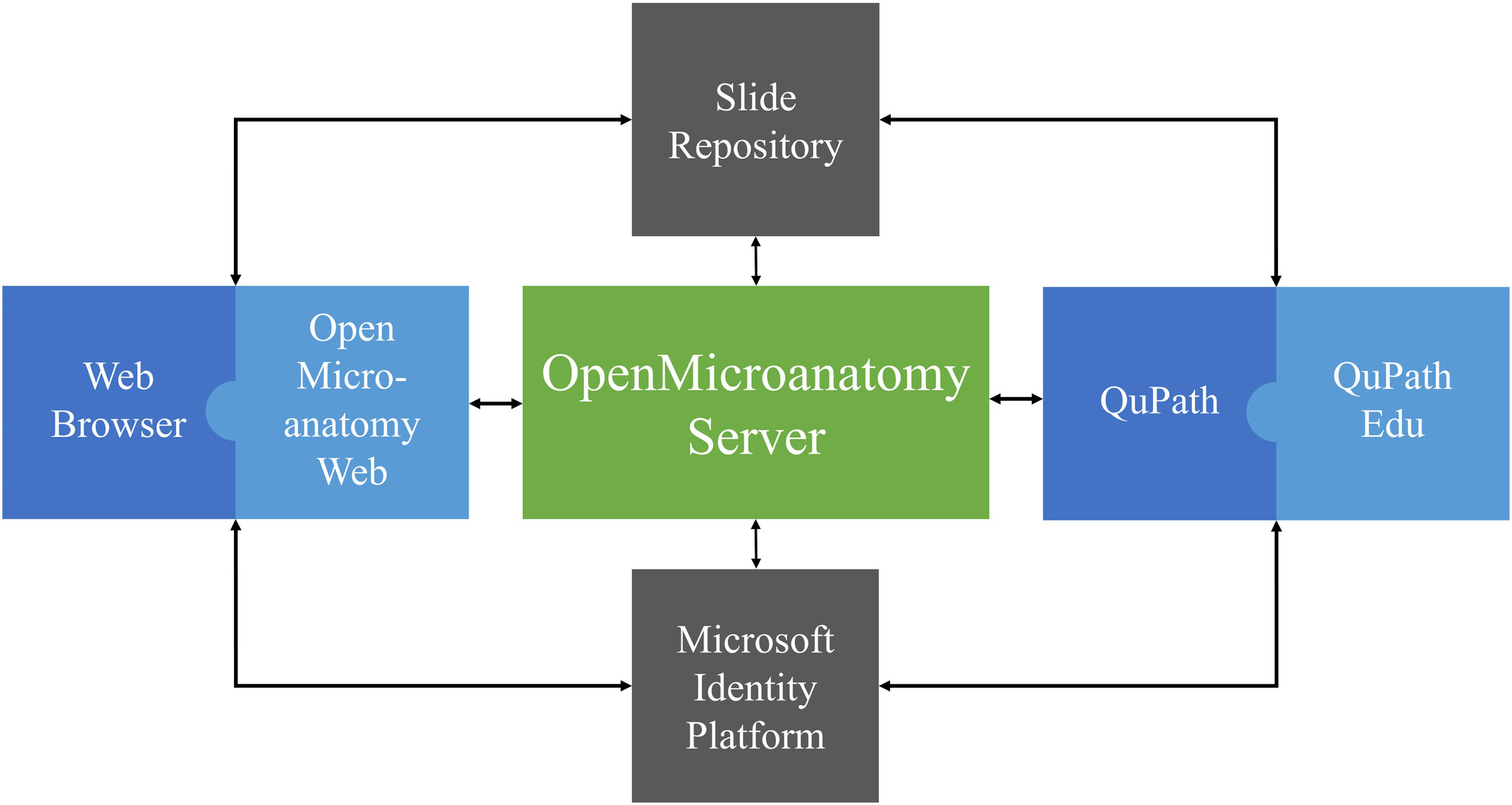
QuPath Edu and OpenMicroanatomy: Open-source virtual microscopy tools for medical education
- First Published: 18 November 2024
A complete workflow from embalmed specimens to life-like 3D virtual models for veterinary anatomy teaching
- First Published: 20 December 2024
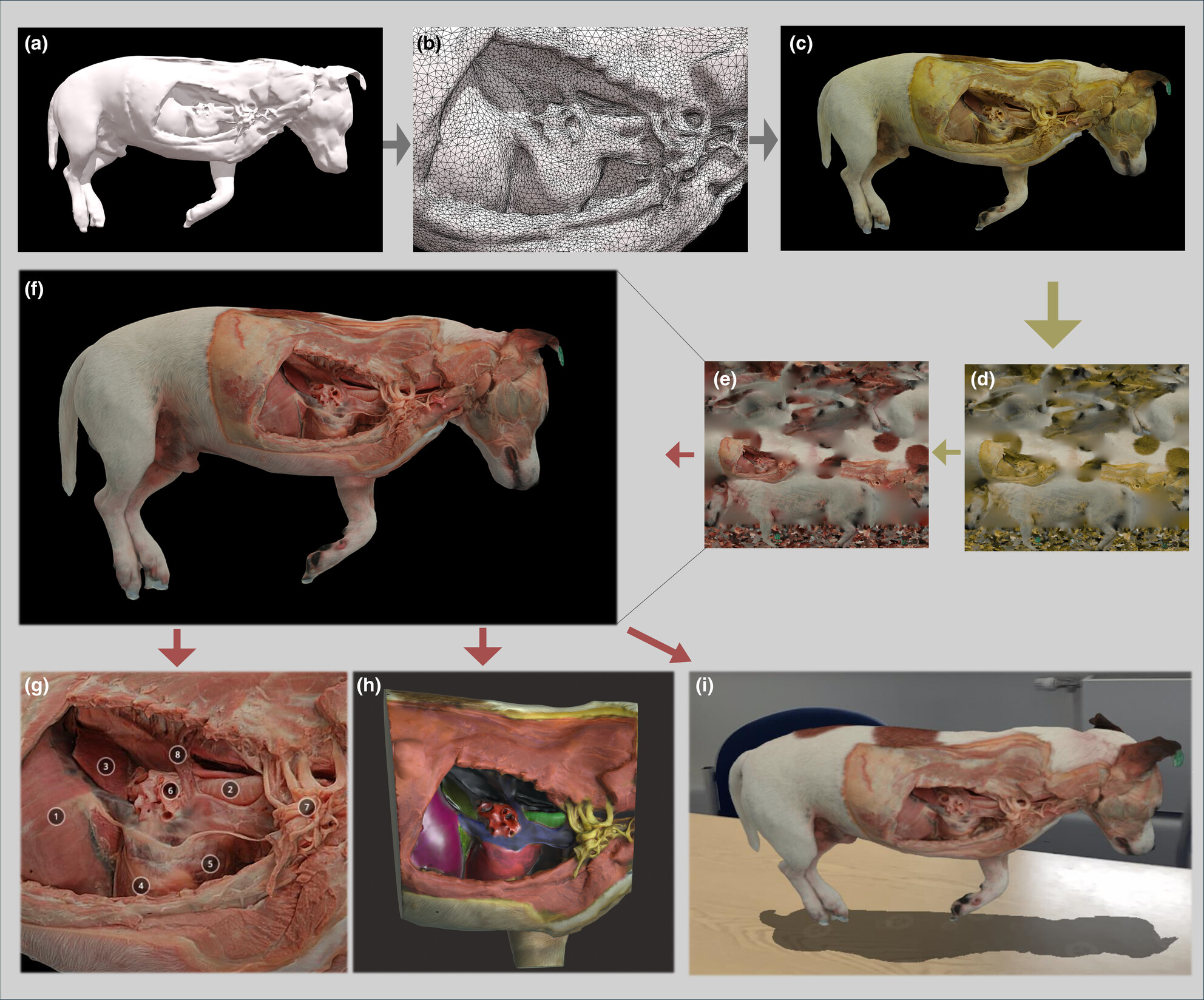
This study introduces a workflow using the Liverpool-Whitwell embalming protocol and photogrammetry to create realistic 3D digital models from veterinary specimens. These models, enhanced with digital tools and stored in a cloud repository, are integrated into the University of Liverpool's Virtual Learning Environment, offering remote access to high-quality anatomical resources. This method enhances educational delivery, specimen quality, and logistical efficiency, revolutionising anatomical education and improving learning outcomes.
Reviving the anatomic past: Breathing new life into historic anatomical teaching tools
- First Published: 03 December 2022
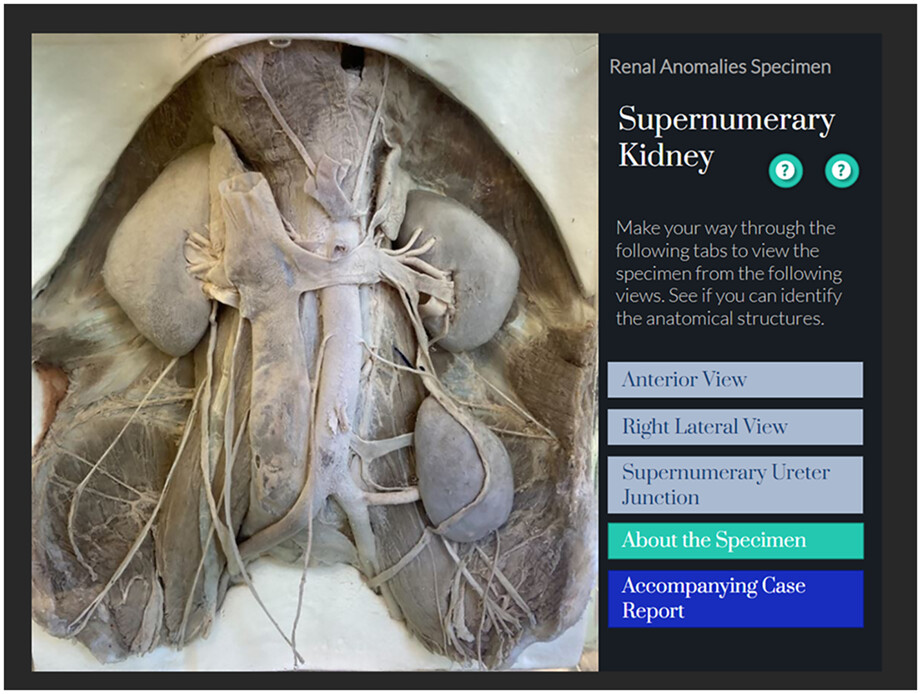
The last two decades have seen a shift in the way anatomy education is delivered. With the introduction of blended learning, cadaveric dissection is no longer the be all and end all and, in many cases, the continuing role of anatomical teaching artifacts has declined after decades of prominence. While some institutions have abandoned their archaic anatomical collections and medical museums completely, others have invested in their technological enhancement. We describe the integration of historical teaching artefacts into contemporary anatomy education through the development of an interactive online e-platform and shed light on the enduring pedagogic value of past anatomical teaching specimen.
A new brain-cutting device and ultraviolet resin-mounted human brain slices as a teaching adjunct for neuroanatomy education
- First Published: 08 September 2022
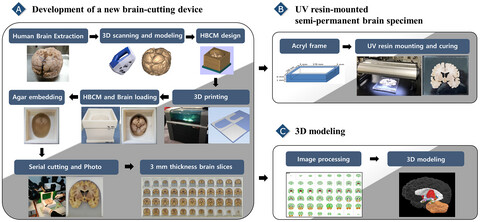
We developed a new three-dimensional (3D) printed device (human brain-cutting mold, HBCM) for creating human brain slices; moreover, we demonstrated a simple method for creating semi-permanent ultraviolet (UV) resin-mounted brain slice specimens for neuroanatomy education. We obtained brain slices of uniform thickness (3 mm) through the HBCM; the resultant brain slices were optimal for assessing morphological details of the human brain.
On the importance of integrating comparative anatomy and One Health perspectives in anatomy education
- First Published: 24 October 2021

Acquiring a robust knowledge of comparative anatomy as part of the medical curriculum helps in understanding diseases better. This review article converges the ideas discussed in a symposium on One Health arranged during the IFAA2019 and prioritises an action plan of integrating veterinary knowledge into the medical curriculum.
COVID-19 and anatomy: Stimulus and initial response
- First Published: 06 July 2020

The outbreak of COVID-19, resulting from widespread transmission of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, represents one of the foremost current challenges to societies across the globe, with few areas of life remaining untouched. Here, we detail the immediate impact that COVID-19 has had on the teaching and practice of anatomy, providing specific examples of the varied responses from several UK, Irish and German universities and medical schools. Alongside significant issues for, and suspension of, body donation programmes, the widespread closure of university campuses has led to challenges in delivering anatomy education via online methods, a particular problem for a practical, experience-based subject such as anatomy. We discuss the short-term consequences of COVID-19 for body donation programmes and anatomical education, and highlight issues and challenges that will need to be addressed in the medium to long term in order to restore anatomy education and practice throughout the world.
Challenges in creating dissectible anatomical 3D prints for surgical teaching
- First Published: 01 February 2019
3D scanning and printing skeletal tissues for anatomy education
- First Published: 05 May 2016
From cradle to grave via the dissection room: the role of foetal and infant bodies in anatomical education from the late 1700s to early 1900s
- First Published: 30 June 2016
Anatomical Society core regional anatomy syllabus for undergraduate medicine: the Delphi process
- First Published: 27 November 2015
The Anatomical Society core regional anatomy syllabus for undergraduate medicine
- First Published: 27 November 2015
A retrospective and prospective look at medical education in the United States: trends shaping anatomical sciences education
- First Published: 19 April 2013
Building an open academic environment – a new approach to empowering students in their learning of anatomy through ‘Shadow Modules’
- First Published: 30 September 2013
Motivating student learning using a formative assessment journey
- First Published: 30 September 2013
Does learning style influence academic performance in different forms of assessment?
- First Published: 31 October 2013